K8s 中的 CNI 是怎么样执行的?
K8s 中的 CNI 是怎么样执行的?
欢迎加入群聊:885763297,一起学习 k8s
我们在说之前不妨先了解一下什么是 CNI?CNI 又是做什么用的?我们该如何使用 CNI?
CNI (Container Network Interface), a Cloud Native Computing Foundation project, consists of a specification and libraries for writing
plugins to configure network interfaces in Linux containers, along with a number of supported plugins. CNI concerns itself only with
network connectivity of containers and removing allocated resources when the container is deleted. Because of this focus, CNI has a wide
range of support and the specification is simple to implement.
以上摘自 https://github.com/containernetworking/cni/ 通俗的来说:CNI 全称叫做 Container Network Interface 即:容器网络接口,属于一个
CNCF 项目,是一种规范或标准和库。用于配置容器网络,以及一些受支持的插件。CNI 特点就是只关心容器的网络连接,并在删除容器时删除分配的资源。正是由于这个原因,CNI 得到了广泛的支持,并且规范易于实现。
准确的来说想要实现 CNI 规范只需要实现以下接口中的内容,即:添加网络、删除网络。
type CNI interface {
AddNetworkList(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfigList, rt *RuntimeConf) (types.Result, error)
CheckNetworkList(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfigList, rt *RuntimeConf) error
DelNetworkList(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfigList, rt *RuntimeConf) error
AddNetwork(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfig, rt *RuntimeConf) (types.Result, error)
CheckNetwork(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfig, rt *RuntimeConf) error
DelNetwork(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfig, rt *RuntimeConf) error
GetNetworkCachedResult(net *NetworkConfig, rt *RuntimeConf) (types.Result, error)
ValidateNetworkList(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfigList) ([]string, error)
ValidateNetwork(ctx context.Context, net *NetworkConfig) ([]string, error)
}
CNI 大家感兴趣可以查看容器网络接口规范 后续的文章会说到如何使用 CNI。实现了 CNI 规范的一些插件如下,这些只是一部分。
- bridge: 创建一个网桥,将主机和容器添加到其中。
- ipvlan: 在容器中添加 ipvlan 接口。
- loopback: 将 loopback 接口的状态设置为 up。
- macvlan: 创建一个新的 MAC 地址,将所有到该地址的通信转发给容器。
- vlan: 分配一个 vlan 设备。
- host-device: 将已经存在的设备移动到容器中。
- flannel: 生成与 flannel 配置文件相对应的接口。
回到正题,CNI 既然负责管理容器的网络,那我们找到负责创建 pod 的 kubelet 的入口:
kubernetes 版本基于 v1.13.0
pluginSettings := dockershim.NetworkPluginSettings{
HairpinMode: kubeletconfiginternal.HairpinMode(kubeCfg.HairpinMode),
NonMasqueradeCIDR: nonMasqueradeCIDR,
PluginName: crOptions.NetworkPluginName,
PluginConfDir: crOptions.CNIConfDir,
PluginBinDirString: crOptions.CNIBinDir,
MTU: int(crOptions.NetworkPluginMTU),
}
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
603-610 行,这个可以很清楚的看出这时设置了网络插件的一些参数,但是并没有调用其本身。
switch containerRuntime {
case kubetypes.DockerContainerRuntime:
// 创建并启动作为 grpc 服务器运行的 CRI shim。
streamingConfig := getStreamingConfig(kubeCfg, kubeDeps, crOptions)
ds, err := dockershim.NewDockerService(kubeDeps.DockerClientConfig, crOptions.PodSandboxImage, streamingConfig,
&pluginSettings, runtimeCgroups, kubeCfg.CgroupDriver, crOptions.DockershimRootDirectory, !crOptions.RedirectContainerStreaming)
... ...
case kubetypes.RemoteContainerRuntime:
// No-op.
break
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unsupported CRI runtime: %q", containerRuntime)
}
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
617-654 行,从switch 可以看出如果容器处于 Runtime 状态就调用 NewDockerService 并且将上面刚设置的一些参数同样转递了过去,可以肯定就是在这里调用的。
func NewDockerService(config *ClientConfig, podSandboxImage string, streamingConfig *streaming.Config, pluginSettings *NetworkPluginSettings,
cgroupsName string, kubeCgroupDriver string, dockershimRootDir string, startLocalStreamingServer bool) (DockerService, error) {
... ...
