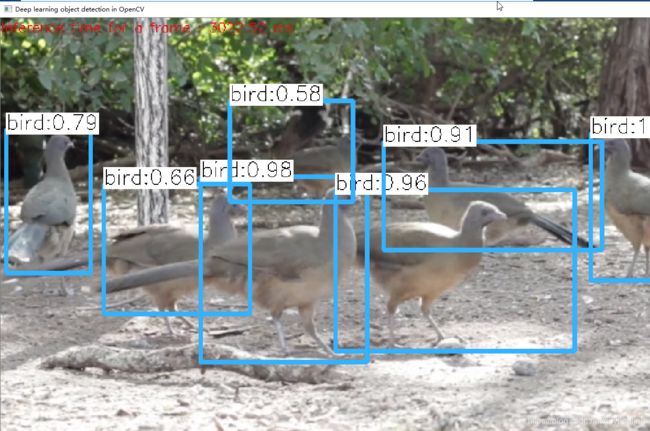
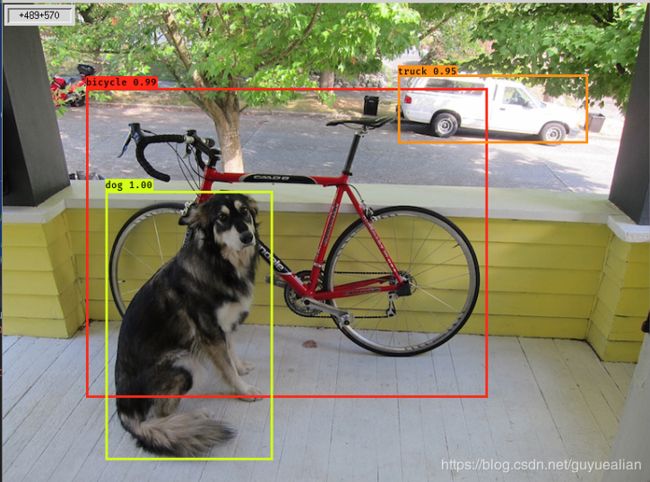
OpenCV+yolov3实现目标检测(C++,Python)
OpenCV+yolov3实现目标检测(C++,Python)
目标检测算法主要分为两类:一类是基于Region Proposal(候选区域)的算法,如R-CNN系算法(R-CNN,Fast R-CNN, Faster R-CNN),它们是two-stage(两步法)的,需要先使用Selective search或者CNN网络(RPN)产生Region Proposal,然后再在Region Proposal上做分类与回归。而另一类是Yolo,SSD这类one-stage算法(一步法),其仅仅使用一个CNN网络直接预测不同目标的类别与位置。第一类方法是准确度高一些,但是速度慢,而第二类算法是速度快,但是准确性要低一些。
YOLO是一种比SSD还要快的目标检测网络模型,作者在其论文中说FPS是Fast R-CNN的100倍,这里首先简单的介绍一下YOLO网络基本结构,然后通过OpenCV C++调用Darknet的,实现目标检测。OpenCV在3.3.1的版本中开始正式支持Darknet网络框架并且支持YOLO1与YOLO2以及YOLO Tiny网络模型的导入与使用。后面测试,OpenCV3.4.2也支持YOLO3 。另外,OpenCV dnn模块目前支持Caffe、TensorFlow、Torch、PyTorch等深度学习框架,关于《OpenCV调用TensorFlow预训练模型》可参考鄙人的另一份博客:https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/80570120
关于《OpenCV+yolov2-tiny实现目标检测(C++)》请参考我的另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/82950283
本博客源码都放在Github上:https://github.com/PanJinquan/opencv-learning-tutorials/tree/master/dnn_tutorial,麻烦给个“Star”哈
参考资料:
《Deep Learning based Object Detection using YOLOv3 with OpenCV ( Python / C++ )》:
官网博客:https://www.learnopencv.com/deep-learning-based-object-detection-using-yolov3-with-opencv-python-c/
《YOLOv3 + OpenCV 实现目标检测(Python / C ++)》:https://blog.csdn.net/haoqimao_hard/article/details/82081285
Github参考源码:https://github.com/spmallick/learnopencv/tree/master/ObjectDetection-YOLO
darknt yolo官网:https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/
目录
OpenCV+yolov3实现目标检测(C++,Python)
1、YOLO网络
(1)YOLO网络结构
2、OpenCV使用YOLO v3实现目标检测
2.1 C++代码
2.2 Python代码
3、YOLO的缺点
4、参考资料:
1、YOLOv3网络
相比YOLOv2和YOLOv1,YOLOv3最大的变化包括两点:使用残差模型和采用FPN架构。YOLOv3的特征提取器是一个残差模型,因为包含53个卷积层,所以称为Darknet-53,从网络结构上看,相比Darknet-19网络使用了残差单元,所以可以构建得更深。另外一个点是采用FPN架构(Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection)来实现多尺度检测
YOLOv3是到目前为止,速度和精度最均衡的目标检测网络。通过多种先进方法的融合,将YOLO系列的短板(速度很快,不擅长检测小物体等)全部补齐。
1.1 YOLOv3网络结构
参考资料:
《深入理解目标检测与YOLO(从v1到v3)》:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39521554/article/details/80694512
https://blog.csdn.net/leviopku/article/details/82660381
2、OpenCV使用YOLO v3实现目标检测
yolov3模型下载地址:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1TugNSWRZaJz1R6IejRtNiA 提取码: 46mh
2.1 C++代码
// This code is written at BigVision LLC. It is based on the OpenCV project.
