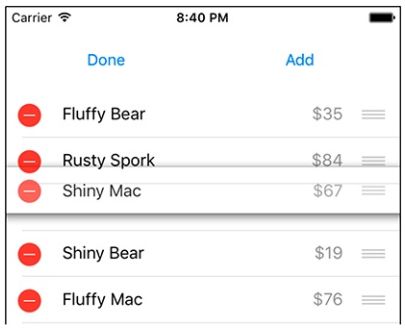
在上一章中,您创建了一个在 UITableView 中显示 Item 实例列表的应用程序。 下一步是允许用户与表进行交互——添加,删除和移动行。 图11.1显示了本章结束后的 Homepwner。
图11.1 编辑模式下的Homepwner
编辑模式
UITableView 有一个 editing 属性,当该属性设置为 true 时,UITableView 进入编辑模式。 表视图处于编辑模式后,表的行可由用户操纵。 根据表视图的配置方式,用户可以更改行的顺序,添加行或删除行。(编辑模式不允许用户编辑行的文本内容。)
但首先,用户需要一个将 UITableView 置于编辑模式的方法。 现在,您将在表的 头部视图(header view) 中添加一个按钮。 头部视图显示在表格的顶部,对于添加 section 范围内 或 表范围内 的标题和控件很有用。它可以是任何 UIView 实例。
请注意,表视图有两种 “header” : table header 和 section header。 同样,也有 table footer 和 section footer(图11.2)。
图11.2 header 和 footer
您正在创建一个头部视图。 它将有两个子视图并且是 UIButton 的实例:一个用于切换编辑模式,另一个用于在表中添加一个新的 Item。 您可以以编程方式创建此视图,但在这种情况下,您将在故事板文件中创建这个视图及其子视图。
首先,我们设置必要的代码。 重新打开 Homepwner.xcodeproj。 在 ItemsViewController.swift 中,实现两个方法。
class ItemsViewController: UITableViewController {
var itemStore: ItemStore!
@IBAction func addNewItem(_ sender: UIButton) {
}
@IBAction func toggleEditingMode(_ sender: UIButton) {
}
现在打开 Main.storyboard。 从对象库中,将 View 拖动到 prototype cell 上方的表视图的最顶部。 这将添加视图作为表视图的 头部视图。 调整这个视图的高度大约为 60 点。 (如果你要确切地修改,可以使用尺寸检查器)。
现在将两个 Button 从对象库拖动到头部视图。 更改文本并定位它们,如图11.3所示。 您不需要和图中一样精确——您将很快添加约束来定位按钮。
图11.3添加按钮到头部视图
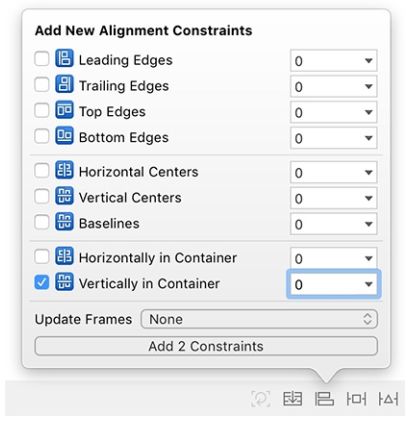
选择这两个按钮并打开 自动布局 Align 菜单。 在 Vertically in Container 选择常量0.确保 Update Frames 设置为 None,然后单击 Add 2 Constraints(图11.4)。
图11.4 对齐(Align)菜单约束
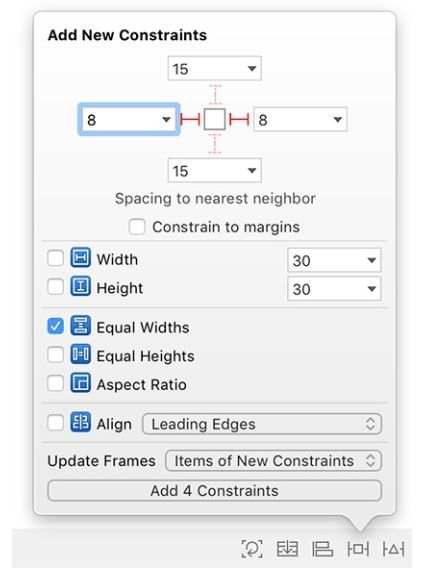
打开 Add New Constraints 菜单并进行配置,如图11.5所示。 确保在键入它们之后保存 前部(leading) 和 尾部(trailing) 约束的值; 有时值不会保存,所以有点棘手。 完成后,单击 Add 4 Constraints。
图11.5 添加新约束
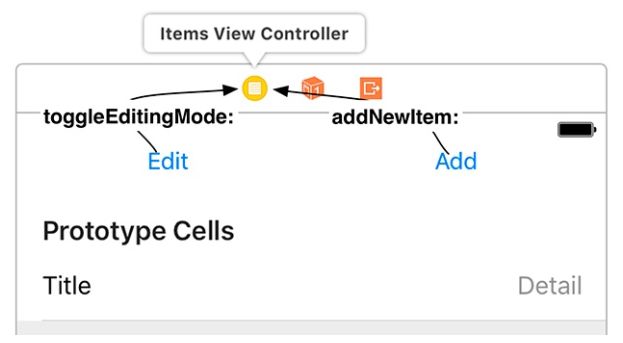
最后,连接两个按钮的动作,如图11.6所示。
图11.6连接两个动作
构建并运行应用程序以查看界面。
现在我们来实现 toggleEditingMode(_ :) 方法。 您可以直接修改 UITableView 的 editing 属性。 但是, UIViewController 也有 editing 属性。 UITableViewController 实例自动设置其表视图的 editing 属性以匹配自己的 editing 属性。 通过在视图控制器本身设置 editing 属性,可以确保界面的其他方面也同时进入或离开编辑模式。例子将在第14章中 UIViewController 的 editButtonItem 看到。
要设置视图控制器的 isEditing 属性,可以调用 setEditing(_:animated :) 方法。 在 ItemsViewController.swift 中,实现 toggleEditingMode(_ :)。
@IBAction func toggleEditingMode(_ sender: UIButton) {
// If you are currently in editing mode...
if isEditing {
// Change text of button to inform user of state
sender.setTitle("Edit", for: .normal)
// Turn off editing mode
setEditing(false, animated: true)
