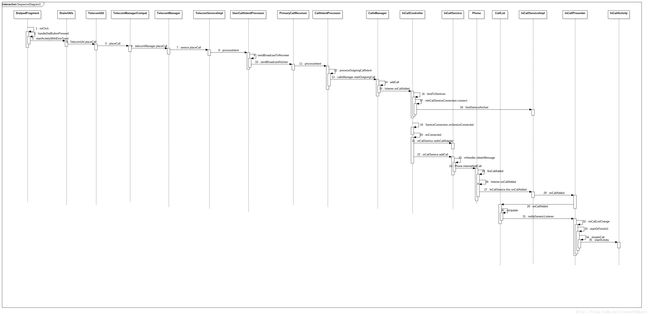
Telephony基础之VoiceCall业务(InCallActivity启动)
首先明确,MO拨号到启动InCallUI界面会依次经过Dialer–>Telecom service–>InCallUI三部分。
在点击拨号盘拨号按钮后通过onClick()会进入DialUtils.startActivityWithErrorToast():
DialpadFragment.java
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
int resId = view.getId();
if (resId == R.id.dialpad_floating_action_button) {
view.performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.VIRTUAL_KEY);
handleDialButtonPressed();
}
...
}
private void handleDialButtonPressed() {
if (isDigitsEmpty()) { // No number entered.
handleDialButtonClickWithEmptyDigits();
} else {
...
} else {
final Intent intent = new CallIntentBuilder(number).
setCallInitiationType(LogState.INITIATION_DIALPAD)
.build();
DialerUtils.startActivityWithErrorToast(getActivity(), intent);
hideAndClearDialpad(false);
}
}
}
DialerUtils.java
public static void startActivityWithErrorToast(Context context, Intent intent, int msgId) {
} else {
context.startActivity(intent);
}
}
}
这里会通过IntentUtil.CALL_ACTION启动Telecom中UserCallActivity,但其实该Activity并不会有一个可是的界面显示,只是作为一个中间转换作用。
public class UserCallActivity extends Activity implements TelecomSystem.Component {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) {
super.onCreate(bundle);
Log.startSession("UCA.oC");
try {
// TODO: Figure out if there is something to restore from bundle.
// See OutgoingCallBroadcaster in services/Telephony for more.
Intent intent = getIntent();
verifyCallAction(intent);
final UserManager userManager = (UserManager) getSystemService(Context.USER_SERVICE);
final UserHandle userHandle = new UserHandle(userManager.getUserHandle());
// Once control flow has passed to this activity, it is no longer guaranteed that we can
// accurately determine whether the calling package has the CALL_PHONE runtime permission.
// At this point in time we trust that the ActivityManager has already performed this
// validation before starting this activity.
new UserCallIntentProcessor(this, userHandle).processIntent(getIntent(),
getCallingPackage(), true /* hasCallAppOp*/);
} finally {
Log.endSession();
}
finish();
}
进入UserCallIntentProcessor().processIntent():
public void processIntent(Intent intent, String callingPackageName,
boolean canCallNonEmergency) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (Intent.ACTION_CALL.equals(action) ||
Intent.ACTION_CALL_PRIVILEGED.equals(action) ||
Intent.ACTION_CALL_EMERGENCY.equals(action)) {
processOutgoingCallIntent(intent, callingPackageName, canCallNonEmergency);
}
}
private void processOutgoingCallIntent(Intent intent, String callingPackageName,
boolean canCallNonEmergency) {
Uri handle = intent.getData();
String scheme = handle.getScheme();
String uriString = handle.getSchemeSpecificPart();
...
int videoState = intent.getIntExtra(
TelecomManager.EXTRA_START_CALL_WITH_VIDEO_STATE,
VideoProfile.STATE_AUDIO_ONLY);
Log.d(this, "processOutgoingCallIntent videoState = " + videoState);
intent.putExtra(CallIntentProcessor.KEY_IS_PRIVILEGED_DIALER,
isDefaultOrSystemDialer(callingPackageName));
// Save the user handle of current user before forwarding the intent to primary user.
