写在开始
本篇主要结合react-native 使用redux的过程,说明使用redux的方法和原理,揭秘Redux单向数据流更新的机制原理,适合有一定Redux基础的同学。
Redux 工作图
Redux原理图
上图是redux的工作原理图,具体每一步骤的实现请见下面的详细分析。
Redux需要懂的七大元素
- combineReducers()
- createStore()
- connect()
- mapStateToProps()
- mapDispatchToProps()
- action
一. combineReducers
将应用整体state划分为不同的reducer,最终合并为rootReducer ===>combineReducers()
1.1reducer
reducer 就是一个方法,接收旧的 state和当前操作 action,返回新的 state。需要注意的是reducer是纯函数,永远不要在reducer里做这些操作:
- 修改传入参数;
- 执行有副作用的操作,如 API 请求和路由跳转;
- 调用非纯函数,如
Date.now()或Math.random()。
1.2combineReducers()用法
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
localCounter:localCounter,
serverCounter:serverCounter
})
1.3combineReducers()作用
- 将子reducer用key-value的形式组成rootReducer,value是该子reducer的实现方法。
- 返回值:一个总reducer,内部包含所有子reducer
1.4combineReducers()关键源码
function combineReducers(reducers) {
var reducerKeys = Object.keys(reducers);
var finalReducers = {};
for (var i = 0; i < reducerKeys.length; i++) {
var key = reducerKeys[i];
...
if (typeof reducers[key] === 'function') {
//reduer数组
finalReducers[key] = reducers[key];
}
}
//reducer的key
var finalReducerKeys = Object.keys(finalReducers);
...
//返回一个function,该方法接收state和action作为参数,其实返回值就是rootReducer
//遍历reducers数组,将action传入每个reducer方法中得到的新状态,与旧状态对比是否变化,若变化则返回新状态,若没有变化则返回旧状态
return function combination() {
...
var hasChanged = false;
var nextState = {};
//遍历reducer数组,执行每个reducer的方法
for (var i = 0; i < finalReducerKeys.length; i++) {
var key = finalReducerKeys[i];
var reducer = finalReducers[key];
var previousStateForKey = state[key];
//传入旧state,action,得到新state
var nextStateForKey = reducer(previousStateForKey, action);
...
nextState[key] = nextStateForKey;
//判断状态是否发生了改变
hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey;
}
//返回值处理后的state
return hasChanged ? nextState : state;
};
}
二. createStore
然后根据 rootReducer创建store===>createStore()
2.1 store
是redux的核心,存储APP的所有状态,只能有一个。改变状态的唯一方法是调用store.dispatch方法
2.2 createStore()作用
- 两种创建方式:
createStore(rootReducer,initialState);createStore(rootReducer,initialState,applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware));
A thunk is a function that wraps an expression to delay its evaluation.简单来说一个 thunk 就是一个封装表达式的函数,封装的目的是延迟执行表达式
可以使用第三方库来增强store,通常会使用redux-thunk库来支持异步方法的dispatch。thunk最终起的作用,对dispatch调用的action进行检查,如果action在第一次调用之后返回的是function,则将(dispatch, getState)作为参数注入到action返回的方法中,执行异步逻辑(相当于开始一个新的action),若有返回对象则进行分发。
- 返回值
{Store} A Redux store that lets you read the state, dispatch actions
and subscribe to changes.
- (1)
dispatch(action): 用于action的分发,改变store里面的state - (2)
subscribe(listener): 注册listener,store里面state发生改变后,执行该listener。返回unsubscrib()方法,用于注销当前listener。Redux采用了观察者模式,store内部维护listener数组,用于存储所有通过store.subscribe注册的listener - (3)
getState(): 读取store里面的state - (4)
replaceReducer(): 替换reducer,改变state修改的逻辑
2.3 源码分析
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
...
if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
if (typeof enhancer !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Expected the enhancer to be a function.');
}
//返回增强store
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState);
}
var currentState = preloadedState;
var currentListeners = [];
var nextListeners = currentListeners;
var isDispatching = false;
/**
* 返回当前状态
*/
function getState() {
return currentState;
}
/**
* 注册`listener`,维护一个listener的数组
* `store`里面`state`发生改变后,执行该`listener`
* 观察者模式实现的关键
*/
function subscribe(listener) {
...
nextListeners.push(listener);
//返回一个注销listener的方法
return function unsubscribe() {
...
var index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener);
nextListeners.splice(index, 1);
};
}
/**
* Dispatches an action. It is the only way to trigger a state change.