} else {
// Change text of button to inform user of state
sender.setTitle("Done", for: .normal)
// Enter editing mode
setEditing(true, animated: true)
}
}
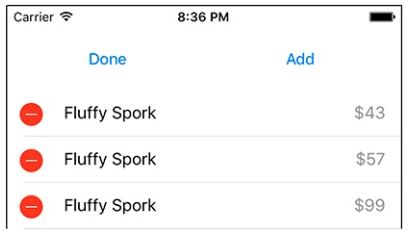
构建并运行您的应用程序。 点击 Edit 按钮,UITableView 将进入编辑模式(图11.7)。
图11.7 编辑模式下的UITableView
添加行
在运行时,有两个通用的界面用于在表视图中添加行。
- 表格视图cell上方的按钮:通常用于添加有详细视图的记录。 例如,在
联系人(Contacts)应用中,当您遇到新人并想要取消他或她的信息时,您可以点击一个按钮。 - 具有绿色加号的cell:通常用于向记录添加新字段,例如当您要在
联系人(Contacts)应用程序中为个人记录添加生日时。 在编辑模式下,点击添加生日(add birthday)旁边的绿色加号。
在本练习中,您将使用第一个选项,并在标题视图中创建一个新按钮。 当点击此按钮时,新行将添加到 UITableView。
在 ItemsViewController.swift 中,实现 addNewItem(_ :)。
@IBAction func addNewItem(_ sender: UIButton) {
// Make a new index path for the 0th section, last row
let lastRow = tableView.numberOfRows(inSection: 0)
let indexPath = IndexPath(row: lastRow, section: 0)
// Insert this new row into the table
tableView.insertRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
}
构建并运行应用程序。 点击 Add 按钮,...应用程序崩溃。 控制台告诉您,表视图有内部不一致(internal inconsistency) 异常。
记住,最终,UITableView 的 dataSource 决定了表视图应该显示的行数。 插入新行后,表视图有六行(原来的五行加上新行)。 当 UITableView 询问其 dataSource 的行数时,ItemsViewController 会咨询该 store 并返回应该有五行。 UITableView 无法解决这种不一致并引发异常。
您必须确保 UITableView 及其 dataSource 在插入新行之前通过向 ItemStore 中添加 Item 来改变行数。
在 ItemsViewController.swift 中,更新 addNewItem(_ :)。
@IBAction func addNewItem(_ sender: UIButton) {
Make a new index path for the 0th section, last row
let lastRow = tableView.numberOfRows(inSection: 0)
let indexPath = IndexPath(row: lastRow, section: 0)
Insert this new row into the table
tableView.insertRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
Create a new item and add it to the store
let newItem = itemStore.createItem()
// Figure out where that item is in the array
if let index = itemStore.allItems.index(of: newItem) {
let indexPath = IndexPath(row: index, section: 0)
// Insert this new row into the table
tableView.insertRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
}
}
运行应用程序。 点击 Add 按钮,新行将滑动到表的底部位置。 请记住,视图对象的作用是将模型对象呈现给用户; 更新视图而不更新模型对象没什么卵用。
现在您可以添加行和 item,您不再需要将五个随机项目放入 store 的代码。
打开 ItemStore.swift 并删除初始化程序代码。
init() {
for _ in 0..<5 {
createItem()
}
}
构建并运行应用程序。 首次启动应用程序时,不再有任何行,但您可以通过点击 Add 按钮添加一些行。
删除行
在编辑模式中,带有减号(如图11.7所示)的红色圆圈是删除控件,然后点击一个应该会删除该行。 但是,在这一点上,您实际上不能删除该行。 (尝试看看。)在表视图删除一行之前,它会在其数据源上调用关于建议删除的方法,并等待确认。
