TensorRT Samples: MNIST(Plugin, add a custom layer)
关于TensorRT的介绍可以参考: http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/78469551
GitHub: https://github.com/fengbingchun/CUDA_Test
以下是参考TensorRT 2.1.2中的samplePlugin.cpp文件改写的通过IPlugin添加一个全连接层实现对手写数字0-9识别的测试代码,plugin.cpp文件内容如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "common.hpp"
// reference: TensorRT-2.1.2/samples/samplePlugin/samplePlugin.cpp
// demonstrates how to add a custom layer to TensorRT. It replaces the final fully connected layer of the MNIST sample with a direct call to cuBLAS
namespace {
typedef std::tuple DATA_INFO; // intput width, input height, output size, input blob name, output blob name
int caffeToGIEModel(const std::string& deployFile, // name for caffe prototxt
const std::string& modelFile, // name for model
const std::vector& outputs, // network outputs
unsigned int maxBatchSize, // batch size - NB must be at least as large as the batch we want to run with)
nvcaffeparser1::IPluginFactory* pluginFactory, // factory for plugin layers
nvinfer1::IHostMemory *&gieModelStream, Logger logger) // output stream for the GIE model
{
// create the builder
nvinfer1::IBuilder* builder = nvinfer1::createInferBuilder(logger);
// parse the caffe model to populate the network, then set the outputs
nvinfer1::INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetwork();
nvcaffeparser1::ICaffeParser* parser = nvcaffeparser1::createCaffeParser();
parser->setPluginFactory(pluginFactory);
bool fp16 = builder->platformHasFastFp16();
const nvcaffeparser1::IBlobNameToTensor* blobNameToTensor = parser->parse(deployFile.c_str(),
modelFile.c_str(), *network, fp16 ? nvinfer1::DataType::kHALF : nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT);
// specify which tensors are outputs
for (auto& s : outputs)
network->markOutput(*blobNameToTensor->find(s.c_str()));
// Build the engine
builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize);
builder->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20);
builder->setHalf2Mode(fp16);
nvinfer1::ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildCudaEngine(*network);
CHECK(engine != nullptr);
// we don't need the network any more, and we can destroy the parser
network->destroy();
parser->destroy();
// serialize the engine, then close everything down
gieModelStream = engine->serialize();
engine->destroy();
builder->destroy();
nvcaffeparser1::shutdownProtobufLibrary();
}
int doInference(nvinfer1::IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize, const DATA_INFO& info)
{
const nvinfer1::ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine();
// input and output buffer pointers that we pass to the engine - the engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings(),
// of these, but in this case we know that there is exactly one input and one output.
CHECK(engine.getNbBindings() == 2);
void* buffers[2];
// In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors.
// note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings()
int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(std::get<3>(info).c_str()),
outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(std::get<4>(info).c_str());
// create GPU buffers and a stream
cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<0>(info) * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * std::get<2>(info) * sizeof(float));
cudaStream_t stream;
cudaStreamCreate(&stream);
// DMA the input to the GPU, execute the batch asynchronously, and DMA it back:
cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * std::get<1>(info) * std::get<0>(info) * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream);
context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr);
cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * std::get<2>(info)*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream);
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
// release the stream and the buffers
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]);
cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]);
return 0;
}
class FCPlugin: public nvinfer1::IPlugin
{
public:
FCPlugin(const nvinfer1::Weights* weights, int nbWeights, int nbOutputChannels) : mNbOutputChannels(nbOutputChannels)
{
// since we want to deal with the case where there is no bias, we can't infer
// the number of channels from the bias weights.
