A Brief Introduction for Visual Question Answer
Visual Question Answer (VQA) 是对视觉图像的自然语言问答,作为视觉理解 (Visual Understanding) 的一个研究方向,连接着视觉和语言,模型需要在理解图像的基础上,根据具体的问题然后做出回答。本文将简短的对VQA做一个调研,涉及一小部分论文,作为入门。
一切从一篇17年发表在期刊Computer Vision and Image Understanding上的survey说起。
Visual question answering: A survey of methods and datasets, Qi Wu et.al
Visual Question Answering (VQA) is a challenging task that has received increasing attention from both the computer vision and the natural language processing communities. Given an image and a question in natural language, it requires reasoning over visual elements of the image and general knowledge to infer the correct answer. In the first part of this survey, we examine the state of the art by comparing modern approaches to the problem. We classify methods by their mechanism to connect the visual and textual modalities. In particular, we examine the common approach of combining convolutional and recurrent neural networks to map images and questions to a common feature space. We also discuss memory-augmented and modular architectures that interface with structured knowledge bases. In the second part of this survey, we review the datasets available for training and evaluating VQA systems. The various datatsets contain questions at different levels of complexity, which require different capabilities and types of reasoning. We examine in depth the question/answer pairs from the Visual Genome project, and evaluate the relevance of the structured annotations of images with scene graphs for VQA. Finally, we discuss promising future directions for the field, in particular the connection to structured knowledge bases and the use of natural language processing models.
