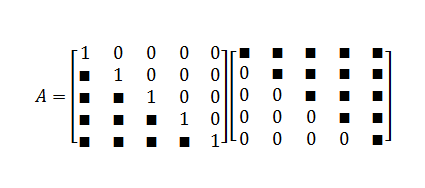Java Math3 Linear Algebra (线性代数)
文章目录
- 1、基础知识
- 2、Real matrices:实矩阵
- 3、Real vectors:实向量
- 4、Solving linear systems:线性系统求解
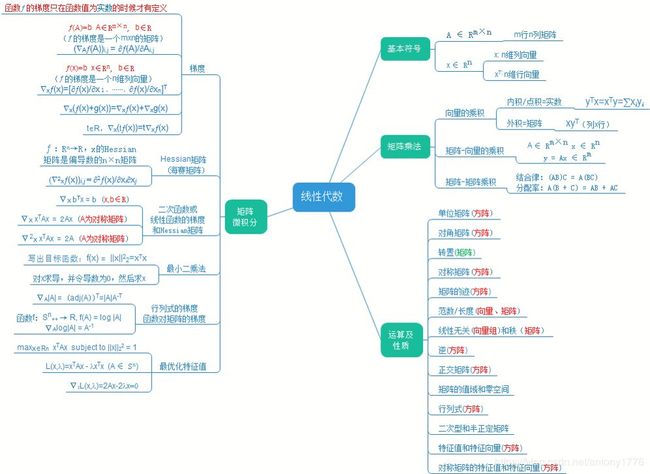
- 5、线性代数知识点脑图
1、基础知识
线性代数是数学的一个分支,它的研究对象是向量,向量空间(或称线性空间),线性变换和有限维的线性方程组。
- 线性(linear)指量与量之间按比例、成直线的关系,在数学上可以理解为一阶导数为常数的函数。
- 非线性(non-linear)则指不按比例、不成直线的关系,一阶导数不为常数。
重要定理
- 每一个线性空间都有一个基。
- 对一个 n 行 n 列的非零矩阵 A,如果存在一个矩阵 B 使 AB = BA =E(E是单位矩阵),则 A 为非奇异矩阵(或称可逆矩阵),B为A的逆阵。
- 矩阵非奇异(可逆)当且仅当它的行列式不为零。
- 矩阵非奇异当且仅当它代表的线性变换是个自同构。
- 矩阵半正定当且仅当它的每个特征值大于或等于零。
- 矩阵正定当且仅当它的每个特征值都大于零。
- 解线性方程组的克拉默法则。
- 判断线性方程组有无非零实根的增广矩阵和系数矩阵的关系。
术语
| 英文 | 中文 |
|---|---|
| real matrix | 实数矩阵 |
| decomposition algorithms | 分解算法 |
| transpose | 转置 |
| determinant | 行列式 |
| eigenvalue, eigenvector | 特征值, 特征向量 |
| singular value, singular vector | 奇异值, 奇异向量 |
| square matrix | 方阵 |
| coefficient matrix | 系数矩阵 |
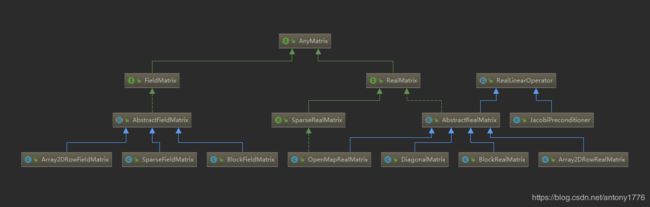
2、Real matrices:实矩阵
矩阵是高等代数学中的常见工具,也常见于统计分析等应用数学学科中。 [2] 在物理学中,矩阵于电路学、力学、光学和量子物理中都有应用;计算机科学中,三维动画制作也需要用到矩阵。 矩阵的运算是数值分析领域的重要问题。将矩阵分解为简单矩阵的组合可以在理论和实际应用上简化矩阵的运算。对一些应用广泛而形式特殊的矩阵,例如稀疏矩阵和准对角矩阵,有特定的快速运算算法。
参考:https://baike.baidu.com/item/矩阵/18069?fr=aladdin
由 m × n 个数 a i j a_{ij} aij 排成的 m 行 n 列的数表称为 m 行 n 列的矩阵,简称 m × n 矩阵。记作:

元素是实数的矩阵称为实矩阵,元素是复数的矩阵称为复矩阵。而行数与列数都等于n的矩阵称为n阶矩阵或n阶方阵 。
矩阵运算在科学计算中非常重要 ,而矩阵的基本运算包括矩阵的加法,减法,数乘,转置。把矩阵A的行和列互相交换所产生的矩阵称为A的转置矩阵( A T A^T AT ) ,这一过程称为矩阵的转置:

两个矩阵的乘法仅当第一个矩阵A的列数和另一个矩阵B的行数相等时才能定义。如A是m×n矩阵和B是n×p矩阵,它们的乘积C是一个m×p矩阵 C = ( c i j ) C=(c_{ij}) C=(cij),它的一个元素:

m × n m\times{n} m×n 矩阵A的对角元素之和称为矩阵A的迹(trace), 记作 t r ( A ) tr(A) tr(A)
// Create a real matrix with two rows and three columns, using a factory
// method that selects the implementation class for us.
double[][] matrixData = { {1d,2d,3d}, {2d,5d,3d}};
RealMatrix m = MatrixUtils.createRealMatrix(matrixData);
// One more with three rows, two columns, this time instantiating the
// RealMatrix implementation class directly.
double[][] matrixData2 = { {1d,2d}, {2d,5d}, {1d, 7d}};
RealMatrix n = new Array2DRowRealMatrix(matrixData2);
// Note: The constructor copies the input double[][] array in both cases.
// Now multiply m by n
RealMatrix p = m.multiply(n);
System.out.println(p.getRowDimension()); // 2
System.out.println(p.getColumnDimension()); // 2
// Invert p, using LU decomposition
RealMatrix pInverse = new LUDecomposition(p).getSolver().getInverse();
LUP 分解的思想就是找出三个n×n矩阵L,U,P,满足 P A = L U PA = LU PA=LU . 其中L是一个单位下三角矩阵,U是一个单位上三角矩阵,P是一个置换矩阵。 而满足分解条件的矩阵L,U,P称为矩阵A的一个LUP分解。
调用 walkIn 方法来遍历数据元素:
public void metricTest2() {
double[][] matrixData2 = { {1d,2d, 3d}, {2d,5d, 6d}, {1d, 7d, 2d}};
RealMatrix n = new Array2DRowRealMatrix(matrixData2);
n.walkInColumnOrder(new RealMatrixChangingVisitor() {
@Override
public void start(int rows, int columns, int startRow, int endRow, int startColumn, int endColumn) {
System.out.println(String.format("start: %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d", rows, columns, startRow, endRow, startColumn, endColumn));
}
@Override
public double visit(int row, int column, double value) {
System.out.println(String.format("visit: %d, %d, %f", row, column, value));
return value;
}
@Override
public double end() {
return 0;
}
});
}
输出信息如下:
start: 3, 3, 0, 2, 0, 2
visit: 0, 0, 1.000000
visit: 1, 0, 2.000000
visit: 2, 0, 1.000000
visit: 0, 1, 2.000000
visit: 1, 1, 5.000000
visit: 2, 1, 7.000000
visit: 0, 2, 3.000000
visit: 1, 2, 6.000000
visit: 2, 2, 2.000000
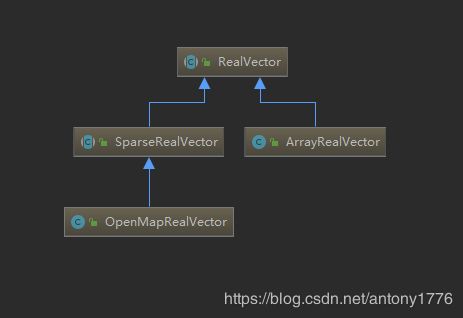
3、Real vectors:实向量
支持的操作有:
- 向量加、减、乘、除
- 标量加、减、乘、除,幂
- 函数映射(比如,cos,sin …)
- 点乘,外乘
- Distance and norm according to norms L1, L2 and Linf
RealVectorFormat 可用于向量的格式化(输入/输出)。
4、Solving linear systems:线性系统求解
DecompositionSolver 实现类可用于求解线性方程组,RealMatrix 实例中保存了方程组的系数矩阵,求解过程分为两步:
- 分解系数矩阵;
- 求解
例如,以下线性方程组 A X = B AX=B AX=B, 其中 A 为系数矩阵,B 为常数向量:
2x + 3y - 2z = 1
-x + 7y + 6x = -2
4x - 3y - 5z = 1
首先,分解系数矩阵(本例中,使用 LU 分解法):
RealMatrix coefficients =
new Array2DRowRealMatrix(new double[][] { { 2, 3, -2 }, { -1, 7, 6 }, { 4, -3, -5 } },
false);
DecompositionSolver solver = new LUDecomposition(coefficients).getSolver();
接下来,创建 RealVector 数组来存放常数向量 B, 并调用 solve(RealVector) 来求解:
RealVector constants = new ArrayRealVector(new double[] { 1, -2, 1 }, false);
RealVector solution = solver.solve(constants);
求解的结果 solution 包含 x, y, z 的值。
矩阵的 LU 分解,参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/bigmonkey/archive/2018/08/29/9555710.html
在线性代数中, LU分解(LU Decomposition)是矩阵分解的一种,可以将一个矩阵分解为一个单位下三角矩阵和一个上三角矩阵的乘积(有时是它们和一个置换矩阵的乘积)。LU分解主要应用在数值分析中,用来解线性方程、求反矩阵或计算行列式。
首先,将 A 表示成一个下三角矩阵 L 和上三角矩阵 U 的乘积,成为 A 的 LU 分解:
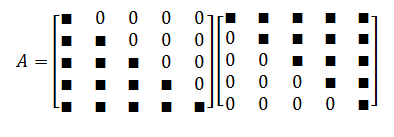
更进一步,使下三角矩阵的对角元数都为 1:
不同类型的求解算法会有不同的限定条件:
| 算法名称 | 系数矩阵 | 问题类型 |
|---|---|---|
| LU | 方阵 | 精确求解 |
| Cholesky | 对称正定 | 精确求解 |
| QR | 任意 | 最小二乘求解 |
| eigen decomposition | 方阵 | 精确解 |
| SVD | 任意 | 最小二乘求解 |