游戏编程中的人工智能技术-遗传算法入门(三)
先请教大家一个问题,为什么我的遗传算法入门(一)一直处于“待审核”状态?
好,言归正传,继续研究代码。先看看CBobsMap类的定义。
class CBobsMap
{
private:
//storage for the map
static const int map[MAP_HEIGHT][MAP_WIDTH]; //设计一个数组,用来构造地图
static const int m_iMapWidth;//地图的宽度
static const int m_iMapHeight;//地图的高度
//index into the array which is the start point
static const int m_iStartX; //起始点的x坐标
static const int m_iStartY; //起始点的y坐标
//and the finish point
static const int m_iEndX; //终止点的x坐标
static const int m_iEndY; //终止点的y坐标
public:
//we can use this array as Bobs memory if rqd
int memory[MAP_HEIGHT][MAP_WIDTH]; //记录下Bob走过的路线,重新定义一个地图数组
CBobsMap()
{
ResetMemory(); //路线记忆清零
}
//takes a string of directions and see's how far Bob
//can get. Returns a fitness score proportional to the
//distance reached from the exit.
double TestRoute(const vector &vecPath, CBobsMap &memory);//走迷宫了!该如何操作?
//given a surface to draw on this function uses the windows GDI
//to display the map.
void Render(const int cxClient, const int cyClient, HDC surface);
//draws whatever path may be stored in the memory
void MemoryRender(const int cxClient, const int cyClient, HDC surface);
void ResetMemory();
}; 在AI算法的使用中,最关键的是什么?是算法的理论吗?我感觉最关键的应该是如何将算法应用到实际中去。在本游戏中,如何构造一个算法的具体实现,最为关键。
接下来研究TestRoute()函数。
double CBobsMap::TestRoute(const vector &vecPath, CBobsMap &Bobs)
{
int posX = m_iStartX;
int posY = m_iStartY;
for (int dir=0; dir= m_iMapHeight) || (map[posY+1][posX] == 1) )
{
break;
}
else
{
posY += 1;
}
break;
case 2: //East
//check within bounds and that we can move
if ( ((posX+1) >= m_iMapWidth ) || (map[posY][posX+1] == 1) )
{
break;
}
else
{
posX += 1;
}
break;
case 3: //West
//check within bounds and that we can move
if ( ((posX-1) < 0 ) || (map[posY][posX-1] == 1) )
{
break;
}
else
{
posX -= 1;
}
break;
}//end switch
//mark the route in the memory array
Bobs.memory[posY][posX] = 1;
}//next direction
//now we know the finish point of Bobs journey, let's assign
//a fitness score which is proportional to his distance from
//the exit
int DiffX = abs(posX - m_iEndX);
int DiffY = abs(posY - m_iEndY);
//we add the one to ensure we never divide by zero. Therefore
//a solution has been found when this return value = 1
return 1/(double)(DiffX+DiffY+1);
}
这个函数的作用是根据实际游戏情境设计遗传算法的染色体,并计算他的适应度函数。
一句一句来。
double CBobsMap::TestRoute(const vector &vecPath, CBobsMap &Bobs) int posX = m_iStartX;
int posY = m_iStartY;Bob开始走路了!这个是Bob的初始位置。
for (int dir=0; dir那么在本程序中,染色体的基因个数为多少呢?
在Define.h中有定义:
#define WINDOW_WIDTH 450
#define WINDOW_HEIGHT 300
#define MAP_WIDTH 15
#define MAP_HEIGHT 10
#define CROSSOVER_RATE 0.7
#define MUTATION_RATE 0.001
#define POP_SIZE 140
#define CHROMO_LENGTH 30
#define GENE_LENGTH 2
#endif
可以通过调试看到实际染色体长度。在CgaBob类中,函数UpdateFitnessScores()中如下所示
void CgaBob::UpdateFitnessScores()
{
m_iFittestGenome = 0;
m_dBestFitnessScore = 0;
m_dTotalFitnessScore = 0;
CBobsMap TempMemory;
//update the fitness scores and keep a check on fittest so far
for (int i=0; i vecDirections = Decode(m_vecGenomes[i].vecBits);这个就是染色体
//get it's fitness score
m_vecGenomes[i].dFitness = m_BobsMap.TestRoute(vecDirections, TempMemory);//TestRoute的第一个向量参数,即表示染色体
//update total
m_dTotalFitnessScore += m_vecGenomes[i].dFitness;
//if this is the fittest genome found so far, store results
if (m_vecGenomes[i].dFitness > m_dBestFitnessScore)
{
m_dBestFitnessScore = m_vecGenomes[i].dFitness;
m_iFittestGenome = i;
m_BobsBrain = TempMemory;
//Has Bob found the exit?
