开启Android应用调试选项的工具XDebug的介绍
本文博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/QQ1084283172/article/details/81187769
最近这段时间比较郁闷,就不分享和学习比较复杂的Android逆向技巧和工具了,每天进步一点就好。这里介绍一下,作者deskid编写的开启Android应用调试选项的工具XDebug,该工具也是基于Xposed框架实现的,也就是在Android应用的启动之前,设置Android应用的调试选项标志为开启,这样Android应用启动的时候,就可以调试模式进行启动。
作者的github地址:https://github.com/deskid/XDebug
XDebug工具就是在Android应用启动之前,开启Android应用的调试选项,这样在DDMS中就可以看到原来不显示的Android进程都显示出来了,Android应用也可以使用 adb shell am -D 命令进行调试启动了。当我们点击Android系统的Home界面上Android应用的图标,然后该Android应用就会被Launcher所启动,在Android应用的Activity界面显示之前,会经过一系列的复杂流程处理,这些流程的过程可以参考老罗的博文进行学习,这里只谈论涉及到XDebug工具部分,先看下XDebug工具的编写Xposed代码:
package com.github.debugxposed;
import android.os.Process;
import de.robv.android.xposed.IXposedHookLoadPackage;
import de.robv.android.xposed.IXposedHookZygoteInit;
import de.robv.android.xposed.XC_MethodHook;
import de.robv.android.xposed.XposedBridge;
import de.robv.android.xposed.callbacks.XC_LoadPackage;
/**
* Created by deskidz on 12/5/16.
*/
public class XDebugable implements IXposedHookLoadPackage, IXposedHookZygoteInit {
private static final int DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER = 0x1;
private XC_MethodHook debugAppsHook = new XC_MethodHook() {
@Override
protected void beforeHookedMethod(MethodHookParam param)
throws Throwable {
XposedBridge.log("-- beforeHookedMethod :" + param.args[1]);
int id = 5;
int flags = (Integer) param.args[id];
// 修改类android.os.Process的start函数的第6个传入参数
if ((flags & DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) == 0) {
// 增加开启Android调试选项的标志
flags |= DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER;
}
param.args[id] = flags;
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
XposedBridge.log("-- app debugable flags to 1 :" + param.args[1]);
}
}
};
@Override
public void handleLoadPackage(final XC_LoadPackage.LoadPackageParam loadPackageParam) throws Throwable {
}
// 实现的接口IXposedHookZygoteInit的函数
@Override
public void initZygote(final IXposedHookZygoteInit.StartupParam startupParam) throws Throwable {
// /frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
// Hook类android.os.Process的start函数
XposedBridge.hookAllMethods(Process.class, "start", debugAppsHook);
}
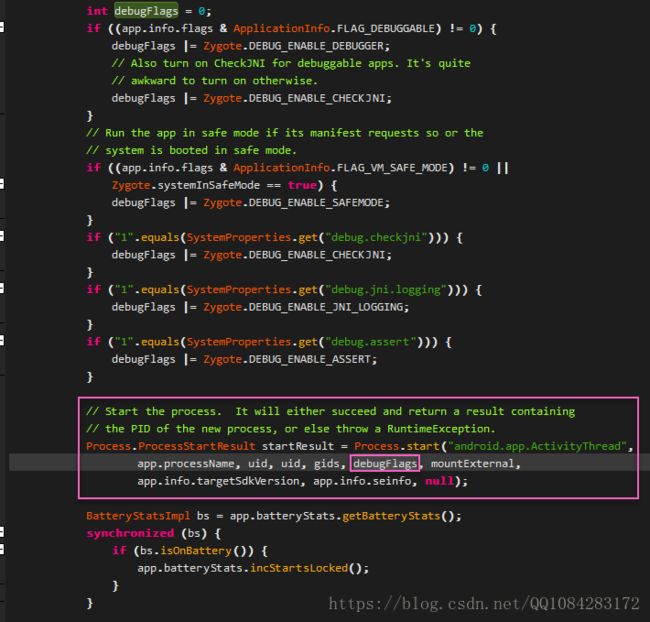
}作者deskid选择在Android应用启动调用类android.os.Process的start函数之前,修改该函数的第6个传入参数,增加开启Android应用的调试选项的调试选项标记。类android.os.Process的start函数是在Android应用启动时调用类com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService的函数startProcessLocked被调用的。
源码路径:
http://androidxref.com/5.1.0_r1/xref/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java#2893
在类android.os.Process中start函数的实现代码如下:
/**
* Start a new process.