intent.putExtra(CallIntentProcessor.KEY_INITIATING_USER, mUserHandle);
sendBroadcastToReceiver(intent);
}
private boolean sendBroadcastToReceiver(Intent intent) {
intent.putExtra(CallIntentProcessor.KEY_IS_INCOMING_CALL, false);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
intent.setClass(mContext, PrimaryCallReceiver.class);
Log.d(this, "Sending broadcast as user to CallReceiver");
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM);
return true;
}
对intent做一些处理后,以广播方式发出,在 PrimaryCallReceiver接收:
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Log.startSession("PCR.oR");
synchronized (getTelecomSystem().getLock()) {
getTelecomSystem().getCallIntentProcessor().processIntent(intent);
}
Log.endSession();
}
这就进入CallIntentProcessor().processIntent(),在该方法中取出了intent中携带的各中参数传入CallsManager.startOutgoingCall()用于创建Call对象,
CallsManager.startOutgoingCall()创建Telecom Call对象以此向上构建Telecom Framework Call和InCallUI Call对象,进而去启动InCallUI。
返回后,继续在processOutgoingCallIntent()中调broadcaster.processIntent()…–>CallsManager.placeOutgoingCall()向下进行拨号流程。
此处,我们只分析向上启动InCAllUI的流程。
public void processIntent(Intent intent) {
...
Call call = callsManager
.startOutgoingCall(handle, phoneAccountHandle, clientExtras, initiatingUser);
if (call != null) {
// Asynchronous calls should not usually be made inside a BroadcastReceiver because once
// onReceive is complete, the BroadcastReceiver's process runs the risk of getting
// killed if memory is scarce. However, this is OK here because the entire Telecom
// process will be running throughout the duration of the phone call and should never
// be killed.
NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster broadcaster = new NewOutgoingCallIntentBroadcaster(
context, callsManager, call, intent, callsManager.getPhoneNumberUtilsAdapter(),
isPrivilegedDialer);
final int result = broadcaster.processIntent();
final boolean success = result == DisconnectCause.NOT_DISCONNECTED;
if (!success && call != null) {
disconnectCallAndShowErrorDialog(context, call, result);
}
}
}
CallsManager.startOutgoingCall()
Call startOutgoingCall(Uri handle, PhoneAccountHandle phoneAccountHandle, Bundle extras,
UserHandle initiatingUser) {
boolean isReusedCall = true;
Call call = reuseOutgoingCall(handle);
// Create a call with original handle. The handle may be changed when the call is attached
// to a connection service, but in most cases will remain the same.
if (call == null) {
call = new Call(getNextCallId(), mContext,
this,
mLock,
mConnectionServiceRepository,
mContactsAsyncHelper,
mCallerInfoAsyncQueryFactory,
mPhoneNumberUtilsAdapter,
handle,
null /* gatewayInfo */,
null /* connectionManagerPhoneAccount */,
null /* phoneAccountHandle */,
Call.CALL_DIRECTION_OUTGOING /* callDirection */,
false /* forceAttachToExistingConnection */,
false /* isConference */
);
call.initAnalytics();
......
addCall(call);
}
在addCall()中:
private void addCall(Call call) {
....
for (CallsManagerListener listener : mListeners) {
if (Log.SYSTRACE_DEBUG) {
Trace.beginSection(listener.getClass().toString() + " addCall");
}
listener.onCallAdded(call);
if (Log.SYSTRACE_DEBUG) {
Trace.endSection();
}
}
}
这里通过分发Listener进入InCallController.onCallAdded():
public void onCallAdded(Call call) {
if (!isBoundToServices()) {
bindToServices(call);
} else {
...
try {
inCallService.addCall(parcelableCall);
} catch (RemoteException ignored) {
}
}
Log.i(this, "Call added to components: %s", componentsUpdated);
}
}
总体来说,这里就会去在InCallController中通过跨进程的绑定InCallUI中的InCallServiceImpl来把Call对象给到InCallUI用来启动InCallActivity。
public void bindToServices(Call call) {
....
// [HTC_PHONE] s Zoey if VzwInCallServiceImpl is enable, not show InCallUI
if (shouldShowInCallUI()) {
mInCallServiceConnection.connect(call);
}
// [HTC_PHONE] e Zoey if VzwInCallServiceImpl is enable, not show InCallUI
....