if (m_vecGenomes[i].dFitness == 1)
{
//is so, stop the run
float a = m_vecGenomes[i].dFitness;
vector b = m_vecGenomes[i].vecBits;
m_bBusy = false;
}
}
TempMemory.ResetMemory();
}//next genome
} 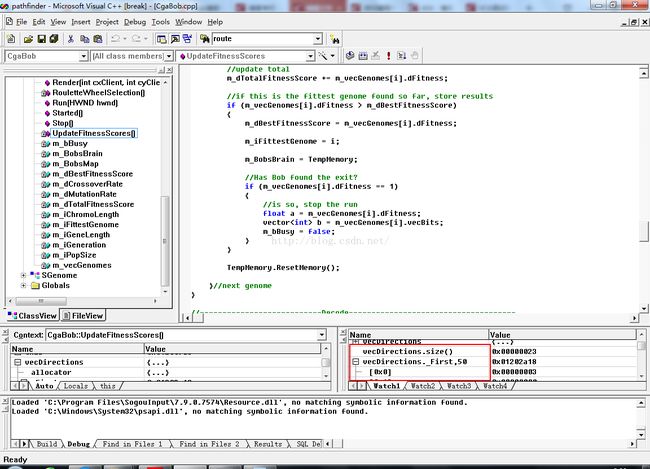

可以看到 vecDirections的长度到0x22结束,对应十进制就是34。
以上是解释染色体的长度为多少。
接下来继续分析程序。
for (int dir=0; dir到了其中的一个基因了。一共有四个case, case 0, case 1, case 2, case 3。即00,01,10,11。为基因的种类,分别表示向北走一步,向南走一步,向东走一步,向西走一步。 vecPath[dir]储存了这个基因。即vecPath[dir]=00,01,10,11.
这个是编程思想的关键,以后再实际操作中,首先要考虑如何来根据游戏来构造染色体?本例中,因为Bob要走迷宫,那么实际操作是向北走一步,向南走一步,向东走一步,向西走一步,则可以用00.01.10.11来表示每个操作。
if ( ((posY-1) < 0 ) || (map[posY-1][posX] == 1) )如果不是上述两种情况,则Bob可往北走一步,则Bob的位置变化一格。即posY -= 1;再break
case 1: //South
//check within bounds and that we can move
if ( ((posY+1) >= m_iMapHeight) || (map[posY+1][posX] == 1) )
{
break;
}
else
{
posY += 1;
}
break;
case 2: //East
//check within bounds and that we can move
if ( ((posX+1) >= m_iMapWidth ) || (map[posY][posX+1] == 1) )
{
break;
}
else
{
posX += 1;
}
break;
case 3: //West
//check within bounds and that we can move
if ( ((posX-1) < 0 ) || (map[posY][posX-1] == 1) )
{
break;
}
else
{
posX -= 1;
}
break;
}//end switch
同上。
Bobs.memory[posY][posX] = 1;
int DiffX = abs(posX - m_iEndX);
int DiffY = abs(posY - m_iEndY);
//we add the one to ensure we never divide by zero. Therefore
//a solution has been found when this return value = 1
return 1/(double)(DiffX+DiffY+1);适应度函数的计算,适应值为Bob离迷宫出口的距离值,这个程序中,没有用实际距离,而只是将x坐标和y坐标简单的相加。为了取适应度的最大值,当然要 return 1/(double)(DiffX+DiffY+1);啦。
可以通过调试看到实际染色体长度。在CgaBob类中,函数UpdateFitnessScores()中如下所示