linux--shell脚本常用脚本命令
什么是shell?
shell也是操作系统中的一个软件,他包含zailinux内核的外面,为了用户和内核之间的交互提供了一个接口
系统中的命令用shell去解释
shell接收到系统回应的输出并显示其到屏幕上
什么是shell脚本?
脚本是一种解释型语言 ##命令需要解释器解释,运行效率慢
用shell脚本保存执行动作
用脚本判定命令的执行条件
用脚本来实现动作的批量生产的执行
1.diff 和path
diff命令在最简单的情况下,比较给定的两个文件的不同。如果使用“-”代替“文件”参数,则要比较的内容将来自标准输入。diff命令是以逐行的方式,比较文本文件的异同处。如果该命令指定进行目录的比较,则将会比较该目录中具有相同文件名的文件,而不会对其子目录文件进行任何比较操作。
patch 命令用于打补丁,补丁文件是使用diff产生的,
patch 命令失败或拒绝接受补丁时,会产生一个和原文件同名,以”.rej”为后缀的差异文件。
当知道 -b 时,会产生一个和原文件同名,以”.orig”为后缀的备份文件。
diff
a是 add在增加
d 是delete是删除
c是change 改变
[root@localhost mnt]# vim hehe
[root@localhost mnt]# cat hehe
xixixi
linux
[root@localhost mnt]# vim xixi
[root@localhost mnt]# cat xixi
hehehehe
linux
[root@localhost mnt]# diff xixi hehe ##对比xixi 和 hehe文件
1c1
< hehehehe ##第一行改为hehehehe
---
> xixixi
2a3
>

目录的比较
root@localhost mnt]# mkdir westos
[root@localhost mnt]# mkdir linux
[root@localhost mnt]# touch westos/file1
[root@localhost mnt]# diff westos linux -r
Only in westos: file1 ##只有westos目录有file1文件
path补丁
diff -u hehe xixi (对比两个文件的不同,要把hehe文件变为xixi文件需要改变什么)
[root@localhost mnt]# cat hehe
hehe
linux
[root@localhost mnt]# cat xixi
xixi
linux
[root@localhost mnt]# diff -u hehe xixi > hehe.path (生成path补丁)
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
[root@localhost mnt]# patch hehe hehe.path (将补丁hehe的补丁起名为hehe。path)
[root@localhost mnt]# cat hehe
[root@localhost mnt]# cat xixi
备份文件
[root@localhost mnt]# vim hehe
[root@localhost mnt]# cat hehe
hehe
linux
[root@localhost mnt]# cat xixi
xixi
linux
[root@localhost mnt]# patch -b hehe hehe.path (运行shell时保存文件到hehe。orig)
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
heh hehe hehe.orig hehe.path xixi
[root@localhost mnt]# cat hehe
[root@localhost mnt]# cat xixi
root@localhost mnt]# cat hehe.orig
2.sort和uniq
sort命令是在Linux里非常有用,它将文件进行排序,并将排序结果标准输出
sort -n ##纯数字排序(按大小排序)
sort -r ##倒叙
sort -u ##去掉重复数字
sort -o ##出处到指定文件
sort -t ##指定分隔符
sort -k ##指定要排列的序
sort -nu file (倒叙并去掉重复数字)
sort -nr file (倒叙并且按照纯数字排列)
[root@localhost mnt]# sort -t : -n file (两列都按照纯数字排列)
[root@localhost mnt]# sort -t : -k 2 file (指定第二列)
uniq
uniq命令用于报告或忽略文件中的重复行,一般与sort命令结合使用
uniq
对重复字符作相应的处理
uniq -u ##显示唯一的行
uniq -d ##显示重复的行
uniq -c ##每行显示一次并统计重复次数
root@localhost mnt]# cat file
1
2
2
3
4
5
5
11
11
23
26
1
4
3
[root@localhost mnt]# sort -n file | uniq
[root@localhost mnt]# sort -n file | uniq -u (显示不重复的数字)
[root@localhost mnt]# sort -n file | uniq -c (重复数字)
[root@localhost mnt]# sort -n file | uniq -d (显示重复数字)
3.test命令
-eq 是等于
-ge 大于等于
-gt 大于
-le 小于等于
-lt 小于
-ne 不等于
-ef 两个的链接相同
-nt file1建立时间新与file2
-ot file1建立时间旧与file2
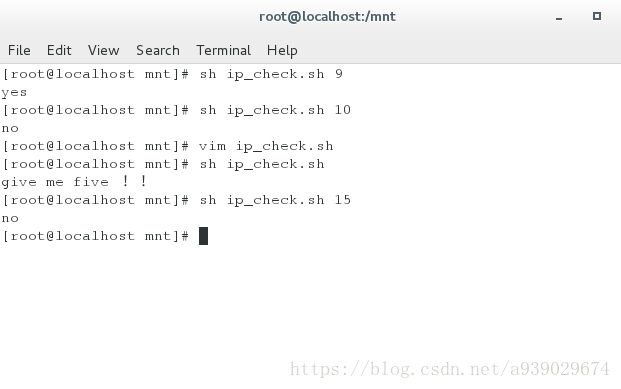
root@localhost mnt]# sh ip_check.sh 9
yes
[root@localhost mnt]# sh ip_check.sh 10
no
[root@localhost mnt]# vim ip_check.sh
[root@localhost mnt]# sh ip_check.sh
give me five !!
