- K近邻算法_分类鸢尾花数据集
_feivirus_
算法机器学习和数学分类机器学习K近邻
importnumpyasnpimportpandasaspdfromsklearn.datasetsimportload_irisfromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_splitfromsklearn.metricsimportaccuracy_score1.数据预处理iris=load_iris()df=pd.DataFrame(data=ir
- python画出分子化学空间分布(UMAP)
Sakaiay
python
利用umap画出分子化学空间分布图安装pipinstallumap-learn下面是用一个数据集举的例子importtorchimportumapimportpandasaspdimportnumpyasnpimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportseabornassnsfromsklearn.manifoldimportTSNEfromrdkit.Chemimport
- 分类算法可视化方法
dundunmm
数据挖掘分类数据挖掘人工智能可视化
可视化方法可以用于帮助理解分类算法的决策边界、性能和在不同数据集上的行为。下面列举几个常见的可视化方法。1.决策边界可视化这种方法用于可视化不同分类算法在二维特征空间中如何分隔不同类别。对于理解决策树、支持向量机(SVM)、逻辑回归和k近邻(k-NN)等模型的行为非常有用。importnumpyasnpimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfromsklearn.datasets
- conda安装包报PackagesNotFoundError错误
张遥
数据分析pythonanaconda
先查找包(base)bash-3.2$anacondasearch-tcondasklearn返回包的相关信息根据对应的包的包名使用如下命令(base)bash-3.2$anacondashowcorjos/sklearn-pandas会直接给出安装命令condainstall--channelhttps://conda.anaconda.org/corjossklearn-pandas
- 【ML】支持向量机SVM及Python实现(详细)
2401_84009698
程序员支持向量机python算法
fromsklearn.preprocessingimportStandardScalerfrommatplotlib.colorsimportListedColormapfromsklearn.svmimportSVC###2.1加载数据样本加载样本数据及其分类标签iris=datasets.load_iris()X=iris.data[:,[2,3]]#按花瓣划分#X=iris.data[:,
- python3.7安装keras教程_python 3.7 安装 sklearn keras(tf.keras)
weixin_39641103
#1sklearn一般方法网上有很多教程,不再赘述。注意顺序是numpy+mkl,然后scipy的环境,scipy,然后sklearn#2anocondaanaconda原始的环境已经自带了sklearn,这里说一下新建环境(比如创建了一个tensorflow的环境),activatetensorflow2.0,然后condainstallsklearn即可,会帮你把各种需要的库都安装。#kera
- # Seaborn热图修改画布大小|Seaborn热图修改横纵坐标大小|Seaborn删除注释|Seaborn删除调色板|Seaborn注释添加标注文字|Seaborn删除刻度线
Red Red
生信小技巧python开发语言ux笔记学习方法
Seaborn热图修改画布大小|Seaborn热图修改横纵坐标大小|Seaborn删除注释|Seaborn删除调色板|Seaborn注释添加标注文字|Seaborn删除刻度线查看图片importmatplotlibaspltplt.show()修改画布大小#导入需要用到的相关包importseabornassnsimportpandasaspdimportmatplotlibfromsklearn
- 推荐算法学习记录2.2——kaggle数据集的动漫电影数据集推荐算法实践——基于内容的推荐算法、协同过滤推荐
萱仔学习自我记录
推荐算法学习pythonmatplotlib开发语言
1、基于内容的推荐:这种方法根据项的相关信息(如描述信息、标签等)和用户对项的操作行为(如评论、收藏、点赞等)来构建推荐算法模型。它可以直接利用物品的内容特征进行推荐,适用于内容较为丰富的场景。#1.基于内容的推荐算法fromsklearn.feature_extraction.textimportTfidfVectorizerfromsklearn.metrics.pairwiseimport
- 30、基于SelectFromModel和LassoCV的特征选择
凌晨思索
30、基于SelectFromModel和LassoCV的特征选择importmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportnumpyasnpfromsklearn.datasetsimportload_diabetesfromsklearn.feature_selectionimportSelectFromModelfromsklearn.linear_modelimportLasso
- 01-30
姬汉斯
今天看的是关于文档识别和分类的处理案例。利用多项式贝叶斯公式计算TF-IDF值,以此计算出文档中的词频,文档频率等数据属性,TFIDFVectorizer类用于进行整理,NTLK包进行标注处理,计算文档中各个字符的权重,通过分类器进行分类处理。Sklearn在其中依然有巨大作用,还在熟悉其特性
- Python处理大数据,如何提高处理速度
RS&
#pythonpython大数据pandas
Python处理大数据,如何提高处理速度?一、利用大数据分析工具Dask:https://dask.org/Dask简介:Dask支持Pandas的DataFrame和NumpyArray的数据结构,并且既可在本地计算机上运行,也可以扩展到在集群上运行。Dask可支持pandas、Numpy、Sklearn、XGBoost、XArray、RAPIDS等等。原理及使用方法:https://blog.
