hbase的批量数据导入-bulkload技术应用
Hbase的批量的数据导入
Hbase的数据导入有如下的几种方式
- 使用java API的方式
java API中的put操作可以将数据导入到hbase中 其中包含单条和批量导入两种方式
@Test
public void test5() throws IOException {
// 获取Hbase配置文件的对象
// HBaseConfiguration conf=(HBaseConfiguration) HBaseConfiguration.create();
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
// 设置conf的zk访问路径
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop01:2181,hadoop02:2181,hadoop03:2181");
// 创建hbase连接
Connection conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
System.out.println(conn);
// 获取dml的句柄
// 一个Htable对象代表一个表
HTable table = (HTable) conn.getTable(TableName.valueOf("test1"));
// 数据导入 重点****************
// 插入单条数据 Put对象是封装需要插入的数据,每一条数据都要封装一个普通对象
Put put = new Put("rk001".getBytes());
// 参数1是列簇 参数2 是列 参数3 是值
put.addColumn("info1".getBytes(), "age".getBytes(), "100".getBytes());
table.put(put);
}
// 批量数据导入 list
// 先将插入的数据放在list集合(也就是放在内存中)并没有提交,等放置完成之后一起提交,这种情况有可能出现内存溢出,因为list集合太大的话就Juin占满内存
@Test
public void test6() throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取Hbase配置文件的对象
// HBaseConfiguration conf=(HBaseConfiguration) HBaseConfiguration.create();
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
// 设置conf的zk访问路径
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop01:2181,hadoop02:2181,hadoop03:2181");
// 创建hbase连接
Connection conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
System.out.println(conn);
// 获取dml的句柄
// 一个Htable对象代表一个表
HTable table = (HTable) conn.getTable(TableName.valueOf("test1"));
// 创建list
List<Put> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Put put = new Put(("rk" + i).getBytes());
put.addColumn("info1".getBytes(), "age".getBytes(), ("" + i).getBytes());
list.add(put);
}
table.put(list);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用时:" + (end - start));
}
// 利用本地缓存批量数据导入,本地缓存是基于磁盘的,不会占用太多的内存,但是这种方式是没有list集合的方法速度快
@Test
public void test7() throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取Hbase配置文件的对象
// HBaseConfiguration conf=(HBaseConfiguration) HBaseConfiguration.create();
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
// 设置conf的zk访问路径
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop01:2181,hadoop02:2181,hadoop03:2181");
// 创建hbase连接
Connection conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
System.out.println(conn);
// 获取dml的句柄
// 一个Htable对象代表一个表
HTable table = (HTable) conn.getTable(TableName.valueOf("test1"));
// 设置是否需要自动刷新自动提交put对象,默认true,默认一条数据就会提交一次
// 将参数改为false 不会立即提交,达到我们设定的值才会提交
table.setAutoFlushTo(false);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Put put = new Put(("rk" + i).getBytes());
put.addColumn("info1".getBytes(), "age".getBytes(), ("" + i).getBytes());
// 这时候不会自动提交到hbase了 提交到本地缓存了
table.put(put);
// 如果设置缓存的大小一般就不用设置指定条数提交了,但是这两种方式注意最后提交一次
table.setWriteBufferSize(10 * 1024 * 1024);// 这是设置缓存的大小,
if (i % 3000 == 0) {
table.flushCommits();
}
}
table.flushCommits();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用时:" + (end - start));
}
2.使用mapreduce job的方式进行导入
具体的导入的方式可以参考下面的博客
https://blog.csdn.net/CHANGGUOLONG/article/details/90732931
这篇博客详细介绍了Hbase的Mapreduce操作,并有相关案例
3.采用bulkload的方式进行导入
- 什么是bulkload呢
在put数据时会先将数据的更新操作信息和数据信息写入WAL,在写入到WAL后,数据就会被放到MemStore中,当MemStore满后数据就会被flush到磁盘(即形成HFile文件),在这过程涉及到的flush,split,compaction等操作都容易造成节点不稳定,数据导入慢,耗费资源等问题,在海量数据的导入过程极大的消耗了系统性能,避免这些问题最好的方法就是使用BlukLoad的方式来加载数据到HBase中。
首先明白一点:Hbase中的内容再hdfs中是以Hfile文件格式进行存储的, HBase中每张Table在根目录(/HBase)下用一个文件夹存储,Table名为文件夹名,在Table文件夹下每个Region同样用一个文件夹存储,每个Region文件夹下的每个列族也用文件夹存储,而每个列族下存储的就是一些HFile文件,HFile就是HBase数据在HFDS下存储格式,其整体目录结构如下:
/hbase////
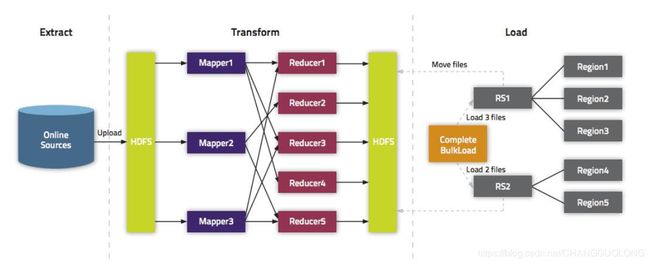
具体怎样实现呢?