*/
var currentReducer = reducer;
function dispatch(action) {
//类型校验...
try {
isDispatching = true;
//执行rootReducer,得到新的state
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action);
} finally {
isDispatching = false;
}
var listeners = currentListeners = nextListeners;
//循环遍历,执行listener,通知数据改变了,listeners具体是什么?看容器组件
for (var i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
listeners[i]();
}
return action;
}
/**
* Replaces the reducer currently used by the store to calculate the state.
*/
function replaceReducer(nextReducer) {
currentReducer = nextReducer;
dispatch({ type: ActionTypes.INIT });
}
//返回值
return _ref2 = {
dispatch: dispatch,
subscribe: subscribe,
getState: getState,
replaceReducer: replaceReducer
}, _ref2[_symbolObservable2['default']] = observable, _ref2;
}
三. Provider
将store传递给应用中的View===>
3.1
3.2 作用:将store传递给其子组件
将store设置到子组件的context中,这样应用的所有子组件就默认都拿到了store
3.3 源码
var Provider = function (_Component) {
_inherits(Provider, _Component);
//用于指定子组件可直接访问的上下文数据,所以子组件可以直接访问store了
Provider.prototype.getChildContext = function getChildContext() {
return { store: this.store, storeSubscription: null };
};
function Provider(props, context) {
_classCallCheck(this, Provider);
var _this = _possibleConstructorReturn(this, _Component.call(this, props, context));
_this.store = props.store;
return _this;
}
Provider.prototype.render = function render() {
return _react.Children.only(this.props.children);
};
return Provider;
}(_react.Component);
exports.default = Provider;
四. connect
如何将react中的UI组件与redux的状态、事件关联起来====>connect()方法
4.0 UI组件和容器组件
React-Redux 将所有组件分成两大类:UI 组件(presentational component)和容器组件(container component)。
UI组件:
①只负责 UI 的呈现,不带有任何业务逻辑
②没有状态(即不使用this.state这个变量)
③所有数据都由参数(this.props)提供
④不使用任何 Redux 的 API
容器组件:
①负责管理数据和业务逻辑,不负责 UI 的呈现
②带有内部状态
③使用 Redux 的 API
4.1connect()生成容器组件
- 通过
传递store是给容器redux的容器组件
用于从 UI 组件生成容器组件。connect的意思,就是将这两种组件连起来。
connect方法接受两个参数:mapStateToProps和mapDispatchToProps。它们定义了 UI 组件的业务逻辑
let ConnectCounter = connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(Counter)
4.2 作用
connect是一个高阶函数,首先传入mapStateToProps、mapDispatchToProps,然后返回一个生产Component的函数wrapWithConnect(),然后再将真正的Component作为参数传入wrapWithConnect(MyComponent),这样就生产出一个经过包裹的Connect组件(也就是容器组件)。
容器组件具有如下特点:
- (1)通过this.context获取祖先Component的store,也就是通过
传递过来的store。 - (2)props包括stateProps、dispatchProps、parentProps,合并在一起得到nextState,作为props传给真正的Component,这样在真正组件中就能通过this.props获取到各种数据和方法。
- (3)componentDidMount调用store.subscribe(listener)注册监听方法,对store的变化进行订阅,当store变化的时候,更新渲染view。
- (4)componentWillUnmount时注销订阅
4.3源码分析
注意订阅的实现
var Connect = function (_Component) {
_inherits(Connect, _Component);
/*
* 构造函数中,构造一个订阅对象,属性有this.store,方法this.onStateChange.bind(this)
*/
function Connect(props, context) {
...
//获取store。
//从父组件或context中获取store。这里使用的是从context中获取
//storeKey = _ref$storeKey === undefined ? 'store' : _ref$storeKey,
_this.store = props[storeKey] || context[storeKey];
...
//初始化订阅逻辑
_this.initSubscription();
return _this;
}
//初始化订阅方法
Connect.prototype.initSubscription = function initSubscription() {
if (!shouldHandleStateChanges) return;
var parentSub = (this.propsMode ? this.props : this.context)[subscriptionKey];
//wym: 调用的是Subscription.js中方法,向store内部注册一个listener---this.onStateChange.bind(this)
this.subscription = new _Subscription2.default(this.store, parentSub, this.onStateChange.bind(this));
this.notifyNestedSubs = this.subscription.notifyNestedSubs.bind(this.subscription);
};
//当数据状态发生改变时
Connect.prototype.onStateChange = function onStateChange() {
this.selector.run(this.props);
if (!this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate) {
this.notifyNestedSubs();
} else {
this.componentDidUpdate = this.notifyNestedSubsOnComponentDidUpdate;
//设置state,view会自动重新渲染
this.setState(dummyState);
}
};
Connect.prototype.getChildContext = function getChildContext() {
...