// dockershim 目前只支持 CNI 插件。
pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs = cni.SplitDirs(pluginSettings.PluginBinDirString)
cniPlugins := cni.ProbeNetworkPlugins(pluginSettings.PluginConfDir, pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs)
cniPlugins = append(cniPlugins, kubenet.NewPlugin(pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs))
... ...
}
pkg/kubelet/dockershim/docker_service.go
239-241 行,跟踪 NewDockerService 函数来到这里。cniPlugins := cni.ProbeNetworkPlugins(pluginSettings.PluginConfDir, pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs) 它执行了具体的函数,使用探针方式获取当前环境的网络插件,我们接着往下找一下。
func ProbeNetworkPlugins(confDir string, binDirs []string) []network.NetworkPlugin {
old := binDirs
binDirs = make([]string, 0, len(binDirs))
// dir 为 CNI 的默认值:/opt/cni/bin
for _, dir := range old {
if dir != "" {
binDirs = append(binDirs, dir)
}
}
plugin := &cniNetworkPlugin{
defaultNetwork: nil,
// loNetwork 负责生成 lo 网卡,必不可少。
loNetwork: getLoNetwork(binDirs),
execer: utilexec.New(),
confDir: confDir,
binDirs: binDirs,
}
// 探测过程中同步 NetworkConfig。
plugin.syncNetworkConfig()
return []network.NetworkPlugin{plugin}
}
pkg/kubelet/dockershim/network/cni/cni.go
121-126 行,调用 cniNetworkPlugin 函数。在查看 cniNetworkPlugin 函数之前,我们先查看一下 NetworkPlugin 函数
// NetworkPlugin 是 kubelet 网络插件的接口
type NetworkPlugin interface {
// 初始化插件。这将在调用任何其他方法之前被精确地调用一次
Init(host Host, hairpinMode kubeletconfig.HairpinMode, nonMasqueradeCIDR string, mtu int) error
// 在各种事件上调用,比如: NET_PLUGIN_EVENT_POD_CIDR_CHANGE
Event(name string, details map[string]interface{})
// 返回插件的名称。这将用于搜索一个插件的名字
Name() string
// 返回一组 NET_PLUGIN_CAPABILITY_*
Capabilities() utilsets.Int
// SetUpPod 是在创建了 pod 的 infra 容器之后,但在启动 pod 的其他容器之前调用的方法
SetUpPod(namespace string, name string, podSandboxID kubecontainer.ContainerID, annotations, options map[string]string) error
// TearDownPod 是在删除 pod 的 infra 容器之前调用的方法
TearDownPod(namespace string, name string, podSandboxID kubecontainer.ContainerID) error
// GetPodNetworkStatus 是获取容器的 ipv4 或 ipv6 地址的方法
GetPodNetworkStatus(namespace string, name string, podSandboxID kubecontainer.ContainerID) (*PodNetworkStatus, error)
// 如果网络插件处于错误状态,则状态返回错误
Status() error
}
pkg/kubelet/dockershim/network/plugins.go
47-76 行,显而易见,这里定义了插件的所有接口。我们再返回查看 cniNetworkPlugin 函数。
type cniNetworkPlugin struct {
network.NoopNetworkPlugin
loNetwork *cniNetwork
sync.RWMutex
defaultNetwork *cniNetwork
host network.Host
execer utilexec.Interface
nsenterPath string
confDir string
binDirs []string
podCidr string
}
pkg/kubelet/dockershim/network/cni/cni.go
43-57 行,我想现在大家应该明白了这个 cniNetworkPlugin 结构体实现了 NetworkPlugin 函数中定义的所有接口。
我们接着查看上面负责同步网络配置的 ProbeNetworkPlugins 函数。
func (plugin *cniNetworkPlugin) syncNetworkConfig() {
network, err := getDefaultCNINetwork(plugin.confDir, plugin.binDirs)
if err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Unable to update cni config: %s", err)
return
}
plugin.setDefaultNetwork(network)
}
pkg/kubelet/dockershim/network/cni/cni.go
200-207 行,跟踪 ProbeNetworkPlugins 来到这里。这里主要做了探测网络并设置默认网络
这里可以总结一下 CNI 的第一步就是:以探针的方式获取当前的网络环境。
接着从 pkg/kubelet/dockershim/docker_service.go 来看。
... ...
