redis源码分析之异步进程保存数据rdb文件和aof文件源码分析
=====================================================
redis源码学习系列文章:
redis源码分析之sha1算法分析
redis源码分析之字典源码分析
redis源码分析之内存编码分析intset, ziplist编码分析
redis源码分析之跳跃表
redis源码分析之内存淘汰策略的原理分析
redis源码分析之对象系统源码分析string, list链表,hash哈希,set集合,zset有序集合
redis源码分析之异步进程保存数据rdb文件和aof文件源码分析
=====================================================
前言
redis中的有两个保存数据的方式一种是保存二进制文件.rdb的文件和aof的文件,.rdb文件是redis缓存数据库默认持久化方式在redis.conf中的配置save 9000 1 意思是9000秒内修改过一次就保存数据到rdb文件中的
还有一种方式aof文件这种文件的格式是人可以识别的文本格式appendonly 字段配置yes就是保存aof的格式了
分析流程
- rdb的文件格式分析
- rdb的机制
- aof的机制
正文
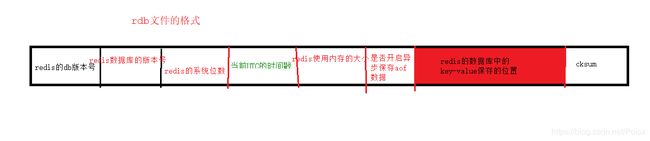
一, rdb的文件格式分析
1. redis中保存rdb的文件个数如下图
2, rdb文件中的保存string对象
3. rdb文件保存list对象
4. rdb文件保存hash对象
5. 保存这些数据redis的api
保存数据的长度函数
int rdbSaveLen(rio *rdb, uint64_t len) {
unsigned char buf[2];
size_t nwritten;
if (len < (1<<6)/*64 == 0X40*/) {
/* Save a 6 bit len */
buf[0] = (len&0xFF)|(RDB_6BITLEN<<6);
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,buf,1) == -1) return -1;
nwritten = 1;
} else if (len < (1<<14)/*16384 == 0X40000*/) {
/* Save a 14 bit len */ // 数据为14位的高两位为 01
buf[0] = ((len>>8)&0xFF)|(RDB_14BITLEN<<6); // 0100 0000
buf[1] = len&0xFF;
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,buf,2) == -1) return -1;
nwritten = 2;
} else if (len <= UINT32_MAX) {
/* Save a 32 bit len */
buf[0] = RDB_32BITLEN;
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,buf,1) == -1) return -1;
uint32_t len32 = htonl(len);
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,&len32,4) == -1) return -1;
nwritten = 1+4;
} else {
/* Save a 64 bit len */
buf[0] = RDB_64BITLEN;
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,buf,1) == -1) return -1;
len = htonu64(len);
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,&len,8) == -1) return -1;
nwritten = 1+8;
}
return nwritten;
}
保存redis中的标志位的函数
int rdbSaveType(rio *rdb, unsigned char type) {
return rdbWriteRaw(rdb,&type,1);
}
保存redis中的所有编码数据过的函数
/**
* 保存redis中的所有编码数据过的函数
* @param rdb 写入文件信息
* @param o key-value中的value的使用的编码的数据结构
*/
int rdbSaveObjectType(rio *rdb, robj *o) {
switch (o->type) {
case OBJ_STRING:
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_STRING);
case OBJ_LIST:
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) // 快速列表0X0E
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_LIST_QUICKLIST);
else
serverPanic("Unknown list encoding");
case OBJ_SET:
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET)
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_SET_INTSET);
else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT)
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_SET);
else
serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");
case OBJ_ZSET:
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST)
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_ZSET_ZIPLIST);
else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST)
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_ZSET_2);
else
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
case OBJ_HASH:
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST)
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_HASH_ZIPLIST);
else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT)
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_HASH);
else
serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");
case OBJ_STREAM:
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_STREAM_LISTPACKS);
case OBJ_MODULE:
return rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_TYPE_MODULE_2);
default:
serverPanic("Unknown object type");
}
return -1; /* avoid warning */
}
key-value的数据所有的编码
/**
* 保存key-value中的数据 大于20字节就需要使用zlf压缩算法, 数据是字符是数据的且长度小于11给字节的
* @param rdb 写入的文件的信息
* @param s 要写入的数据的
* @param len 要写入的数据的长度
*/
ssize_t rdbSaveRawString(rio *rdb, unsigned char *s, size_t len) {
int enclen;
ssize_t n, nwritten = 0;
/* Try integer encoding */
//redis的版本的位数64位 在hex中的是0X40,在redis中的key或者value是数字且长度小于11时不需要的纪录保存的数据的长度直接包数据就可以了
if (len <= 11) {
unsigned char buf[5];
// 尝试把数据转换数字字符串
if ((enclen = rdbTryIntegerEncoding((char*)s,len,buf)) > 0) {
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,buf,enclen) == -1) return -1;
return enclen;
}
}
/* Try LZF compression - under 20 bytes it's unable to compress even
* aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa so skip it */
// 字符长度大于的20字节就使用加密算法LZF算法进行去重
if (server.rdb_compression && len > 20) {
n = rdbSaveLzfStringObject(rdb,s,len);
if (n == -1) return -1;
if (n > 0) return n;
/* Return value of 0 means data can't be compressed, save the old way */
}
/* Store verbatim */
// 这边正常写入数据到文件中的没有加密
if ((n = rdbSaveLen(rdb,len)) == -1) return -1;
nwritten += n;
if (len > 0) {
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,s,len) == -1) return -1;