}
这个方法封装的比较复杂,但最终都会通过mInCallServiceConnection.connect(call)调到InCallServiceBindingConnection.connect(),在此处真正进行对InCallService(实际是InCallUI中的InCallServiceImpl)进行bind:
@Override
public boolean connect(Call call) {
if (mIsConnected) {
Log.event(call, Log.Events.INFO, "Already connected, ignoring request.");
return true;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(InCallService.SERVICE_INTERFACE);
intent.setComponent(mInCallServiceInfo.getComponentName());
if (call != null && !call.isIncoming() && !call.isExternalCall()){
intent.putExtra(TelecomManager.EXTRA_OUTGOING_CALL_EXTRAS,
call.getIntentExtras());
intent.putExtra(TelecomManager.EXTRA_PHONE_ACCOUNT_HANDLE,
call.getTargetPhoneAccount());
}
Log.i(this, "Attempting to bind to InCall %s, with %s", mInCallServiceInfo, intent);
mIsConnected = true;
if (!mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent, mServiceConnection,
Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE | Context.BIND_FOREGROUND_SERVICE,
UserHandle.CURRENT)) {
Log.w(this, "Failed to connect.");
mIsConnected = false;
}
....
}
这里的Intent intent = new Intent(InCallService.SERVICE_INTERFACE);其中Intent.Action==SERVICE_INTERFACE = “android.telecom.InCallService”;其指向的就是InCallUI中的InCallServiceImpl extends InCallService:
在绑定service以后会返回InCallServiceBinder对象:
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new InCallServiceBinder();
}
然后进入
private final ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.startSession("ICSBC.oSC");
synchronized (mLock) {
try {
Log.d(this, "onServiceConnected: %s %b %b", name, mIsBound, mIsConnected);
mIsBound = true;
if (mIsConnected) {
// Only proceed if we are supposed to be connected.
onConnected(service);
}
} finally {
Log.endSession();
}
}
}
这onConnected()方法逐步调到InCallController.onConnected():
private boolean onConnected(InCallServiceInfo info, IBinder service) {
Trace.beginSection("onConnected: " + info.getComponentName());
Log.i(this, "onConnected to %s", info.getComponentName());
IInCallService inCallService = IInCallService.Stub.asInterface(service);
mInCallServices.put(info, inCallService);
try {
inCallService.setInCallAdapter(
new InCallAdapter(
mCallsManager,
mCallIdMapper,
mLock,
info.getComponentName().getPackageName()));
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(this, e, "Failed to set the in-call adapter.");
Trace.endSection();
return false;
}
// Upon successful connection, send the state of the world to the service.
List calls = orderCallsWithChildrenFirst(mCallsManager.getCalls());
Log.i(this, "Adding %s calls to InCallService after onConnected: %s, including external " +
"calls", calls.size(), info.getComponentName());
int numCallsSent = 0;
for (Call call : calls) {
try {
if (call.isExternalCall() && !info.isExternalCallsSupported()) {
continue;
}
// Track the call if we don't already know about it.
addCall(call);
numCallsSent += 1;
inCallService.addCall(ParcelableCallUtils.toParcelableCall(
call,
true /* includeVideoProvider */,
mCallsManager.getPhoneAccountRegistrar(),
info.isExternalCallsSupported()));
} catch (RemoteException ignored) {
}
}
....
}
这里非常关键,通过IInCallService inCallService = IInCallService.Stub.asInterface(service);在InCallController中获得可操作InCallUI中InCallServiceImpl对象的引用inCallService。然后调用了关键的inCallService.setInCallAdapter(),通过这个方法将Telecom service中的InCallAdapter对象设到了Phone的实例中。接着远程调用inCallService.addCall(ParcelableCallUtils.toParcelableCall(call)将Telecom Service call序列化后传给InCallUI用于构建Telecom Framework Call:
@Override
public void addCall(ParcelableCall call) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_ADD_CALL, call).sendToTarget();
}
case MSG_ADD_CALL:
mPhone.internalAddCall((ParcelableCall) msg.obj);
break;
final void internalAddCall(ParcelableCall parcelableCall) {
Call call = new Call(this, parcelableCall.getId(), mInCallAdapter,
parcelableCall.getState());
mCallByTelecomCallId.put(parcelableCall.getId(), call);
mCalls.add(call);
checkCallTree(parcelableCall);
call.internalUpdate(parcelableCall, mCallByTelecomCallId);
fireCallAdded(call);
}
注意这里Telecom Framework Call的构造方法有传入InCallAdapter对象,这是后面会用到的用于从上到下进行通话控制的。之后调用了fireCallAdded(call):
private void fireCallAdded(Call call) {
for (Listener listener : mListeners) {
listener.onCallAdded(this, call);
}
}
这里的listener是在前面构建Phone对象时传入的mPhoneListener:
/** ${inheritDoc} */
@Override
public void onCallAdded(Phone phone, Call call) {
InCallService.this.onCallAdded(call);
}
这里的InCallService.this实际就是InCallServiceImpl实例:
@Override
public void onCallAdded(Call call) {
InCallServiceHelper.preSetup();
InCallPresenter.getInstance().onCallAdded(call);
}
进入InCallPresenter.getInstance().onCallAdded():
public void onCallAdded(final android.telecom.Call call) {
/*if (shouldAttemptBlocking(call)) {
// maybeBlockCall(call); // not follow Google design
} else {*/
if (call.getDetails()
.hasProperty(android.telecom.Call.Details.PROPERTY_IS_EXTERNAL_CALL)) {
mExternalCallList.onCallAdded(call);
} else {
mCallList.onCallAdded(call);
}
....