[root@localhost mnt]# sh ip_check.sh 15
no
cat ip_check.sh
#!/bin/bash
[ -z "$1" ] && { ##当输入为0的时候,输出 give me five ! !
echo give me five !! ## exit 1 退出
exit 1
}
[ "10" -gt "$1" -a "$1" -gt "0" ] && { ##当10 大于这个数时且这个数大于0时
echo "yes" ## 输出yes
} ||{
echo "no" ##否则输出no
}
软链接:
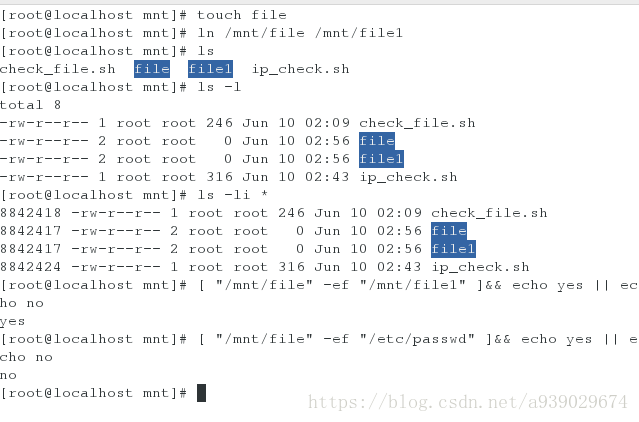
[root@localhost mnt]# touch file
[root@localhost mnt]# ln /mnt/file /mnt/file1 (用file软链接file1)
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
check_file.sh file file1 ip_check.sh
[root@localhost mnt]# ls -l
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 246 Jun 10 02:09 check_file.sh
-rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Jun 10 02:56 file
-rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Jun 10 02:56 file1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 316 Jun 10 02:43 ip_check.sh
[root@localhost mnt]# ls -li *
8842418 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 246 Jun 10 02:09 check_file.sh
8842417 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Jun 10 02:56 file
8842417 -rw-r--r-- 2 root root 0 Jun 10 02:56 file1
8842424 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 316 Jun 10 02:43 ip_check.sh
[root@localhost mnt]# [ "/mnt/file" -ef "/mnt/file1" ]&& echo yes || echo no ( /mnt/file 是否和 /mnt/file1 是链接关系,如果是输出yes ,如果不是,输出no)
yes
[root@localhost mnt]# [ "/mnt/file" -ef "/etc/passwd" ]&& echo yes || echo no (/mnt/file 是否和 /etc/passwd是链接关系,如果是输出yes ,如果不是,输出no)
no
[root@localhost mnt]# vim file.sh
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -e (file文件是否存在)
yes
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -f (file文件是不是不同文件)
yes
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -L (file文件是不是软链接)
no
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -S (file文件套接字)
no
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -b (file文件是不是快设备)
no
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -d (file文件是不是目录)
no
[root@localhost mnt]# sh file.sh -c (file文件是不是关键字)
no