nwritten += len;
}
return nwritten;
}
/**
* 编码数据是数字类型
* @param value 数字
* @param enc 转换后的字符串
*/
int rdbEncodeInteger(long long value, unsigned char *enc) {
if (value >= -(1<<7) /*-128 == 0X80*/ && value <= (1<<7)-1 /*127 == 0x7F*/) {
enc[0] = (RDB_ENCVAL<<6)/*0XC0即192*/|RDB_ENC_INT8; // 0XC0
enc[1] = value&0xFF;
return 2;
} else if (value >= -(1<<15)/*-32768 == 0X8000*/ && value <= (1<<15)-1 /*32767 == 0X7FFF*/) {
enc[0] = (RDB_ENCVAL<<6)|RDB_ENC_INT16;// 0XC1
enc[1] = value&0xFF;
enc[2] = (value>>8)&0xFF;
return 3;
} else if (value >= -((long long)1<<31) /*-2147483648 == 0X80000000*/ && value <= ((long long)1<<31)-1 /*2147483647 == 0X7FFFFFFF*/) {
enc[0] = (RDB_ENCVAL<<6)|RDB_ENC_INT32;// 0XC2
enc[1] = value&0xFF;
enc[2] = (value>>8)&0xFF;
enc[3] = (value>>16)&0xFF;
enc[4] = (value>>24)&0xFF;
return 5;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
二, rdb的机制
1, rdb的触发的机制
rdb默认是配置
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
意思是 900秒更新一次就开启异步进程保存数据的rdb文件中的
for (j = 0; j < server.saveparamslen; j++) {
struct saveparam *sp = server.saveparams + j;
/* Save if we reached the given amount of changes,
* the given amount of seconds, and if the latest bgsave was
* successful or if, in case of an error, at least
* CONFIG_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY seconds already elapsed. */
// server.dirty这个全局变量是纪录修改数据的次数
if (server.dirty >= sp->changes &&
server.unixtime - server.lastsave > sp->seconds &&
(server.unixtime - server.lastbgsave_try >
CONFIG_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY ||
server.lastbgsave_status == C_OK))
{
serverLog(LL_NOTICE, "%d changes in %d seconds. Saving...",
sp->changes, (int)sp->seconds);
rdbSaveInfo rsi, *rsiptr;
rsiptr = rdbPopulateSaveInfo(&rsi);
// rdb文件保存数据的操作
rdbSaveBackground(server.rdb_filename, rsiptr);
break;
}
}
2, rdb是怎么开启异步进程保存又如何做到数据同步呢
redis使用管道进程通信的redis业务进程同步数据分为3种情况
- 客户端正常的操作纪录
- 客户端使用阻塞式的即是事务获取信息
- redis数据中的有ttl过期的, redis的最大内存的使用机制释放
我们先看看redis开启进程流程
/**
*开启异步进程保存数据
* @param filename 要保存到文件名
* @param rsi 信息
*/
int rdbSaveBackground(char *filename, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
pid_t childpid;
long long start;
if (server.aof_child_pid != -1 || server.rdb_child_pid != -1) return C_ERR;
server.dirty_before_bgsave = server.dirty;
server.lastbgsave_try = time(NULL);
// 开启管道用于业务进程于异步保存数据进程之间的通信
openChildInfoPipe();
start = ustime();
if ((childpid = fork()) == 0) {
int retval;
/* Child */
// 关闭父进程垃圾
closeListeningSockets(0);
redisSetProcTitle("redis-rdb-bgsave");
retval = rdbSave(filename,rsi);
if (retval == C_OK) {
size_t private_dirty = zmalloc_get_private_dirty(-1);
if (private_dirty) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,
"RDB: %zu MB of memory used by copy-on-write",
private_dirty/(1024*1024));
}
server.child_info_data.cow_size = private_dirty;
sendChildInfo(CHILD_INFO_TYPE_RDB);
}
exitFromChild((retval == C_OK) ? 0 : 1);
} else {
/* Parent */
server.stat_fork_time = ustime()-start;
server.stat_fork_rate = (double) zmalloc_used_memory() * 1000000 / server.stat_fork_time / (1024*1024*1024); /* GB per second. */
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("fork",server.stat_fork_time/1000);
if (childpid == -1) {
closeChildInfoPipe();
server.lastbgsave_status = C_ERR;
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Can't save in background: fork: %s",
strerror(errno));
return C_ERR;
}
serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"Background saving started by pid %d",childpid);
server.rdb_save_time_start = time(NULL);
server.rdb_child_pid = childpid;
server.rdb_child_type = RDB_CHILD_TYPE_DISK;
updateDictResizePolicy();
return C_OK;
}
return C_OK; /* unreached */
}
/**
* 保存数据到文件
* @param rdb 文件
* @param error 错误码
* @param flags
* @param rsi 要保持文件的信息结构体
*/
int rdbSaveRio(rio *rdb, int *error, int flags, rdbSaveInfo *rsi) {
dictIterator *di = NULL;
dictEntry *de;
char magic[10];
int j;
uint64_t cksum;
size_t processed = 0;
if (server.rdb_checksum)
rdb->update_cksum = rioGenericUpdateChecksum;
snprintf(magic,sizeof(magic),"REDIS%04d",RDB_VERSION);
// 保持redis的的db的版本号
if (rdbWriteRaw(rdb,magic,9) == -1) goto werr;
if (rdbSaveInfoAuxFields(rdb,flags,rsi) == -1) goto werr;
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
redisDb *db = server.db+j;
dict *d = db->dict;
// 数据库中的字典没有数据直接返回
if (dictSize(d) == 0) continue;
di = dictGetSafeIterator(d);
/* Write the SELECT DB opcode */
// 1. redis的数据的的标志位是以0XFE区分的
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_SELECTDB) == -1) goto werr;
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,j) == -1) goto werr;
/* Write the RESIZE DB opcode. We trim the size to UINT32_MAX, which
* is currently the largest type we are able to represent in RDB sizes.
