Spring Security源码解析(一.基础知识点与流程介绍)
目录
一、Authentication,AuthenticationManager,AuthenticationProvider
二、UserDetails,UserDetailsService,UserCache,User
三、SecurityContext,SecurityContextHolder
四、WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
五、总结
首先回想一下我们最早学习java web的时候,是怎么做登录认证的。
- 首先制作登录页面(login.html)和登录认证endpoint(LoginController)
- 填写用户名、密码后Post提交表单给LoginController进行认证
- java后台编写UserService、UserDao,根据用户名、密码搜索数据库判断用户信息。如果符合条件,则将用户信息存入session,并设置cookie存储jsessionid,失效时间为半小时,跳转到主页;如果不符合条件重新定位到login.html
- 用户登录成功后,带着cookie横行无阻,因为自定义过滤器UserFilter判断session中是否有用户信息,有就放行。
- 用户执行注销操作,java后台清除session和cookie,并跳转到登录页面。
Spring Security其实就是帮我们封装了一些类,简化了我们的代码。如果按照Spring Security的思路来做登录认证,应该是下面这样
- 用户编写WebSecurityConfigurerApdater的继承类,配置HttpSecurity,包括formLogin,antMatcher,hasRole等等。
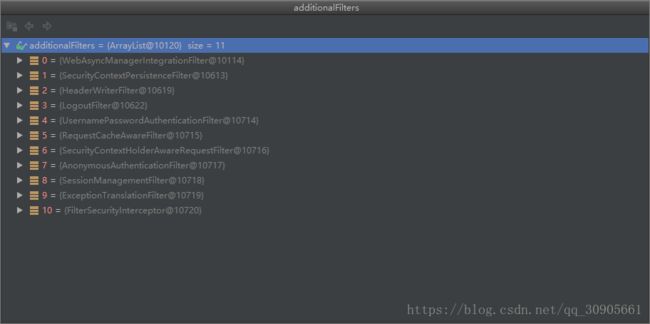
- 项目启动自动装配FilterChain,访问不同uri对应不同的Filter Chain。
- 用户输入账号、密码点击登录,FilterChainProxy中的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter获取request中的用户名、密码,验证身份信息
- doFilter()过程中会执行ProviderManager.authenticate(),即遍历所有AuthenticationProvider执行authenticate()方法。
- authenticate()方法中会调用userDetailService,用户自定义类继承UserDetailService,并重写其中的方法loadUserByUsername(),从数据库中获取用户信息进行比对
- 比对成功后将用户信息和角色信息整合成Authentication,并存入SecurityContext中,同时将SecurityContext也存入session中,跳转到主页面。
- 比对失败,SecurityContext中没有Authentication,FilterChain进行到最后一步FilterSecurityInterceptor,判断用户角色是否能访问request中的访问地址即资源。如果不行则报错跳转到指定页面;如果成功则进入request调用的资源。
- 注销操作由LogoutFilter执行,执行session.invalidate()和SecurityContextHolder.clearContext()。
Spring Security的核心思想是用户授权和资源认证。认证访问系统的用户,而授权则是用户可以访问的资源
认证是调用authenticationManager.authenticate()方法来获得证书authentication,一般我们采用用户名、密码方式认证,那么authentication的实现类就是UsernamePasswordAuthentication。
授权是让用户可以访问哪些资源,一般在WebSecurityConfigurerApdater的继承类中编写。
authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/static/**","/webjars/**","/resources/**").permitAll()整个spring security的核心思想是:通过用户名、密码验证后获取信息Authentication,将此信息存入session中保存。以后每次访问都通过session中的属性SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT获取Authentication作为通行证。
上面简单介绍了Spring Security的验证流程,接下来我们具体讲解各个关键知识点。
一、Authentication,AuthenticationManager,AuthenticationProvider
Authentication代表证书,有了这个证书我们就无需每次请求都要重新认证身份信息,证书是对用户信息的一个简单封装。
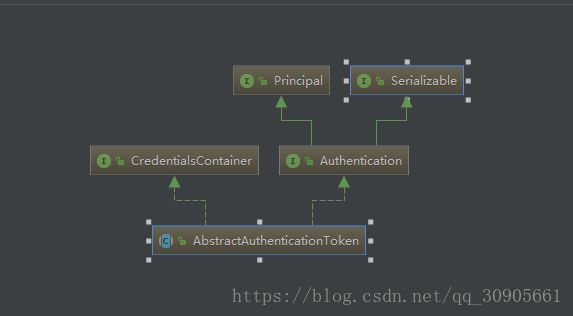
Authentication的继承关系大致如下,其中Principal代表用户主体的概念,如用User,login id或者username代表一个entity,主要方法有equals()和getName();
Authentication用于存储身份验证信息,接口内容如下,包括getAuthorities(),getDetails(),getPrinciple(),getCredentials()以及isAuthenticated()。注意Authentication是没有失效时间的!!!
