spring mvc的DataBinder、Validator、BeanWrapper、ConversionService、Formatter
很多人对spring mvc的请求处理流程都不陌生,今天我们要展开讲解的是请求体数据body的绑定、验证、格式化、类型转换,它是怎样实现的呢?其实就是大家熟悉的HandlerAdapter干的事情。
为何要讲这个呢?其实和我最近的工作内容是分不开的,刚好在设计开发一个数据聚合组件(它主要是解决微服务化后vo 拆分之疼),当然后续会开源出来的。
目录
spring mvc知识回顾
BeanWrapper
ConversionService
Formatter
DataBinder
四者关系图
Validator
非Spring MVC的使用
Spring MVC的使用
HttpMessageConverter和ConversionService是什么关系?
spring mvc知识回顾
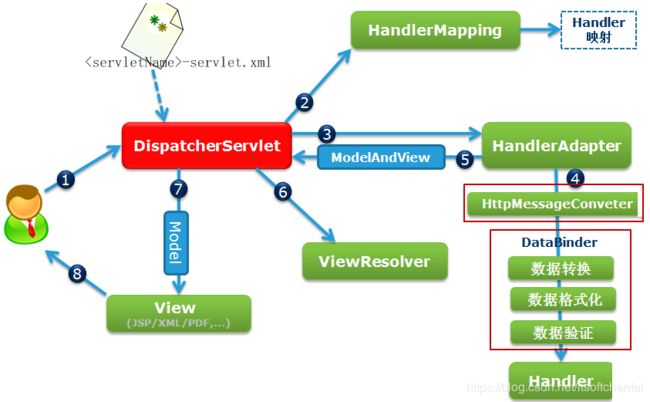
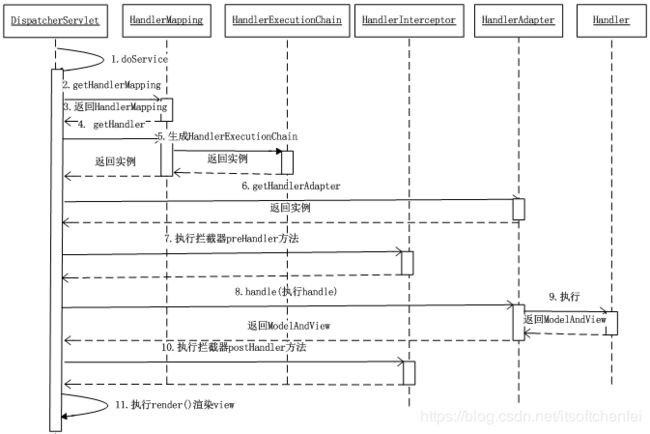
| 1 | 用户向服务器发送请求,请求被Spring的DispatcherServlet(简称DS)捕获 |
| 2~5 | DS 首先对URL进行解析,得到请求资源标识符(URI),然后根据该URI,调用HandlerMapping获得该Handler配置的所有相关的对象(包括Handler对象以及Handler对象对应的拦截器),最后以HandlerExecutionChain对象的形式返回 |
| 6~7 | DS 根据获得的Handler,选择一个合适的HandlerAdapter(如果成功获得HandlerAdapter后,此时将开始执行拦截器的preHandler(...)方法) |
| 8 | 提取Request中的模型数据,填充Handler入参,开始执行Handler(Controller)。 在填充Handler的入参过程中,根据你的配置,Spring将帮你做一些额外的工作:验证、格式化、类型转换 HttpMessageConveter:将请求消息(如Json、xml等数据)转换成一个对象,将对象转换为指定的响应信息。 |
| 9 | Handler执行完成后,向DS返回一个ModelAndView对象 |
| 10 | 此时DS将开始执行拦截器的postHandler(...)方法 |
| 11 | DS根据返回的ModelAndView,选择一个适合的ViewResolver(必须是已经注册到Spring容器中的ViewResolver)。并调用 该ViewResolver 结合Model和View,来渲染视图。将渲染结果返回给客户端。 |
在8中是有关spring mvc request vo的处理,其实Spring官方文档有专门有些章节阐述“Validation, Data Binding, and Type Conversion”,其实用法很简单,但它内部是如何实现的却鲜有人知晓。
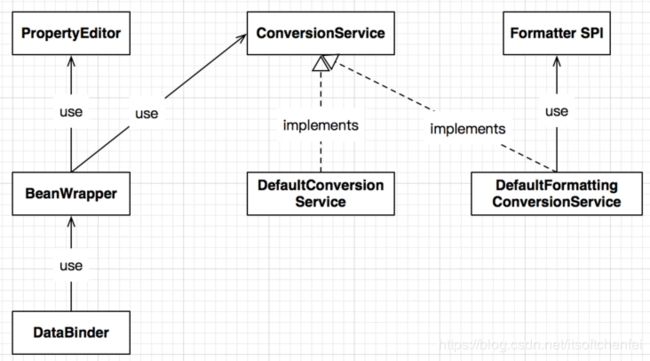
BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper是一个方便开发人员使用字符串来对Java Bean的属性执行get、set操作的工具类。它为那些UI类app提供了极大的便利,是以字符串和用户交互的。
Foo foo = new Foo();
BeanWrapperImpl fooWrapper = new BeanWrapperImpl(foo);
fooWrapper.setPropertyValue("intProperty", "1");
Object intProperty = fooWrapper.getPropertyValue("intProperty");另外,BeanWrapper内部使用了两种机制:
1. PropertyEditor
BeanWrapper和java bean的内省模式密切关联,之前的文章分享过,而PropertyEditor(只提供了String >> Object的转换)隶属于Java Bean规范。
2. ConversionService
Spring自3.0之后提供的替代PropertyEditor的机制
注:按照Spring官方文档的说法,当容器内没有注册ConversionService的时候,会退回使用PropertyEditor机制。
ConversionService
ConversionService及其相关一套类型转换机制是一套通用的类型转换SPI,相比PropertyEditor只提供String >> Object的转换,ConversionService能够提供任意Object >> Object的转换。
由此我们可以看出,Spring为何要使用ConversionService替代PropertyEditor有三个原因:
- ConversionService功能更强大,支持的类型转换范围更广
- ConverterFactory支持一整个class hierarchy的转换(也就是多态),PropertyEditor则不行
- Java Bean这个规范最初是和Java GUI(Swing)一起诞生的,PropertyEditor接口里有大量和GUI相关的方法,显然已经过时了。顺便提一句,Java Bean和POJO不是一个概念,Java Bean不仅有setter、getter,还有一系列和Java GUI配套的东西。
Formatter
Formatter SPI是另外一套和PropertyEditor类似的,String<->Object的转换机制,但是有两个优点:
- 接口更干净,没有关于GUI的部分,只有 Printer.print() 和 Parser.parse() 两个方法
- 基于注解,支持同一类型的属性根据不同的格式来做String<->Object的转换。比如日期类型,一个字段的格式是yyyy-MM-dd,另一个格式是yyyyMMdd,如果利用PropertyEditor是比较麻烦,但是在这里就可以利用
@DateTimeFormat来达到这个效果。
Spring提供了DefaultFormattingConversionService来支持Formatter SPI,也就是说如果要使用Formatter SPI,依然可以利用ConversionService接口。
注:Formatter SPI必须基于注解才可以使用,这点和ConversionService基于类型不同。
DataBinder
DataBinder主要提供了两个功能:
- 利用BeanWrapper,给对象的属性设值
- 在设值的同时做Validation
//引自org.springframework.validation;
public class DataBinder implements PropertyEditorRegistry, TypeConverter {