* However this does not limit the actual size of the DB to load since
* these sizes are just hints to resize the hash tables. */
uint64_t db_size, expires_size;
db_size = dictSize(db->dict);
expires_size = dictSize(db->expires);
//保存redis数据库字典的标记位 [0XFB]
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_RESIZEDB) == -1) goto werr;
// 保存数据的中的字典个数
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,db_size) == -1) goto werr;
//保存ttl数据过期的字典个数
if (rdbSaveLen(rdb,expires_size) == -1) goto werr;
/* Iterate this DB writing every entry */
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
sds keystr = dictGetKey(de);
robj key, *o = dictGetVal(de);
long long expire;
initStaticStringObject(key,keystr);
expire = getExpire(db,&key);
// 保持数据库中的key-value
if (rdbSaveKeyValuePair(rdb,&key,o,expire) == -1) goto werr;
/* When this RDB is produced as part of an AOF rewrite, move
* accumulated diff from parent to child while rewriting in
* order to have a smaller final write. */
// 这个是redis为防止管道破裂而要业务进程的发送数据
if (flags & RDB_SAVE_AOF_PREAMBLE &&
rdb->processed_bytes > processed+AOF_READ_DIFF_INTERVAL_BYTES)
{
processed = rdb->processed_bytes;
aofReadDiffFromParent();
}
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
di = NULL; /* So that we don't release it again on error. */
}
/* If we are storing the replication information on disk, persist
* the script cache as well: on successful PSYNC after a restart, we need
* to be able to process any EVALSHA inside the replication backlog the
* master will send us. */
if (rsi && dictSize(server.lua_scripts)) {
di = dictGetIterator(server.lua_scripts);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
robj *body = dictGetVal(de);
if (rdbSaveAuxField(rdb,"lua",3,body->ptr,sdslen(body->ptr)) == -1)
goto werr;
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
di = NULL; /* So that we don't release it again on error. */
}
/* EOF opcode */
if (rdbSaveType(rdb,RDB_OPCODE_EOF) == -1) goto werr;
/* CRC64 checksum. It will be zero if checksum computation is disabled, the
* loading code skips the check in this case. */
cksum = rdb->cksum;
memrev64ifbe(&cksum);
if (rioWrite(rdb,&cksum,8) == 0) goto werr;
return C_OK;
werr:
if (error) *error = errno;
if (di) dictReleaseIterator(di);
return C_ERR;
}
/**
* 保存业务进程的数据到server.aof_child_diff中
*/
ssize_t aofReadDiffFromParent(void) {
char buf[65536]; /* Default pipe buffer size on most Linux systems. */
ssize_t nread, total = 0;
while ((nread =
read(server.aof_pipe_read_data_from_parent,buf,sizeof(buf))) > 0) {
server.aof_child_diff = sdscatlen(server.aof_child_diff,buf,nread);
total += nread;
}
return total;
}
下面我们就看看业务进程是怎么三种情况发送数据到异步数据进程的
第一种情况: 正常客户请求的数据纪录发送
/**
* 执行客户的命令
* @param c 客户端
* @param flags 访问权限
*/
void call(client *c, int flags) {
long long dirty, start, duration;
int client_old_flags = c->flags;
struct redisCommand *real_cmd = c->cmd;
/* Sent the command to clients in MONITOR mode, only if the commands are
* not generated from reading an AOF. */
// 发送信息给哨兵
if (listLength(server.monitors) &&
!server.loading &&
!(c->cmd->flags & (CMD_SKIP_MONITOR | CMD_ADMIN)))
{
replicationFeedMonitors(c, server.monitors, c->db->id, c->argv, c->argc);
}
/* Initialization: clear the flags that must be set by the command on
* demand, and initialize the array for additional commands propagation. */
c->flags &= ~(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF | CLIENT_FORCE_REPL | CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP);
redisOpArray prev_also_propagate = server.also_propagate;
redisOpArrayInit(&server.also_propagate);
/* Call the command. */
// dirty是纪录该操作是否生效的有几种情况是不生效的
// 例如: blpop的命令
dirty = server.dirty;
start = ustime();
// backcall -->cmd client exec cmd
c->cmd->proc(c);
duration = ustime() - start;
dirty = server.dirty - dirty;
if (dirty < 0) dirty = 0;
/* When EVAL is called loading the AOF we don't want commands called
* from Lua to go into the slowlog or to populate statistics. */
if (server.loading && c->flags & CLIENT_LUA)
flags &= ~(CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG | CMD_CALL_STATS);
/* If the caller is Lua, we want to force the EVAL caller to propagate
* the script if the command flag or client flag are forcing the
* propagation. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_LUA && server.lua_caller) {
if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_REPL)
server.lua_caller->flags |= CLIENT_FORCE_REPL;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_AOF)
server.lua_caller->flags |= CLIENT_FORCE_AOF;
}
/* Log the command into the Slow log if needed, and populate the
* per-command statistics that we show in INFO commandstats. */
if (flags & CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG && c->cmd->proc != execCommand) {
char *latency_event = (c->cmd->flags & CMD_FAST) ?