// dockershim 目前只支持 CNI 插件。
pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs = cni.SplitDirs(pluginSettings.PluginBinDirString)
cniPlugins := cni.ProbeNetworkPlugins(pluginSettings.PluginConfDir, pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs)
cniPlugins = append(cniPlugins, kubenet.NewPlugin(pluginSettings.PluginBinDirs))
netHost := &dockerNetworkHost{
&namespaceGetter{ds},
&portMappingGetter{ds},
}
plug, err := network.InitNetworkPlugin(cniPlugins, pluginSettings.PluginName, netHost, pluginSettings.HairpinMode, pluginSettings.NonMasqueradeCIDR, pluginSettings.MTU)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("didn't find compatible CNI plugin with given settings %+v: %v", pluginSettings, err)
}
... ...
上面皆以执行完毕,下面就是就是执行:InitNetworkPlugin 运行网络插件。
// InitNetworkPlugin 插入与 networkPluginName 匹配的插件。插件名唯一。
func InitNetworkPlugin(plugins []NetworkPlugin, networkPluginName string, host Host, hairpinMode kubeletconfig.HairpinMode, nonMasqueradeCIDR string, mtu int) (NetworkPlugin, error) {
if networkPluginName == "" {
// 如果没有执行网络插件的话默认为 `no_op` 插件
plug := &NoopNetworkPlugin{}
plug.Sysctl = utilsysctl.New()
// 初始化
if err := plug.Init(host, hairpinMode, nonMasqueradeCIDR, mtu); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return plug, nil
}
pluginMap := map[string]NetworkPlugin{}
allErrs := []error{}
for _, plugin := range plugins {
name := plugin.Name()
if errs := validation.IsQualifiedName(name); len(errs) != 0 {
allErrs = append(allErrs, fmt.Errorf("network plugin has invalid name: %q: %s", name, strings.Join(errs, ";")))
continue
}
if _, found := pluginMap[name]; found {
allErrs = append(allErrs, fmt.Errorf("network plugin %q was registered more than once", name))
continue
}
pluginMap[name] = plugin
}
// 从下面以及上面的循环和输出语句可以看出,这里是为了匹配网络插件
chosenPlugin := pluginMap[networkPluginName]
if chosenPlugin != nil {
// 执行初始化函数
err := chosenPlugin.Init(host, hairpinMode, nonMasqueradeCIDR, mtu)
if err != nil {
allErrs = append(allErrs, fmt.Errorf("Network plugin %q failed init: %v", networkPluginName, err))
} else {
klog.V(1).Infof("Loaded network plugin %q", networkPluginName)
}
} else {
allErrs = append(allErrs, fmt.Errorf("Network plugin %q not found.", networkPluginName))
}
return chosenPlugin, utilerrors.NewAggregate(allErrs)
}
这里可以总结一下 CNI 的第二步就是:执行 Init 函数。
下面就是最后一步,添加 Add()、删除 Del() 网络。先上一张广为流传的操作网络的流程图:
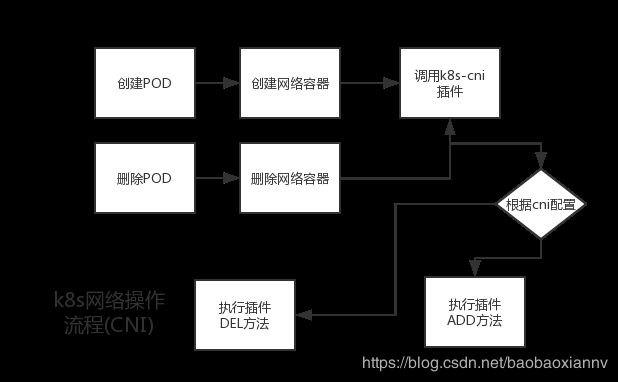
来自:http://www.sohu.com/a/129910066_515888
我们回到 pkg/kubelet/dockershim/network/cni/cni.go 中,已知 cniNetworkPlugin 实现了插件的所有接口,我们找到 SetUpPod 函数。
func (plugin *cniNetworkPlugin) SetUpPod(namespace string, name string, id kubecontainer.ContainerID, annotations, options map[string]string) error {
if err := plugin.checkInitialized(); err != nil {
return err
}
// 获取指定 ID 的容器的 namespace 的路径。
netnsPath, err := plugin.host.GetNetNS(id.ID)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("CNI failed to retrieve network namespace path: %v", err)