public void bind(PropertyValues pvs) {
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ? (MutablePropertyValues)pvs : new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
this.doBind(mpvs);
}
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
this.checkAllowedFields(mpvs);
this.checkRequiredFields(mpvs);
this.applyPropertyValues(mpvs);
}
protected void applyPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
try {
this.getPropertyAccessor().setPropertyValues(mpvs, this.isIgnoreUnknownFields(), this.isIgnoreInvalidFields());
} catch (PropertyBatchUpdateException var7) {
PropertyAccessException[] var3 = var7.getPropertyAccessExceptions();
int var4 = var3.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
PropertyAccessException pae = var3[var5];
this.getBindingErrorProcessor().processPropertyAccessException(pae, this.getInternalBindingResult());
}
}
}
}前四者关系图
ConversionService有两种实现,也就是说,如果要支持Formatter SPI,只需要让BeanWrapper切换使用不同的ConversionService即可。
- DefaultConversionService,不支持Formatter SPI
- DefaultFormattingConversionService,支持Formatter SPI
Validator
Validator较简单,如果类路径上存在 Bean Validation(例如,Hibernate Validator),则将LocalValidatorFactoryBean 注册为全局Validator,以便与@Valid一起使用在controller 方法参数上。
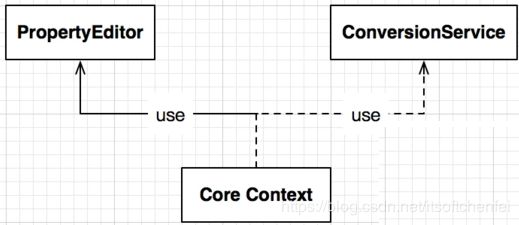
非Spring MVC的使用
Spring Core Context(要解析spring xml的)其实也使用ConversionService,但是是非强制的。让Spring Core Context使用conversionService的方式很简单,配置一个名字叫做conversionService的Bean即可。需要注意的是,因为这个Bean是在非常早的时候就被使用的(AbstractApplicationContext#L834),因此它最好不要依赖过多的其他的Bean,避免造成启动失败。
Spring在读取xml配置文件的时候,因为xml文件实际上是一个文本文件,所有值的设置都是String,这个时候如果给bean的复杂类型属性设置值,它会用到PropertyEditor或ConversionService。
例子中的color属性是Color类型,这时就会利用到PropertyEditor和ConversionService。
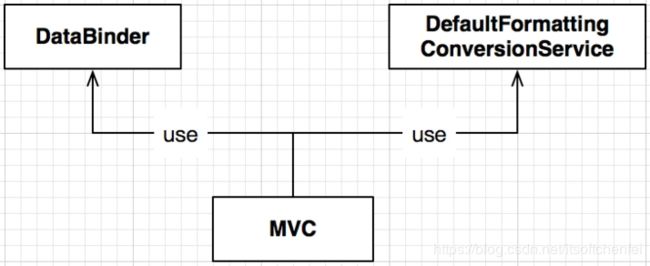
Spring MVC的使用
Spring MVC对于conversionService的使用比较特殊,它自己会注册一个名字叫做mvcConversionService类型为DefaultFormattingConversionService的Bean。因此会存在以下陷阱:
- 如果Core Context中也定义了一个ConversionService,那么在MVC环境下,会有两个ConversionService的Bean。
- 针对Core Context的
ConversionService做的Customize如FormatterRegistrar、ConverterRegistry、FormatterRegistry、ConversionServiceFactoryBean、FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean是不会应用到MVC的那个ConversionService上。
上图在后面源码中细讲,对于mvcConversionService的配置途径见“DataBinder”或“MVC Config API”。
HttpMessageConverter和ConversionService是什么关系?
个人理解,可以他们是不同的两种东西,二者各司其职,前者转换请求body信息和响应body信息,后者用于请求参数的转换。都可以接受文本信息,最终解析成对象。根本的区别:
HttpMessageConvert
官方文档中的说明:We can use the @RequestBody annotation on the argument of a Controller method to indicate that the body of the HTTP Request is deserialized to that particular Java entity. To determine the appropriate converter, Spring will use the “Content-Type” header from the client request.
对,@RequestBody决定了要使用HttpMessageConverter,而Content-Type则是选择具体某一个配置器。HttpMessageConverter
,默认有很多配置器:StringHttpMessageConverter,ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter,SourceHttpMessageConverter,FormHttpMessageConverter 。 ConversionService
它使用的是 WebDataBinder (extends DataBinder),处理url或@RequestParam等非@RequestBody参数,它数据绑定是这样的流程:
- 将ServletRequest对象及处理方法入参对象实例传给DataBinder
- DataBinder 调用转配在Spring Web上下文中的ConversionService进行数据类型转换、数据格式化等工作,将ServletRequest中的消息填充到入参对象中
- 调用 Validator 对已经绑定的请求信息数据的入参对象进行数据合法性校验,生成数据绑定结果 BindingResult。BindingResult 包含完成绑定的入参对象和相应的校验错误对象。而后将 BindingResult 中的入参对象及校验错误对象赋给处理方法的入参。
// 引自org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.support.HandlerMethodInvoker
// 进行数据类型转换、填充并验证
private Object[] resolveHandlerArguments(Method handlerMethod, Object handler,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, ExtendedModelMap implicitModel) throws Exception {
Class[] paramTypes = handlerMethod.getParameterTypes();
Object[] args = new Object[paramTypes.length];
// controller方法的每个参数
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new SynthesizingMethodParameter(handlerMethod, i);
methodParam.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
GenericTypeResolver.resolveParameterType(methodParam, handler.getClass());
String paramName = null;
String headerName = null;
boolean requestBodyFound = false;
String cookieName = null;
String pathVarName = null;
String attrName = null;
boolean required = false;
String defaultValue = null;
boolean validate = false;
Object[] validationHints = null;
int annotationsFound = 0;
Annotation[] paramAnns = methodParam.getParameterAnnotations();
for (Annotation paramAnn : paramAnns) {
if (RequestParam.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
RequestParam requestParam = (RequestParam) paramAnn;
paramName = requestParam.name();
required = requestParam.required();
defaultValue = parseDefaultValueAttribute(requestParam.defaultValue());
annotationsFound++;
}
else if (RequestHeader.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
RequestHeader requestHeader = (RequestHeader) paramAnn;
headerName = requestHeader.name();
required = requestHeader.required();
defaultValue = parseDefaultValueAttribute(requestHeader.defaultValue());
annotationsFound++;
}
else if (RequestBody.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
requestBodyFound = true;
annotationsFound++;
}
else if (CookieValue.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
CookieValue cookieValue = (CookieValue) paramAnn;
cookieName = cookieValue.name();
required = cookieValue.required();
defaultValue = parseDefaultValueAttribute(cookieValue.defaultValue());
annotationsFound++;
}
else if (PathVariable.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
PathVariable pathVar = (PathVariable) paramAnn;
pathVarName = pathVar.value();
annotationsFound++;
}
else if (ModelAttribute.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
ModelAttribute attr = (ModelAttribute) paramAnn;
attrName = attr.value();
annotationsFound++;
}
else if (Value.class.isInstance(paramAnn)) {
defaultValue = ((Value) paramAnn).value();
}
else {
Validated validatedAnn = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(paramAnn, Validated.class);
if (validatedAnn != null || paramAnn.annotationType().getSimpleName().startsWith("Valid")) {
validate = true;