删除 cell 时,您必须做两件事情:从 UITableView 中删除该行,并从 ItemStore 中删除与之相关联的 Item。 要将其关闭,ItemStore 必须知道如何从其中删除对象。
在 ItemStore.swift 中,实现一个新的方法来删除特定的 item。
func removeItem(_ item: Item) {
if let index = allItems.index(of: item) {
allItems.remove(at: index)
}
}
你将会实现 tableView(_:commit:forRow :),一个 UITableViewDataSource 协议的方法。(这个方法在 ItemsViewController 上调用,请记住,尽管 ItemStore 是保存数据的地方,而 ItemsViewController 才是表视图的 dataSource。)
当在数据源上调用 tableView(_:commit:forRowAt :) 时,会传递两个额外的参数。 第一个是 UITableViewCellEditingStyle,在这种情况下,它是 .delete。 另一个参数是表中行的 IndexPath。
在 ItemsViewController.swift 中,实现此方法使 ItemStore 删除正确的对象,并通过在表视图上调用 deleteRows(at:with :) 方法来确认删除行。
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, commit editingStyle: UITableViewCellEditingStyle, forRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
// If the table view is asking to commit a delete command...
if editingStyle == .delete {
let item = itemStore.allItems[indexPath.row]
// Remove the item from the store
itemStore.removeItem(item)
// Also remove that row from the table view with an animation
tableView.deleteRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
}
}
构建并运行应用程序,创建一些行,然后删除一行。 它就会消失。请注意,滑动删除也可以。
移动行
要更改 UITableView 中的行顺序,您将使用 UITableViewDataSource 协议中的另一个方法——tableView(_:moveRowAt:to :)。
要删除一行,您必须在 UITableView 上调用 deleteRows(at :),以确认删除。 但是,移动一行不需要确认:表视图会自动移动该行,并通过调用 tableView(_:moveRowAt:to :) 方法来报告数据源发生了移动。 实现此方法来更新数据源以匹配新顺序。
但是,在实现此方法之前,您需要给 ItemStore 一个方法来更改其 allItems 数组中 item 的顺序。
在 ItemStore.swift 中,实现这个新方法。
func moveItem(from fromIndex: Int, to toIndex: Int) {
if fromIndex == toIndex {
return
}
// Get reference to object being moved so you can reinsert it
let movedItem = allItems[fromIndex]
// Remove item from array
allItems.remove(at: fromIndex)
// Insert item in array at new location
allItems.insert(movedItem, at: toIndex)
}
在 ItemsViewController.swift 中,实现 tableView(_:moveRowAt:to :) 来更新 store。
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, moveRowAt sourceIndexPath: IndexPath, to destinationIndexPath: IndexPath) {
// Update the model
itemStore.moveItem(from: sourceIndexPath.row, to: destinationIndexPath.row)
}
运行你的应用程序。 添加几个 item,然后点击编辑,并查看每一行侧面的新的重新排序控件(三条水平线)。 触摸并按住重新排序控件并将该行移动到新位置(图11.8)。
