第五周学习总结
一,类的继承格式
在 Java 中通过 extends 关键字可以申明一个类是从另外一个类继承而来的,一般形式如下:
class 父类 {
}
class 子类 extends 父类 {
}
二,this和super的区别
this
1.调用类中的成员变量,this.成员变量
2.调用类中的成员方法,this.成员方法
3.本类构造方法调用本类其他构造,第一行使用this
super
1.子类调用父类中的构造方法,super.构造方法名
2.子类调用父类有参构造方法,super.方法名(参数);
3.子类调用父类变量,super.变量名;
4.super必须使用在子类构造方法第一行
三,抽象类的定义及使用规则:
包含一个抽象方法的类必须是抽象类;抽象类和抽象方法都要使用abstract关键字声明;抽象方法只需要声明而不需要实现;抽象类必须被子类继承,子类(如果不是抽象类)必须覆写抽象类中的全部抽象方法。
四,final
final声明的类不能有子类;
final声明的方法不能被子类所覆写;
final声明的变量及成为常量。
1.已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码、结果截图。)
①统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数。
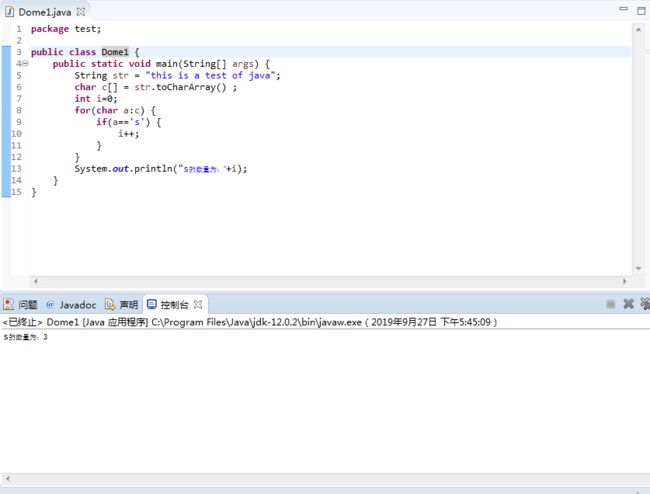
package test;
public class Dome1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "this is a test of java";
char c[] = str.toCharArray() ;
int i=0;
for(char a:c) {
if(a=='s') {
i++;
}
}
System.out.println("s的数量为:"+i);
}
}
②统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数。
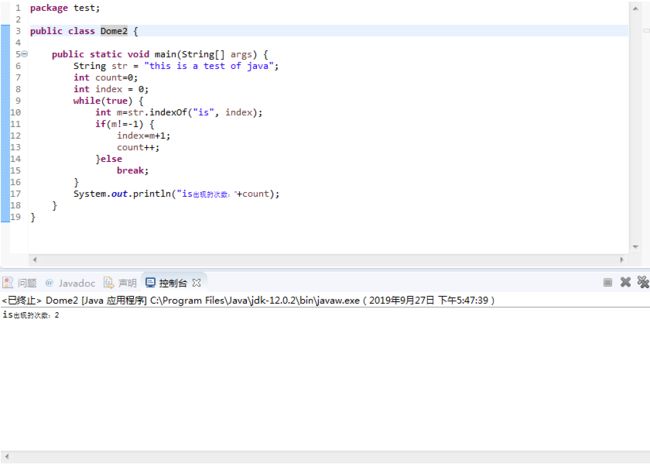
package test;
public class Dome2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "this is a test of java";
int count=0;
int index = 0;
while(true) {
int m=str.indexOf("is", index);
if(m!=-1) {
index=m+1;
count++;
}else
break;
}
System.out.println("is出现的次数:"+count);
}
}
③统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
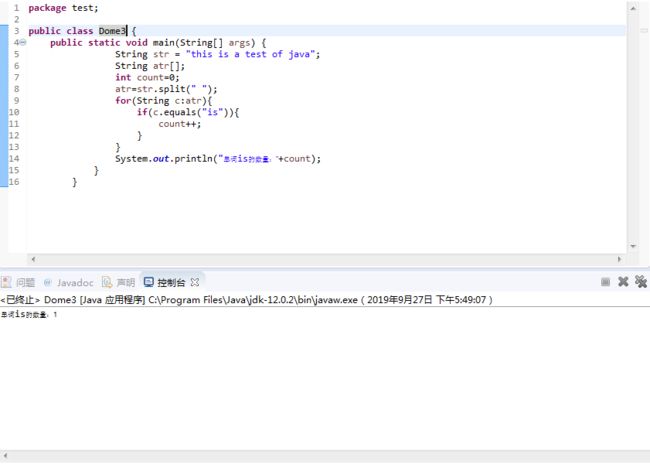
package test;
