python链家网高并发异步爬虫asyncio+aiohttp+aiomysql异步存入数据
原文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/PyKK2019/p/aiohttp_spider.html
很多小伙伴初学python时都会学习到爬虫,刚入门时会使用requests、urllib这些同步的库进行单线程爬虫,速度是比较慢的,后学会用scrapy框架进行爬虫,速度很快,原因是scrapy是基于twisted多线程异步IO框架。
本例使用的asyncio也是一个异步IO框架,在python3.5以后加入了协程的关键字async,能够将协程和生成器区分开来,更加方便使用协程。
经过测试,平均1秒可以爬取30个详情页信息
可以使用asyncio.Semaphore来控制并发数,达到限速的效果
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
:author: KK
:url: http://github.com/PythonerKK
:copyright: © 2019 KK <[email protected]>
"""
import asyncio
import re
import aiohttp
from pyquery import PyQuery
import aiomysql
from lxml import etree
pool = ''
#sem = asyncio.Semaphore(4) 用来控制并发数,不指定会全速运行
stop = False
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/61.0.3163.100 Safari/537.36'
}
MAX_PAGE = 10
TABLE_NAME = 'data' #数据表名
city = 'zh' #城市简写
url = 'https://{}.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pg{}/' #url地址拼接
urls = [] #所有页的url列表
links_detail = set() #爬取中的详情页链接的集合
crawled_links_detail = set() #爬取完成的链接集合,方便去重
async def fetch(url, session):
'''
aiohttp获取网页源码
'''
# async with sem:
try:
async with session.get(url, headers=headers, verify_ssl=False) as resp:
if resp.status in [200, 201]:
data = await resp.text()
return data
except Exception as e:
print(e)
def extract_links(source):
'''
提取出详情页的链接
'''
pq = PyQuery(source)
for link in pq.items("a"):
_url = link.attr("href")
if _url and re.match('https://.*?/\d+.html', _url) and _url.find('{}.lianjia.com'.format(city)):
links_detail.add(_url)
print(links_detail)
def extract_elements(source):
'''
提取出详情页里面的详情内容
'''
try:
dom = etree.HTML(source)
id = dom.xpath('//link[@rel="canonical"]/@href')[0]
title = dom.xpath('//title/text()')[0]
price = dom.xpath('//span[@class="unitPriceValue"]/text()')[0]
information = dict(re.compile('(.*?)(.*?) ').findall(source))
information.update(title=title, price=price, url=id)
print(information)
asyncio.ensure_future(save_to_database(information, pool=pool))
except Exception as e:
print('解析详情页出错!')
pass
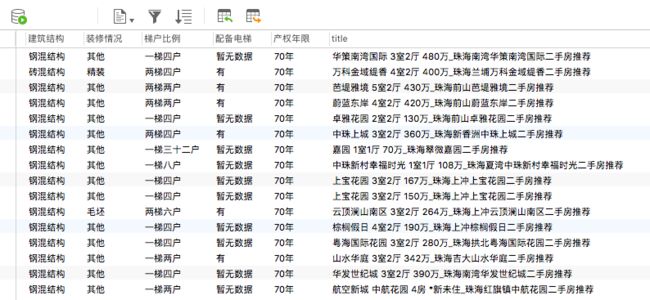
async def save_to_database(information, pool):
'''
使用异步IO方式保存数据到mysql中
注:如果不存在数据表,则创建对应的表
'''
COLstr = '' # 列的字段
ROWstr = '' # 行字段
ColumnStyle = ' VARCHAR(255)'
for key in information.keys():
COLstr = COLstr + ' ' + key + ColumnStyle + ','
ROWstr = (ROWstr + '"%s"' + ',') % (information[key])
# 异步IO方式插入数据库
async with pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor() as cur:
try:
await cur.execute("SELECT * FROM %s" % (TABLE_NAME))
await cur.execute("INSERT INTO %s VALUES (%s)"%(TABLE_NAME, ROWstr[:-1]))
print('插入数据成功')
except aiomysql.Error as e:
await cur.execute("CREATE TABLE %s (%s)" % (TABLE_NAME, COLstr[:-1]))
await cur.execute("INSERT INTO %s VALUES (%s)" % (TABLE_NAME, ROWstr[:-1]))
except aiomysql.Error as e:
print('mysql error %d: %s' % (e.args[0], e.args[1]))
async def handle_elements(link, session):
'''
获取详情页的内容并解析
'''
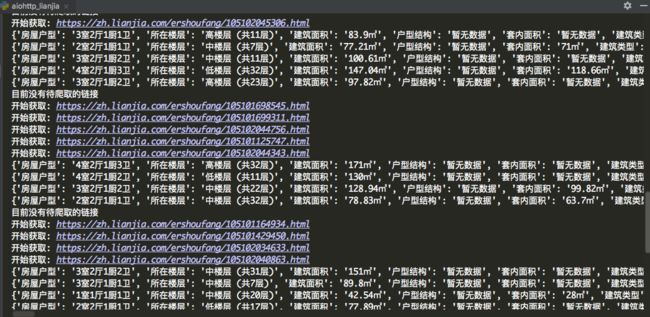
print('开始获取: {}'.format(link))
source = await fetch(link, session)
#添加到已爬取的集合中
crawled_links_detail.add(link)
extract_elements(source)
async def consumer():
'''
消耗未爬取的链接
'''
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
while not stop:
if len(urls) != 0:
_url = urls.pop()
source = await fetch(_url, session)
print(_url)
extract_links(source)
if len(links_detail) == 0:
print('目前没有待爬取的链接')
await asyncio.sleep(2)
continue
link = links_detail.pop()
if link not in crawled_links_detail:
asyncio.ensure_future(handle_elements(link, session))
async def main(loop):
global pool
pool = await aiomysql.create_pool(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306,
user='root', password='xxxxxx',
db='aiomysql_lianjia', loop=loop, charset='utf8',
autocommit=True)
for i in range(1, MAX_PAGE):
urls.append(url.format(city, str(i)))
print('爬取总页数:{} 任务开始...'.format(str(MAX_PAGE)))
asyncio.ensure_future(consumer())
if __name__ == '__main__':
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
asyncio.ensure_future(main(loop))
loop.run_forever()