这篇论文介绍了一些方法,数据集以及未来的研究方向。其中方法大部分是16年前的,调研将会涉及几篇17年后的论文。
Method
VQA的模型一般是先分别对图像和问题提取特征,然后联合这两个做一些多模态融合(如element-wise product, MCB,MFB),attention,知识补充等处理,最终经过分类器输出answer。关于特征提取,对于图像image:使用VGG,Resnet,... pretrained on object recognition/detection;对于问题question:使用LSTM, GRU, ... GloVe word embedding。
论文将目前的方法归为四类(四种 tips/tricks 用于VQA):
1. 联合嵌入方法(joint embedding approaches)
学习视觉与自然语言的两个不同模态特征在一个共同的特征空间的嵌入表达(embedding)。
-
简单方式:
简单的多模态的特征融合方法有element-wise product (multiply) / element-wise sum, concatenation,增加额外层的 concatenation + FCL/CNN/LSTM 等等。
concatenation + LSTM方式,来自Ask Your Neurons: A Neural-based Approach to Answering Questions about Images, ICCV 2015, Fig 1.
除了这些,一些论文提出了其他解决方案,这里只列举几个: -
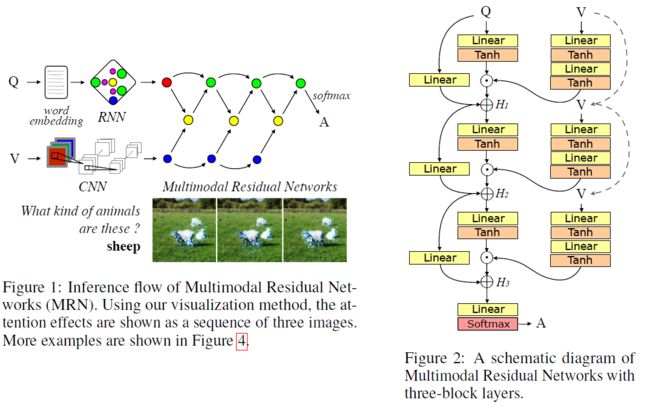
MRN, Multimodal Residual Learning for Visual QA, 16
这篇论文使用Q经过一层Neural得到权重,乘以V经过两层映射得到的特征,并经过多级残差连接。
-
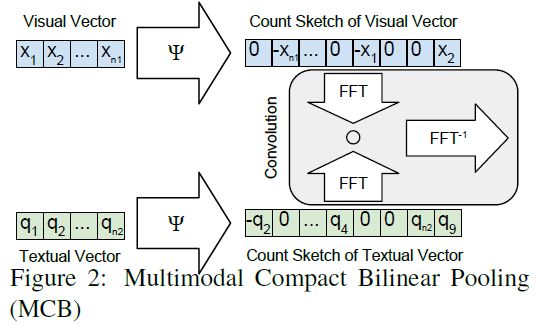
MCB, Multimodal Compact Bilinear Pooling for Visual Question Answering and Visual Grounding
Bilinear源于Bilinear CNN,通过对两个CNN得到的两个特征,然后进行外积。论文将其用在多模态融合之中。
两个向量x,q,进行outer product 外积后线性变换W,得到隐含表达z。
然而,当x,q,z维度很大时,W的参数将十分巨大。为了解决这个问题,论文提出MCB的方法:
视觉特征x和文本特征q经过一个算法(具体可以看原论文),得到一个表达,然后经过卷积/FFT得到融合后的结果。
总体框架如图:
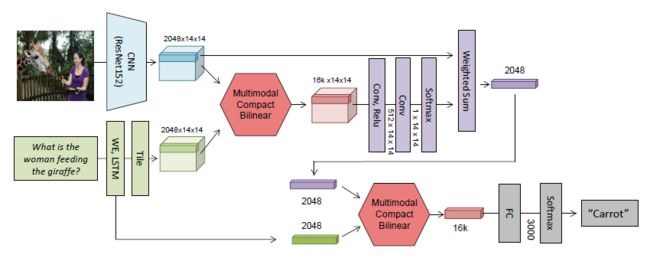
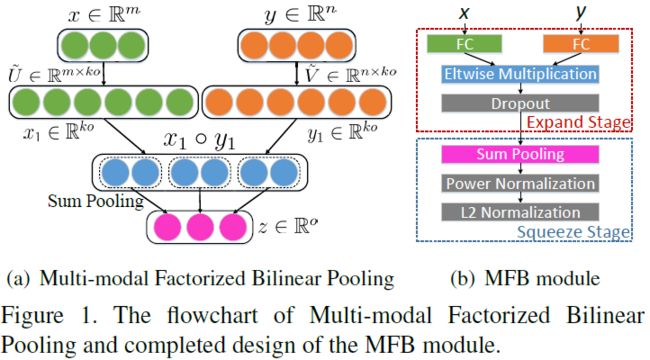
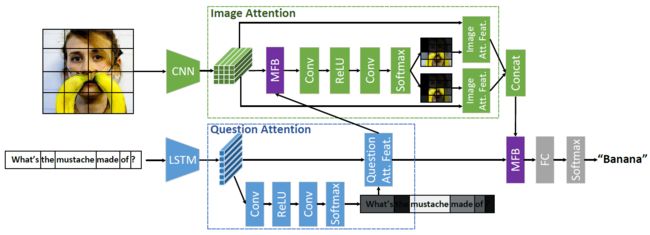
MCB作为一个模块被用于结合图像特征和文本特征。 MFB, Multi-modal Factorized Bilinear Pooling with Co-Attention Learning for Visual Question Answering, ICCV 2017
同MCB类似,MFB也是用于融合图像和文本特征。论文使用矩阵分解及sum pooling方法,
矩阵分解(Factorized): z_i=x^T W_i y, W_i \ \in R^{m \times n}, 将W_i分解为U_iV_i^T, 最后得到 z_i=1^T(U_i^Tx \circ V_i^Ty) (关于更多细节可参考原文)
总的框架比MCB多了question attention:
- ...