"fast-command" : "command";
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded(latency_event, duration / 1000);
slowlogPushEntryIfNeeded(c, c->argv, c->argc, duration);
}
if (flags & CMD_CALL_STATS) {
/* use the real command that was executed (cmd and lastamc) may be
* different, in case of MULTI-EXEC or re-written commands such as
* EXPIRE, GEOADD, etc. */
real_cmd->microseconds += duration;
real_cmd->calls++;
}
/* Propagate the command into the AOF and replication link */
if (flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE &&
(c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP) != CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP)
{
int propagate_flags = PROPAGATE_NONE;
/* Check if the command operated changes in the data set. If so
* set for replication / AOF propagation. */
// 判断客户端的命令是否执行成功
// 如果成功就通知aof rdb save的服务器保存数据的操作
if (dirty) propagate_flags |= (PROPAGATE_AOF | PROPAGATE_REPL);
/* If the client forced AOF / replication of the command, set
* the flags regardless of the command effects on the data set. */
// 精确到是redis服务需要那种的操作
if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_REPL) propagate_flags |= PROPAGATE_REPL;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_FORCE_AOF) propagate_flags |= PROPAGATE_AOF;
/* However prevent AOF / replication propagation if the command
* implementations called preventCommandPropagation() or similar,
* or if we don't have the call() flags to do so. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP ||
!(flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL))
propagate_flags &= ~PROPAGATE_REPL;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP ||
!(flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF))
propagate_flags &= ~PROPAGATE_AOF;
/* Call propagate() only if at least one of AOF / replication
* propagation is needed. Note that modules commands handle replication
* in an explicit way, so we never replicate them automatically. */
// 异步保存数据的进程开启了
if (propagate_flags != PROPAGATE_NONE && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_MODULE))
propagate(c->cmd, c->db->id, c->argv, c->argc, propagate_flags);
}
/* Restore the old replication flags, since call() can be executed
* recursively. */
//还原现场的的状态
c->flags &= ~(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF | CLIENT_FORCE_REPL | CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP);
c->flags |= client_old_flags &
(CLIENT_FORCE_AOF | CLIENT_FORCE_REPL | CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP);
/* Handle the alsoPropagate() API to handle commands that want to propagate
* multiple separated commands. Note that alsoPropagate() is not affected
* by CLIENT_PREVENT_PROP flag. */
// 这里我没有看懂 是什么原因使用这种方式难道上面的还不够吗???? 还需这种发生操作
// 1. spop弹出队利中的数据的个数
// 2. 如果大于的现有的队利的个数就不需要纪录了
// 3. 小于现有的队礼的个数就要纪录数据的了弹出的数据具体的那些数据key-value
// 思考: 为什么大于时就不会纪录了,小于就要纪录具体弹出的数据的key-value呢
// 这个有可能弹出数据错误数据的, 不知道弹出具体那个key-value, 而设计这个模式为
if (server.also_propagate.numops) {
int j;
redisOp *rop;
if (flags & CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE) {
for (j = 0; j < server.also_propagate.numops; j++) {
rop = &server.also_propagate.ops[j];
int target = rop->target;
/* Whatever the command wish is, we honor the call() flags. */
if (!(flags&CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF)) target &= ~PROPAGATE_AOF;
if (!(flags&CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL)) target &= ~PROPAGATE_REPL;
// aof异步保存数据的进程开启了
if (target)
propagate(rop->cmd, rop->dbid, rop->argv, rop->argc, target);
}
}
redisOpArrayFree(&server.also_propagate);
}
server.also_propagate = prev_also_propagate;
server.stat_numcommands++;
}
第二种情况客户端使用事务获取信息的
例如: blpop 命令
/**
* 这个设计挺巧妙的 要学习哦
* blpop 等待
* 这个操作是不会在main loop 记录下来的是因为 全局的 server.dirty没有加一的操作,正好于压入的操作一起通知异步写入数据的进程对应的函数handleClientsBlockedOnKeys
* @param c 客户端
* @param btyes
* @param keys客户事务key值
* @param numkeys 个数
* @param timeout 延迟的秒数
* @param target 对方
* @param ids 是redis5.0新出来一种数据结构压缩的哦
*/
void blockForKeys(client *c, int btype, robj **keys, int numkeys, mstime_t timeout, robj *target, streamID *ids) {
dictEntry *de;
list *l;
int j;
c->bpop.timeout = timeout;
c->bpop.target = target;
if (target != NULL) incrRefCount(target);
for (j = 0; j < numkeys; j++) {
/* The value associated with the key name in the bpop.keys dictionary
* is NULL for lists and sorted sets, or the stream ID for streams. */
void *key_data = NULL;
if (btype == BLOCKED_STREAM) {
key_data = zmalloc(sizeof(streamID));
memcpy(key_data,ids+j,sizeof(streamID));
}
/* If the key already exists in the dictionary ignore it. */
if (dictAdd(c->bpop.keys,keys[j],key_data) != DICT_OK) {
zfree(key_data);
continue;
}
incrRefCount(keys[j]);
/* And in the other "side", to map keys -> clients */
de = dictFind(c->db->blocking_keys,keys[j]);
if (de == NULL) {
int retval;
/* For every key we take a list of clients blocked for it */
l = listCreate();
// 看到吧放到blocking_keys中的了
retval = dictAdd(c->db->blocking_keys,keys[j],l);
incrRefCount(keys[j]);
serverAssertWithInfo(c,keys[j],retval == DICT_OK);
} else {
l = dictGetVal(de);
}
listAddNodeTail(l,c);
}
blockClient(c,btype);
}
有人插入的操作时
/**
* 只有另一个客户端使用阻塞式的获取数据的时,这个客户端插入数据的时会触发该方法保持数据跟发布订阅差不多
* 会触发另一个方法 handleClientsBlockedOnKeys
* @param db 数据库
* @param key 事务的key
*/
void signalKeyAsReady(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
