[mxnet] mxnet60分钟入门Gluon教程
mxnet60分钟入门Gluon教程代码下载,适合做过深度学习的人使用。入门教程地址:
https://beta.mxnet.io/guide/getting-started/crash-course/index.html
mxnet安装方法:pip install mxnet
1 在mxnet中使用ndarray处理数据
ndarray类似numpy,在mxnet下通过ndarray处理数据,ndarry类似与numpy。
# pip install -U mxnet 安装mxnet库
# 如
from mxnet import nd
# jupyter 多行输出
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
Get started
基本操作
# 建立2行3列的矩阵
nd.array(((1,2,3),(5,6,7)))
[[1. 2. 3.]
[5. 6. 7.]]
# 建立2行3列的矩阵,用1填充
x = nd.ones((2,3))
x
[[1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1.]]
# 建立2行3列的矩阵,用随机数填充
y = nd.random.uniform(-1,1,(2,3))
y
[[0.09762704 0.18568921 0.43037868]
[0.6885315 0.20552671 0.71589124]]
# 建立2行3列的矩阵,用2.0填充
x = nd.full((2,3), 2.0)
x
[[2. 2. 2.]
[2. 2. 2.]]
# 查看变量x的维度,大小,类型
(x.shape, x.size, x.dtype)
((2, 3), 6, numpy.float32)
Operations
运算
# 对应元素相乘
x * y
[[0.19525409 0.37137842 0.86075735]
[1.377063 0.41105342 1.4317825 ]]
# 返回e的y幂次方
y.exp()
[[1.1025515 1.204048 1.5378398]
[1.9907899 1.2281718 2.0460093]]
# 将y转置后进行x,y矩阵乘法
nd.dot(x, y.T)
[[1.4273899 3.219899 ]
[1.4273899 3.219899 ]]
indexing
切片
# 读取第2第3个数的值,nd序号从0开始
y[1,2]
[0.71589124]
# 读取第2列到第3列的值
y[:,1:3]
[[0.18568921 0.43037868]
[0.20552671 0.71589124]]
# 读取第2列到第3列的值,并将赋值为4
y[:,1:3] = 4
y
[[0.09762704 4. 4. ]
[0.6885315 4. 4. ]]
Converting between MXNet NDArray and NumPy
mxnet的ndarry与numpy互相转换
# 将x转换为numpy格式
a = x.asnumpy()
(type(a), a)
(numpy.ndarray, array([[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]], dtype=float32))
# 将numpy数组转换ndarray格式
nd.array(a)
[[2. 2. 2.]
[2. 2. 2.]]
2 通过mxnet的Gluon模块建立网络
Gluon包是MXNet的高级封装接口,易于使用,同时保持了底层API的大部分灵活性。Gluon包为深入学习提供了一个清晰、简洁、简单的API。它使得在不牺牲训练速度的情况下,使得建立和训练深度学习模型更加容易。
from mxnet import nd
# 载入gluon包
from mxnet.gluon import nn
Create your neural network’s first layer
# 建立输出节点为2的全连接层(dense层,类似keras)
layer = nn.Dense(2)
layer
Dense(None -> 2, linear)
# 使用默认的方法初始权重
layer.initialize()
# 生成3行4列的矩阵
x = nd.random.uniform(-1,1,(3,4))
# 输入x到layer层
layer(x)
[[ 0.0009278 -0.00674768]
[-0.02683341 0.00671751]
[ 0.00798804 0.02131375]]
# 打印权重数据
layer.weight.data()
[[-0.01631819 -0.00312688 0.0408415 0.04370362]
[ 0.00404529 -0.0028032 0.00952624 -0.01501013]]
Chain layers into a neural network
# 建立一个Sequential序贯模型
# nn.Sequential用法类似与nn.Dense,但都是nn.Block的子类
net = nn.Sequential()