- 自动安装第三方库python,python第三方库自动安装脚本
杏仁菌子
自动安装第三方库python
#python第三方库自动安装脚本,需要在cmd中运行此脚本#BatchInstall.pyimportoslibs={"numpy","matplotlib","pillow","sklearn","requests",\"jieba","beautifulsoup4","wheel","networkx","sympy",\"pyinstaller","django","flask","wer
- XGBoost调参demo(Python)
妄念驱动
机器学习算法python机器学习XGBoostpython
XGBoost我们用的是保险公司的一份数据#各种库importpandasaspdimportnumpyasnpimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfromsklearn.linear_modelimportLogisticRegressionfromsklearn.ensembleimportRandomForestClassifierfromsklearn.metricsi
- 机器学习实战----波士顿房价预测模型
永远偷渡不了的非洲人
机器学习机器学习sklearnpython
波士顿房价模型预测是一个回归问题,可以采用r2_score方法来作为评价指标。importnumpyasnpimportpandasaspdfromsklearn.metricsimportr2_score#从sklearn的数据库中导入波士顿房产数据fromsklearn.datasetsimportload_bostonfromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrai
- python机器学习算法--贝叶斯算法
在下小天n
机器学习python机器学习算法
1.贝叶斯定理在20世纪60年代初就引入到文字信息检索中,仍然是文字分类的一种热门(基准)方法。文字分类是以词频为特征判断文件所属类型或其他(如垃圾邮件、合法性、新闻分类等)的问题。原理牵涉到概率论的问题,不在详细说明。sklearn.naive_bayes.GaussianNB(priors=None,var_smoothing=1e-09)#Bayes函数·priors:矩阵,shape=[n
- Python中sklearn实现随机森林RF回归与变量重要性影响程度排序分析
疯狂学习GIS
本文详细介绍在Python中,实现随机森林(RandomForest,RF)回归与变量重要性分析、排序的代码编写与分析过程。其中,关于基于MATLAB实现同样过程的代码与实战,大家可以点击查看这篇博客1(https://blog.csdn.net/zhebushibiaoshifu/article/details/114806478)。 本文分为两部分,第一部分为代码的分段讲解,第二部分为完
- 机器学习小组第三周:简单的数据预处理和特征工程
-Helslie
机器学习机器学习
学习目标●无量纲化:最值归一化、均值方差归一化及sklearn中的Scaler●缺失值处理●处理分类型特征:编码与哑变量●处理连续型特征:二值化与分段学习资料首先,参考:《机器学习的敲门砖:归一化与KD树》及《特征工程系列:特征预处理(上)》中相关部分。其次,其他知识点可参考推荐博文:sklearn中的数据预处理和特征工程。20200311数据归一化在量纲不同的情况下,对于部分算法不能反映样本中每
- Python图像纹理分割
2401_84585316
程序员python开发语言
将下图左右两种不同类型的纹理区域分开,方法输出结果是一幅与该图像等大小的二值图像,左边为0,右边为1,或者相反,灰色边框线在设计的方法中不作考虑,自行去除。2️⃣实现源码importmatplotlib.imageasmpimgimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportnumpyasnpfromcv2importcv2fromsklearn.multiclassimpor
- 鸢尾花的简单分类器
Oneshot_fea8
importpandasaspdfromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_splitfromscipy.spatial.distanceimporteuclideanimportnumpyasnpDATA_FILE='./data_ai/Iris.csv'SPECIES=['Iris-setosa',#山鸢尾'Iris-versicolor',#变色鸢
- ARIMA-temp-humidity
TuringSnowy
笔记
importpandasaspdimportnumpyasnpimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfromstatsmodels.tsa.statespace.sarimaximportSARIMAXfromstatsmodels.graphics.tsaplotsimportplot_acf,plot_pacffromsklearn.metricsimportmean_squ
