在Android中弹出式菜单(以下称弹窗)是使用十分广泛一种菜单呈现的方式,弹窗为用户交互提供了便利。关于弹窗的实现大致有以下两种方式AlertDialog和PopupWindow,当然网上也有使用Activity并配合Dialog主题的方式实现弹窗,有兴趣的朋友也可以去研究一下。对于AlertDialog和PopupWindow两者的最主要区别也有以下两点:
1 、位置是否固定。 AlertDialog在位置显示上是固定的,而PopupWindow则相对比较随意,能够在主屏幕上的任意位置显示。
2、是否会阻塞UI线程。 AlertDialog在显示的时候不会阻塞UI线程,而PopupWindow在显示的时候会阻塞UI线程。
PopupWindow在android.widget包下,Google官方文档对PopupWindow的描述是:
"A popup window that can be used to display an arbitrary view. The popupwindow is a floating container that appears on top of the current activity."
也就是说PopupWindow是一个以弹窗方式呈现的控件,可以用来显示任意视图(View),而且会浮动在当前活动(activity)的顶部”。因此我们可以通过PopupWindow实现各种各样的弹窗效果,进行信息的展示或者是UI交互,由于PopupWindow自定义布局比较方便,而且在显示位置比较自由不受限制,因此受到众多开发者的青睐。
废话不多说,进入正题。
PopupWindow的使用
其实PopupWindow的使用非常简单,总的来说分为两步:
1、调用PopupWindow的构造器创建PopupWindow对象,并完成一些初始化设置。
2、调用PopupWindow的showAsDropDown(View view)将PopupWindow作为View组件的下拉组件显示出来;或调用PopupWindow的showAtLocation()方法将PopupWindow在指定位置显示出来。
创建并完成初始化设置:
PopupWindow popupWindow =new PopupWindow(this);
popupWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
popupWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
popupWindow.setContentView(LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.layout_popupwindow_style01,null));
popupWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(0x00000000));
popupWindow.setOutsideTouchable(false);
popupWindow.setFocusable(true);
其中,setWidth、setHeight和setContentView三者必须实现,否则将不会显示任何视图。
setwidth和setHeight的参数值可以是具体的数值,也可以是MATCH_PARENT或者是WRAP_CONTENT。
setContentView则是为PopupWindow设置视图内容。
setFocusable顾名思义就是让PopupWindow获得焦点。
setBackgroundDrawable从字面理解就是为PopupWindow设置一个背景。
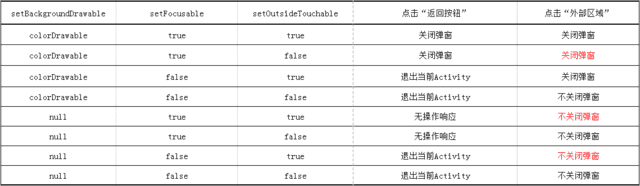
setOutsideTouchable则表示PopupWindow内容区域外的区域是否响应点击事件,Android官方给出的文档则表示点击内容区域外的区域是否关闭窗口,那么设置为true应该就是表示关闭,设置为false就是表示不关闭咯! 那么我们就动手试一下吧,验证一下是不是和我们想象的相吻合:
实验结果似乎和我们想象的不太一样,于是试着上网找找结果看得出如下结论:setFocusable确实是让PopupWindow获得焦点,获得焦点的PopupWindow能够处理物理按钮的点击事件,否则点击事件将向上传递由Activity处理,这也能够解释为什么在setFocusable(false)的情况下点击返回按钮会退出当前Activity。关于焦点设置需要注意的一点是:如果PopupWindow中有Editor的话,focusable必须要为true。
可是还是有一点我似乎不太明白,为什么设置setOutsideTouchable(true),点击外部区域还是不会关闭窗口呢,这似乎与Google官方给出的解释有点出入,于是试着从源码寻找答案:
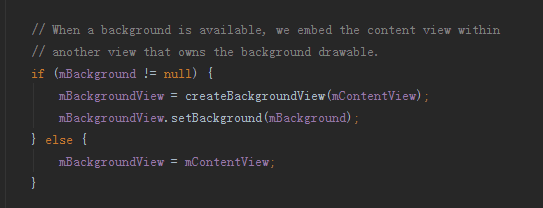
不看不知道,原来另有玄机,外部点击事件的响应还与backgroundDrawable有关,在backgroundDrawable!=null的情况下,PopupWindow会以backgroundDrawable作为背景生成一个根据contentView和backgroundDrawable生成一个PopupBackgroundView并返回,而如果在backgroundDrawable==null的情况下,则直接返回contentView。于是乎接着往下搜索,原来PopupBackgroundView是一个内部私有类继承至FrameLayout,且该类完成了对onKey和onTouch事件的分发处理。因为contentView我们并没有进行onKey和onTouch事件的分发处理,所以在backgroundDrawable==null的情况下,即使PopupWindow获得屏幕焦点,PopupWindow也不能处理物理按键的点击事件,因此就算点击返回按钮也会没有任何反应,更别说外部点击事件的响应了。这样也就能解释为什么在backgroundDrawable==null的情况下点击返回键或者是点击外部区域都不会关闭窗口了,因此我们在使用PopupWindow的时候都会设置焦点并且再设置一个背景,但为了不影响显示效果可以设置一个全透明背景:
setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(0x00000000));
但是,眼尖的朋友已经发现,还有一种情况似乎解释不通在setBackgroundDrawable(new ColorDrawable(0x00000000))、setOutsideTouchable(false)、setFocusable(true)的情况下,话说背景也有了,也设置焦点了,为什么setOutsideTouchable(false)点击外部区域还是会关闭窗口呢? 说实话看了半天源码也没能明白个啥意思,好吧,这可能也是Android的一个Bug,只能想办法去解决,于是我想着是否可以重写setOutsideTouchable方法和setContentView方法来解决问题呢。在setContentView的时候,使contentView获得焦点并添加按键监听事件,于是在任何情况下都能响应返回按钮的点击事件了。在setOutsideTouchable的时候判断为true的话就设置PopupWindow的backgroundDrawable,如果backgroundDrawable==null的话,就新建一个透明背景,也不影响显示效果。
重写setContentView():
@Override
public void setContentView (View contentView) {
if(contentView !=null) {
super.setContentView(contentView);
contentView.setFocusable(true); //
contentView.setFocusableInTouchMode(true); //
contentView.setOnKeyListener( new View.OnKeyListener(){
@Override
public boolean onKey(View v,int keyCode, KeyEvent event){
switch(keyCode) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK:
dismiss();
return true;
default:
break; }
return false; } });
}
}
重写setOutsideTouchable():
@Override
public void setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable){
super.setOutsideTouchable(touchable);
if(touchable) {
if(mBackgroundDrawable ==null) {
mBackgroundDrawable =new ColorDrawable(0x00000000); }
super.setBackgroundDrawable(mBackgroundDrawable);
}else{
super.setBackgroundDrawable(null);
}
}
尝试着运行一遍, Bingo! 完美解决!!!