readyList *rl;
/* No clients blocking for this key? No need to queue it. */
// 看到没有该事务就返回就直接接着下一步走呗
if (dictFind(db->blocking_keys,key) == NULL) return;
/* Key was already signaled? No need to queue it again. */
if (dictFind(db->ready_keys,key) != NULL) return;
/* Ok, we need to queue this key into server.ready_keys. */
rl = zmalloc(sizeof(*rl));
rl->key = key;
rl->db = db;
incrRefCount(key);
listAddNodeTail(server.ready_keys,rl);
/* We also add the key in the db->ready_keys dictionary in order
* to avoid adding it multiple times into a list with a simple O(1)
* check. */
incrRefCount(key);
serverAssert(dictAdd(db->ready_keys,key,NULL) == DICT_OK);
}
时候处理呢就在客户插入的后处理的
int processCommand(client *c) {
/* The QUIT command is handled separately. Normal command procs will
* go through checking for replication and QUIT will cause trouble
* when FORCE_REPLICATION is enabled and would be implemented in
* a regular command proc. */
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr, "quit")) {
addReply(c, shared.ok);
c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
return C_ERR;
}
// redis search [cmd] --> [SET][GET][MSET]
/* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions
* such as wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
if (!c->cmd) {
flagTransaction(c);
sds args = sdsempty();
int i;
for (i = 1; i < c->argc && sdslen(args) < 128; i++)
args = sdscatprintf(args, "`%.*s`, ", 128 - (int)sdslen(args), (char*)c->argv[i]->ptr);
addReplyErrorFormat(c, "unknown command `%s`, with args beginning with: %s",
(char*)c->argv[0]->ptr, args);
sdsfree(args);
return C_OK;
}
else if ((c->cmd->arity > 0 && c->cmd->arity != c->argc) ||
(c->argc < -c->cmd->arity)) {
// 检查命令行参数的个数是否符合要求
flagTransaction(c);
addReplyErrorFormat(c, "wrong number of arguments for '%s' command",
c->cmd->name);
return C_OK;
}
/* Check if the user is authenticated */
if (server.requirepass && !c->authenticated && c->cmd->proc != authCommand)
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.noautherr);
return C_OK;
}
/* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here.
* However we don't perform the redirection if:
* 1) The sender of this command is our master.
* 2) The command has no key arguments. */
if (server.cluster_enabled &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_LUA &&
server.lua_caller->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
!(c->cmd->getkeys_proc == NULL && c->cmd->firstkey == 0 &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand))
{
int hashslot;
int error_code;
clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c, c->cmd, c->argv, c->argc,
&hashslot, &error_code);
if (n == NULL || n != server.cluster->myself) {
if (c->cmd->proc == execCommand) {
discardTransaction(c);
}
else {
flagTransaction(c);
}
clusterRedirectClient(c, n, hashslot, error_code);
return C_OK;
}
}
/* Handle the maxmemory directive.
*
* First we try to free some memory if possible (if there are volatile
* keys in the dataset). If there are not the only thing we can do
* is returning an error.
*
* Note that we do not want to reclaim memory if we are here re-entering
* the event loop since there is a busy Lua script running in timeout
* condition, to avoid mixing the propagation of scripts with the propagation
* of DELs due to eviction. */
// 内存淘汰机制更新 在配置是否redis的内存的大小
if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) {
int out_of_memory = freeMemoryIfNeeded() == C_ERR;
/* freeMemoryIfNeeded may flush slave output buffers. This may result
* into a slave, that may be the active client, to be freed. */
if (server.current_client == NULL) return C_ERR;
/* It was impossible to free enough memory, and the command the client
* is trying to execute is denied during OOM conditions? Error. */
if ((c->cmd->flags & CMD_DENYOOM) && out_of_memory) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.oomerr);
return C_OK;
}
}
/* Don't accept write commands if there are problems persisting on disk
* and if this is a master instance. */
int deny_write_type = writeCommandsDeniedByDiskError();
if (deny_write_type != DISK_ERROR_TYPE_NONE &&
server.masterhost == NULL &&
(c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE ||
c->cmd->proc == pingCommand))
{
flagTransaction(c);
if (deny_write_type == DISK_ERROR_TYPE_RDB)
addReply(c, shared.bgsaveerr);
else
addReplySds(c,
sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),
"-MISCONF Errors writing to the AOF file: %s\r\n",
strerror(server.aof_last_write_errno)));
return C_OK;
}
/* Don't accept write commands if there are not enough good slaves and
* user configured the min-slaves-to-write option. */
if (server.masterhost == NULL &&
server.repl_min_slaves_to_write &&
server.repl_min_slaves_max_lag &&
c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE &&
server.repl_good_slaves_count < server.repl_min_slaves_to_write)
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.noreplicaserr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Don't accept write commands if this is a read only slave. But
* accept write commands if this is our master. */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE)
{
addReply(c, shared.roslaveerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Only allow SUBSCRIBE and UNSUBSCRIBE in the context of Pub/Sub */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PUBSUB &&