};
/*
* 组件状态完成时,向store注册监听方法
*/
Connect.prototype.componentDidMount = function componentDidMount() {
if (!shouldHandleStateChanges) return;
//实际调用this.store.subscribe(this.onStateChange);
//向store注册监听方法
this.subscription.trySubscribe();
this.selector.run(this.props);
if (this.selector.shouldComponentUpdate) this.forceUpdate();
};
Connect.prototype.componentWillUnmount = function componentWillUnmount() {
//注销订阅
if (this.subscription) this.subscription.tryUnsubscribe();
this.subscription = null;
...
};
Connect.prototype.render = function render() {
var selector = this.selector;
selector.shouldComponentUpdate = false;
if (selector.error) {
throw selector.error;
} else {
return (0, _react.createElement)(WrappedComponent, this.addExtraProps(selector.props));
}
};
return Connect;
}(_react.Component);
五.mapStateToProps()
建立一个从(外部的)state对象到(UI 组件的)props对象的映射关系。mapStateToProps会订阅 Store,每当state更新的时候,就会自动执行,重新计算 UI 组件的参数,从而触发 UI 组件的重新渲染
六. mapDispatchToProps
- 用来建立 UI 组件的方法到store.dispatch方法的映射,它定义了哪些用户的操作应该当作 Action,传给 Store。
- 它可以是一个函数,也可以是一个对象。(只是不同的写法,作用一样)
七. Action
Action 是把数据从应用传到 store 的有效载荷。它是 store 数据的唯一来源。一般来说你会通过 store.dispatch() 将 action 传到 store。
分为:
- 同步 action ,返回的是一个对象,要求是纯净的函数。
纯净:没有特殊情况、没有副作用,没有 API 请求、没有变量修改,单纯执行计算。
- 异步action,返回的是一个方法,这个函数会被Redux Thunk middleware执行。这个函数并不需要保持纯净;它还可以带有副作用,包括执行异步 API 请求。
Redux中的观察者模式
redux之所以能够当state变化后,更新绑定的视图,是因为内部实现的观察者模式
观察者模式的实现
1. store提供了注册监听的方法===>subscribe(listener)
- store内部维护listener数组,用于存储所有通过store.subscrib注册的listener,store里面state发生改变(即为调用
store.dispatch())后,依次执行数组中的listener。 - store.subscrib返回unsubscrib方法,用于注销当前listener。
调用store.dispatch()的时候做了两件事:
(1)更新当前state: currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action);
(2)依次执行数组中的listener。
2. Connect组件中,向store中注册监听方法
- ①构造方法中:初始化订阅逻辑,将listener:this.onStateChange.bind(this)传递给Subscription.js。
- ②componentDidMount方法中,调用store.subscribe(listener)注册监听方法:
onStateChange()。
onStateChange方法中,当判断需要更新数据时,调用的是this.setState(state);
===》根据react机制,则会重新渲染view
- ③在componentWillUnmount方法中,注销订阅
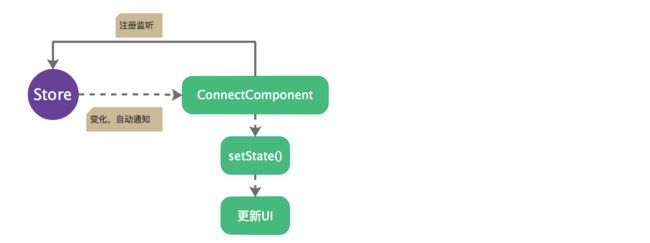
Redux原理图
根据以上的源码分析,redux的工作流可用下图进行概括。
redux创建过程概括
- 将一个APP的状态分解成不同的reducer,最后创建store(有整个数据state,有分发action的方法,有注册listener的方法)
- 将store通过
组件传递给容器组件 - 容器组件通过UI组件,mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps通过connect()转化而来
- 将UI交互事件,外部输入事件写成action,用来触发reducer
redux更新数据过程概括
- 在UI组件上有交互操作,或外部输入(网络请求)时,====>写成Action
- store.dispatch(action),结果:
(1)合成新的state,新的state通过mapStateToProps()传递给UI组件,
(2)执行通过store.subscribe()注册的listener - listener具体逻辑:调用setState()设置信息数值,触发View的自动render