public class Dome3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "this is a test of java";
String atr[];
int count=0;
atr=str.split(" ");
for(String c:atr){
if(c.equals("is")){
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("单词is的数量:"+count);
}
}
④实现该字符串的倒序输出
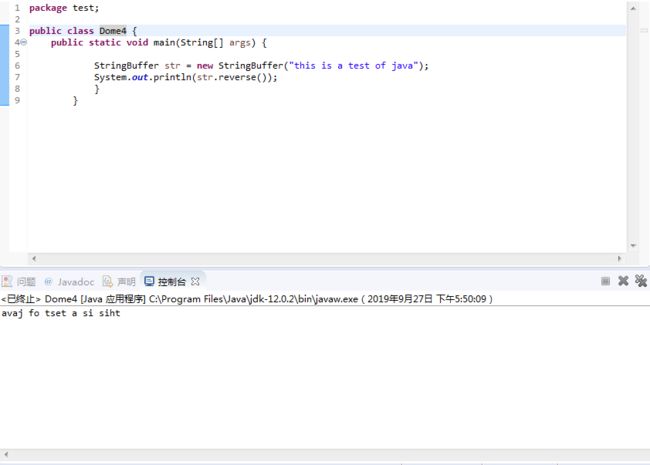
package test;
public class Dome4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("this is a test of java");
System.out.println(str.reverse());
}
}
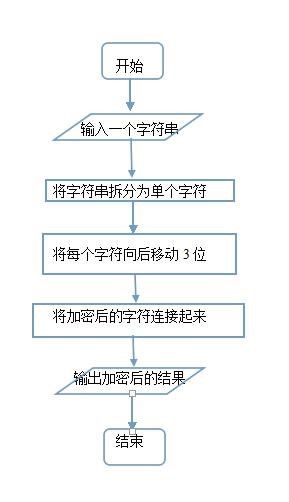
2.请编写一个程序,使用下述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串。要求源代码、结果截图。
package test;
import java.util.*;
public class Dome5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
char s[] = str.toCharArray();
char asc=0;
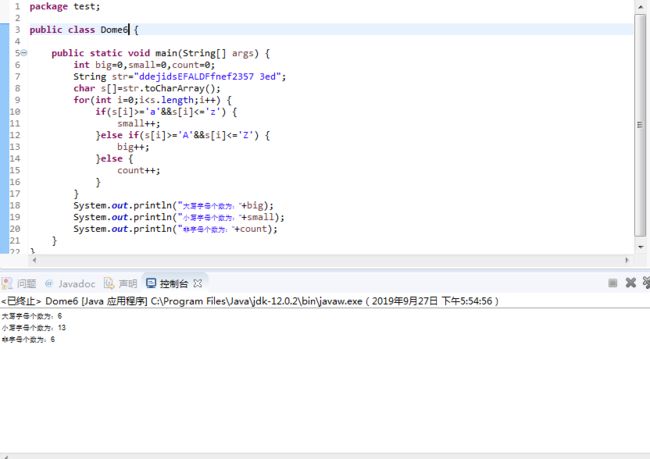
for(int i=0;i3.已知字符串“ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed”。输出字符串里的大写字母数,小写英文字母数,非英文字母数。
package test;
public class Dome6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int big=0,small=0,count=0;
String str="ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed";
char s[]=str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i='a'&&s[i]<='z') {
small++;
}else if(s[i]>='A'&&s[i]<='Z') {
big++;
}else {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字母个数为:"+big);
System.out.println("小写字母个数为:"+small);
System.out.println("非字母个数为:"+count);
}
}