图11.8移动一行
请注意,简单地实现 tableView(_:moveRowAt:to :) 会导致重新排序控件出现。 UITableView 可以在运行时询问其数据源是否实现了 tableView(_:moveRowAt:to :)。 如果是,则表视图会在表视图进入编辑模式时添加重新排序控件。
显示用户警报
在本节中,您将了解用户警报以及配置和显示用户警报的不同方法。 用户警报可以为您的应用程序提供更好的用户体验,因此您会经常使用它们。
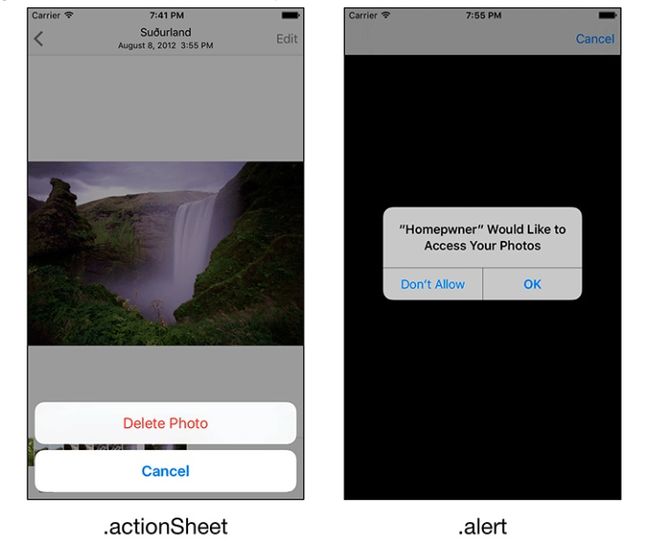
警报通常用于警告用户一个重要的动作即将发生,同时给他们机会取消该动作。 当您要显示警报时,您将创建一个具有首选样式的 UIAlertController 实例。 两种可用的样式是 UIAlertControllerStyle.actionSheet 和 UIAlertControllerStyle.alert (图11.9)。
图11.9 UIAlertController样式
.actionSheet 样式用于向用户呈现要从中选择的动作列表。 .alert 类型用于显示关键信息,要求用户决定如何继续。 这个区别可能看起来很微妙,但是如果用户决定取消选择,或者动作不重要的话,那么一个 .actionSheet 可能是最好的选择。
您将使用 UIAlertController 来确认 item 的删除。 您将使用 .actionSheet 样式,因为警报的目的是确认或取消可能的破坏性操作。
打开 ItemsViewController.swift 并修改 tableView(_:commit:forRowAt :),要求用户确认或取消 删除 item。
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, commit editingStyle: UITableViewCellEditingStyle, forRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
// If the table view is asking to commit a delete command...
if editingStyle == .delete {
let item = itemStore.allItems[indexPath.row]
let title = "Delete \(item.name)?"
let message = "Are you sure you want to delete this item?"
let ac = UIAlertController(title: title, message: message, preferredStyle: .actionSheet)
// Remove the item from the store
itemStore.removeItem(item)
// Also remove that row from the table view with an animation
tableView.deleteRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
}
}
在确定用户想要删除项目之后,您将创建一个具有适当标题和消息的 UIAlertController 实例,描述将要执行的操作。 此外,您为该警报指定 .actionSheet 样式。
显示警报时用户可以选择的动作是 UIAlertAction 的实例,您可以添加多个操作,而不管警报的样式。 使用 addAction(_ :) 方法将动作添加到 UIAlertController 中。
在 tableView(_:commit:forRowAt :) 中的动作工作表中添加必要的操作。
...
let ac = UIAlertController(title: title, message: message, preferredStyle: .actionSheet)
let cancelAction = UIAlertAction(title: "Cancel", style: .cancel, handler: nil)
ac.addAction(cancelAction)
let deleteAction = UIAlertAction(title: "Delete", style: .destructive, handler: { (action) -> Void in
// Remove the item from the store
self.itemStore.removeItem(item)
// Also remove that row from the table view with an animation
self.tableView.deleteRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
})
ac.addAction(deleteAction)
...
