【深度学习】TensorFlow命令笔记
【深度学习】 TensorFlow命令笔记
- tf.argmax
- tf.concat
- tf.constant
- tf.contrib.layers.l1_regularizer和tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer
- tf.convert_to_tensor
- tf.contrib.slim.conv2d
- tf.contrib.slim.fully_connected
- tf.contrib.slim.max_pool2d
- tf.equal
- tf.expand_dims
- tf.flags
- tf.logging.set_verbosity
- tf.name_scope
- tf.nn.conv2d
- 卷积计算
- 对卷积的理解
- 关于zero-padding
- tensorflow相关命令
- tf.nn.max_pool和tf.nn.avg_pool
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits和tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
- tf.placeholder
- tf.reduce_mean
- tf.slice
- tf.split
- tf.truncated_normal
- tf.unstack
- tf.Variable和tf.get_variable
- tf.variable_scope
- tf.GPUOptions和tf.ConfigProto
- tf.Session和tf.global_variables_initializer
- tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer和tf.train.AdamOptimizer
- tf.train.exponential_decay
- tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage
- tf.train.slice_input_producer、tf.train.batch和tf.train.shuffle_batch
- tf.read_file
- tf.image.decode_jpeg和tf.image.decode_png
- tf.image.convert_image_dtype
- tf.image.resize_images
- tf.image.random_flip_up_down和tf.image.flip_up_down
- tf.image.random_flip_left_right和tf.image.filp_left_right
- tf.image.transpose_image
- tf.image.random_brightness和tf.image.adjust_brightness
- tf.image.random_contrast和tf.image.adjust_contrast
- tf.trainable_variables
- tf.train.Saver
- 卷积神经网络样例
- 结语
tf.argmax
返回最大值
tf.argmax(input, axis)
- input:一个多维数据
- axis:根据axis取值的不同返回按input某一维度依次取得的最大值的索引
- 返回一个向量,每个元素是按顺序得到的最大值的索引
tf.concat
张量拼接
tf.concat([tensor1, tensor2, tensor3,...], axis)
- [tensor1, tensor2, tensor3,…]:多个张量,每个张量的shape必需相同
- axis:根据axis取值的不同,将多个张量按某一维度拼接在一起
- 返回拼接后的张量
tf.constant
创建常数张量
tf.constant(value, dtype=None, shape=None, name=None, verity_shape=False)
- value:可以是一个数值,也可以是一个列表list。如果是一个数,那么这个常量中所有值的按该数来赋值。如果是list,那么len(value)一定要小于等于shape展开后的长度。赋值时,先将value中的值逐个存入。不够的部分,则全部存入value的最后一个值。
- dtype:表示数据类型,一般是tf.float32、tf.float64或tf.int32、tf.int64
- shape:表示张量形状
- verity_shape:默认是False,如果为True会检查value和shape是否相符,不相符则报错
tf.contrib.layers.l1_regularizer和tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer
L1正则和L2正则,一般在损失函数后添加
正则化的目的是限制参数过多或者过大,避免模型更加复杂,避免过拟合
L1正则:
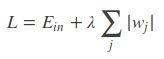
L2正则:

其中, E i n E_{in} Ein 是未包含正则化项的训练样本误差, λ λ λ 是可调的正则化参数
L1正则可以保证模型的稀疏性,也就是某些参数等于0;L2正则可以保证模型的稳定性,也就是参数的值不会太大或太小
L1的公式不可导,L2的公式可导,优化带L1正则化的损失函数要更加复杂
tf.contrib.layers.l1_regularizer(lambda)(weights)
tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(lambda)(weights)
- lambda是正则化权重系数
- weights是参数
当参数很多时,每组参数每组参数的加正则项很不方便,通过下面的代码简化
import tensorflow as tf
def get_weight(shape, lambda):
var = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape), dtype = tf.float32)
tf.add_to_collection(
"losses", tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(lambda)(var))
// 参数正则的结果加入集合“losses”
return var
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2))
