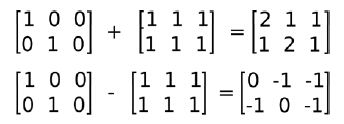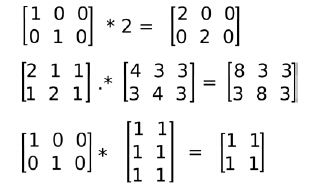opencv mat操作总结
现在一写代码就忘了怎么赋值、怎么取元素,还是写得太少。现把目前用到的总结一下。
文章目录
- Mat 访问元素
- 矩阵显示函数
- Mat 初始化
- 数据类型
- 数组初始化
- 深拷贝、浅拷贝
- Mat转化为数组
- 列向量转换成对角向量
- 转置
- 求逆
- SVD
- 加减乘除
- 加减法
- 矩阵乘法
- divide
- multiply
Mat 访问元素
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/bendanban/article/details/30527785
- 使用Mat的成员函数at<>()
template<typename _Tp> _Tp& at(int i0, int i1);
Vec3b pix;
for (int r = 0; r < im.rows; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < im.cols; c++)
{
pix = im.at<Vec3b>(r,c);
pix = pix*scale;
om.at<Vec3b>(r,c) = pix;
}
}
- 使用Mat的成员函数ptr<>()
template<typename _Tp> _Tp* ptr(int i0=0);
Vec3b *ppix_im(NULL);
Vec3b *ppix_om(NULL);
for (int r = 0; r < im.rows; r++)
{
ppix_im = im.ptr<Vec3b>(r);
ppix_om = om.ptr<Vec3b>(r);
for (int c = 0; c < im.cols; c++)
{
ppix_om[c] = ppix_im[c]*scale;
}
}
我的理解:
Vec3b pix;
for (int r = 0; r < im.rows; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < im.cols; c++)
{
pix = im.ptr<Vec3b>(r)[c];//注意括号不同
pix = pix*scale;
om.ptr<Vec3b>(r)[c] = pix;
}
}
- 使用迭代器
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it_im, itEnd_im;
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it_om;
it_im = im.begin<Vec3b>();
itEnd_im = im.end<Vec3b>();
it_om = om.begin<Vec3b>();
for (; it_im != itEnd_im; it_im++, it_om++)
{
*it_om = (*it_im)*scale;
}
- 使用Mat_简化索引
Mat_这个类的元素访问比较容易一点,把原Mat类的对象可以直接赋值给Mat_对象,当然赋值操作并不会开辟新的数据空。也就是说使用Mat_时,不会在内存拷贝上花时间。
Mat_<Vec3b> im_, om_;
im_ = im;
om_ = om;
for (int r = 0; r < im.rows; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < im.cols; c++)
{
om_(r,c) = im_(r,c) * scale;
}
}
- 使用OpenCV原有的实现
使用*运算符重载
om = im*scale;
- 测试代码
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test.cpp
> Author: aban
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 2014年06月13日 星期五 18时47分19秒
************************************************************************/
#include 矩阵显示函数
//可以直接:
cout<<m<<endl;
//或者通过函数:
void printMat(Mat & m){
for (int row = 0; row < m.rows; row++){
for (int col = 0; col < m.cols; col++){
cout<<m.at<float>(row,col)<<" ";
}
// float* ptr = (float*)(m.data.ptr + row * m.step);//第row行数据的起始指针
// for (int col = 0; col < m.cols; col++)
// cout<<*(ptr+3*col)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
Mat 初始化
数据类型
CV_8UC1// 8位无符号单通道
CV_8UC3// 8位无符号3通道
CV_8UC4
CV_32FC1// 32位浮点型单通道
CV_32FC3// 32位浮点型3通道
CV_32FC4
// 初始化方法
cv::Mat mz = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(5,5),CV_8UC1); // 全零矩阵
cv::Mat mo = cv::Mat::ones(cv::Size(5,5),CV_8UC1); // 全1矩阵
cv::Mat me = cv::Mat::eye(cv::Size(5,5),CV_32FC1); // 对角线为1的对角矩阵
cout<<"mz = "<<endl<<mz<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"mo = "<<endl<<mo<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"me = "<<endl<<me<<endl<<endl;
Mat mat = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1);
数组初始化
1、直接初始化
Mat_<float> T_L = (Mat_<float>(3, 1) << -518.97666, 01.20629, 9.14632);
2、利用数组初始化
float A[4][3] = { 0 };
Mat A_mat = Mat(4, 3, CV_32F, A);//如果是double类型用64
深拷贝、浅拷贝
浅拷贝是指当图像之间进行赋值时,图像数据并未发生复制,而是两个对象都指向同一块内存块。比如:
Mat img2=img1; //拷贝方式为浅拷贝
flip(img2,img2,1); //在原地进行镜像变换
深拷贝是指新创建的图像拥有原始图像的崭新拷贝,即拷贝图像和原始图像在内存中存放在不同地方。OpenCV中可以通过下面两种方式实现深拷贝。
//1.
Mat img1;
img.copyTo(img1);
//2.