}
// Windows 没有 loNetwork,只有与 Linux 一起提供
if plugin.loNetwork != nil {
// 给容器添加 lo 网卡
if _, err = plugin.addToNetwork(plugin.loNetwork, name, namespace, id, netnsPath, annotations, options); err != nil {
return err
}
}
_, err = plugin.addToNetwork(plugin.getDefaultNetwork(), name, namespace, id, netnsPath, annotations, options)
return err
}
274-292 行,我们跟踪 addToNetwork 函数。
func (plugin *cniNetworkPlugin) addToNetwork(network *cniNetwork, podName string, podNamespace string, podSandboxID kubecontainer.ContainerID, podNetnsPath string, annotations, options map[string]string) (cnitypes.Result, error) {
rt, err := plugin.buildCNIRuntimeConf(podName, podNamespace, podSandboxID, podNetnsPath, annotations, options)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Error adding network when building cni runtime conf: %v", err)
return nil, err
}
pdesc := podDesc(podNamespace, podName, podSandboxID)
netConf, cniNet := network.NetworkConfig, network.CNIConfig
klog.V(4).Infof("Adding %s to network %s/%s netns %q", pdesc, netConf.Plugins[0].Network.Type, netConf.Name, podNetnsPath)
res, err := cniNet.AddNetworkList(netConf, rt)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Error adding %s to network %s/%s: %v", pdesc, netConf.Plugins[0].Network.Type, netConf.Name, err)
return nil, err
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Added %s to network %s: %v", pdesc, netConf.Name, res)
return res, nil
}
312-329 行,调用 buildCNIRuntimeConf 函数,下面只是一些判断。我们查看 buildCNIRuntimeConf 函数。
func (plugin *cniNetworkPlugin) buildCNIRuntimeConf(podName string, podNs string, podSandboxID kubecontainer.ContainerID, podNetnsPath string, annotations, options map[string]string) (*libcni.RuntimeConf, error) {
rt := &libcni.RuntimeConf{
ContainerID: podSandboxID.ID,
NetNS: podNetnsPath,
IfName: network.DefaultInterfaceName,
Args: [][2]string{
{"IgnoreUnknown", "1"},
{"K8S_POD_NAMESPACE", podNs},
{"K8S_POD_NAME", podName},
{"K8S_POD_INFRA_CONTAINER_ID", podSandboxID.ID},
},
}
... ...
}
352-420 行,这个函数执行了非常多的东西,但我们只需要看 libcni 调用了 RuntimeConf 函数。这时候看导入 "github.com/containernetworking/cni/libcni" 实际已经执行到了 cni 项目,我们可以前往 github 查看一下这个函数具体写了一些什么。
func (c *CNIConfig) addNetwork(ctx context.Context, name, cniVersion string, net *NetworkConfig, prevResult types.Result, rt *RuntimeConf) (types.Result, error) {
c.ensureExec()
pluginPath, err := c.exec.FindInPath(net.Network.Type, c.Path)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
newConf, err := buildOneConfig(name, cniVersion, net, prevResult, rt)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 执行添加函数并返回。
return invoke.ExecPluginWithResult(ctx, pluginPath, newConf.Bytes, c.args("ADD", rt), c.exec)
}
cni/libcni/api.go 236-246 行。
这里可以总结一下 CNI 的第三步就是:执行 Add() or Del() 函数。
删除网络和添加网络的逻辑顺序是完全相同的,这里就不一一写出来了。如果大家发现有错误欢迎留言指点。