JAVA SE 8 学习笔记(五)并发增强
1.原子值
java5开始,提供了一些原子操作的类,如AtomicInteger、AtomicLong等
这些类提供了诸如incrementAndGet这样的原子操作方法。
单数如果想进行复杂操作,则需要使用compareAndSet进行循环处理
do {
// .. 计算
} while (!atomicLong.compareAndSet(old, new));
在java8中提供了updateAndGet和accumulateAndGet方法
atomicLong,updateAndGet(x -> Max.max(x, observed));
atomicLong.accumulateAndGet(observed, Math::max);
同时也提供了返回原始值的对应方法:getAndUpdate、getAndAccumulate
------------------------------------------------------
当大量线程访问同一个原始值时,由于乐观锁重试次数太多会导致性能下降
Java8为此提供了LongAdder和LongAccumulator解决该问题
其思想为将初始值变为多个中立元素,计算时不同线程可以对不同元素进行操作,最后再将操作结果合并。
例如:
LongAccumulator adder = new LongAccumulator (Long::sum, 0);
adder.accumulate(value);
此时在LongAccumulator 中包含多个中立元素a1,a2...aN.该例子下中立元素初始值都为零。当调用accumulate方法累加value时,这些变量的其中之一被更新为ai = ai op v。在这个实力中ai = ai + v;
而最后调用get方法的时候,结果为a1 op a2 op ... aN. 在上述例子中为a1+a2+...aN
------------------------------------------------------
java8中还添加了StampedLock类实现乐观读
调用tryOptimisticRead方法时会获取一个印戳,当读取值并检测印戳有效,则可以使用这个值,否则会获得一个阻塞所有写锁的读锁
例:
public class Vector {
private int size;
private Object[] elements;
private StampedLock lock = new StampedLock();
public Object get(int n) {
long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();
Object[] currentElements = elements;
int currentSize = size;
if (!lock.validate(stamp)) { // Someone else had a write lock
stamp = lock.readLock(); // Get a pessimistic lock
currentElements = elements;
currentSize = size;
lock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
return n < currentSize ? currentElements[n] : null;
}
...2.ConcurrentHashMap改进
1. 更新值
concurrentHashMap在更新数值的时候虽然是线程安全的,但是在计算更新值的时候由于不能保证线程安全,更新的值可能是错误的。
一种补救措施是使用replace
例:
do {
oldValue = map.get(word);
newValue = oldValue == null ? 1 : oldValue + 1;
} while (!map.replace(key, oldValue, newValue));map.putIfAbsent(word, new LongAdder());
map.get(word).increment();如果需要复杂计算,compute方法可以通过一个函数来计算新的值
map.compute(word, (k, v) -> v == null ? 1 : v + 1);xxxIfPresent和xxxIfAbsent方法分别表示已经存在值或者尚未存在值的情况下才进行操作
merge方法可以在key第一次加入时做一些特殊操作,第二个参数表示键尚未存在时的初始值
map.merge(word, 1L, (existingValue, newValue) -> existingValue + newValue);map.merge(word, 1L, Long::sum);
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
2. 批量数据操作
・search会对每个键值对领用一个函数,直到函数返回非null,search会终止并返回函数结果
・reduce会通过提供的累计函数,将所有键值对组合起来
・foreach会对所有键值对应用一个函数
每个操作都有4个版本:
• operation Keys : 对键操作
• operation Values : 对值操作
• operation: 对键和值操作
• operation Entries : 对 Map.Entry 对象操作.
