Flask框架学习笔记—常用插件(flask-script,flask-caching)
文章目录
- 1. flask-script
- 2. flask-caching
Flask是一个微型框架,除了Flask自带的核心功能外,其他大部分功能都需要利用Flask提供的插件
优点:灵活,可以根据项目功能需求灵活使用需要的插件
缺点:核心功能较少,针对稍大的项目每次都需要自己集成插件
1. flask-script
flask-script扩展提供向Flask插入外部脚本的功能,包括运行一个开发用的服务器,一个定制的python shell,设置数据库的脚本及其他运行在web应用之外的命令行任务。使得脚本和系统分开
(1) 安装
pip install flask-script
(2) 初始化
# app.py
from flask import Flask
from flask_script import Manager
app = Flask(__name__)
# 初始化
manager = Manager(app=app)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 调用
manager.run()
(3) 使用
这时候就可以在命令行中使用了,如下:
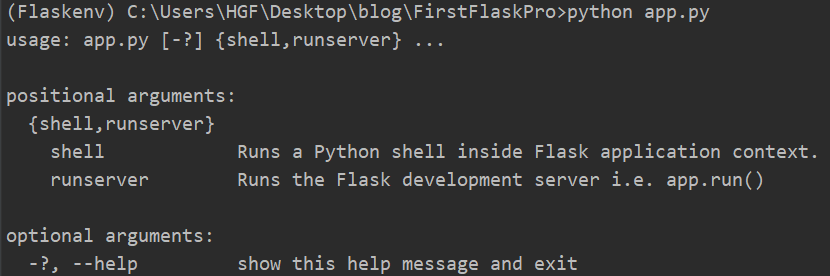
将app.py文件名该为manage.py,这是启动服务器的命令就与Django一样了,如下:
python manage.py runserver
还可以接收参数
python manage.py runserver -p 8000 -h 0 -d -r
其中:
p:端口
h:主机
d:调试模式
r:重启
一般情况下,我们会使用-d和-r
2. flask-caching
flask-caching插件用于缓存
(1) 安装
pip install flask-caching
(2) 初始化
from flask import Flask
from flask_caching import Cache
app = Flask(__name__)
cache = Cache(config={
'CACHE_TYPE': 'simple' # 缓存类型,使用本地python字典缓存
})
cache.init_app(app=app)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
(3) 使用装饰器缓存视图函数
import time
from flask import Flask, render_template
from flask_caching import Cache
app = Flask(__name__)
cache = Cache(config={ 'CACHE_TYPE': 'simple' })
cache.init_app(app=app)
@app.route('/index/')
@cache.cached(timeout=20)
def index():
time.sleep(5)
return render_template('index.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
运行服务器,访问/index/时,会先睡眠5秒,再显示页面,之后20秒内访问,都会从缓存中取,20秒后缓存失效
(4) 使用get获取cache和set设置cache
import time
from flask import Flask, render_template
from flask_caching import Cache
app = Flask(__name__)
cache = Cache(config={'CACHE_TYPE': 'simple'})
cache.init_app(app=app)
@app.route('/index/')
def index():
# 从缓存中获取key=cache_data的内容
cache_data = cache.get('cache_data')
if cache_data:
# 如果有缓存,则直接返回
return cache_data
else:
time.sleep(5)
res = render_template('index.html')
cache.set('cache_data', res, timeout=20)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
(5) 注意事项
如果使用的是flask-cache库,flask1.0之后版本需要将jinja2ext.py文件中的源码:
from flask.ext.cache import make_template_fragment_key
修改为:
from flask_cache import make_template_fragment_key