# Add a sequence of layers.
# lenet,用到了卷积层,池化层,全连接层
net.add(# Similar to Dense, it is not necessary to specify the input channels
# by the argument `in_channels`, which will be automatically inferred
# in the first forward pass. Also, we apply a relu activation on the
# output. In addition, we can use a tuple to specify a non-square
# kernel size, such as `kernel_size=(2,4)`
nn.Conv2D(channels=6, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'),
# One can also use a tuple to specify non-symmetric pool and stride sizes
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2),
nn.Conv2D(channels=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2),
# The dense layer will automatically reshape the 4-D output of last
# max pooling layer into the 2-D shape: (x.shape[0], x.size/x.shape[0])
nn.Dense(120, activation="relu"),
nn.Dense(84, activation="relu"),
nn.Dense(10))
net
Sequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), Activation(relu))
(1): MaxPool2D(size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2), padding=(0, 0), ceil_mode=False, global_pool=False, pool_type=max, layout=NCHW)
(2): Conv2D(None -> 16, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), Activation(relu))
(3): MaxPool2D(size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2), padding=(0, 0), ceil_mode=False, global_pool=False, pool_type=max, layout=NCHW)
(4): Dense(None -> 120, Activation(relu))
(5): Dense(None -> 84, Activation(relu))
(6): Dense(None -> 10, linear)
)
# 初始化网络
net.initialize()
# Input shape is (batch_size, color_channels, height, width)
x = nd.random.uniform(shape=(4,1,28,28))
y = net(x)
y.shape
(4, 10)
# 输出第一层权重的维度以及第6层偏置的维度
(net[0].weight.data().shape, net[5].bias.data().shape)
((6, 1, 5, 5), (84,))
Create a neural network flexibly
通过nn.Block创建一个更加灵活的神经网络结构,主要有两部分:
- __ init __ create the layers 创建层
- forward define the forward function 确定前向传播层函数功能
class MixMLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
# Run `nn.Block`'s init method
super(MixMLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.blk = nn.Sequential()
self.blk.add(nn.Dense(3, activation='relu'),
nn.Dense(4, activation='relu'))
self.dense = nn.Dense(5)
def forward(self, x):
y = nd.relu(self.blk(x))
print(y)
return self.dense(y)
net = MixMLP()
net
MixMLP(
(blk): Sequential(
(0): Dense(None -> 3, Activation(relu))
(1): Dense(None -> 4, Activation(relu))
)
(dense): Dense(None -> 5, linear)
)
# 初始化网络
net.initialize()
x = nd.random.uniform(shape=(2,2))
net(x)
[[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
# 打印权重
net.blk[1].weight.data()
[[-0.02634858 0.05334064 0.02748809]
[ 0.06669661 -0.01711474 0.01647211]
[-0.04485548 0.00594983 -0.06654498]
[ 0.04964591 -0.06058505 0.03413684]]
3 训练神经网络
本节我们将导入数据,建立网络模型,并进行训练。最后通过matplotlib进行绘图和基准测试benchmarking
# Uncomment the following line if matplotlib is not installed.
# !pip install matplotlib
from mxnet import nd, gluon, init, autograd
from mxnet.gluon import nn
from mxnet.gluon.data.vision import datasets, transforms
from IPython import display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
Get data
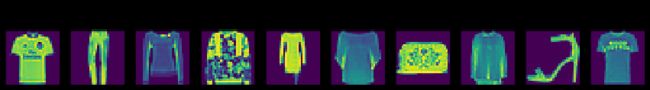
手写数字mnist数据集是深度学习中最常用的数据集之一。但要得到99%的准确度太简单了。这里我们使用了一个类似但稍微复杂的数据集,叫做FashionMNIST。目标不再是对数字进行分类,而是对服装类型进行分类。数据集可以通过Gluon的data.vision.datases模块自动下载。
mnist_train = datasets.FashionMNIST(train=True)
X, y = mnist_train[0]
#FashioniMMIST图像为28*28d的灰度图,y为类别标签
('X shape: ', X.shape, 'X dtype', X.dtype, 'y:', y)
('X shape: ', (28, 28, 1), 'X dtype', numpy.uint8, 'y:', 2)
# text_labels为分类名
text_labels = ['t-shirt', 'trouser', 'pullover', 'dress', 'coat',
'sandal', 'shirt', 'sneaker', 'bag', 'ankle boot']
# 提取前十个数据
X, y = mnist_train[0:10]
# plot images
# 以png格式显示图片
display.set_matplotlib_formats('png')
_, figs = plt.subplots(1, X.shape[0], figsize=(15, 15))
for f,x,yi in zip(figs, X,y):
# 3D->2D by removing the last channel dim
f.imshow(x.reshape((28,28)).asnumpy())
ax = f.axes
ax.set_title(text_labels[int(yi)])
ax.title.set_fontsize(14)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show();
为了将图像输入Gulon模型,我们用ToTensor将图像转换为浮点数据,同时对其进行标准化,标准化均值和方差分别为0.13和0.31
transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(0.13, 0.31)])
mnist_train = mnist_train.transform_first(transformer)
为了使得训练效果更好,我们将打乱数据,同时设定num_workers=4即四个线程来设置读取数据的进程数,目的是:用多进程加速数据的读取
batch_size = 256
train_data = gluon.data.DataLoader(
mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
返回的train_data是一个包含图像和其对应标签的iterable object
# 打印数据
for data, label in train_data:
print(data.shape, label.shape)
break
(256, 1, 28, 28) (256,)
最后我们创建验证集数据
mnist_valid = gluon.data.vision.FashionMNIST(train=False)
valid_data = gluon.data.DataLoader(
mnist_valid.transform_first(transformer),
batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=4)
Define the model
我们建立一个模型,用常用的Xavier法来初始化
net = nn.Sequential()
net.add(nn.Conv2D(channels=6, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2),
nn.Conv2D(channels=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Dense(120, activation="relu"),
nn.Dense(84, activation="relu"),
nn.Dense(10))
net.initialize(init=init.Xavier())
# 定义loss
softmax_cross_entropy = gluon.loss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义训练器,设定学习率为0.1
trainer = gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(), 'sgd', {'learning_rate': 0.1})
Training
# 我们创造一个辅助函数来计算精度
def acc(output, label):
# output: (batch, num_output) float32 ndarray
# label: (batch, ) int32 ndarray
# asscalar()表示返回值的标量
return (output.argmax(axis=1) == label.astype('float32')).mean().asscalar()
# 训练网络2个epochs
for epoch in range(2):
train_loss, train_acc, valid_acc = 0., 0., 0.