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
/**
* 一般在JPAEntity中继承UserDetail,重写该方法,
* 存储验证信息Authority集合
* GrantedAuthority是个接口,有方法 String getAuthority();
* GrantedAuthority代表授权,a representation of the granted authority,
* getAuthority()是String类型,一般用SimpleGrantedAuthority(role)来实例化
*/
Collection getAuthorities();
/**
* 返回证明用户身份的证书,一般是用户密码
*/
Object getCredentials();
/**
* 身份验证request额外的细节,如IP地址,和证书序列号
*/
Object getDetails();
/**
* 返回用户身份,一般是继承了UserDetail的Entity
*/
Object getPrincipal();
/**
* 如果是true,则表示token已经验证通过了,无需再调用AuthenticationManager进行验证
*/
boolean isAuthenticated();
/**
* 见isAuthenticated()
*/
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}介绍完了Authentication,再来聊聊AuthenticationManager和AuthenticationProvider。它们两个都是提供authenticate方法的接口,不同的是AuthenticationProvider多了一个supports()方法。一般采用AuthenticationProvider进行authenticate验证
public interface AuthenticationManager {
/**
* 验证传入的authentication信息
* 验证成功则返回一个包含authorities,并设置isAuthorized=true的完整Authentication
* 验证失败则抛出异常
* @param authentication the authentication request object
*
* @return a fully authenticated object including credentials
*
* @throws AuthenticationException if authentication fails
*/
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}public interface AuthenticationProvider {
/**
* 和AuthenticationManager中的authenticate方法一致
* @throws AuthenticationException if authentication fails.
*/
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
/**
* 判断AuthenticationProvider是否支持authentication的补全
*/
boolean supports(Class authentication);
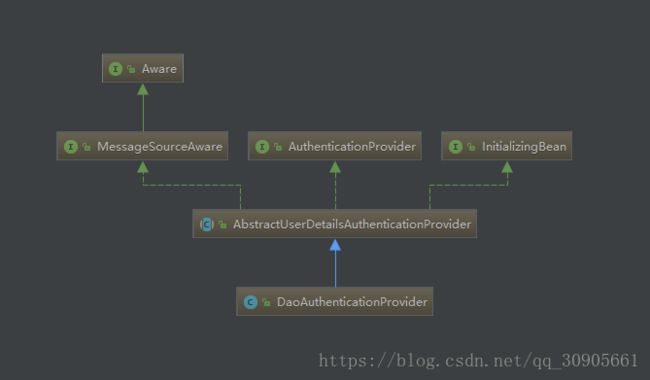
}AuthenticationProvider的抽象类AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider提供了authenticate和(abstract)retrieveUser() 方法。
DaoAuthenticationProvider继承了AbstractUserDetialsAuthenticationProvider,并没有重写authenticate方法,但实现了抽象方法retrieveUser(),通过username从用户自定义UserDetailService(或者系统内置的InMemoryUserDetailsManager)中获取UserDetails,再与authentication进行比对
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException
继承关系如下
二、UserDetails,UserDetailsService,UserCache,User
UserDetails提供基本用户信息,如getUserName(),getPassword(),List getAuthorities()等。
但一般不会直接使用UserDetails存用户信息,而是包装后放到Authentication中的principle和authorities中。
一般自定义用户实体类需要继承UserDetails。
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
// 角色
Collection getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}UserDetailsService就简单了,只有一个方法loadUserByUsername,通过用户名找用户信息UserDetails。
用户可以编写实体类继承该接口,实现loadUserByUsername(从数据库里查询),也可以利用auth.inMemoryAuthentication()创建InMemoryUserDetailsManager。
public interface UserDetailsService {
/**
* Locates the user based on the username. In the actual implementation, the search
* may possibly be case sensitive, or case insensitive depending on how the
* implementation instance is configured. In this case, the UserDetails
* object that comes back may have a username that is of a different case than what
* was actually requested..