以search为例,有以下几个方法:
U searchKeys(long threshold, BiFunction f)
U searchValues(long threshold, BiFunction f)
U search(long threshold, BiFunction f)
U searchEntries(long threshold, BiFunction
threshold为并行阀值,如果包含的元素数量超过阀值,操作会以并行方式执行,如果希望永远以单线程执行,请使用Long.MAX_VALUE
foreach和reduce方法除了上述形式外,还有另一种形式,可以提供一个转换器函数,首先会应用转换器函数,然后再将结果传递给消费者函数
map.forEach(threshold,
(k, v) -> k + " -> " + v, // Transformer
System.out::println); // ConsumerInteger maxlength = map.reduceKeys(threshold,
String::length, // Transformer
Integer::max); // Accumulator对于int、long和double,reduce操作提供了专门的方法。以toXXX开头,需要将输入值转换为原始类型值,并指定一个默认值和累加器函数
long sum = map.reduceValuesToLong(threshold,
Long::longValue, // Transformer to primitive type
0, // Default value for empty map
Long::sum); // Primitive type accumulator
3. Set视图
java8没有提供concurrenHashSet类,但是可以通过concurrentHashMap类通过虚假值获得一个映射
静态方法newKeySet会返回一个Set
Set words = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet(); 如果你已经有一个映射,keySet方法会返回所有键的Set,但是你不能向这个set中添加元素,因为无法向map添加相应的值
于是,一个接收默认值的keySet方法可以解决上述问题,通过这个默认值向set中添加元素
Set words = map.keySet(1L);
words.add("Java"); 3.并行数组操作
Arrays提供许多并行化操作
parallelSort可以进行并行排序,并且可以指定范围
String contents = new String(Files.readAllBytes(
Paths.get("alice.txt")), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // Read file into string
String[] words = contents.split("[\\P{L}]+"); // Split along nonletters
Arrays.parallelSort(words);values.parallelSort(values.length / 2, values.length); // 对上半部排序parallelSetAll方法会根据提供的 计算函数对参数values的每一个值进行计算并更新
Arrays.parallelSetAll(values, i -> i % 10);
// Fills values with 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 . . .parallelPrefix将数组中每个元素替换为指定关联操作前缀的积累
假设array [1, 2, 3, 4, ...],执行完Arrays.parallelPrefix(values, (x, y) -> x * y)之后,array的结果为
[1, 1 × 2, 1 × 2 × 3, 1 × 2 × 3 × 4, ...]
4.可完成的Future
在过去,Future获取结果的方法为get,并且调用后会一直阻塞等待get返回结果
CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture contents = readPage(url);
CompletableFuture> links = contents.thenApply(Parser::getLinks); Future流水线类似Steam流水线,经过一个或多个转换过程,最后由一个终止操作结束。
如下代码可以启动一个流水线
CompletableFuture contents
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> blockingReadPage(url)); 接下来可以调用thenApply或者thenApplyAsync方法,在同一个线程或者另一个线程中运行另一个操作。
最终这些步骤执行完毕,需要将结果保存在某个地方,需要一个终止操作,例如:
CompletableFuture links
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> blockingReadPage(url))
.thenApply(Parser::getLinks)
.thenAccept(System.out::println); thenAccept方法接收一个Consumer接口(返回类型为void),理想情况下不需要调用Future的get方法
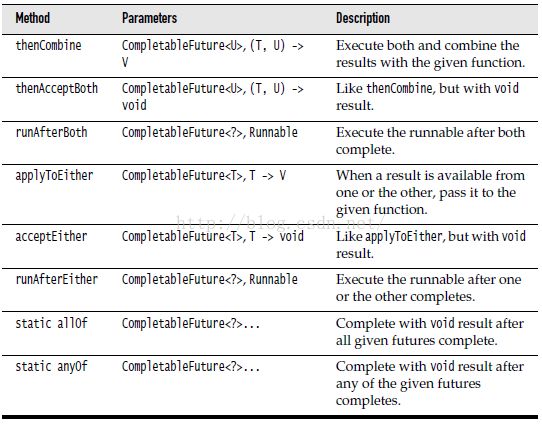
以下是一些常用方法:
thenCompose方法做的事就是,假设同时有两个调用链,T->CompletableFuture和U->CompletableFuture
类似的常用方法如下: