OpenCV—python 视频分析背景提取与前景提取
文章目录
- 一、算法
- 二、代码
- MOG2(Mixture of Gaussian) 与 KNN对比
- Kmeans
- 行人检测代码
OpenCV中支持的两种背景提取算法都是 基于模型密度评估,然后在 像素级对图像进行前景与背景分类的方法,它们具有相同的假设前提 – 各个像素之间是没有相关性的,跟它们算法思想不同的方法主要是基于马尔可夫随机场理论,认为每个像素跟周围的像素是有相关性关系,但是基于马尔可夫随机场的方法速度与执行效率都堪忧!所以OpenCV中没有实现。
基于像素分类的背景分析方法
- 自适应的背景提取(无参数化/ KNN)
- 基于GMM的背景提取
- 基于模糊积分的背景提取
这些背景建模的方法一般都可以分为如下三步完成
一、算法
实现对前景与背景像素级别的建模,最常见的是RGB像素的概率密度分布,当对象没有变化的时候,通过连续的 N N N帧进行建模生成背景模型
p ( B D ∣ x → ( t ) ) p ( F G ∣ x → ( t ) ) = p ( x → ( t ) ∣ B G ) p ( B G ) p ( x → ( t ) ∣ F G ) p ( F G ) \frac{p(BD|\overrightarrow{x}^{(t)})}{p(FG|\overrightarrow{x}^{(t)})} = \frac{p(\overrightarrow{x}^{(t)}|BG)p(BG)}{p(\overrightarrow{x}^{(t)}|FG)p(FG)} p(FG∣x(t))p(BD∣x(t))=p(x(t)∣FG)p(FG)p(x(t)∣BG)p(BG)
p ( x → ( t ) ∣ B G ) > c t h r ( = p ( x → ( t ) ∣ F G ) / p ( B G ) ) p(\overrightarrow{x}^{(t)}|BG)> c_{thr}(=p(\overrightarrow{x}^{(t)}|FG)/p(BG)) p(x(t)∣BG)>cthr(=p(x(t)∣FG)/p(BG))
高斯混合模型(GMM)方式正好满足这种方式,对高斯混合模型中的每个componet进行建模,计算表达如下:
p ^ ( x → ∣ X T , B G + F G ) = ∑ m = 1 M π ^ m N ( x → ; μ → ^ m , σ ^ m 2 I ) \hat{p}(\overrightarrow{x}| \mathscr{X}_T,BG+FG) = \sum_{m=1}^M \hat{\pi}_m\mathscr{N}(\overrightarrow{x};\hat{\overrightarrow{\mu}}_m,\hat{\sigma}_m^2 I) p^(x∣XT,BG+FG)=m=1∑Mπ^mN(x;μ^m,σ^m2I)
在更新的时候,会考虑分布直接相似程度,当马氏距离相似度小于3的时候,肯能GMM的主成分维持不变,当大于3以后就会当成一个新的componet,丢弃前面最小的,维持模型。参数 α \alpha α 用来控制更新。
π ^ m ← π ^ m + α ( o ( t ) − π ^ m ) \hat{\pi}_m \leftarrow \hat{\pi}_m + \alpha (o^{(t)}-\hat{\pi}_m) π^m←π^m+α(o(t)−π^m)
μ ⃗ ^ m ← μ ^ m + o m ( t ) ( α / π ^ m ) δ ⃗ m \hat{\vec{\mu}}_m \leftarrow \hat{\mu}_m + o_{m}^{(t)} (\alpha /\hat{\pi}_m)\vec{\delta}_m μ^m←μ^m+om(t)(α/π^m)δm
σ ^ m 2 ← σ ^ m 2 + o m ( t ) ( α / π ^ m ) δ ⃗ m T δ ⃗ m − σ ^ m 2 \hat{\sigma}_m^2 \leftarrow \hat{\sigma}_m^2 + o_{m}^{(t)} (\alpha /\hat{\pi}_m)\vec{\delta}_m^T \vec{\delta}_m- \hat{\sigma}_m^2 σ^m2←σ^m2+om(t)(α/π^m)δmTδm−σ^m2
基于GMM的核密度估算需要考虑初始输入componet数目参数、OpenCV中实现的另外一种方法是基于简单的核密度估算方法,然后通过KNN对输出的每个像素进行前景与背景分类,实现了更加快速的背景分析。非参数话的模型更新
p ^ n o n − p a r a m e t r i c ( x → ∣ X T , B G ) ≈ 1 T V ∑ m = t − T t b ( m ) K ( ∣ ∣ x → ( m ) − x → ∣ ∣ D ) \hat{p}_{non-parametric}(\overrightarrow{x}| \mathscr{X}_T,BG) \approx \frac{1}{TV} \sum_{m=t-T}^{t} b^{(m)} \mathscr{K} \left ( \frac{||\overrightarrow{x}^{(m)}-\overrightarrow{x}||}{D} \right ) p^non−parametric(x∣XT,BG)≈TV1m=t−T∑tb(m)K(D∣∣x(m)−x∣∣)
上述两种方法都是基于像素分类,采用非此即彼的方法,没有考虑到像素之间相似度的关联性,在实际应用场景中有些情况会带来问题。所以还有一种相似度进行模糊积分决策方法,它的算法流程如下:
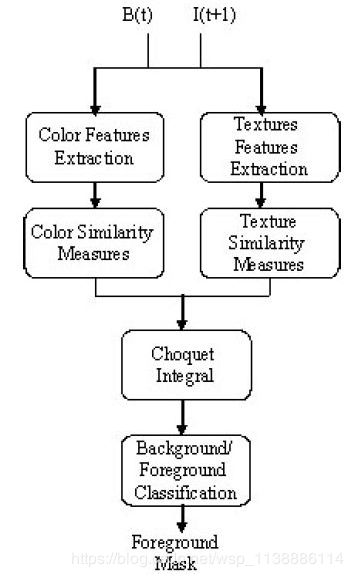
其中颜色相似性度量如下:
S k C ( x , y ) = { I k C ( x , y ) I k B ( x , y ) i f I k C ( x , y ) < I k B ( x , y ) 1 i f I k C ( x , y ) = I k B ( x , y ) I k B ( x , y ) I k C ( x , y ) i f I k C ( x , y ) > I k B ( x , y ) S_{k}^{C}(x,y) = \left\{\begin{matrix} \frac{I_{k}^{C}(x,y)}{I_{k}^{B}(x,y)} & \mathrm{if} & I_{k}^{C}(x,y)
纹理相似度度量(纹理特征LBP特征)
S T ( x , y ) = { L C ( x , y ) L B ( x , y ) i f L C ( x , y ) < L B ( x , y ) 1 i f L C ( x , y ) = L B ( x , y ) L B ( x , y ) L C ( x , y ) i f L C ( x , y ) > L B ( x , y ) S^{T}(x,y) = \left\{\begin{matrix} \frac{L^{C}(x,y)}{L^{B}(x,y)} & \mathrm{if} & L^{C}(x,y)
OpenCV在release模块中相关API
Ptr<BackgroundSubtractorMOG2> cv::createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2(
int history = 500,
double varThreshold = 16,
bool detectShadows = true
)
参数解释
History表示的是历史帧数多少,这个跟作者论文提到的采样有关计算模型建立有关系
varThreshold表示马氏距离的阈值
detectShadows是否检测阴影
二、代码
MOG2(Mixture of Gaussian)
import cv2
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(r"C:\Users\xxx\Videos\mouse.mp4")
mog = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
se = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
while True:
ret, image = capture.read()
if ret is True:
fgmask = mog.apply(image)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(fgmask, 220, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
binary = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, se)
backgimage = mog.getBackgroundImage()
cv2.imshow("backgimage", backgimage)
cv2.imshow("frame", image)
cv2.imshow("binary", binary)
c = cv2.waitKey(50)
if c == 27:
break
else:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
MOG2(Mixture of Gaussian) 与 KNN对比
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('./data/mouse.mp4')
knn_sub = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorKNN()
mog2_sub = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
mog_sub_mask = mog2_sub.apply(frame)
knn_sub_mask = knn_sub.apply(frame)
cv2.imshow('original', frame)
cv2.imshow('MOG2', mog_sub_mask)
cv2.imshow('KNN', knn_sub_mask)
key = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xff
if key == 27 or key == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Kmeans
检测的物体需要色彩相近,才能有好效果
'''
Extract panel :kmeans聚类
'''
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
def panelAbstract(srcImage):
# read pic shape
imgHeight,imgWidth = srcImage.shape[:2]
imgHeight = int(imgHeight);imgWidth = int(imgWidth)
# 均值聚类提取前景:二维转一维
imgVec = np.float32(srcImage.reshape((-1,3)))
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,10,1.0)
flags = cv2.KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS
ret,label,clusCenter = cv2.kmeans(imgVec,2,None,criteria,10,flags)
clusCenter = np.uint8(clusCenter)
clusResult = clusCenter[label.flatten()]
imgres = clusResult.reshape((srcImage.shape))
imgres = cv2.cvtColor(imgres,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
bwThresh = int((np.max(imgres)+np.min(imgres))/2)
_,thresh = cv2.threshold(imgres,bwThresh,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
threshRotate = cv2.merge([thresh,thresh,thresh])
# 确定前景外接矩形
#find contours
imgCnt,contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
minvalx = np.max([imgHeight,imgWidth]);maxvalx = 0
minvaly = np.max([imgHeight,imgWidth]);maxvaly = 0
maxconArea = 0;maxAreaPos = -1
for i in range(len(contours)):
if maxconArea < cv2.contourArea(contours[i]):
maxconArea = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
maxAreaPos = i
objCont = contours[maxAreaPos]