*
* @param username the username identifying the user whose data is required.
*
* @return a fully populated user record (never null)
*
* @throws UsernameNotFoundException if the user could not be found or the user has no
* GrantedAuthority
*/
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}UserCache可以代替UserDetailsService获得用户基本信息UserDetail,如果有缓存则不用每次都执行loadUserByUsername,只需从UserCache中调用UserDetail getUserFromCache(String Username)方法即可。如果没有缓存就执行loadUserByUsername,并把获取的UserDetail存入缓存中。
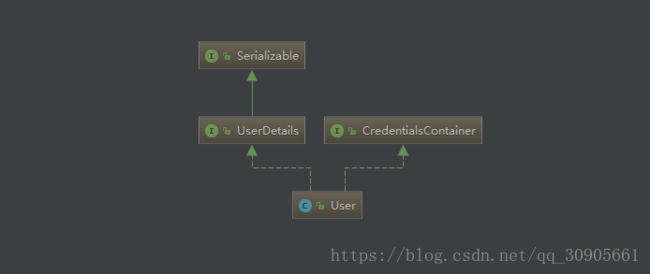
User继承了UserDetails和CredentialsContainer两个接口,常用于UserDetailsService中返回loadUserByUsername()方法的结果(代替自己定义的User实体),但注意的是,必须每次返回的都是新建的User,因为它不是immutable。CredentialsContainer用于清除敏感信息。
User包含属性和方法如下,
private String password;
private final String username;
private final Set authorities;
private final boolean accountNonExpired;
private final boolean accountNonLocked;
private final boolean credentialsNonExpired;
private final boolean enabled;
// 继承自CredentialsContainer,继承该方法的类如Authentication需要把敏感信息credential给去除掉
public void eraseCredentials() {
password = null;
} 三、SecurityContext,SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContext是存储Authentication的容器,结构如下。登录时用户名密码验证成功后获得Authentication,将其存入SecurityContext中,再将SecurityContext存到session里面,如俄罗斯套娃一般。
public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable {
Authentication getAuthentication();
void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication);
}SecurityContextHolder专门用来操作SecurityContext,有static方法setSecurityContext()和getSecurityContext()等。
它的生命周期是一次request,FilterChain中的SecurityContextPersistenceFilter一开始会通过session中的属性“SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT”获取securityContext,并存入SecurityContextHolder中。
如果session中没有属性"SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT",那么会进入UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter进行登录验证,验证成功会按照authentication ——》securityContext——》session的顺序进行存放,一次请求最后会执行SecurityContextHolder.clearContext()操作,详见下图。
如果是注销用户,则会在FilterChain进行到LogoutFilter时,执行注销操作,大意是先执行session.invalidate(),再执行SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(),最后跳转到指定的页面(一般是登录页面,可在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter中配置)
四、WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
这个东西牛掰了,它是spring security的默认http配置。我们可以用它的实现类配合@EnableWebSecurity完成下面功能,也是我们唯一需要手动配置的地方。
- 要求用户在进入你的应用的任何URL之前都进行验证
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();//所有请求必须登陆后访问
}- 创建一个用户名是“user”,密码是“password”,角色是“ROLE_USER”的用户
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
// inMemoryAuthentication()对应的UserDetailsService是inMemoryUserDetailsManager
// enable in memory based authentication with a user named
// "user" and "admin"
.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER").and()
.withUser("admin").password("password").roles("USER", "ADMIN");
}- 启用HTTP Basic和基于表单的验证
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()//所有请求必须登陆后访问
// basic验证
.and().httpBasic()
// 表单验证
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/main")
.failureUrl("/login?error")
.permitAll()//登录界面,错误界面可以直接访问
.and()
.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessUrl("/login")
.permitAll();//注销请求可直接访问
}- Spring Security将会自动生成一个登陆页面和登出成功页面
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的核心方法有以下三个
- configure(HttpSecurtiy http)
- configure(WebSecurity web)
- configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)
// order顺序是100,数值越小越先执行
@Order(100)
public abstract class WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter implements
WebSecurityConfigurer {
/* 可以在inMemoryAuthentication中设置两个用户,包含对应的密码和权限
* auth
*.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER").and()
* .withUser("admin").password("password").roles("USER", "ADMIN");
*
* 也可以设置UserDetailsService,passwordEncoder
* auth.userDetailsService(new myUserDetailsService())
* .passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder());;
*/
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr = true;
}
/**
* Override this method to configure {@link WebSecurity}. For example, if you wish to
* ignore certain requests.