// 输入特征占位 shape=None x 2
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1))
// label占位 shape=None x 1
batch_size = 8
layer_dimension = [2, 10, 10, 10, 1]
n_layers = len(layer_dimension)
cur_layer = x
in_dimension = layer_dimension[0]
for i in range(1, n_layers):
// 从第二层起每一层循环
out_dimension = layer_dimension[i]
weight = get_weight([in_dimension, out_dimension], 0.001)
bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[out_dimension]))
cur_layer = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(cur_layer, weight) + bias)
// 完成一次正向传播
in_dimension = layer_dimension[i]
mse_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_ - cur_layer))
// 损失函数
tf.add_to_collection("losses", mse_loss)
// 损失函数加入集合losses
loss = tf.add_n(tf.get_collection("losses"))
// 损失函数加所有参数的正则结果,得到最终的带正则化的损失函数
tf.convert_to_tensor
将python的某一数据类型转化成TensorFlow的张量
tf.convert_to_tensor(data, dtype)
- data:转化成张量的数据
- dtype:是data的数据类型
- 比如:tf.convert_to_tensor(str, dtype=tf.string) 将字符串类型的数据str转化为张量
tf.contrib.slim.conv2d
创建卷积层
tf.contrib.slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=1, padding='SAME', data_format=None, rate=1, activation_fn=nn.relu, normalizer_fn=None, normalizer_params=None, weights_initializer=initializers.xavier_initializer(), weights_regularizer=None, biases_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(), biases_regularizer=None, reuse=None, variables_collections=None, outputs_collections=None, trainable=True, scope=None)
- inputs:输入卷积层的张量
- num_outputs:指定卷积核的个数,也就是输出张量的channel数
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长,默认为1
- padding:padding的方式选择,默认为SAME
- data_format:指定输入的input的格式,inputs的形状为[batch_size, height, width, channels]和data_format 是NHWC相匹配,[batch_size, channels, height, width]和NCHW 相匹配
- rate:使用空洞卷积的膨胀率,默认为1,即为普通卷积,rate=n代表卷积核中相邻两两数之间插入了n-1个0,注意卷积核边界点外圈也插入n-1个零,这样组成新kernel_size的卷积核
- activation_fn:激活函数的指定,默认为ReLU函数
- normalizer_fn:指定正则化函数
- normalizer_params:指定正则化函数的参数
- weights_initializer:指定权重的初始化方式
- weights_regularizer:权重正则化方式
- biases_initializer:指定biase的初始化方式
- biases_regularizer:biases正则化方式
- reuse:指定是否共享层或者变量
- variable_collections:指定所有变量被添加的集合
- outputs_collections:指定输出被添加的集合
- trainable:卷积层的参数是否可被训练,默认为True,也就是可训练
- scope:共享变量所指的variable_scope
tf.contrib.slim.fully_connected
创建全卷积层
tf.contrib.slim.fully_connected(inputs, num_outputs, activation_fn=nn.relu, normalizer_fn=None, normalizer_params=None, weights_initializer=initializers.xavier_initializer(), weights_regularizer=None, biases_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(), biases_regularizer=None, reuse=None, variables_collections=None, outputs_collections=None, trainable=True, scope=None)
- inputs:至少秩为2的张量,最后一个维度为静态值;即:"[batch_size, depth]", “[None, None, None, channels]”
- num_output:全连接层输出单元的数量
- activation_fn:激活函数。默认值为ReLU函数。显式地将其设置为None以跳过它并保持线性激活
- normalizer_fn:用来代替“偏差”的归一化函数。如果提供“normalizer_fn”,则忽略“biases_initializer”和“biases_regularizer”,并且不会创建或添加“bias”。默认设置为None
- normalizer_params:规范化函数参数