c->cmd->proc != pingCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != subscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != unsubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != psubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != punsubscribeCommand) {
addReplyError(c, "only (P)SUBSCRIBE / (P)UNSUBSCRIBE / PING / QUIT allowed in this context");
return C_OK;
}
/* Only allow commands with flag "t", such as INFO, SLAVEOF and so on,
* when slave-serve-stale-data is no and we are a slave with a broken
* link with master. */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state != REPL_STATE_CONNECTED &&
server.repl_serve_stale_data == 0 &&
!(c->cmd->flags & CMD_STALE))
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.masterdownerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Loading DB? Return an error if the command has not the
* CMD_LOADING flag. */
if (server.loading && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_LOADING)) {
addReply(c, shared.loadingerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Lua script too slow? Only allow a limited number of commands. */
if (server.lua_timedout &&
c->cmd->proc != authCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != replconfCommand &&
!(c->cmd->proc == shutdownCommand &&
c->argc == 2 &&
tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'n') &&
!(c->cmd->proc == scriptCommand &&
c->argc == 2 &&
tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'k'))
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.slowscripterr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Exec the command */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand)
{
queueMultiCommand(c);
addReply(c, shared.queued);
}
else {
call(c, CMD_CALL_FULL);
c->woff = server.master_repl_offset;
// 客户端使用阻塞式获取数据和通知异步进程aof保存操作纪录的数据
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnKeys();
}
return C_OK;
}
/**
* 处理客户端事务并发送信息到异步保持数据进程
*/
void handleClientsBlockedOnKeys(void) {
while(listLength(server.ready_keys) != 0) {
list *l;
/* Point server.ready_keys to a fresh list and save the current one
* locally. This way as we run the old list we are free to call
* signalKeyAsReady() that may push new elements in server.ready_keys
* when handling clients blocked into BRPOPLPUSH. */
l = server.ready_keys;
server.ready_keys = listCreate();
while(listLength(l) != 0) {
listNode *ln = listFirst(l);
readyList *rl = ln->value;
/* First of all remove this key from db->ready_keys so that
* we can safely call signalKeyAsReady() against this key. */
dictDelete(rl->db->ready_keys,rl->key);
/* Serve clients blocked on list key. */
robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(rl->db,rl->key);
if (o != NULL && o->type == OBJ_LIST) {
dictEntry *de;
/* We serve clients in the same order they blocked for
* this key, from the first blocked to the last. */
de = dictFind(rl->db->blocking_keys,rl->key);
if (de) {
//得到该需要该信息的客户端的链表
list *clients = dictGetVal(de);
int numclients = listLength(clients);
while(numclients--) {
listNode *clientnode = listFirst(clients);
client *receiver = clientnode->value;
if (receiver->btype != BLOCKED_LIST) {
/* Put at the tail, so that at the next call
* we'll not run into it again. */
listDelNode(clients,clientnode);
listAddNodeTail(clients,receiver);
continue;
}
robj *dstkey = receiver->bpop.target;
int where = (receiver->lastcmd &&
receiver->lastcmd->proc == blpopCommand) ?
LIST_HEAD : LIST_TAIL;
robj *value = listTypePop(o,where);
if (value) {
/* Protect receiver->bpop.target, that will be
* freed by the next unblockClient()
* call. */
if (dstkey) incrRefCount(dstkey);
unblockClient(receiver);
// 1. 通知阻塞式的客户端有信息了
// 2. aof异步保存数据的操作
if (serveClientBlockedOnList(receiver,
rl->key,dstkey,rl->db,value,
where) == C_ERR)
{
/* If we failed serving the client we need
* to also undo the POP operation. */
listTypePush(o,value,where);
}
if (dstkey) decrRefCount(dstkey);
decrRefCount(value);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
if (listTypeLength(o) == 0) {
dbDelete(rl->db,rl->key);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",rl->key,rl->db->id);
}
/* We don't call signalModifiedKey() as it was already called
* when an element was pushed on the list. */
}
/* Serve clients blocked on sorted set key. */
else if (o != NULL && o->type == OBJ_ZSET) {
dictEntry *de;
/* We serve clients in the same order they blocked for
* this key, from the first blocked to the last. */
de = dictFind(rl->db->blocking_keys,rl->key);
if (de) {
list *clients = dictGetVal(de);
int numclients = listLength(clients);
unsigned long zcard = zsetLength(o);
while(numclients-- && zcard) {
listNode *clientnode = listFirst(clients);
client *receiver = clientnode->value;
if (receiver->btype != BLOCKED_ZSET) {
/* Put at the tail, so that at the next call
* we'll not run into it again. */
listDelNode(clients,clientnode);
listAddNodeTail(clients,receiver);
continue;
}
int where = (receiver->lastcmd &&
receiver->lastcmd->proc == bzpopminCommand)
? ZSET_MIN : ZSET_MAX;
// 删除过期的阻塞的客户端
unblockClient(receiver);
// 发送给阻塞式的客户端的信息
genericZpopCommand(receiver,&rl->key,1,where,1,NULL);
zcard--;
/* Replicate the command. */
robj *argv[2];
struct redisCommand *cmd = where == ZSET_MIN ?