PopupWindow的显示:
PopupWindow的显示大致又可以分为两类:
相对于视图中某个控件的相对位置(默认位于控件的正左下方)和相对于父控件的相对位置;
相对于视图中某个控件的相对位置:
showAsDropDown(View anchor):相对某个控件的位置(正左下方),无偏移。
showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff):相对某个控件的位置,同时可以设置偏移。
showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff, int gravity):相对某个控件的位置,对齐方式(尝试过,但似乎没有效果),同时可以设置偏移。
相对于父控件的相对位置:
showAtLocation(View parent, int gravity, int x, int y):相对于父控件的位置,同时可以设置偏移量。
setOutsideTouchable.gif
好了,关于PopupWindow的使用就介绍到这里。如果文中有什么叙述不当的地方,希望能够指出,期待您的意见,我们一起交流。最后附上我自己尝试去写的BasePopupWindow基类,包含窗口出现和消失的一个背景渐变动画,可以使窗口出现消失显得不那么生硬,BasePopupWindow:
public class BasePopupWindow extends PopupWindow{
private Context mContext;
private float mShowAlpha =0.88f;
private Drawable mBackgroundDrawable;
public BasePopupWindow(Context context){
this.mContext = context;
initBasePopupWindow(); }
@Override
public void setOutsideTouchable(booleantouchable){
super.setOutsideTouchable(touchable);
if(touchable) {
if(mBackgroundDrawable ==null) {
mBackgroundDrawable =new ColorDrawable(0x00000000); }
super.setBackgroundDrawable(mBackgroundDrawable);
}else{
super.setBackgroundDrawable(null); }
}
@Override
public void setBackgroundDrawable( Drawable background){
mBackgroundDrawable = background;
setOutsideTouchable(isOutsideTouchable()); }
/**
* 初始化BasePopupWindow的一些信息
* */
private void initBasePopupWindow(){
setAnimationStyle(android.R.style.Animation_Dialog);
setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
setOutsideTouchable(true);//默认设置outside点击无响应setFocusable(true);
}
@Override
public void setContentView(View contentView){
if(contentView !=null) {
contentView.measure(View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
super.setContentView(contentView);
addKeyListener(contentView); }
}
public Context getContext(){
returnmContext; }
@Override
public void showAtLocation(View parent,int gravity,intx,inty){
super.showAtLocation(parent, gravity, x, y);
showAnimator().start();
}
@Override public void showAsDropDown(View anchor){
super.showAsDropDown(anchor);
showAnimator().start();
}
@Override
public void showAsDropDown(View anchor,int xoff,int yoff){
super.showAsDropDown(anchor, xoff, yoff);
showAnimator().start();
}
@Override
public void showAsDropDown(View anchor,intxoff,intyoff,int gravity){
super.showAsDropDown(anchor, xoff, yoff, gravity);
showAnimator().start();
}
@Override
public void dismiss(){
super.dismiss();
dismissAnimator().start();
}
/**
* 窗口显示,窗口背景透明度渐变动画
* */
private ValueAnimator showAnimator(){
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1.0f, mShowAlpha);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate( ValueAnimator animation){
floatalpha = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
setWindowBackgroundAlpha(alpha);
} });
animator.setDuration(360);
return animator; }
/**
* 窗口隐藏,窗口背景透明度渐变动画
* */
private ValueAnimator dismissAnimator(){
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(mShowAlpha,1.0f);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation){
float alpha = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
setWindowBackgroundAlpha(alpha); } });
animator.setDuration(320);
return animator;
}
/**
* 为窗体添加outside点击事件
* */
private void addKeyListener(View contentView){
if(contentView !=null) {
contentView.setFocusable(true);
contentView.setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
contentView.setOnKeyListener(new View.OnKeyListener() {
@Override public boolean onKey(View view,int keyCode, KeyEvent event){
switch(keyCode) {
caseKeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK :
dismiss();
return true;
default:
break;
}
return false;
}
});
}
}
/**
* 控制窗口背景的不透明度
* */
private void setWindowBackgroundAlpha(float alpha){
Window window = ((Activity)getContext()).getWindow();
WindowManager.LayoutParams layoutParams = window.getAttributes();
layoutParams.alpha = alpha;
window.setAttributes(layoutParams);
}
}
原文链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/825d1cc9fa79