系统内部有这样一个类
/**
*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ArrayBackedTag;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.Cell;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.CellComparator;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.KeyValue;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.KeyValueUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.Tag;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TagType;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TagUtil;
import org.apache.yetus.audience.InterfaceAudience;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.exceptions.DeserializationException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.security.visibility.CellVisibility;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Emits sorted Puts.
* Reads in all Puts from passed Iterator, sorts them, then emits
* Puts in sorted order. If lots of columns per row, it will use lots of
* memory sorting.
* @see HFileOutputFormat2
* @see CellSortReducer
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Public
public class PutSortReducer extends
Reducer<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put, ImmutableBytesWritable, KeyValue> {
// the cell creator
private CellCreator kvCreator;
@Override
protected void
setup(Reducer<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put, ImmutableBytesWritable, KeyValue>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
this.kvCreator = new CellCreator(conf);
}
@Override
protected void reduce(
ImmutableBytesWritable row,
java.lang.Iterable<Put> puts,
Reducer<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put,
ImmutableBytesWritable, KeyValue>.Context context)
throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException
{
// although reduce() is called per-row, handle pathological case
long threshold = context.getConfiguration().getLong(
"putsortreducer.row.threshold", 1L * (1<<30));
Iterator<Put> iter = puts.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
TreeSet<KeyValue> map = new TreeSet<>(CellComparator.getInstance());
long curSize = 0;
// stop at the end or the RAM threshold
List<Tag> tags = new ArrayList<>();
while (iter.hasNext() && curSize < threshold) {
// clear the tags
tags.clear();
Put p = iter.next();
long t = p.getTTL();
if (t != Long.MAX_VALUE) {
// add TTL tag if found
tags.add(new ArrayBackedTag(TagType.TTL_TAG_TYPE, Bytes.toBytes(t)));
}
byte[] acl = p.getACL();
if (acl != null) {
// add ACL tag if found
tags.add(new ArrayBackedTag(TagType.ACL_TAG_TYPE, acl));
}
try {
CellVisibility cellVisibility = p.getCellVisibility();
if (cellVisibility != null) {
// add the visibility labels if any
tags.addAll(kvCreator.getVisibilityExpressionResolver()
.createVisibilityExpTags(cellVisibility.getExpression()));
}
} catch (DeserializationException e) {
// We just throw exception here. Should we allow other mutations to proceed by
// just ignoring the bad one?
throw new IOException("Invalid visibility expression found in mutation " + p, e);
}
for (List<Cell> cells: p.getFamilyCellMap().values()) {
for (Cell cell: cells) {
// Creating the KV which needs to be directly written to HFiles. Using the Facade
// KVCreator for creation of kvs.
KeyValue kv = null;
TagUtil.carryForwardTags(tags, cell);
if (!tags.isEmpty()) {
kv = (KeyValue) kvCreator.create(cell.getRowArray(), cell.getRowOffset(),
cell.getRowLength(), cell.getFamilyArray(), cell.getFamilyOffset(),
cell.getFamilyLength(), cell.getQualifierArray(), cell.getQualifierOffset(),
cell.getQualifierLength(), cell.getTimestamp(), cell.getValueArray(),
cell.getValueOffset(), cell.getValueLength(), tags);
} else {
kv = KeyValueUtil.ensureKeyValue(cell);
}
if (map.add(kv)) {// don't count duplicated kv into size
curSize += kv.heapSize();
}
}
}
}
context.setStatus("Read " + map.size() + " entries of " + map.getClass()
+ "(" + StringUtils.humanReadableInt(curSize) + ")");
int index = 0;
for (KeyValue kv : map) {
context.write(row, kv);
if (++index % 100 == 0)
context.setStatus("Wrote " + index);
}
// if we have more entries to process
if (iter.hasNext()) {
// force flush because we cannot guarantee intra-row sorted order
context.write(null, null);
}
}
}
}
这个类是干什么呢? 它继承了reducer的类,那么他就能实现reduce端的功能,而且这个类都已经进行了具体的实现,就是说具体的方法系统都已经搞好了,我们直接嗲用就好了,说白了就是可以直接将map端的发来的数据用通过reduce转换成Hfile文件保存到hdfs中,但是要求map端输出的数据(key value)的格式必须满足
/***********************************************
*
1::F::1::10::48067
2::M::56::16::70072
3::M::25::15::55117
4::M::45::7::02460
5::M::25::20::55455
6::F::50::9::55117
7::M::35::1::06810
8::M::25::12::11413
9::M::25::17::61614
10::F::35::1::95370
11::F::25::1::04093
通过bluckload将hdfs中的数据导入hbase中
***********************************************/
public class Testbulkload {
static class MyMapper extends Mapper{
//map端正常读取文档中的数据,将
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] datas = value.toString().split("::");
if(datas.length==5) {
//将ID封装成rowkey,为什么封装成这种格式呢,因为reduce端需要
ImmutableBytesWritable rk = new ImmutableBytesWritable(datas[0].getBytes());
Put put=new Put(rk.get());
put.addColumn("info".getBytes(), "sex".getBytes(), datas[1].getBytes());
put.addColumn("info".getBytes(), "age".getBytes(), datas[2].getBytes());
put.addColumn("info".getBytes(), "jobid".getBytes(), datas[3].getBytes());
put.addColumn("info".getBytes(), "zipcode".getBytes(), datas[4].getBytes());
context.write(rk, put);
}
}
/**
* org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce;中已经给我们封装好了一个类,这个类的源码如下