2. 注意力机制(attention mechanisms)
注意力机制已经广泛应用到NLP,image caption,VQA等中,在VQA中,attention能够根据具体的问题Q,把重点集中在想要的图像特征中(权重),最后给出答案。
如上图所示,通过问题Q的特征和图像特征组合,经过网络,公式或者其他方法得到每个图像特征V = (v_1, ..., v_k)的权重,将权重乘上V,再联合输入到分类器or生成器中产生answer。
除了图像上的attention外,MFB的论文还对问题Q本身也做一个attetion,并把两个attention称为co-attention。
3. 组合模型(compositional models)
把模型分解为模块的组合的方法,模块化有利于任务分解,重用等。survey论文主要介绍了两篇论文:
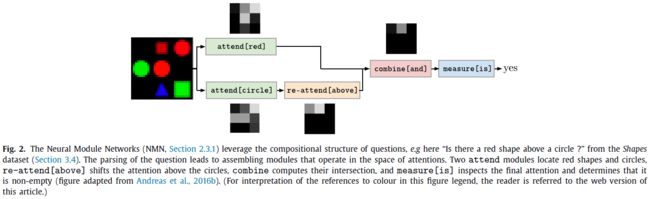
(1)The Neural Module Networks (NMN)
这篇论文的大致思路是将问题进行语义分析,得到语法树,然后使用特定的模块来代替树的每个节点,最后构成一个总的模型,如下图所示的一个例子“Is there a red shape above a circle?”。
(2)Dynamic Memory Networks
动态记忆就是将输入重复经过一个记忆模块,更新记忆,最后得到一个最终记忆,然后得到answer。这种方法把模型分为四个模块(跟一篇阅读理解/QA的论文ask me anything的结构类似):问题模块,图像模块,记忆模块,输出模块。
4. 知识增强方法(knowledge base-enhanced approaches)
结合图片以外的额外的知识,如关于某个词的描述。
下面将给出一篇相关的论文:
- Image Captioning and Visual Question Answering Based on Attributes and External Knowledge, PAMI 17
从title中可以知道这篇论文的两个贡献:
(1) Attributes
属性是一个高层的概念的表达(从人的角度看)。一般我们提取到的特征是高层的,隐含语义,不可解释的,而这篇论文使用了高层的属性来表达特征向量V_{attr},每个值表示对应属性的概率。下图是image caption的框架:
属性是从图片的captions中提取词,然后去常见词得到的一个集合。Predict是多属性Multi-label预测,然后训练得到输出为 V_{attr}的网络。第二部分利用得到的属性向量 V_{attr},使用LSTM来生成caption。
这种高层的语义属性用来生成caption的方法,我觉得是不妥的,因为虽然它得到很多属性的概率值,但是丢失了属性之间的关系,比如位置信息等等。
(2) External Knowledge
额外知识的获取是从DBpedia中获取前5个属性的相关描述,然后转换为向量表达。最后联合文档向量,属性向量,captions向量,问题来生成问题答案。
这种额外的知识是比较简单的,就是一段关于属性的语言描述,更复杂包括知识图谱运用或者隐含知识表达等等知识的利用将有利于问答。有监督学习学习到的是数据中包含的知识,但是我们的训练数据并不能覆盖整个世界的所有知识,这是一个弊端。如何利用好 知识与推理正是目前深度学习的一个挑战。
Datasets
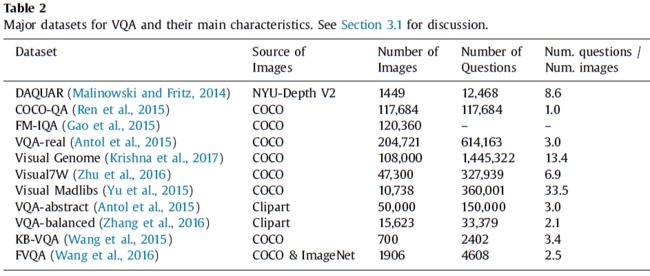
论文给出了13个数据集,除了下表的,还有Diagrams(一个图表的数据集),Shapes(一个形状,颜色的物体的合成数据集)。根据答案的类型可以分为两种:open-ended(开放式的)和multiple choice(多选项的)。
其中 VQA, Visual Genome是比较常用的数据集。
- VQA
这个从16年开始就有challenge比赛,基于COCO的图,是最常用的数据集,目前是2.0版本,相比于1.0平衡了问题类型的数量和一个问题会对应几张图。
例子:
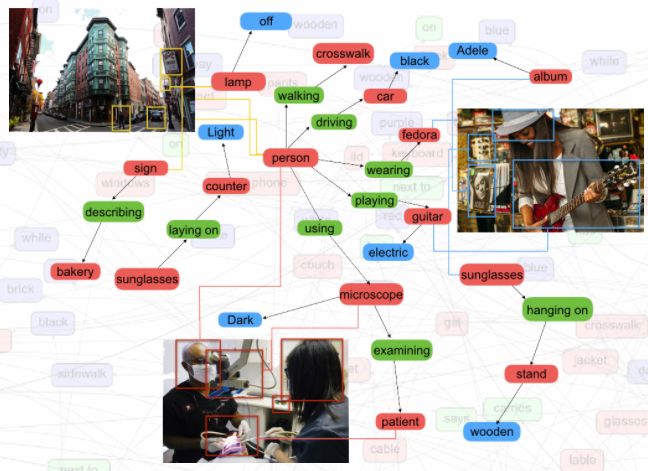
- Visual Genome
斯坦福的一个数据集,它不仅包含图片,问题和答案,还包含了Region Descriptions,Object Instances,Attributes,Relationships。