第一个动作的标题为 “Cancel”,并使用 .cancel 样式创建。.cancel 样式会显示为标准蓝色字体。 此操作将允许用户退出删除项目。 处理程序参数允许在发生该动作时执行闭包。 因为不需要其他动作,所以将 nil 作为参数传递。
第二个动作的标题为 “Delete”,并使用 .dructructive 样式创建。 因为破坏性的行为应该被明确标注和注意到,.dructructive 风格会产生明亮的红色文字。 如果用户选择此动作,则需要删除 item 和表视图 cell。 这一切都在传递给动作的构造器的 'handle' 闭包中完成。
现在已经添加了动作,可以向用户显示警报控制器。 因为 UIAlertController 是 UIViewController 的子类,所以您可以使用 模态(modally) 将其呈现给用户。 模态视图控制器(modal view controller) 接管整个屏幕,直到其完成工作。
要以视图方式呈现视图控制器,您可以在其视图位于屏幕上的视图控制器上调用 present(_:animated:completion :)。 要呈现的视图控制器被传递给它,并且该视图控制器的视图接管屏幕。
...
let deleteAction = UIAlertAction(title: "Delete", style: .destructive, handler: { (action) -> Void in
// Remove the item from the store
self.itemStore.removeItem(item)
// Also remove that row from the table view with an animation
self.tableView.deleteRows(at: [indexPath], with: .automatic)
})
ac.addAction(deleteAction)
// Present the alert controller
present(ac, animated: true, completion: nil)
...
构建并运行应用程序并删除一个 item。 将提供一个动作以供您确认删除(图11.10)。
图11.10 删除 item
设计模式
设计模式(design pattern) 解决了常见的软件工程问题。 设计模式不是代码的实际代码段,而是可以在应用程序中使用的抽象概念或方法。 良好的设计模式是任何开发人员有价值和强大的工具。
在开发过程中始终如一地使用设计模式可以减少解决问题的精神开销,从而可以更轻松,快速地创建复杂的应用程序。 以下是您已经使用的一些设计模式:
-
委托模式(Delegation):一个对象将某些功能委托给另一个对象。 当文本字段的内容更改时,您通过 UITextField 使用委托来通知。 -
数据源模式(Data source):数据源与委托类似,但不是对另一个对象做出反应,而是在请求时,数据源负责向另一个对象提供数据。 您之前已将数据源模式与表视图一起使用过:每个表视图都有一个数据源,它至少负责告诉表视图要显示多少行以及每个索引路径应显示哪个单元格。 -
Model-View-Controller:应用程序中的每个对象都可以满足三个角色之一。 模型对象是数据。 视图显示UI。 控制器提供将模型和视图结合在一起的胶水。 -
目标 - 动作对(Target-action pairs):当特定事件发生时,一个对象调用另一个对象的方法。 目标是有一个方法被调用的对象,动作是被调用的方法。 例如,您使用具有按钮的目标动作对:当触发事件发生时,将会在另一个对象(通常是视图控制器)上调用一个方法。
苹果在使用这些设计模式时非常一致,因此了解和识别它们非常重要。 继续阅读这本书,留意这些模式! 认识它们将帮助您更轻松地学习新的课程和框架。
青铜挑战:重命名删除按钮
删除行时,会出现一个确认按钮,标有 Delete。 尝试将此按钮的标签更改为 Remove。
白银挑战:防止重新排序
表格视图总是显示一个最后一行,表示 “No more items!”(这部分挑战与上一章的挑战是一样的,如果你已经完成了,你可以复制你之前的代码 )现在,令最后一行不能移动。
黄金挑战:真正防止重新排序
完成银牌挑战后,您可能会注意到,即使您不能移动 No more items! 行本身,您仍然可以拖动其下的其他行。 做到这一点——无论什么——No more items! 行永远不会被淘汰出最后的位置。 最后,使它不可被删除。