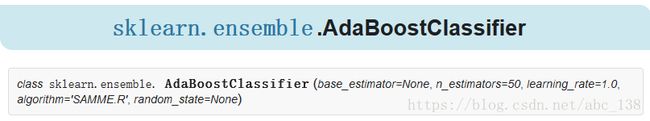
- 基于Python的机器学习系列(16):扩展 - AdaBoost
会飞的Anthony
信息系统机器学习人工智能python机器学习开发语言
简介在本篇中,我们将扩展之前的AdaBoost算法实现,深入探索其细节并进行一些修改。我们将重点修复代码中的潜在问题,并对AdaBoost的实现进行一些调整,以提高其准确性和可用性。1.修复Alpha计算中的问题在AdaBoost中,如果分类器的错误率e为0,则计算出的权重α将是未定义的。为了解决这个问题,我们可以在计算过程中向分母中添加一个非常小的值,以避免除零错误。2.调整学习率sklearn
- 机器学习基础(四)——决策树与随机森林
Bayesian小孙
机器学习基础决策树机器学习随机森林
决策树与随机森林文章目录决策树与随机森林一、知识概要(一)二、决策树使用的算法三、sklearn决策树API四、决策树的案例1.数据清洗2.特征工程3.调用决策树API五、集成学习方法-随机森林1.知识概要(二)2.集成学习API3.随机森林的案例importpandasaspdfromsklearn.feature_extractionimportDictVectorizerfromsklear
- 文本分析之关键词提取(TF-IDF算法)
SEVEN-YEARS
tf-idf
键词提取是自然语言处理中的一个重要步骤,可以帮助我们理解文本的主要内容。TF-IDF(TermFrequency-InverseDocumentFrequency)是一种常用的关键词提取方法,它基于词频和逆文档频率的概念来确定词语的重要性。准备工作首先,我们需要准备一些工具和库,包括Pandas、jieba(结巴分词)、sklearn等。Pandas:用于数据处理。jieba:用于中文分词。skl
- 使用SVM进行评论情感分析
github_czy
支持向量机机器学习人工智能
importpandasaspdfromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_splitfromsklearn.feature_extraction.textimportTfidfVectorizerfromsklearn.svmimportSVCfromsklearn.metricsimportaccuracy_score,precision_score
- sklearn 评估模型 常用函数
小Z资本
sklearn人工智能python
`sklearn.metrics`是scikit-learn库中的一个模块,它提供了许多用于评估预测模型性能的指标和工具。这些指标和工具可以帮助你了解模型在训练集和测试集上的表现,以及模型是否能够很好地泛化到未见过的数据。以下是一些`sklearn.metrics`中常用的函数和指标:1.**分类指标**:-`accuracy_score`:计算分类准确率。-`classification_rep
- [sklearn] 分类指标解惑
PigeonGuan
sklearn分类人工智能
首先查看metrics官方文档:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/api/sklearn.metrics.htmlweighted/macro/micro/samples的区别weighted和samplesweighted这个参数在roc_auc_score函数中,其实就是考虑了trueinstance的情况(也就是需要传一个sample_weights的参数?)。
- 计算机毕业设计Hadoop+Spark知识图谱体育赛事推荐系统 体育赛事热度预测系统 体育赛事数据分析 体育赛事可视化 体育赛事大数据 机器学习 大数据毕业设计 大数据毕设 机器学习 人工智能
计算机毕业设计大全
开发技术前端:vue.js、element-ui、echarts后端:springboot、mybatis大数据:spark、hadoop数据库:mysql关系型数据库、neo4j图数据库算法:协同过滤推荐算法、MLP深度学习模型、SVD神经网络混合推荐算法、lstm模型、KNN、CNN、Sklearn、K-Means第三方平台:百度AI、阿里云短信、支付宝沙箱支付爬虫:Pythonchrome-
- PyTorch深度学习模型训练流程的python实现:回归
moyao_miao
python人工智能深度学习pytorch回归
回归的流程与分类基本一致,只需要把评估指标改动一下就行。回归输出的是损失曲线、R^2曲线、训练集预测值与真实值折线图、测试集预测值散点图与真实值折线图。输出效果如下:注意:预测值与真实值图像处理为按真实值排序,图中呈现的升序与数据集趋势无关。代码如下:fromfunctoolsimportpartialimportnumpyasnpimportpandasaspdfromsklearn.prepr
- 在sklearn中如何实现参数网格搜索(GridSearch)?