assert(nbWeights == 2);
mKernelWeights = copyToDevice(weights[0].values, weights[0].count);
mBiasWeights = copyToDevice(weights[1].values, weights[1].count);
assert(mBiasWeights.count == 0 || mBiasWeights.count == nbOutputChannels);
mNbInputChannels = int(weights[0].count / nbOutputChannels);
}
// create the plugin at runtime from a byte stream
FCPlugin(const void* data, size_t length)
{
const char* d = reinterpret_cast(data), *a = d;
mNbInputChannels = read(d);
mNbOutputChannels = read(d);
int biasCount = read(d);
mKernelWeights = deserializeToDevice(d, mNbInputChannels * mNbOutputChannels);
mBiasWeights = deserializeToDevice(d, biasCount);
assert(d == a + length);
}
~FCPlugin()
{
cudaFree(const_cast(mKernelWeights.values));
cudaFree(const_cast(mBiasWeights.values));
}
int getNbOutputs() const override
{
return 1;
}
nvinfer1::Dims getOutputDimensions(int index, const nvinfer1::Dims* inputs, int nbInputDims) override
{
assert(index == 0 && nbInputDims == 1 && inputs[0].nbDims == 3);
assert(mNbInputChannels == inputs[0].d[0] * inputs[0].d[1] * inputs[0].d[2]);
return nvinfer1::DimsCHW(mNbOutputChannels, 1, 1);
}
void configure(const nvinfer1::Dims* inputDims, int nbInputs, const nvinfer1::Dims* outputDims, int nbOutputs, int maxBatchSize) override
{
}
int initialize() override
{
cudnnCreate(&mCudnn); // initialize cudnn and cublas
cublasCreate(&mCublas);
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&mSrcDescriptor); // create cudnn tensor descriptors we need for bias addition
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&mDstDescriptor);
return 0;
}
virtual void terminate() override
{
cublasDestroy(mCublas);
cudnnDestroy(mCudnn);
}
virtual size_t getWorkspaceSize(int maxBatchSize) const override
{
return 0;
}
virtual int enqueue(int batchSize, const void*const * inputs, void** outputs, void* workspace, cudaStream_t stream) override
{
float kONE = 1.0f, kZERO = 0.0f;
cublasSetStream(mCublas, stream);
cudnnSetStream(mCudnn, stream);
cublasSgemm(mCublas, CUBLAS_OP_T, CUBLAS_OP_N, mNbOutputChannels, batchSize, mNbInputChannels, &kONE,
reinterpret_cast(mKernelWeights.values), mNbInputChannels,
reinterpret_cast(inputs[0]), mNbInputChannels, &kZERO,
reinterpret_cast(outputs[0]), mNbOutputChannels);
if (mBiasWeights.count) {
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(mSrcDescriptor, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, 1, mNbOutputChannels, 1, 1);
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(mDstDescriptor, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, batchSize, mNbOutputChannels, 1, 1);
cudnnAddTensor(mCudnn, &kONE, mSrcDescriptor, mBiasWeights.values, &kONE, mDstDescriptor, outputs[0]);
}
return 0;
}
virtual size_t getSerializationSize() override
{
// 3 integers (number of input channels, number of output channels, bias size), and then the weights:
return sizeof(int)*3 + mKernelWeights.count*sizeof(float) + mBiasWeights.count*sizeof(float);
}
virtual void serialize(void* buffer) override
{
char* d = reinterpret_cast(buffer), *a = d;
write(d, mNbInputChannels);
write(d, mNbOutputChannels);
write(d, (int)mBiasWeights.count);
serializeFromDevice(d, mKernelWeights);
serializeFromDevice(d, mBiasWeights);
assert(d == a + getSerializationSize());
}
private:
template void write(char*& buffer, const T& val)
{
*reinterpret_cast(buffer) = val;
buffer += sizeof(T);
}
template T read(const char*& buffer)
{
T val = *reinterpret_cast(buffer);
buffer += sizeof(T);
return val;
}
nvinfer1::Weights copyToDevice(const void* hostData, size_t count)
{
void* deviceData;
cudaMalloc(&deviceData, count * sizeof(float));
cudaMemcpy(deviceData, hostData, count * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
return nvinfer1::Weights{ nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, deviceData, int64_t(count) };
}
void serializeFromDevice(char*& hostBuffer, nvinfer1::Weights deviceWeights)
{
cudaMemcpy(hostBuffer, deviceWeights.values, deviceWeights.count * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
hostBuffer += deviceWeights.count * sizeof(float);
}
nvinfer1::Weights deserializeToDevice(const char*& hostBuffer, size_t count)
{
nvinfer1::Weights w = copyToDevice(hostBuffer, count);
hostBuffer += count * sizeof(float);
return w;
}
int mNbOutputChannels, mNbInputChannels;
cudnnHandle_t mCudnn;
cublasHandle_t mCublas;
nvinfer1::Weights mKernelWeights, mBiasWeights;