- weights_initializer:权值的初始化器
- weights_regularizer:可选的权重正则化器
- biases_initializer:用于偏差的初始化器。如果没有人跳过bias
- biases_regularizer:可选的偏差调整器
- reuse:是否应该重用层及其变量。如果为了能够重用层范围,则必须给出
- variables_collections:所有变量的可选集合列表,或包含每个变量的不同集合列表的字典
- outputs_collections:用于添加输出的集合
- trainable:如果“True”则参数可训练
- scope:variable_scope的可选作用域
- 返回值:一系列运算结果的张量变量
tf.contrib.slim.max_pool2d
创建最大池化层
tf.contrib.slim.max_pool2d(inputs, kernel_size, stride=2, padding='VALID', data_format=DATA_FORMAT_NHWC, outputs_collections=None, scope=None)
- inputs:输入池化层的张量
- kernel_size:滤波核尺寸
- stride:步长,默认为2
- padding:padding的方式选择,默认为VALID
- data_format:指定输入的input的格式,inputs的形状为[batch_size, height, width, channels]和data_format 是NHWC相匹配,[batch_size, channels, height, width]和NCHW 相匹配
- outputs_collections:指定输出被添加的集合
- scope:共享变量所指的variable_scope
tf.equal
逐个元素进行判断是否相等
tf.equal(x, y, name=None)
- 如果相等就是True,不相等,就是False
tf.expand_dims
tensorflow张量增加维度
tf.expand_dims(tensor, axis)
- axis:指定维度
- axis为0时,在最前面加一个维度
- axis为1时,在第一个维度后面加一个维度,以此类推
- axis为-1时,在最后加一个维度
tf.flags
用于传递和解析命令行参数,相当于python的argparse
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("str_name", "str", "str_descrip")
- 定义一个字符串类型的参数
- 括号中第一个参数是定义的这个参数的名称,第二个是默认值,第三个是描述
tf.flags.DEFINE_boolean("bool_name", True, "bool_descrip")
- 定义一个布尔类型的参数
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("int_name", num, "int_descrip")
- 定义一个整形类型的参数
FLAGS = tf.flags.FlAGS
- 使定义的参数生效,并通过FLAGS使用
FLAGS.str_name
//值为"str"
FLAGS.bool_name
//值为True
FLAGS.int_name
//值为num
tf.logging.set_verbosity
设置输出日志最低等级
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.DEBUG)
- 输出DEBUG级别,以及高于DEBUG级别的日志信息
在TensorFlow中有函数可以直接log打印。
TensorFlow使用五个不同级别的日志消息,按照上升的顺序它们是:
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARN
- ERROR
- FATAL
tf.name_scope
解决命名冲突问题
with tf.name_scope("name"):
或
with tf.name_scope("name") as scope:
- name:该命名区域的名称
- 在某个tf.name_scope()指定的区域中定义的所有对象及各种操作,他们的“name”属性上会增加该命名区的区域名,用以区别对象属于哪个区域
tf.nn.conv2d
卷积计算
卷积核虽然是3x3、5x5之类,但是一个卷积核用在一个多channel的张量上时,卷积核对应每个channel的值是不同的。比如一个5x5x5的张量,3x3的卷积核做卷积,卷积核实际维度是3x3x5,卷积核的5个channel的值各不相同。
对卷积的理解
从函数(或者说映射、变换)的角度理解。 卷积过程是在图像每个位置进行线性变换映射成新值的过程,将卷积核看成权重,若拉成向量记为w,图像对应位置的像素拉成向量记为x,则该位置卷积结果为y=w′x+b,即向量内积+偏置,将x变换为y。从这个角度看,多层卷积是在进行逐层映射,整体构成一个复杂函数,训练过程是在学习每个局部映射所需的权重,训练过程可以看成是函数拟合的过程。
从模版匹配的角度理解,认为卷积核定义了某种模式,卷积运算是在计算每个位置与该模式的相似程度,或者说每个位置具有该模式的分量有多少,当前位置与该模式越像,响应越强。
一个卷积核代表一种模式,缺乏泛化能力。通过多层卷积,来将简单模式组合成复杂模式,通过这种灵活的组合来保证具有足够的表达能力和泛化能力。
浅层layer学到的特征为简单的边缘、角点、纹理、几何形状、表面等,到深层layer学到的特征则更为复杂抽象,为狗、人脸、键盘等等。
卷积神经网络每层的卷积核权重是由数据驱动学习得来。
数据驱动卷积神经网络逐层学到由简单到复杂的特征,复杂模式是由简单模式组合而成。
以上内容参考自卷积神经网络之卷积计算、作用与思想
关于zero-padding
如果使用了zero-padding,输出的尺寸计算方式如下:
- out-length = |in-length/stride-length|,即:输出长度等于输入长度除以步长,然后向上取整
如果不使用zero-padding,遵循:
- 不足一次移动了就扔掉的原则
tensorflow相关命令
filter_weight = tf.get_variable("weights", [5, 5, 3, 16], initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
//5x5的卷积核,输入的深度为3,输出深度为16
biases = tf.get_variable("biases", [16], initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