Mat img1=img.clone();
Mat转化为数组
Mat转化为数组可以用以下两种方法:
- Mat中提供ptr函数
用ptr访问任意一行像素的首地址,然后当做指针来读取这一行的数据,适合一行一行的横向访问
Mat M1;
float* row1 = M1.ptr<float>(0);//获取第一行首地址
float b[4] = { 0 };
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
b[i]=row1[i];//第一行的第i个数赋给b[i]
}
- 使用Mat的成员函数at<>()
直接给i,j赋值就可以随意访问图像中任何一个像素,其中j表示第j行,i表示该行第i个像素。如果访问所有的变量,效率很低。
M1.at<float>(2, 0)//第三行第一个元素的值
列向量转换成对角向量
W = Mat::diag(D_inv);
转置
// 转置
Mat m1= Mat::eye(2,3, CV_32F);
Mat m1t = m1.t();
//Mat m1t = m1.transpose();
求逆
// 求逆
Mat meinv = me.inv();
//cv::Mat::inv(int method = DECOMP_LU)//default
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| DECOMP_LU | Gaussian elimination with the optimal pivot element chosen. |
| DECOMP_SVD | singular value decomposition (SVD) method; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix src1 can be singular |
| DECOMP_EIG | eigenvalue decomposition; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical |
| DECOMP_CHOLESKY | Cholesky L L T LL^T LLT factorization; the matrix src1 must be symmetrical and positively defined |
| DECOMP_QR | QR factorization; the system can be over-defined and/or the matrix src1 can be singular |
| DECOMP_NORMAL | while all the previous flags are mutually exclusive, this flag can be used together with any of the previous; it means that the normal equations s r c 1 T ⋅ s r c 1 ⋅ d s t = s r c 1 T s r c 2 src1^T⋅src1⋅dst=src1^Tsrc2 src1T⋅src1⋅dst=src1Tsrc2 are solved instead of the original system s r c 1 ⋅ d s t = s r c 2 src1⋅dst=src2 src1⋅dst=src2 |
SVD
//SVD (InputArray src, int flags=0)
SVD svd(mat);
Mat U = svd.u;
Mat VT = svd.vt;
Mat W = svd.w;//列向量
// mat = U*W*Vt
//伪逆:Mat mat_inv = V*W_inv*UT;
//W_inv:
////Mat I3 = Mat::ones(3,1,CV_32F);
////divide(I3,D,D_inv);
////Mat W_inv = Mat::diag(D_inv)
加减乘除
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/iracer/article/details/51296631
加减法
//逐元素
cv::Mat a= Mat::eye(Size(3,2), CV_32F);
cv::Mat b= Mat::ones(Size(3,2), CV_32F);
cv::Mat c= a+b;
cv::Mat d= a-b;
矩阵乘法
Mat m1= Mat::eye(2,3, CV_32F); //使用cv命名空间可省略cv::前缀,下同
Mat m2= Mat::ones(3,2, CV_32F);
cout<<"m1 = "<<endl<<m1<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"m2 = "<<endl<<m2<<endl<<endl;
// Scalar by matrix
cout << "\nm1.*2 = \n" << m1*2 << endl;
// matrix per element multiplication
cout << "\n(m1+2).*(m1+3) = \n" << (m1+1).mul(m1+3) << endl;
// Matrix multiplication
cout << "\nm1*m2 = \n" << m1*m2 << endl;
divide
C++: void divide(InputArray src1, InputArray src2, OutputArray dst, double scale=1, int dtype=-1)
C++: void divide(double scale, InputArray src2, OutputArray dst, int dtype=-1)
Parameters:
src1 – first input array.
src2 – second input array of the same size and type as src1.
scale – scalar factor.
dst – output array of the same size and type as src2.
dtype – optional depth of the output array; if -1, dst will have depth src2.depth(), but in case of an array-by-array division, you can only pass -1 when src1.depth()==src2.depth().
The functions divide divide one array by another:
dst(I) = saturate(src1(I)*scale/src2(I)) \texttt{dst(I) = saturate(src1(I)*scale/src2(I))} dst(I) = saturate(src1(I)*scale/src2(I))
or a scalar by an array when there is no src1 :
dst(I) = saturate(scale/src2(I)) \texttt{dst(I) = saturate(scale/src2(I))} dst(I) = saturate(scale/src2(I))
When src2(I) is zero, dst(I) will also be zero. Different channels of multi-channel arrays are processed independently.
multiply
C++: void multiply(InputArray src1, InputArray src2, OutputArray dst, double scale=1, int dtype=-1 )
Parameters:
src1 – first input array.
src2 – second input array of the same size and the same type as src1.
dst – output array of the same size and type as src1.
scale – optional scale factor.
The function multiply calculates the per-element product of two arrays:
dst ( I ) = saturate ( scale ⋅ src1 ( I ) ⋅ src2 ( I ) ) \texttt{dst} (I)= \texttt{saturate} ( \texttt{scale} \cdot \texttt{src1} (I) \cdot \texttt{src2} (I)) dst(I)=saturate(scale⋅src1(I)⋅src2(I))