//It is subject to the license terms in the LICENSE file found in this distribution and at http://opencv.org/license.html
// Usage example: ./object_detection_yolo.out --video=run.mp4
// ./object_detection_yolo.out --image=bird.jpg
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
;
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn;
using namespace std;
string pro_dir = "E:/opencv-learning-tutorials/"; //项目根目录
// Initialize the parameters
float confThreshold = 0.5; // Confidence threshold
float nmsThreshold = 0.4; // Non-maximum suppression threshold
int inpWidth = 416; // Width of network's input image
int inpHeight = 416; // Height of network's input image
vector classes;
// Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence using non-maxima suppression
void postprocess(Mat& frame, const vector& out);
// Draw the predicted bounding box
void drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat& frame);
// Get the names of the output layers
vector getOutputsNames(const Net& net);
void detect_image(string image_path, string modelWeights, string modelConfiguration, string classesFile);
void detect_video(string video_path, string modelWeights, string modelConfiguration, string classesFile);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// Give the configuration and weight files for the model
String modelConfiguration = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov3/yolov3.cfg";
String modelWeights = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov3/yolov3.weights";
string image_path = pro_dir + "data/images/bird.jpg";
string classesFile = pro_dir + "data/models/yolov3/coco.names";// "coco.names";
//detect_image(image_path, modelWeights, modelConfiguration, classesFile);
string video_path = pro_dir + "data/images/run.mp4";
detect_video(video_path, modelWeights, modelConfiguration, classesFile);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void detect_image(string image_path, string modelWeights, string modelConfiguration, string classesFile) {
// Load names of classes
ifstream ifs(classesFile.c_str());
string line;
while (getline(ifs, line)) classes.push_back(line);
// Load the network
Net net = readNetFromDarknet(modelConfiguration, modelWeights);
net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_OPENCL);
// Open a video file or an image file or a camera stream.
string str, outputFile;
cv::Mat frame = cv::imread(image_path);
// Create a window
static const string kWinName = "Deep learning object detection in OpenCV";
namedWindow(kWinName, WINDOW_NORMAL);
// Stop the program if reached end of video
// Create a 4D blob from a frame.
Mat blob;
blobFromImage(frame, blob, 1 / 255.0, cvSize(inpWidth, inpHeight), Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
//Sets the input to the network
net.setInput(blob);
// Runs the forward pass to get output of the output layers
vector outs;
net.forward(outs, getOutputsNames(net));
// Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence
postprocess(frame, outs);
// Put efficiency information. The function getPerfProfile returns the overall time for inference(t) and the timings for each of the layers(in layersTimes)
vector layersTimes;
double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000;
double t = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimes) / freq;
string label = format("Inference time for a frame : %.2f ms", t);
putText(frame, label, Point(0, 15), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
// Write the frame with the detection boxes
imshow(kWinName, frame);
cv::waitKey(30);
}
void detect_video(string video_path, string modelWeights, string modelConfiguration, string classesFile) {
string outputFile = "./yolo_out_cpp.avi";;
// Load names of classes
ifstream ifs(classesFile.c_str());
string line;
while (getline(ifs, line)) classes.push_back(line);
// Load the network
Net net = readNetFromDarknet(modelConfiguration, modelWeights);
net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CPU);
// Open a video file or an image file or a camera stream.
VideoCapture cap;
//VideoWriter video;
Mat frame, blob;
try {
// Open the video file
ifstream ifile(video_path);
if (!ifile) throw("error");
cap.open(video_path);
}
catch (...) {
cout << "Could not open the input image/video stream" << endl;
return ;
}
// Get the video writer initialized to save the output video
//video.open(outputFile,
// VideoWriter::fourcc('M', 'J', 'P', 'G'),
// 28,
// Size(cap.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH), cap.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)));
// Create a window
static const string kWinName = "Deep learning object detection in OpenCV";
namedWindow(kWinName, WINDOW_NORMAL);
// Process frames.
while (waitKey(1) < 0)
{
// get frame from the video
cap >> frame;
// Stop the program if reached end of video
if (frame.empty()) {
cout << "Done processing !!!" << endl;
cout << "Output file is stored as " << outputFile << endl;
waitKey(3000);
break;
}
// Create a 4D blob from a frame.