*/
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/hello"); 排除路径拦截
}
// 可以启用httpBasic和表单认证,哪些endpoint需要认证等
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//http.authorizeRequests()方法有多个子节点,每个macher按照他们的声明顺序执行
.authorizeRequests()
//我们指定任何用户都可以访问多个URL的模式。
//任何用户都可以访问以"/resources/","/signup", 或者 "/about"开头的URL。
.antMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll()
//以 "/admin/" 开头的URL只能让拥有 "ROLE_ADMIN"角色的用户访问。
//请注意我们使用 hasRole 方法,没有使用 "ROLE_" 前缀。
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
//任何以"/db/" 开头的URL需要同时具有 "ROLE_ADMIN" 和 "ROLE_DBA"权限的用户才可以访问。
//和上面一样我们的 hasRole 方法也没有使用 "ROLE_" 前缀。
.antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
//任何以"/db/" 开头的URL只需要拥有 "ROLE_ADMIN" 和 "ROLE_DBA"其中一个权限的用户才可以访问。
//和上面一样我们的 hasRole 方法也没有使用 "ROLE_" 前缀。
.antMatchers("/db/**").hasAnyRole("ADMIN", "DBA")
//尚未匹配的任何URL都要求用户进行身份验证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// ...
.formLogin();
}
} 五、总结
目前简单介绍了以下知识点,请读者牢记以下名字和含义,下一章我们将串联起这些知识点进行讲解
- Authentication AuthenticationProvider ProviderManager
- UserDetails UserDetailsService DaoAuthenticationProvider
- SecurityContext SecurityContextHolder
- WebSecurityConfiguererApdater
再反过来看开篇的Spring Security验证过程,是不是有了更全面的认识呢
- 用户编写WebSecurityConfigurerApdater的继承类,配置HttpSecurity,包括formLogin,antMatcher,hasRole等等。
- 项目启动自动装配FilterChainProxy,根据HttpSecurity的配置来初始化一组filters(其实对应不同的URI,都有对应的一组Filters进行身份认证)。
- 用户输入账号、密码点击登录,FilterChain中的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter获取request中的用户名、密码,验证身份信息
- doFilter()过程中会执行ProviderManager.authenticate(),即遍历所有AuthenticationProvider执行authenticate()方法。
- authenticate()方法中会调用userDetailService,用户自定义类继承UserDetailService,并重写其中的方法loadUserByUsername(),从数据库中获取用户信息进行比对
- 比对成功后将用户信息和角色信息整合成Authentication,并存入SecurityContext中,同时将SecurityContext也存入session中,跳转到主页面。
- 比对失败,SecurityContext中没有Authentication,FilterChain进行到最后一步FilterSecurityInterceptor,判断用户角色是否能访问request中的访问地址即资源。如果不行则报错跳转到指定页面;如果成功则进入request调用的资源。
- 注销操作由LogoutFilter执行,执行session.invalidate()和SecurityContextHolder.clearContext()。