OpenCV访问像素点的灰度值
1.Mat矩阵数值的存储方式
这里以指针的方式访问图像素为例
(1)单通道
定义一个单通道图像:
cv::Mat img_1 = (320, 640, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));对于单通道M(i,j)即为第i行j列的其灰度值;程序中表示为:
img_1.ptr(i)[j]; (2)多通道
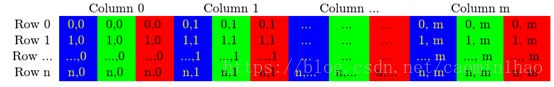
这里以RGB图像为例,每一个子列依次为B、G、R,,第一个分量是蓝色,第二个是绿色,第三个是红色。
定义一个3通道BGR图像:
cv::Mat img_1 = (320, 640, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0 ,0));对于多通道M(i,j*3)即为第i行j列的B通道其灰度值,M(i,j*3+1) 即为第i行j列的G通道其灰度值,M(i,j*3+1) 即为第i行j列的B通 道其灰度值;程序中表示为:
第i行j列的B通道其灰度值:
img_1.ptr(i)[j*3]; 第i行j列的G通道其灰度值:
img_1.ptr(i)[j*3+1]; 第i行j列的R通道其灰度值:
img_1.ptr(i)[j*3+2];
2.示例程序,以三种方法(指针,at,迭代器)
////获得图像像素值
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void get_setImagePixel3(char *imagePath, int x, int y)
{
Mat image = imread(imagePath, 1);
//得宽高
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
int channels = image.channels();
if (channels == 1)
{
//得到初始位置的迭代器
Mat_::iterator it = image.begin();
//得到终止位置的迭代器
Mat_::iterator itend = image.end();
int pixel = *(it + y * w + x);
cout << "灰度图像,处的灰度值为" << pixel << endl;
}
else
{
//得到初始位置的迭代器
Mat_::iterator it = image.begin();
//得到终止位置的迭代器
Mat_::iterator itend = image.end();
//读取
it = it + y * w + x;
int b = (*it)[0];
cout << b << endl;
int g = (*it)[1];
cout << g << endl;
int r = (*it)[2];
cout << r << endl;
//设置像素值
(*it)[0] = 255;
(*it)[1] = 255;
(*it)[2] = 255;
}
imshow("cc", image);
}
int main()
{
vector v = {1,2,3,4,6};
cout << "*********通过指针访问像素的灰度值********************" << endl;
//通过指针访问像素的灰度值
//单通道
Mat img1(20, 30, CV_32FC1, Scalar(0));
img1.ptr(19)[25] = 23456.1789;
cout << "img(19,25):" << img1.ptr(19)[25] <(19)[25]) << endl;
Mat img = imread("test1.jpg");
int numRow = img.rows;
int numCol = img.cols;
int numCol_channel = img.cols*img.channels();
cout << "numRow:" << numRow << endl;
cout << "numCol:" << numCol << endl;
cout << "numCol_channel:" << numCol_channel << endl;
cout << "45行,483列B通道灰度值" << int(img.ptr(45)[483*3]) << endl;
cout << "45行,483列G通道灰度值" << int(img.ptr(45)[483*3+1]) << endl;
cout << "45行,483列R通道灰度值" << int(img.ptr(45)[483*3+2]) << endl;
Mat img_B(numRow, numCol, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
Mat img_G(numRow, numCol, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
Mat img_R(numRow, numCol, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < numRow; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < numCol; j++)
{
img_B.ptr(i)[j*3] = img.ptr(i)[j*3];
img_G.ptr(i)[j*3+1] = img.ptr(i)[j*3+1];
img_R.ptr(i)[j*3+2] = img.ptr(i)[j*3+2];
}
}
imshow("img", img);
imshow("img_B", img_B);
imshow("img_G", img_G);
imshow("img_R", img_R);
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "*********at只适合灰度值为8位的图像********************" << endl;
//注意:at只适合灰度值为8位的图像
//单通道
Mat img3(20, 30, CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
cout << "img(7,8)" << int(img3.at(7, 8)) << endl;
//多通道
Mat img4(20, 30, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0));
//BGR通道
cout << "B通道灰度值" << int(img4.at(3, 4)[0]) << endl;
cout << "G通道灰度值" << int(img4.at(3, 4)[1]) << endl;
cout << "R通道灰度值" << int(img4.at(3, 4)[2]) << endl;
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}