2401_85761762
sklearn人工智能python
深入理解Scikit-learn中的参数网格搜索(GridSearch)引言在机器学习模型的开发过程中,超参数的调整对于模型性能有着至关重要的影响。Scikit-learn(简称sklearn),作为Python中一个广泛使用的机器学习库,提供了强大的工具来帮助我们进行超参数的优化。其中,GridSearchCV是实现参数网格搜索的利器。本文将详细介绍GridSearchCV的使用方法,并探讨其在
- sklearn preprocessing
perfectmanman
代码
sklearnpreprocessing代码代码来自Anaconda软件里sklearn模块init.py"""The:mod:`sklearn.preprocessing`moduleincludesscaling,centering,normalization,binarizationandimputationmethods."""from.dataimportBinarizerfrom.da
- Enum 枚举
120153216
enum枚举
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Kavlez/p/4268601.html Enumeration
于Java 1.5增加的enum type...enum type是由一组固定的常量组成的类型,比如四个季节、扑克花色。在出现enum type之前,通常用一组int常量表示枚举类型。比如这样:
public static final int APPLE_FUJI = 0
- Java8简明教程
bijian1013
javajdk1.8
Java 8已于2014年3月18日正式发布了,新版本带来了诸多改进,包括Lambda表达式、Streams、日期时间API等等。本文就带你领略Java 8的全新特性。
一.允许在接口中有默认方法实现
Java 8 允许我们使用default关键字,为接口声明添
- Oracle表维护 快速备份删除数据
cuisuqiang
oracle索引快速备份删除
我知道oracle表分区,不过那是数据库设计阶段的事情,目前是远水解不了近渴。
当前的数据库表,要求保留一个月数据,且表存在大量录入更新,不存在程序删除。
为了解决频繁查询和更新的瓶颈,我在oracle内根据需要创建了索引。但是随着数据量的增加,一个半月数据就要超千万,此时就算有索引,对高并发的查询和更新来说,让然有所拖累。
为了解决这个问题,我一般一个月会进行一次数据库维护,主要工作就是备
- java多态内存分析
麦田的设计者
java内存分析多态原理接口和抽象类
“ 时针如果可以回头,熟悉那张脸,重温嬉戏这乐园,墙壁的松脱涂鸦已经褪色才明白存在的价值归于记忆。街角小店尚存在吗?这大时代会不会牵挂,过去现在花开怎么会等待。
但有种意外不管痛不痛都有伤害,光阴远远离开,那笑声徘徊与脑海。但这一秒可笑不再可爱,当天心
- Xshell实现Windows上传文件到Linux主机
被触发
windows
经常有这样的需求,我们在Windows下载的软件包,如何上传到远程Linux主机上?还有如何从Linux主机下载软件包到Windows下;之前我的做法现在看来好笨好繁琐,不过也达到了目的,笨人有本方法嘛;
我是怎么操作的:
1、打开一台本地Linux虚拟机,使用mount 挂载Windows的共享文件夹到Linux上,然后拷贝数据到Linux虚拟机里面;(经常第一步都不顺利,无法挂载Windo
- 类的加载ClassLoader
肆无忌惮_
ClassLoader
类加载器ClassLoader是用来将java的类加载到虚拟机中,类加载器负责读取class字节文件到内存中,并将它转为Class的对象(类对象),通过此实例的 newInstance()方法就可以创建出该类的一个对象。
其中重要的方法为findClass(String name)。
如何写一个自己的类加载器呢?