}
public void onCallAdded(final android.telecom.Call telecommCall) {
Trace.beginSection("onCallAdded");
final Call call = new Call(telecommCall);
....
if (call.getState() == Call.State.INCOMING ||
call.getState() == Call.State.CALL_WAITING) {
onIncoming(call, call.getCannedSmsResponses());
} else {
updateMuteStateForSRVCC(call);
onUpdate(call);
....
}
此处根据Telecom Framework Call创建出对应的InCallUI Call对象,同时设置了监听。之后因为Call.state=DIALING调用onUpdate(call):
public void onUpdate(Call call) {
Trace.beginSection("onUpdate");
onUpdateCall(call);
notifyGenericListeners();
Trace.endSection();
}
public void notifyGenericListeners() {
for (Listener listener : mListeners) {
listener.onCallListChange(this);
}
}
进入InCallPresenter:
@Override
public void onCallListChange(CallList callList) {
....
InCallState newState = getPotentialStateFromCallList(callList);
InCallState oldState = mInCallState;
Log.d(this, "onCallListChange oldState= " + oldState + " newState=" + newState);
newState = startOrFinishUi(newState);
终于看到曙光了,这里的startOrFinishUi(newState)就是去启动InCallUI通话界面InCallActivity了,传入的newState是InCallState对象,该对象专门用来表征通话界面状态的。
private InCallState startOrFinishUi(InCallState newState) {
Log.d(this, "startOrFinishUi: " + mInCallState + " -> " + newState);
....
if (showCallUi || showAccountPicker) {
if(HtcLiteStateController.getInstance().donotShowUIIfLiteConnected() == false) {
Log.i(this, "Start in call UI");
showInCall(false /* showDialpad */, !showAccountPicker /* newOutgoingCall */);
}
}
....
public void showInCall(final boolean showDialpad, final boolean newOutgoingCall, boolean pendingAnswer) {
Log.i(this, "Showing InCallActivity");
Intent intent = getInCallIntent(showDialpad, newOutgoingCall);
//+[HTC_PHONE]Need to show dialog for user to select video type
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_SHOW_ANSWER_SELECT_DIALOG, pendingAnswer);
//+[HTC_PHONE]Need to show dialog for user to select video type
mContext.startActivity(intent);
}
OK,InCallActivity终于启动起来了,至于启动起来的界面是什么样的,在之后的关于InCallUI布局一节再来分析。
这里再来说几点零碎的认识:
1,在这个流程,即MO startInCallUI流程中,涉及了Dialer,Telecom Service,Telecom Framework,InCallUI四部分,Dialer不谈,只谈后面三部分。剩下的三个部分从进程角度来讲是运行在两个进程里:1.system_server 2.InCallUI 。其中Telecom Service是运行在system_server中的(android:process=“system”)。而Telecom Framework中的主要java 类是抽象出来放在框架层里,以提供给InCallUI实现或调用的,如InCallService.java,Phone.java,Call.java其并没有运行在一个单独的进程,而是在InCallUI进程中来使用。
2,Telecom service与InCallUI是通过AIDL实现了跨进程的双向互通的。具体实现的类文件是:InCallController.java InCallAdapter.java(Telecom service); InCallService.java InCallAdapter.java(Telecom Framework); InCallServiceImpl.java(InCallUI)。其中Telecom Service通过绑定service–>InCallServiceImpl获得InCallServiceBinder的binder对象用以操作InCallUI。同时调用前面说到的inCallService.setInCallAdapter()传给InCallUI一个在Telecom service中实现了AIDL接口的InCallAdapter extends IInCallAdapter.Stub对象,这就使得InCallUI中持有了操作Telecom service的接口。后面需要分析的HOLD Call, END Call等就需用到这个接口。简单流程如下:
InCallUI Call–>Telecom Framework Call–>Telecom Framwork InCallAdapter–>Telecom Service InCallAdapter