//偏置
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter_weight, strides = [1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
//input是输入卷积核的张量, strides第一个元素和最后一个元素必须是1,分别对应batch维度的步长和输入深度维度的步长
//tensorflow中padding有两种选择,“SAME”是使用zero-padding,“VALID”是不使用zero-padding
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
//
actived_conv = tf.nn.relu(bias)
//
tf.nn.max_pool和tf.nn.avg_pool
卷积层使用的滤波器是横跨整个深度的,池化层使用的滤波器只影响一个深度上的节点
pool = tf.nn.max_pool(actived_conv, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
//tf.nn.max_pool是最大池化
//tf.nn.avg_pool是平均池化
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits和tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
交叉熵损失函数,多用于分类问题
cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=None, logits=None)
- labels:真实标签(one-hot处理过)
- logits:网络输出的结果
具体的执行流程分为两步:
- 先对网络最后一层的输出做一个softmax,这一步通常是求取输出属于某一类的概率,对于单label样本而言,输出就是一个num_classes大小的向量([Y1, Y2, Y3…]其中Y1,Y2,Y3…分别代表了是属于该类的概率)
softmax的公式是:

- softmax的输出向量[Y1, Y2, Y3…]和样本的实际标签做一个交叉熵,公式如下:

其中 y i , y_i^, yi,是真实标签, y i y_i yi是softmax的输出结果
显而易见,预测越准确,结果的值越小,最后求一个平均,得到我们想要的loss
注意,这个函数的返回值并不是一个数,而是一个向量,如果要求交叉熵,我们要再做一步tf.reduce_sum操作,就是对向量里面所有元素求和,最后才得到 H y , ( y ) H_{y^,}(y) Hy,(y)
如果求loss,则要做一步tf.reduce_mean操作,对向量求均值
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=None, logits=None)
- labels:真实标签(未经one-hot处理)
- logits:网络输出的结果
回归问题多使用均方误差(MSE)
mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_ - y))
//MSE
tf.placeholder
在神经网络构建graph时在模型中占位,分配必要的内存
tf.placeholder(dtype, shape, name)
- dtype:数据类型,常用tf.float32或tf.float64等
- shape:数据形状
- name:数据名称
- tf.placeholder占位的变量,需要在sess.run()中使用一个名为feed_dict的字典赋初始值,否则会报错
tf.reduce_mean
计算张量沿指定轴的平均值
tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor, axis=None, keep_dims=False, name=None, reduction_indices=None)
- axis:指定的轴,如果不指定,则计算所有元素的均值
- keep_dims:是否降维度,设置为True,输出的结果保持输入tensor的形状,设置为False,输出结果会降低维度
tf.slice
张量切片
tf.slice(input, begin, size, name=None)
- input:是你输入的tensor,就是被切的那个
- begin:是每一个维度的起始位置
- size:相当于问每个维度拿几个元素出来
参考博客:https://www.jianshu.com/p/71e6ef6c121b
tf.split
张量拆分,不改变维度
tf.split(value, num_or_size_splits, axis=0)
- value:原始张量
- num_or_size_splits:拆分的份数
- axis:指定维度
- 返回一个list,里面是拆分后的每个张量
tf.truncated_normal
产生截断正态分布随机数
tf.truncated_normal(shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32, seed=None, name=None)
- shape:输出张量的维度
- mean:均值
- stddev:标准差
- dtype:输出数据类型
- seed:随机种子,若 seed 赋值,每次产生相同随机数
- name:名称
- 取值范围为 [ mean - 2 * stddev, mean + 2 * stddev ]
tf.unstack
张量拆分,拆分后降低维度
tf.unstack(value, num_or_size_splits, axis=0)
- value:原始张量
- num_or_size_splits:拆分的份数
- axis:指定维度
- 返回一个list,里面是拆分后的每个张量
tf.Variable和tf.get_variable
- tf.Variable
设定一个初始化参数
tf.Variable(initializer, name, trainable)
- initializer:初始化参数
- name:这个参数的自定义名称
- trainable:如果为True,则将变量添加到图形集合GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES
- 通过tf.Variable设定的初始化参数,需要在session中sess.run()才能使用
- 可以通过tf.global_variables_initializer()全部初始化
- tf.get_variable
获取一个已经存在的变量或者创建一个新的变量