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t mSrcDescriptor, mDstDescriptor;
};
// integration for serialization
class PluginFactory : public nvinfer1::IPluginFactory, public nvcaffeparser1::IPluginFactory
{
public:
// caffe parser plugin implementation
bool isPlugin(const char* name) override
{
return !strcmp(name, "ip2");
}
virtual nvinfer1::IPlugin* createPlugin(const char* layerName, const nvinfer1::Weights* weights, int nbWeights) override
{
// there's no way to pass parameters through from the model definition, so we have to define it here explicitly
static const int NB_OUTPUT_CHANNELS = 10;
assert(isPlugin(layerName) && nbWeights == 2 && weights[0].type == nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT && weights[1].type == nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT);
assert(mPlugin.get() == nullptr);
mPlugin = std::unique_ptr(new FCPlugin(weights, nbWeights, NB_OUTPUT_CHANNELS));
return mPlugin.get();
}
// deserialization plugin implementation
nvinfer1::IPlugin* createPlugin(const char* layerName, const void* serialData, size_t serialLength) override
{
assert(isPlugin(layerName));
assert(mPlugin.get() == nullptr);
mPlugin = std::unique_ptr(new FCPlugin(serialData, serialLength));
return mPlugin.get();
}
// the application has to destroy the plugin when it knows it's safe to do so
void destroyPlugin()
{
mPlugin.release();
}
std::unique_ptr mPlugin{ nullptr };
};
} // namespace
int test_plugin()
{
// stuff we know about the network and the caffe input/output blobs
const DATA_INFO info(28, 28, 10, "data", "prob");
const std::string deploy_file {"models/mnist.prototxt"};
const std::string model_file {"models/mnist.caffemodel"};
const std::string mean_file {"models/mnist_mean.binaryproto"};
Logger logger; // multiple instances of IRuntime and/or IBuilder must all use the same logger
// create a GIE model from the caffe model and serialize it to a stream
PluginFactory pluginFactory;
nvinfer1::IHostMemory* gieModelStream{ nullptr };
caffeToGIEModel(deploy_file, model_file, std::vector{std::get<4>(info).c_str()}, 1, &pluginFactory, gieModelStream, logger);
pluginFactory.destroyPlugin();
nvcaffeparser1::ICaffeParser* parser = nvcaffeparser1::createCaffeParser();
nvcaffeparser1::IBinaryProtoBlob* meanBlob = parser->parseBinaryProto(mean_file.c_str());
parser->destroy();
// deserialize the engine
nvinfer1::IRuntime* runtime = nvinfer1::createInferRuntime(logger);
nvinfer1::ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(gieModelStream->data(), gieModelStream->size(), &pluginFactory);
nvinfer1::IExecutionContext *context = engine->createExecutionContext();
// parse the mean file and subtract it from the image
const float* meanData = reinterpret_cast(meanBlob->getData());
const std::string image_path{ "images/digit/" };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
const std::string image_name = image_path + std::to_string(i) + ".png";
cv::Mat mat = cv::imread(image_name, 0);
if (!mat.data) {
fprintf(stderr, "read image fail: %s\n", image_name.c_str());
return -1;
}
cv::resize(mat, mat, cv::Size(std::get<0>(info), std::get<1>(info)));
mat.convertTo(mat, CV_32FC1);
float data[std::get<1>(info)*std::get<0>(info)];
const float* p = (float*)mat.data;
for (int j = 0; j < std::get<1>(info)*std::get<0>(info); ++j) {
data[j] = p[j] - meanData[j];
}
// run inference
float prob[std::get<2>(info)];
doInference(*context, data, prob, 1, info);
float val{-1.f};
int idx{-1};
for (int t = 0; t < std::get<2>(info); ++t) {
if (val < prob[t]) {
val = prob[t];
idx = t;
}
}
fprintf(stdout, "expected value: %d, actual value: %d, probability: %f\n", i, idx, val);
}
meanBlob->destroy();
if (gieModelStream) gieModelStream->destroy();
// destroy the engine
context->destroy();
engine->destroy();
runtime->destroy();
pluginFactory.destroyPlugin();
return 0;
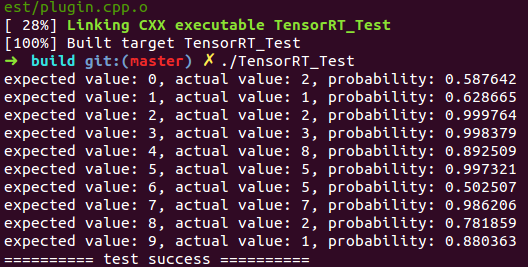
} 执行结果如下(与http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/78552908 中结果一致):
测试代码编译步骤如下(ReadMe.txt):
在Linux下通过CMake编译TensorRT_Test中的测试代码步骤:
1. 将终端定位到CUDA_Test/prj/linux_tensorrt_cmake,依次执行如下命令:
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make (生成TensorRT_Test执行文件)
$ ln -s ../../../test_data/models ./ (将models目录软链接到build目录下)
$ ln -s ../../../test_data/images ./ (将images目录软链接到build目录下)
$ ./TensorRT_Test
2. 对于有需要用OpenCV参与的读取图像的操作,需要先将对应文件中的图像路径修改为Linux支持的路径格式GitHub: https://github.com/fengbingchun/CUDA_Test