*
* If processes are enabled, a new process is created and the
* static main() function of a processClass is executed there.
* The process will continue running after this function returns.
*
*
If processes are not enabled, a new thread in the caller's
* process is created and main() of processClass called there.
*
*
The niceName parameter, if not an empty string, is a custom name to
* give to the process instead of using processClass. This allows you to
* make easily identifyable processes even if you are using the same base
* processClass to start them.
*
* @param processClass The class to use as the process's main entry
* point.
* @param niceName A more readable name to use for the process.
* @param uid The user-id under which the process will run.
* @param gid The group-id under which the process will run.
* @param gids Additional group-ids associated with the process.
* @param debugFlags Additional flags.
* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.
* @param seInfo null-ok SE Android information for the new process.
* @param zygoteArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.
*
* @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.
* @throws RuntimeException on fatal start failure
*
* {@hide}
*/
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}
类android.os.Process中start函数最终调用的类android.os.Process的startViaZygote函数,代码如下;如果Android应用开启了调试模式选项的标志,那么在创建Android应用的进程时,会增加"--enable-debugger"选项,这样Android应用就可以以调试模式进行启动了。
/**
* Starts a new process via the zygote mechanism.
*
* @param processClass Class name whose static main() to run
* @param niceName 'nice' process name to appear in ps
* @param uid a POSIX uid that the new process should setuid() to
* @param gid a POSIX gid that the new process shuold setgid() to
* @param gids null-ok; a list of supplementary group IDs that the
* new process should setgroup() to.
* @param debugFlags Additional flags.
* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.
* @param seInfo null-ok SE Android information for the new process.
* @param extraArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.
* @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.
* @throws ZygoteStartFailedEx if process start failed for any reason
*/
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
synchronized(Process.class) {
ArrayList argsForZygote = new ArrayList();
// --runtime-init, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-init");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-jni-logging");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-safemode");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-checkjni");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-assert");
}
if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_MULTIUSER) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-multiuser");
} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_MULTIUSER_ALL) {
argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-multiuser-all");
}
argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
//TODO optionally enable debuger
//argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
// --setgroups is a comma-separated list
if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("--setgroups=");
int sz = gids.length;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(gids[i]);
}
argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
}
if (niceName != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
}
if (seInfo != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);
}
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(argsForZygote);
}
} 到这里,XDebug工具的原理已经很清楚了,基于作者的思路,也可以Hook类android.os.Process的startViaZygote函数,在该函数执行之前修改其第6个参数,增加Android开启调试选项的标志,谢谢原作者的思路。
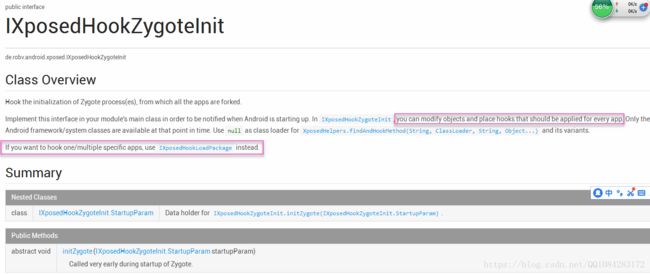
为什么XDebug工具的作者deskid在选择实现Hook类android.os.Process的start函数时,实现的是Xposed框架的de.robv.android.xposed.IXposedHookZygoteInit接口而不是de.robv.android.xposed.IXposedHookLoadPackage接口呢?
如果是选择实现de.robv.android.xposed.IXposedHookLoadPackage接口则Hook类android.os.Process的start函数已经晚了,因为该函数已经执行过了,IXposedHookLoadPackage接口是Hook的Android应用启动时的ActivityThread.handleBindApplication函数,而类android.os.Process的start函数在handleBindApplication函数执行之前,因此这里选择实现IXposedHookZygoteInit接口,并且实现IXposedHookZygoteInit接口的修改对所有启动的App都有影响,下面是Xposed框架的api的说明。
Xposed框架的Api说明文档:https://api.xposed.info/reference/packages.html
有关Xposed源码的学习,后面再研究~