tf.get_variable(name, shape, dtype, ininializer, trainable)
- ininializer:如果创建新的变量,则用它来初始化变量
- trainable:如果为True,则将变量添加到图形集合GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES
例子 1:
global_step = tf.get_variable("step", [], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0), trainable=False)
例子2:
v = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1], name="v"))
v = tf.get_variable("v", shape=[1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1.0))
例子2中两个定义是等价的
tf.variable_scope
声明变量作用域
with tf.variable_scope(name_or_scope, default_name=None, values=None, reuse=None)
- name_or_scope:变量空间的名称,一般为字符串类型
- default_name:当name_or_scope 使用时,它可以忽略。如果name_or_scope是None,则其值赋给空间变量名称
- values:一个Tensor的列表,是传入该scope的tensor参数
- reuse:三种取值,None、False和True。当值为True时,tf.get_variable()不是创建变量,而是获取已有变量
with tf.variable_scope("foo"):
v = tf.get_variable("v", [1], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1.0))
//在命名空间“foo”中,定义一个名字为“v”的变量
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
with tf.variable_scope("foo"):
v = tf.get_variable("v", [1])
//因为命名空间中已经有“v”,所以上面命令报错
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
with tf.variable_scope("foo", resue=True):
v1 = tf.get_variable("v", [1])
print v == v1
//上述命令打印“True”
//当“resue”参数设置为True时,tf.get_variable()不是创建变量,而是获取已有变量
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
with tf.variable_scope("bar", resue=True):
v1 = tf.get_variable("v", [1])
//上面命令报错,因为在命名空间“bar”中不存在变量“v”
tf.variable_scope函数嵌套使用时,reuse的确定:
新建一个嵌套的上下文管理器但不指定reuse,这是reuse的取值会和外面一层保持一致
tf.GPUOptions和tf.ConfigProto
限制GPU资源的使用
- 方法一
gpu_options=tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.7)
//设置GPU显存使用率为70%
config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)
session = tf.Session(config=config)
- 方法二
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.7
//设置GPU显存使用率为70%
session = tf.Session(config=config)
申请动态显存
- 方法一
gpu_options=tf.GPUOptions(allow_growth = True)
config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)
session = tf.Session(config=config)
- 方法二
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
session = tf.Session(config=config
tf.Session和tf.global_variables_initializer
会话
- 方式一
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(...)
sess.close()
- 方式二
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(...)
- 关于tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
//初始化所有变量
仅仅是初始化变量
tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer和tf.train.AdamOptimizer
这是两种常用的优化算法
- tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer
梯度下降算法
tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost_function, global_step=global_step)
//global_step是一个计数器,global_step自动更新为执行该命令的次数
列子:
global_step = tf.get_variable("step", [], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0), trainable=False)
//初始化global_step为0
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOpt.imizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
...