首先写一个便于测试的类Student
- html5写的玫瑰花
知了ing
html5
<html>
<head>
<title>I Love You!</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="c"></canvas>
- google的ConcurrentLinkedHashmap源代码解析
矮蛋蛋
LRU
原文地址:
http://janeky.iteye.com/blog/1534352
简述
ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 是google团队提供的一个容器。它有什么用呢?其实它本身是对
ConcurrentHashMap的封装,可以用来实现一个基于LRU策略的缓存。详细介绍可以参见
http://code.google.com/p/concurrentlinke
- webservice获取访问服务的ip地址
alleni123
webservice
1. 首先注入javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext,
@Resource
private WebServiceContext context;
2. 在方法中获取交换请求的对象。
javax.xml.ws.handler.MessageContext mc=context.getMessageContext();
com.sun.net.http
- 菜鸟的java基础提升之道——————>是否值得拥有
百合不是茶
1,c++,java是面向对象编程的语言,将万事万物都看成是对象;java做一件事情关注的是人物,java是c++继承过来的,java没有直接更改地址的权限但是可以通过引用来传值操作地址,java也没有c++中繁琐的操作,java以其优越的可移植型,平台的安全型,高效性赢得了广泛的认同,全世界越来越多的人去学习java,我也是其中的一员
java组成:
- 通过修改Linux服务自动启动指定应用程序
bijian1013
linux
Linux中修改系统服务的命令是chkconfig (check config),命令的详细解释如下: chkconfig
功能说明:检查,设置系统的各种服务。
语 法:chkconfig [ -- add][ -- del][ -- list][系统服务] 或 chkconfig [ -- level <</SPAN>
- spring拦截器的一个简单实例
bijian1013
javaspring拦截器Interceptor
Purview接口
package aop;
public interface Purview {
void checkLogin();
}
Purview接口的实现类PurviesImpl.java
package aop;
public class PurviewImpl implements Purview {
public void check
- [Velocity二]自定义Velocity指令
bit1129
velocity
什么是Velocity指令
在Velocity中,#set,#if, #foreach, #elseif, #parse等,以#开头的称之为指令,Velocity内置的这些指令可以用来做赋值,条件判断,循环控制等脚本语言必备的逻辑控制等语句,Velocity的指令是可扩展的,即用户可以根据实际的需要自定义Velocity指令
自定义指令(Directive)的一般步骤
&nbs
- 【Hive十】Programming Hive学习笔记
bit1129
programming
第二章 Getting Started
1.Hive最大的局限性是什么?一是不支持行级别的增删改(insert, delete, update)二是查询性能非常差(基于Hadoop MapReduce),不适合延迟小的交互式任务三是不支持事务2. Hive MetaStore是干什么的?Hive persists table schemas and other system metadata.
- nginx有选择性进行限制
ronin47
nginx 动静 限制
http {
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=5r/s;...
server {...
location ~.*\.(gif|png|css|js|icon)$ {
- java-4.-在二元树中找出和为某一值的所有路径 .
bylijinnan
java
/*
* 0.use a TwoWayLinkedList to store the path.when the node can't be path,you should/can delete it.
* 1.curSum==exceptedSum:if the lastNode is TreeNode,printPath();delete the node otherwise
- Netty学习笔记
bylijinnan
javanetty
本文是阅读以下两篇文章时:
http://seeallhearall.blogspot.com/2012/05/netty-tutorial-part-1-introduction-to.html
http://seeallhearall.blogspot.com/2012/06/netty-tutorial-part-15-on-channel.html
我的一些笔记
===
- js获取项目路径
cngolon
js
//js获取项目根路径,如: http://localhost:8083/uimcardprj
function getRootPath(){
//获取当前网址,如: http://localhost:8083/uimcardprj/share/meun.jsp
var curWwwPath=window.document.locati
- oracle 的性能优化
cuishikuan
oracleSQL Server
在网上搜索了一些Oracle性能优化的文章,为了更加深层次的巩固[边写边记],也为了可以随时查看,所以发表这篇文章。
1.ORACLE采用自下而上的顺序解析WHERE子句,根据这个原理,表之间的连接必须写在其他WHERE条件之前,那些可以过滤掉最大数量记录的条件必须写在WHERE子句的末尾。(这点本人曾经做过实例验证过,的确如此哦!