*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//设置用户
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "hadoop");
//创建配置文件对象
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
//设置zk的
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop01:2181,hadoop02:2181,hadoop03:2181");
//设置hdfs的入口
conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "hdfs://高可用组名/");
//启动job
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf);
//设置jar 主类
job.setJarByClass(Testbulkload.class);
//设置map reduce 类
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);//这是自定义的类
job.setReducerClass(PutSortReducer.class);//这是系统已经封装好了的类
//设置map和reduce的输出类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(ImmutableBytesWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Put.class);
//reduce端的,这个不能胡来,系统已经规定好了
job.setOutputKeyClass(ImmutableBytesWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass( KeyValue.class);
//指定输入
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path( "/movie/users/"));
/**
* 设置输出的路径:这里需要注意了
* 常用的FileOutFormat是输出的hdfs的文本的格式,但是这次我们输出的是Hfile的格式,所以这个类就不能使用了
* 系统中还有一个类,HFileOutputFormat2,这个类就是能将reduce输出来的key和value输出到hdfs上生成hfile文件
*/
/**
* 下边这是HFileOutputFormat2的类的注释
* Writes HFiles. Passed Cells must arrive in order.
* Writes current time as the sequence id for the file. Sets the major compacted
* attribute on created @{link {@link HFile}s. Calling write(null,null) will forcibly roll
* all HFiles being written.
*
* 下边句话的意思是如果用这个类作为mapreduce的一部分的话需要用到configureIncrementalLoad(Job, Table, RegionLocator)
* Using this class as part of a MapReduce job is best done
* using {@link #configureIncrementalLoad(Job, Table, RegionLocator)}.
*/
job.setOutputFormatClass(HFileOutputFormat2.class);
//设置路径输出到hdfs的路径
Path out=new Path("/hbase_bulk_out01");
FileSystem fs=FileSystem.get(conf);
if(fs.exists(out)){
fs.delete(out, true);
}
HFileOutputFormat2.setOutputPath(job, out);
//配置 hfile文件 和 表的对应关系
Connection conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
Admin admin = conn.getAdmin();
HTable table = (HTable)conn.getTable(TableName.valueOf("test_bl"));
HFileOutputFormat2.configureIncrementalLoad(job, table,
conn.getRegionLocator(TableName.valueOf("test_bl")));
//提交
job.waitForCompletion(true);
//将 hfile文件 加载到 hbase的对应的表目录下
LoadIncrementalHFiles loader=new LoadIncrementalHFiles(conf);
//将 hfile文件 加载到 hbase的对应的表目录下
/*
* 参数1: hfile文件的输出目录
* 参数2:admin对象 表的管理对象
* 参数3 表名
* 参数4 region 的加载的类 获取region的相关信息
*/
loader.doBulkLoad(out, admin,table,
conn.getRegionLocator(TableName.valueOf("test_bl")));
}
}
执行操作之前需要在hbase中创建一张表,指定列簇,之后运行上边的代码
查看hbase表中的数据
1 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=1
1 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=10
1 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=F
1 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=48067
10 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=35
10 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=1
10 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=F
10 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=95370
100 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=35
100 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=17
100 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
100 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=95401
1000 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=25
1000 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=6
1000 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=F
1000 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=90027
1001 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=25
1001 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=4
1001 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
1001 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=90210
1002 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=50
1002 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=11
1002 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
1002 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=07043
1003 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=25
1003 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=2
1003 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
1003 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=19320
1004 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=25
1004 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=3
1004 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
1004 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=95136
1005 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=35
1005 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=11
1005 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
1005 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=08003
1006 column=info:age, timestamp=1559610691657, value=18
1006 column=info:jobid, timestamp=1559610691657, value=4
1006 column=info:sex, timestamp=1559610691657, value=M
1006 column=info:zipcode, timestamp=1559610691657, value=53220
此过程中应该注意的几个问题
**1.在创建表时对表进行预分区再结合MapReduce的并行计算能有效的加快HFile的生成,通过预分区,可以创建多个空Region,对表进行了预分区后,Reduce数就等于Region数
2.在多列族的情况下,需要进行多次的拼装和context.write,即在一个mapper里面输出多条数据。
3.在跑jar包的时候,可能会遇到ClassNotFound的异常抛出,这个问题只需要在HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh中添加一句export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:/opt/software/hbase-1.2.0-cdh5.14.0/lib/*,就可以让hadoop读到hbase的lib.**