_, step = sess.run(optimizer, global_step)
//step是执行次数
该方法学习率恒定
- tf.train.AdamOptimizer
自适应学习率
beta1、beta2和epsilon是学习率变化相关参数,缺省值不一定最优,需要根据具体情况进行调整
tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08, use_locking=False, name='Adam' ).minimize(cost_function, global_step=global_step)
//global_step使用方法和上面相同
tf.train.exponential_decay
指数衰减法改变学习率
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(base_learning_rate, global_step, decay_step, decay_rate, staircase = False)
//学习率计算公式:
learning_rate = base_learning_rate * decay_rate ^ (global_step / decay_step)
//staircase为True时,global_step / decay_step会被转化为整数
tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage
神经网络在测试时给可训练参数使用滑动平均模型
意在让权重与历史权重有关联,使模型在测试数据上更加robust
训练的权重和测试的权重不相等,测试的权重是训练的权重滑动平均后的结果
import tensorflow as tf
v1 = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.float32)
step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(0.99, step)
//decay为0.99
maintain_averages_op = ems.apply([v1])
//v1作为初始值
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer
sess.run(init_op)
//初始化v1和step
print sess.run([v1, ema.average(v1)])
//输出[0.0, 0.0]
//v1初始化为0.0,影子变量初始为0.0
sess.run(tf.assign(v1, 5))
//将v1的值更新为5
sess.run(maintain_averages_op)
//v1初始化
print sess.run([v1, ema.average(v1)])
//输出[5.0, 4.5]
//v1初始化为5.0,影子变量为min{0.99, (1+step)/(10+step)}*0.0 + (1-min{0.99, (1+step)/(10+step)})*5.0 = 4.5
sess.run(tf.assign(step, 10000))
//step更新为10000
sess.run(tf.assign(v1, 10))
//v1更新为10
sess.run(maintain_averages_op)
//v1初始化
print sess.run([v1, ema.average(v1)])
//输出[10.0, 4.555]
sess.run(maintain_averages_op)
print sess.run([v1, ema.average(v1)])
//输出[10.0, 4.60945]
tf.train.slice_input_producer、tf.train.batch和tf.train.shuffle_batch
tf.train.slice_input_producer(tensor_list, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True, seed=None, capacity=32, shared_name=None, name=None)
//tensor_list是一个列表,两个元素,第一个是全部数据,第二个是顺序对应的全部标签,比如:[image, labels]
//num_epochs是训练epoch个数
//shuffle,布尔类型,设置是否随机打乱数据集
//seed,可选的整数,是生成随机数的种子,在第三个参数设置为shuffle=True的情况下才有用
//capacity,第一个参数中tensor列表的容量
//shared_name,如果设置一个‘shared_name’,则在不同的上下文环境(Session)中可以通过这个名字共享生成的tensor
//name,设置操作的名称
上面命令返回的就是这个tensor列表,tensor[0]就是数据,tensor[1]就是labels。[[tensor[0], tensor[1]]就作为下面这个命令的参数:tensors的输入(可以进行处理后在输入)
tf.train.batch(tensors, batch_size, num_threads=1, capacity=32, enqueue_many=False, shapes=None, dynamic_pad=False, allow_smaller_final_batch=False, shared_name=None, name=None)
//tensor,tensor序列或tensor字典,可以是含有单个样本的序列
//batch_size,设置batch size值
//num_threads,执行tensor入队操作的线程数量,可以设置使用多个线程同时并行执行,提高运行效率,但也不是数量越多越好
//capacity,定义生成的tensor序列的最大容量
//enqueue_many,定义第一个传入参数tensors是多个tensor组成的序列,还是单个tensor
//shapes,默认是推测出的传入的tensor的形状
//dynamic_pad,定义是否允许输入的tensors具有不同的形状,设置为True,会把输入的具有不同形状的tensor归一化到相同的形状