server.zpopminCommand :
server.zpopmaxCommand;
argv[0] = createStringObject(cmd->name,strlen(cmd->name));
argv[1] = rl->key;
incrRefCount(rl->key);
//
propagate(cmd,receiver->db->id,
argv,2,PROPAGATE_AOF|PROPAGATE_REPL);
decrRefCount(argv[0]);
decrRefCount(argv[1]);
}
}
}
/* Serve clients blocked on stream key. */
else if (o != NULL && o->type == OBJ_STREAM) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(rl->db->blocking_keys,rl->key);
stream *s = o->ptr;
/* We need to provide the new data arrived on the stream
* to all the clients that are waiting for an offset smaller
* than the current top item. */
if (de) {
list *clients = dictGetVal(de);
listNode *ln;
listIter li;
listRewind(clients,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *receiver = listNodeValue(ln);
if (receiver->btype != BLOCKED_STREAM) continue;
streamID *gt = dictFetchValue(receiver->bpop.keys,
rl->key);
/* If we blocked in the context of a consumer
* group, we need to resolve the group and update the
* last ID the client is blocked for: this is needed
* because serving other clients in the same consumer
* group will alter the "last ID" of the consumer
* group, and clients blocked in a consumer group are
* always blocked for the ">" ID: we need to deliver
* only new messages and avoid unblocking the client
* otherwise. */
streamCG *group = NULL;
if (receiver->bpop.xread_group) {
group = streamLookupCG(s,
receiver->bpop.xread_group->ptr);
/* If the group was not found, send an error
* to the consumer. */
if (!group) {
addReplyError(receiver,
"-NOGROUP the consumer group this client "
"was blocked on no longer exists");
unblockClient(receiver);
continue;
} else {
*gt = group->last_id;
}
}
if (streamCompareID(&s->last_id, gt) > 0) {
streamID start = *gt;
start.seq++; /* Can't overflow, it's an uint64_t */
/* Lookup the consumer for the group, if any. */
streamConsumer *consumer = NULL;
int noack = 0;
if (group) {
consumer = streamLookupConsumer(group,
receiver->bpop.xread_consumer->ptr,
1);
noack = receiver->bpop.xread_group_noack;
}
/* Emit the two elements sub-array consisting of
* the name of the stream and the data we
* extracted from it. Wrapped in a single-item
* array, since we have just one key. */
addReplyMultiBulkLen(receiver,1);
addReplyMultiBulkLen(receiver,2);
addReplyBulk(receiver,rl->key);
streamPropInfo pi = {
rl->key,
receiver->bpop.xread_group
};
streamReplyWithRange(receiver,s,&start,NULL,
receiver->bpop.xread_count,
0, group, consumer, noack, &pi);
/* Note that after we unblock the client, 'gt'
* and other receiver->bpop stuff are no longer
* valid, so we must do the setup above before
* this call. */
unblockClient(receiver);
}
}
}
}
/* Free this item. */
decrRefCount(rl->key);
zfree(rl);
listDelNode(l,ln);
}
listRelease(l); /* We have the new list on place at this point. */
}
}
第三种情况redis数据中的有ttl过期的, redis的最大内存的使用机制释放
/**
* 删除过期数据的
* @param type
*/
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
/* This function has some global state in order to continue the work
* incrementally across calls. */
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Last DB tested. */
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* When last fast cycle ran. */
int j, iteration = 0;
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;
/* When clients are paused the dataset should be static not just from the
* POV of clients not being able to write, but also from the POV of
* expires and evictions of keys not being performed. */
if (clientsArePaused()) return;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
/* Don't start a fast cycle if the previous cycle did not exit
* for time limit. Also don't repeat a fast cycle for the same period
* as the fast cycle total duration itself. */
if (!timelimit_exit) return;
if (start < last_fast_cycle + ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION*2) return;
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
/* We usually should test CRON_DBS_PER_CALL per iteration, with
* two exceptions:
*
* 1) Don't test more DBs than we have.
* 2) If last time we hit the time limit, we want to scan all DBs
* in this iteration, as there is work to do in some DB and we don't want
* expired keys to use memory for too much time. */
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
/* We can use at max ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC percentage of CPU time
* per iteration. Since this function gets called with a frequency of
* server.hz times per second, the following is the max amount of
* microseconds we can spend in this function. */
timelimit = 1000000*ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION; /* in microseconds. */
/* Accumulate some global stats as we expire keys, to have some idea
* about the number of keys that are already logically expired, but still
* existing inside the database. */
long total_sampled = 0;
long total_expired = 0;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
int expired; // 记录db0中的有多少个hash过期删除的个数
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
/* Increment the DB now so we are sure if we run out of time
* in the current DB we'll restart from the next. This allows to
* distribute the time evenly across DBs. */
current_db++;
/* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle more than 25%
* of the keys were expired. */
do {
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples;
iteration++;
/* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {
db->avg_ttl = 0;
break;
}
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
now = mstime();
/* When there are less than 1% filled slots getting random
* keys is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times...
* The dictionary will be resized asap. */
if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*100/slots < 1)) break;
/* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys
* with an expire set, checking for expired ones. */
expired = 0;
ttl_sum = 0;
ttl_samples = 0;
if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP;
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl;
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now;
// 过期的hash值删除操作
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
total_sampled++;
}
total_expired += expired;
/* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
/* Do a simple running average with a few samples.
* We just use the current estimate with a weight of 2%
* and the previous estimate with a weight of 98%. */
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);
}
/* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to
* expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the
* caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. */
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
elapsed = ustime()-start;
if (elapsed > timelimit) {
timelimit_exit = 1;
server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;
break;
}
}
/* We don't repeat the cycle if there are less than 25% of keys
* found expired in the current DB. */
} while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4);
}
elapsed = ustime()-start;
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000);
/* Update our estimate of keys existing but yet to be expired.