- Shell变量和数组使用详解
daizj
linuxshell变量数组
Shell 变量
定义变量时,变量名不加美元符号($,PHP语言中变量需要),如:
your_name="w3cschool.cc"
注意,变量名和等号之间不能有空格,这可能和你熟悉的所有编程语言都不一样。同时,变量名的命名须遵循如下规则:
首个字符必须为字母(a-z,A-Z)。
中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线(_)。
不能使用标点符号。
不能使用ba
- 编程中的一些概念,KISS、DRY、MVC、OOP、REST
dcj3sjt126com
REST
KISS、DRY、MVC、OOP、REST (1)KISS是指Keep It Simple,Stupid(摘自wikipedia),指设计时要坚持简约原则,避免不必要的复杂化。 (2)DRY是指Don't Repeat Yourself(摘自wikipedia),特指在程序设计以及计算中避免重复代码,因为这样会降低灵活性、简洁性,并且可能导致代码之间的矛盾。 (3)OOP 即Object-Orie
- [Android]设置Activity为全屏显示的两种方法
dcj3sjt126com
Activity
1. 方法1:AndroidManifest.xml 里,Activity的 android:theme 指定为" @android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" 示例: <application
- solrcloud 部署方式比较
eksliang
solrCloud
solrcloud 的部署其实有两种方式可选,那么我们在实践开发中应该怎样选择呢? 第一种:当启动solr服务器时,内嵌的启动一个Zookeeper服务器,然后将这些内嵌的Zookeeper服务器组成一个集群。 第二种:将Zookeeper服务器独立的配置一个集群,然后将solr交给Zookeeper进行管理
谈谈第一种:每启动一个solr服务器就内嵌的启动一个Zoo
- Java synchronized关键字详解
gqdy365
synchronized
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/02/16/2913806.html
多线程的同步机制对资源进行加锁,使得在同一个时间,只有一个线程可以进行操作,同步用以解决多个线程同时访问时可能出现的问题。
同步机制可以使用synchronized关键字实现。
当synchronized关键字修饰一个方法的时候,该方法叫做同步方法。
当s
- js实现登录时记住用户名
hw1287789687
记住我记住密码cookie记住用户名记住账号
在页面中如何获取cookie值呢?
如果是JSP的话,可以通过servlet的对象request 获取cookie,可以
参考:http://hw1287789687.iteye.com/blog/2050040
如果要求登录页面是html呢?html页面中如何获取cookie呢?
直接上代码了
页面:loginInput.html
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html PUB
- 开发者必备的 Chrome 扩展
justjavac
chrome
Firebug:不用多介绍了吧https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/bmagokdooijbeehmkpknfglimnifench
ChromeSnifferPlus:Chrome 探测器,可以探测正在使用的开源软件或者 js 类库https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/chrome-sniffer-pl
- 算法机试题
李亚飞
java算法机试题
在面试机试时,遇到一个算法题,当时没能写出来,最后是同学帮忙解决的。
这道题大致意思是:输入一个数,比如4,。这时会输出:
&n
- 正确配置Linux系统ulimit值
字符串
ulimit
在Linux下面部 署应用的时候,有时候会遇上Socket/File: Can’t open so many files的问题;这个值也会影响服务器的最大并发数,其实Linux是有文件句柄限制的,而且Linux默认不是很高,一般都是1024,生产服务器用 其实很容易就达到这个数量。下面说的是,如何通过正解配置来改正这个系统默认值。因为这个问题是我配置Nginx+php5时遇到了,所以我将这篇归纳进
- hibernate调用返回游标的存储过程
Supanccy2013
javaDAOoracleHibernatejdbc
注:原创作品,转载请注明出处。
上篇博文介绍的是hibernate调用返回单值的存储过程,本片博文说的是hibernate调用返回游标的存储过程。
此此扁博文的存储过程的功能相当于是jdbc调用select 的作用。
1,创建oracle中的包,并在该包中创建的游标类型。
---创建oracle的程
- Spring 4.2新特性-更简单的Application Event
wiselyman
application
1.1 Application Event
Spring 4.1的写法请参考10点睛Spring4.1-Application Event
请对比10点睛Spring4.1-Application Event
使用一个@EventListener取代了实现ApplicationListener接口,使耦合度降低;
1.2 示例
包依赖
<p