//allow_smaller_final_batch,设置为True,表示在tensor队列中剩下的tensor数量不够一个batch_size的情况下,允许最后一个batch的数量少于batch_size, 设置为False,则不管什么情况下,生成的batch都拥有batch_size个样本
tf.train.shuffle_batch和tf.train.batch的区别仅仅是前者会将数据集随机打乱
tf.read_file
读取图片
tf.read_file("路径,可以是tensor类型的列表")
//读取进来的图片需要根据后缀解码
tf.image.decode_jpeg和tf.image.decode_png
解码tf.read_file读取的图片
tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_value, channels)
//第一个参数是tf.read_file读取的图片,第二个参数是图片通道数
tf.image.decode_png(image_value, channels)
tf.image.convert_image_dtype
将image转换为dtype类型
tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype, saturate=False, name=None)
//image,是经过解码的图片
//dtype常用:tf.float32(0-1之间)
//saturate,默认为false,如果为True则在强制转换前裁剪输入
tf.image.resize_images
缩放图片
tf.image.resize_images(image, size, method, align_corners=False)
//image:0-255的图片或者转化为dtype类型的图片都可以
//size:2个元素(new_height, new_width)的1维int32张量,表示图像的新大小
//method:ResizeMethod,默认为ResizeMethod.BILINEAR(双线性插值)
//ResizeMethod.BILINEAR:双线性插值。也可以用method=0表示
//ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR:最近的邻居插值。也可以用method=1表示
//ResizeMethod.BICUBIC:双三次插值。也可以用method=2表示
//ResizeMethod.AREA:区域插值。也可以用method=3表示
//align_corners:布尔型,如果为True,则输入和输出张量的4个拐角像素的中心对齐,并且保留角落像素处的值;默认为False
tf.image.random_flip_up_down和tf.image.flip_up_down
图像上下翻转
tf.image.random_flip_up_down(image, seed=None)
//0-255的图片或者转化为dtype类型的图片都可以
tf.image.file_up_down(image),不是随机的,就是单纯的翻转
tf.image.random_flip_left_right和tf.image.filp_left_right
图像左右翻转
tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image, seed=None)
//0-255的图片或者转化为dtype类型的图片都可以
tf.image.file_left_right(image),不是随机的,就是单纯的翻转
tf.image.transpose_image
通过交换高度和宽度维度来转置图像,也就是沿对角线翻转
tf.image.transpose_image(image)
//0-255的图片或者转化为dtype类型的图片都可以
tf.image.random_brightness和tf.image.adjust_brightness
通过随机因子调整图像亮度
tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta, seed=None)
//0-255的图片或者转化为dtype类型的图片都可以
//max_delta,这里必须是非负的,在-max_delta到max_delta中随机改变亮度
tf.image.adjust_brightness(image, delta),不是随机的,就是根据delta调整亮度
tf.image.random_contrast和tf.image.adjust_contrast
通过随机因子调整图像对比度
tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower, upper, seed=None)
//0-255的图片或者转化为dtype类型的图片都可以
//lower,浮点型,随机对比因子的下限
//upper,浮点型,随机对比因子的上限
tf.image.adjust_contrast(image, delta),不是随机的,就是根据delta调整对比度
tf.trainable_variables
tf.trainable_variables()
//返回所有待训练的变量列表
tf.train.Saver
保存和还原一个神经网络模型
import tensorflow as tf
...
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
...
saver.save(sess, "/path/to/model/model.ckpt")
TensorFlow模型将保存到/path/to/model/model.ckpt文件中。
/path/to/model路径下会保存三个文件:
- model.ckpt.meta 这个文件保存了TensorFlow计算图的结构,可以理解为神经网络的网络结构
- model.ckpt 这个文件保存了TensorFlow程序中每一个变量的取值
- checkpoint 这个文件保存了一个目录下所有的模型文件列表
import tensorflow as tf
...