# 旋转校正前景
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(objCont)
for j in range(len(objCont)):
minvaly = np.min([minvaly,objCont[j][0][0]])
maxvaly = np.max([maxvaly,objCont[j][0][0]])
minvalx = np.min([minvalx,objCont[j][0][1]])
maxvalx = np.max([maxvalx,objCont[j][0][1]])
if rect[2] <=-45:
rotAgl = 90 +rect[2]
else:
rotAgl = rect[2]
if rotAgl == 0:
panelImg = srcImage[minvalx:maxvalx,minvaly:maxvaly,:]
else:
rotCtr = rect[0]
rotCtr = (int(rotCtr[0]),int(rotCtr[1]))
rotMdl = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(rotCtr,rotAgl,1)
imgHeight,imgWidth = srcImage.shape[:2]
#图像的旋转
dstHeight = math.sqrt(imgWidth *imgWidth + imgHeight*imgHeight)
dstRotimg = cv2.warpAffine(threshRotate,rotMdl,(int(dstHeight),int(dstHeight)))
dstImage = cv2.warpAffine(srcImage,rotMdl,(int(dstHeight),int(dstHeight)))
dstRotimg = cv2.cvtColor(dstRotimg,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_,dstRotBW = cv2.threshold(dstRotimg,127,255,0)
imgCnt,contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dstRotBW,cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
maxcntArea = 0;maxAreaPos = -1
for i in range(len(contours)):
if maxcntArea < cv2.contourArea(contours[i]):
maxcntArea = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
maxAreaPos = i
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[maxAreaPos])
#提取前景:panel
panelImg = dstImage[int(y):int(y+h),int(x):int(x+w),:]
return panelImg
if __name__=="__main__":
srcImage = cv2.imread('mouse.png')
a=panelAbstract(srcImage)
cv2.imshow('figa',a)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
行人检测代码
import cv2
datapath = "./people.mp4"
bs = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorKNN(detectShadows = False)#背景减除器,设置阴影检测
#训练帧数
history=20
bs.setHistory(history)
frames=0
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(datapath)
count = 0
while True:
ret, frame = camera.read() # ret=True/False,判断是否读取到了图片
if ret==True:
fgmask = bs.apply(frame) # 计算前景掩码,包含 前景的白色值 以及 阴影的灰色值
if frames < history:
frames += 1
continue
#对原始帧膨胀去噪,
th = cv2.threshold(fgmask.copy(), 244, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
#前景区域形态学处理
th = cv2.erode(th, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (3,3)), iterations = 2)
dilated = cv2.dilate(th, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (8,3)), iterations = 2)
#绘制前景图像的检测框
image, contours, hier = cv2.findContours(dilated, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in contours:
#对轮廓设置最小区域,筛选掉噪点框
if cv2.contourArea(c) > 1000:
#获取矩形框边界坐标
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imwrite("frame%d.jpg" % count, fgmask) #保存处理后的每一帧图片,JPEG格式的图片
cv2.imshow("mog", fgmask)
cv2.imshow("thresh", th)
cv2.imshow("diff", frame & cv2.cvtColor(fgmask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR))
cv2.imshow("detection", frame)
count += 1
if cv2.waitKey(100) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
else:
break
camera.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