* Running average with this sample accounting for 5%. */
double current_perc;
if (total_sampled) {
current_perc = (double)total_expired/total_sampled;
} else
current_perc = 0;
server.stat_expired_stale_perc = (current_perc*0.05)+
(server.stat_expired_stale_perc*0.95);
}
/**
* 删除数据
* @param db 数据库id
* @param de 要删除的节点数据
* @param now
*/
int activeExpireCycleTryExpire(redisDb *db, dictEntry *de, long long now) {
long long t = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
if (now > t) {
sds key = dictGetKey(de);
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key));
// 通知异步进程保持数据
propagateExpire(db,keyobj,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
// redis 删除一次性dict和expare中的hash
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_expire)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",keyobj,db->id);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void propagateExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key, int lazy) {
robj *argv[2];
argv[0] = lazy ? shared.unlink : shared.del;
argv[1] = key;
incrRefCount(argv[0]);
incrRefCount(argv[1]);
// 是否异步保存数据的进程
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF)
feedAppendOnlyFile(server.delCommand,db->id,argv,2);
replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves,db->id,argv,2);
decrRefCount(argv[0]);
decrRefCount(argv[1]);
}
/**
* 追加数据到aof文件中的aof_buf纪录
* @param cmd 执行命令
* @param dictid 数据库id
* @param argv 命令参数
* @param argc 命令个数
*/
void feedAppendOnlyFile(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dictid, robj **argv, int argc) {
sds buf = sdsempty();
robj *tmpargv[3];
/* The DB this command was targeting is not the same as the last command
* we appended. To issue a SELECT command is needed. */
if (dictid != server.aof_selected_db) {
char seldb[64];
snprintf(seldb,sizeof(seldb),"%d",dictid);
buf = sdscatprintf(buf,"*2\r\n$6\r\nSELECT\r\n$%lu\r\n%s\r\n",
(unsigned long)strlen(seldb),seldb);
server.aof_selected_db = dictid;
}
if (cmd->proc == expireCommand || cmd->proc == pexpireCommand ||
cmd->proc == expireatCommand) {
/* Translate EXPIRE/PEXPIRE/EXPIREAT into PEXPIREAT */
buf = catAppendOnlyExpireAtCommand(buf,cmd,argv[1],argv[2]);
} else if (cmd->proc == setexCommand || cmd->proc == psetexCommand) {
/* Translate SETEX/PSETEX to SET and PEXPIREAT */
tmpargv[0] = createStringObject("SET",3);
tmpargv[1] = argv[1];
tmpargv[2] = argv[3];
buf = catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(buf,3,tmpargv);
decrRefCount(tmpargv[0]);
buf = catAppendOnlyExpireAtCommand(buf,cmd,argv[1],argv[2]);
} else if (cmd->proc == setCommand && argc > 3) {
int i;
robj *exarg = NULL, *pxarg = NULL;
/* Translate SET [EX seconds][PX milliseconds] to SET and PEXPIREAT */
buf = catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(buf,3,argv);
for (i = 3; i < argc; i ++) {
if (!strcasecmp(argv[i]->ptr, "ex")) exarg = argv[i+1];
if (!strcasecmp(argv[i]->ptr, "px")) pxarg = argv[i+1];
}
serverAssert(!(exarg && pxarg));
if (exarg)
buf = catAppendOnlyExpireAtCommand(buf,server.expireCommand,argv[1],
exarg);
if (pxarg)
buf = catAppendOnlyExpireAtCommand(buf,server.pexpireCommand,argv[1],
pxarg);
} else {
/* All the other commands don't need translation or need the
* same translation already operated in the command vector
* for the replication itself. */
buf = catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(buf,argc,argv);
}
/* Append to the AOF buffer. This will be flushed on disk just before
* of re-entering the event loop, so before the client will get a
* positive reply about the operation performed. */
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON)
server.aof_buf = sdscatlen(server.aof_buf,buf,sdslen(buf));
/* If a background append only file rewriting is in progress we want to
* accumulate the differences between the child DB and the current one
* in a buffer, so that when the child process will do its work we
* can append the differences to the new append only file. */
// 判断是否异步保存数据的保存的话 aof_child_pid的值不为-1了 所以要保存数据
if (server.aof_child_pid != -1)
aofRewriteBufferAppend((unsigned char*)buf,sdslen(buf));
sdsfree(buf);
}
三, aof的触发的机制
在配置文件中的配置
appendonly yes
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
这个aof异步保存数据的自动保存机制
/* Trigger an AOF rewrite if needed. */
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON &&
server.rdb_child_pid == -1 &&
server.aof_child_pid == -1 &&
server.aof_rewrite_perc &&
server.aof_current_size > server.aof_rewrite_min_size)
{
// 因子 server.aof_rewrite_base_size 关键因子????是已经写入数据的大小
long long base = server.aof_rewrite_base_size ?
server.aof_rewrite_base_size : 1;
long long growth = (server.aof_current_size * 100 / base) - 100;
if (growth >= server.aof_rewrite_perc) {
serverLog(LL_NOTICE, "Starting automatic rewriting of AOF on %lld%% growth", growth);
rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground();
}
}
基本和rdb通知异步进程的信息机制是差不多的
结语
在我的github上会持续更新Redis代码的中文分析,地址送出https://github.com/chensongpoixs/credis_source,共同学习进步
个人博客地址