tic = time.time()
for data, label in train_data:
# forward + backward
with autograd.record():
output = net(data)
loss = softmax_cross_entropy(output, label)
loss.backward()
# update parameters
trainer.step(batch_size)
# calculate training metrics
# 计算loss
train_loss += loss.mean().asscalar()
# 计算acc
train_acc += acc(output, label)
# calculate validation accuracy
for data, label in valid_data:
valid_acc += acc(net(data), label)
print("Epoch %d: loss %.3f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, in %.1f sec" % (
epoch, train_loss/len(train_data), train_acc/len(train_data),
valid_acc/len(valid_data), time.time()-tic))
Epoch 0: loss 0.730, train acc 0.728, test acc 0.812, in 18.5 sec
Epoch 1: loss 0.463, train acc 0.828, test acc 0.856, in 18.6 sec
Save the model
# 保存模型参数
net.save_parameters('net.params')
载入模型进行推理
Prerequisites
from mxnet import nd
from mxnet import gluon
from mxnet.gluon import nn
from mxnet.gluon.data.vision import datasets, transforms
from IPython import display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入网络结构
net = nn.Sequential()
net.add(nn.Conv2D(channels=6, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2),
nn.Conv2D(channels=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Dense(120, activation="relu"),
nn.Dense(84, activation="relu"),
nn.Dense(10))
# 导入模型
net.load_parameters('net.params')
Predict
# 设置训练数据的处理信息
transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(0.13, 0.31)])
# 图像预测
mnist_valid = datasets.FashionMNIST(train=False)
X, y = mnist_valid[:10]
preds = []
for x in X:
x = transformer(x).expand_dims(axis=0)
pred = net(x).argmax(axis=1)
preds.append(pred.astype('int32').asscalar())
# 可视化预测结果
_, figs = plt.subplots(1, 10, figsize=(15, 15))
text_labels = ['t-shirt', 'trouser', 'pullover', 'dress', 'coat',
'sandal', 'shirt', 'sneaker', 'bag', 'ankle boot']
display.set_matplotlib_formats('png')
for f,x,yi,pyi in zip(figs, X, y, preds):
f.imshow(x.reshape((28,28)).asnumpy())
ax = f.axes
ax.set_title(text_labels[yi]+'\n'+text_labels[pyi])
ax.title.set_fontsize(14)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show();
Predict with models from Gluon model zoo
from mxnet.gluon.model_zoo import vision as models
from mxnet.gluon.utils import download
from mxnet import image
# 从预训练的Gluon模型预测图像
net = models.resnet50_v2(pretrained=True)
# 获得标签文件
url = 'http://data.mxnet.io/models/imagenet/synset.txt'
fname = download(url)
with open(fname, 'r') as f:
text_labels = [' '.join(l.split()[1:]) for l in f]
# 随机下载狗的文件
url = 'https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b5/\
Golden_Retriever_medium-to-light-coat.jpg/\
365px-Golden_Retriever_medium-to-light-coat.jpg'
fname = download(url)
x = image.imread(fname)
# 将获得的图像变为224大小
x = image.resize_short(x, 256)
x, _ = image.center_crop(x, (224,224))
plt.imshow(x.asnumpy())
plt.show();
# 设置数据处理方式
def transform(data):
data = data.transpose((2,0,1)).expand_dims(axis=0)
rgb_mean = nd.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((1,3,1,1))
rgb_std = nd.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((1,3,1,1))
return (data.astype('float32') / 255 - rgb_mean) / rgb_std
# 结果分类,并输出top5结果
prob = net(transform(x)).softmax()
idx = prob.topk(k=5)[0]
for i in idx:
i = int(i.asscalar())
print('With prob = %.5f, it contains %s' % (
prob[0,i].asscalar(), text_labels[i]))
With prob = 0.98240, it contains golden retriever
With prob = 0.00809, it contains English setter
With prob = 0.00262, it contains Irish setter, red setter
With prob = 0.00223, it contains cocker spaniel, English cocker spaniel, cocker
With prob = 0.00177, it contains Labrador retriever

![[mxnet] mxnet60分钟入门Gluon教程_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8749b92d44844d1c96a6ebfd3d1eed8a.jpg)