Object hints = (validatedAnn != null ? validatedAnn.value() : AnnotationUtils.getValue(paramAnn));
validationHints = (hints instanceof Object[] ? (Object[]) hints : new Object[]{hints});
}
}
}
if (annotationsFound > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Handler parameter annotations are exclusive choices - " +
"do not specify more than one such annotation on the same parameter: " + handlerMethod);
}
if (annotationsFound == 0) {
Object argValue = resolveCommonArgument(methodParam, webRequest);
if (argValue != WebArgumentResolver.UNRESOLVED) {
args[i] = argValue;
}
else if (defaultValue != null) {
args[i] = resolveDefaultValue(defaultValue);
}
else {
Class paramType = methodParam.getParameterType();
if (Model.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
if (!paramType.isAssignableFrom(implicitModel.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Argument [" + paramType.getSimpleName() + "] is of type " +
"Model or Map but is not assignable from the actual model. You may need to switch " +
"newer MVC infrastructure classes to use this argument.");
}
args[i] = implicitModel;
}
else if (SessionStatus.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
args[i] = this.sessionStatus;
}
else if (HttpEntity.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
// 调用HttpMessageConvert服务
args[i] = resolveHttpEntityRequest(methodParam, webRequest);
}
else if (Errors.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Errors/BindingResult argument declared " +
"without preceding model attribute. Check your handler method signature!");
}
else if (BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(paramType)) {
paramName = "";
}
else {
attrName = "";
}
}
}
if (paramName != null) {
// 调用ConversionService服务
args[i] = resolveRequestParam(paramName, required, defaultValue, methodParam, webRequest, handler);
}
else if (headerName != null) {
// 调用ConversionService服务
args[i] = resolveRequestHeader(headerName, required, defaultValue, methodParam, webRequest, handler);
}
else if (requestBodyFound) {
// 调用HttpMessageConvert服务
args[i] = resolveRequestBody(methodParam, webRequest, handler);
}
else if (cookieName != null) {
// 调用HttpMessageConvert服务
args[i] = resolveCookieValue(cookieName, required, defaultValue, methodParam, webRequest, handler);
}
else if (pathVarName != null) {
// 调用HttpMessageConvert服务
args[i] = resolvePathVariable(pathVarName, methodParam, webRequest, handler);
}
else if (attrName != null) {
// 调用ConversionService服务
WebDataBinder binder =
resolveModelAttribute(attrName, methodParam, implicitModel, webRequest, handler);
boolean assignBindingResult = (args.length > i + 1 && Errors.class.isAssignableFrom(paramTypes[i + 1]));
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
doBind(binder, webRequest, validate, validationHints, !assignBindingResult);
}
args[i] = binder.getTarget();
if (assignBindingResult) {
args[i + 1] = binder.getBindingResult();
i++;
}
implicitModel.putAll(binder.getBindingResult().getModel());
}
}
return args;
}最后,HttpMessageConverter和ConversionService是没有关系的,这点很多人讲的都是错的!