有一些论文用这个数据集的属性信息和问答做数据增强,然后用于VQA数据集。这里可见在有监督学习下数据的重要性。
Perfomance
准确率acc:
下表列出的不是survey论文中的,而是论文 Bottom-Up and Top-Down Attention for Image Captioning
and Visual Question Answering中的, 这论文是CVPR 2018 full oral, winner of the 2017 Visual Question Answering challenge。这篇论文算是较前沿的,在表示图像特征集合V时,不是划分区域的方式,而是在object层面表达特征,然后用于attention选取。论文使用了Faster RCNN来识别object和attributes,称之为bottom-up attention,这也是目前被广泛使用的方式了(从VQA challenge 2018中的方法描述得知)。
其中HDU杭电的方法使用的是前面介绍的MFB,也是他们提出的方法,性能也算不错了。目前的leaderboard(已截止)是:
可以看出目前的方法有了一点点提升,然而还是有许多不足的,比如Number计数类问题的准确率就很低,可见目前的模型对知识,图像理解还差得多()。
从VQA challenge的方法描述中得知bottom-up attention是很多方法采用的。
Facebook FAIR-A的描述:Our long-term goal is to create a VQA library where novel models can be easily composed from existing (or new) modules – visual encoders, question encoders, question-based attention mechanisms, and answer predictors. For our entry, we used Bottom-Up Town-Down attention over bounding-box proposes from the faster-RCNN object detector, attention to the question encoding, used Hadamard product instead of concatenation to combine question and image features. Moreover, we adopted a warm-up based learning schedule, fine-tuned the image features, and augmented our training data using Visual Genome and Visual Dialog datasets as well as image mirroring. Finally, we averaged the predictions from a diverse ensemble of models. These models used image features from Faster R-CNN models with feature pyramid networks with different parameter settings and/or initial seeds.
Discuss
作为需要视觉理解与推理能力的,介于Vision与NLP间的视觉问答VQA,是一个有趣而又充满挑战的问题。它的进步不仅依赖于计算机视觉的发展和自然语言处理的能力,还需要对图像的理解——视觉基础能力,如识别,检测等,同时学习到知识与推理的能力。然而,这条路还有很长的距离要走,或许目前大部分方法只不过是对训练数据的拟合分类,并没有理解,也可能包含着语言先验(见CVPR2018论文Don’t Just Assume; Look and Answer: Overcoming Priors for Visual Question Answering)。因此,一个真正理解图像,能够学习到知识和推理能力的模型才是最终目标。