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
...
saver.restore(sess, "/path/to/model/model.ckpt")
加载保存后的模型
比如,可能有一个之前训练好的五层神经网络模型,但现在想尝试一个六层的神经网络,那么可以将前面五层神经网络中的参数直接加载到新的模型,而仅仅将最后一层神经网络重新训练
为了保存或者加载部分变量,在声明tf.train.Saver类时可以提供一个列表来指定需要保存或者加载的变量
//比如
saver = tf.train.Saver([v1])
//只有变量v1会被加载尽量
//注意要讲其他变量也初始化,否则将报错初始化错误
卷积神经网络样例
import tensorflow as tf
INPUT_NODE = 784
//28x28的图片
OUTPUT_NODE = 10
//10类
IMAGE_SIZE = 28
//长宽都是28
NUM_CHANNELS = 1
//灰度图
MUM_LABELS = 10
//10类
CONV1_DEEP = 32
CONV1_SIZE = 5
//第一层卷积的输出深度和尺寸
CONV2_DEEP = 64
CONV2_SIZE = 5
//第二层卷积的输出深度和尺寸
FC_SIZE = 512
//全连接层的节点个数
//输入batch_size x 28 x 28 x 1
def inference(input_tensor, train, regularizer):
//参数train用来区分训练过程还是测试过程
with tf.variable_scope("layer1-conv1"):
conv1_weights = tf.get_variable("weight", [CONV1_SIZE, CONV1_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS, CONV1_DEEP], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
conv1_biases = tf.get_variable("bias", [CONV1_DEEP], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_tensor, conv1_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv1_biases))
//第一层卷积的输出batch x 28 x 28 x 32
with tf.name_scope("layer2-pool1"):
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1, ksize = [1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
//第一层池化的输出batch x 14 x 14 32
with tf.variable_scope("layer3-conv2"):
conv2_weights = tf.get_variable("weight", [CONV2_SIZE, CONV2_SIZE, CONV1_DEEP, CONV2_DEEP], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
conv2_biases = tf.get_variable("bias", [CONV2_DEEP], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_tensor, conv2_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_biases))
//低二层卷积的输出为batch x 14 x 14 x 64
with tf.name.scope("layer4-pool2"):
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
//第二层池化的输出为batch x 7 x 7 x 64
pool_shape = pool2.get_shape().as_list()
//pool_shape是一个列表
//pool_shape[0]、[1]、[2]、[3]分别对应batch、7、7、64
nodes = pool_shape[1]*pool_shape[2]*pool_shape[3]
//nodes是batch中每一个图片的所有节点数
reshaped = tf.reshape(pool2, [pool_shape[0], nodes])
//把 batch x 7 x 7 x 64 转变为 batch x 3136
//每一行的内容是一个图片的所有节点
with tf.variable_scope("layer5-fc1"):
fc1_weight = tf.get_variable("weight", [nodes, FC_SIZE], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
//nodes x FC_SIZE (3136 x 512)
//每一列是一个特征
//只有全连接层的权重需要加入正则化
if regularizer != None:
tf.add_to_collection("losses", regularizer(fc1_weights))
fc1_biases = tf.get_variable("bias", [FC_SIZE], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshaped, fc1_weight) + fc1_biases)
if train:
fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1, 0.5)
//输出batch x 512,每一个行是batch中每个图片提取的512个特征
with tf.variable_scope("layer6-fc2"):
fc2_weight = tf.get_variable("weight", [FC_SIZE, NUM_LABELS], initializer=tf.trunacted_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
//FC_SIZE x NUM_LABELS (512 x 10)
//十列是十类,每一列都是对512个特征的不同组合方法
if regularizer != None:
tf.add_to_collection("losses", regularizer(fc2_weights))
fc2_biases = tf.get_variable("bias", [NUM_LABELS], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
logit = tf.matmul(fc1, fc2_weights) + fc2_biases
//batch x 10 每一行是每个图片是10类中每一个的依次的置信度
return logit
结语
如果您有修改意见或问题,欢迎留言或者通过邮箱和我联系。
手打很辛苦,如果我的文章对您有帮助,转载请注明出处。