blobFromImage(frame, blob, 1 / 255.0, cvSize(inpWidth, inpHeight), Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false);
//Sets the input to the network
net.setInput(blob);
// Runs the forward pass to get output of the output layers
vector outs;
net.forward(outs, getOutputsNames(net));
// Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence
postprocess(frame, outs);
// Put efficiency information. The function getPerfProfile returns the overall time for inference(t) and the timings for each of the layers(in layersTimes)
vector layersTimes;
double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000;
double t = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimes) / freq;
string label = format("Inference time for a frame : %.2f ms", t);
putText(frame, label, Point(0, 15), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
// Write the frame with the detection boxes
Mat detectedFrame;
frame.convertTo(detectedFrame, CV_8U);
//video.write(detectedFrame);
imshow(kWinName, frame);
}
cap.release();
//video.release();
}
// Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence using non-maxima suppression
void postprocess(Mat& frame, const vector& outs)
{
vector classIds;
vector confidences;
vector boxes;
for (size_t i = 0; i < outs.size(); ++i)
{
// Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the
// ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class
// with the highest score for the box.
float* data = (float*)outs[i].data;
for (int j = 0; j < outs[i].rows; ++j, data += outs[i].cols)
{
Mat scores = outs[i].row(j).colRange(5, outs[i].cols);
Point classIdPoint;
double confidence;
// Get the value and location of the maximum score
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &confidence, 0, &classIdPoint);
if (confidence > confThreshold)
{
int centerX = (int)(data[0] * frame.cols);
int centerY = (int)(data[1] * frame.rows);
int width = (int)(data[2] * frame.cols);
int height = (int)(data[3] * frame.rows);
int left = centerX - width / 2;
int top = centerY - height / 2;
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back((float)confidence);
boxes.push_back(Rect(left, top, width, height));
}
}
}
// Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
// lower confidences
vector indices;
NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices);
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = indices[i];
Rect box = boxes[idx];
drawPred(classIds[idx], confidences[idx], box.x, box.y,
box.x + box.width, box.y + box.height, frame);
}
}
// Draw the predicted bounding box
void drawPred(int classId, float conf, int left, int top, int right, int bottom, Mat& frame)
{
//Draw a rectangle displaying the bounding box
rectangle(frame, Point(left, top), Point(right, bottom), Scalar(255, 178, 50), 3);
//Get the label for the class name and its confidence
string label = format("%.2f", conf);
if (!classes.empty())
{
CV_Assert(classId < (int)classes.size());
label = classes[classId] + ":" + label;
}
//Display the label at the top of the bounding box
int baseLine;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
top = max(top, labelSize.height);
rectangle(frame, Point(left, top - round(1.5*labelSize.height)), Point(left + round(1.5*labelSize.width), top + baseLine), Scalar(255, 255, 255), FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(left, top), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 0, 0), 1);
}
// Get the names of the output layers
vector getOutputsNames(const Net& net)
{
static vector names;
if (names.empty())
{
//Get the indices of the output layers, i.e. the layers with unconnected outputs
vector outLayers = net.getUnconnectedOutLayers();
//get the names of all the layers in the network
vector layersNames = net.getLayerNames();
// Get the names of the output layers in names
names.resize(outLayers.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < outLayers.size(); ++i)
names[i] = layersNames[outLayers[i] - 1];
}
return names;
} 2.2 Python代码
使用cv_dnn_forward获得预测输出outs是三个二维的数组,每个二维数组是一个feature_map的输出结果,feature_map中每一行是一个预测值:
outs:[507*85 =13*13*3*(5+80),
2028*85=26*26*3*(5+80),
8112*85=52*52*3*(5+80)]每一个行:85=[x,y,w,h,confs,class_probs_0,class_probs_1,..,class_probs_78,class_probs_79]
# -*-coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project: tensorflow-yolov3
@File : opencv_dnn_yolov3.py
@Author : panjq
@E-mail : [email protected]
@Date : 2019-01-28 14:36:00
"""
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def read_class(file):
with open(file, 'rt') as f:
classes = f.read().rstrip('\n').split('\n')
return classes
class cv_yolov3(object):
def __init__(self,class_path,net_width,net_height,confThreshold,nmsThreshold):
'''
Initialize the parameters
:param class_path:
:param net_width: default 416, Width of network's input image
:param net_height: default 416,Height of network's input image
:param confThreshold: default 0.5, Confidence threshold
:param nmsThreshold: default 0.5,Non-maximum suppression threshold
'''
self.classes = read_class(class_path)
self.net_width=net_width
self.net_height=net_height
self.confThreshold=confThreshold
self.nmsThreshold=nmsThreshold
def cv_dnn_init(self,modelConfiguration,modelWeights):
'''
Give the configuration and weight files for the model and load the network using them.
eg:
modelConfiguration = "checkpoint-bk/yolov3.cfg";
modelWeights = "checkpoint-bk/yolov3.weights";
:param modelConfiguration:
:param modelWeights:
:return:
'''
self.net = cv.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(modelConfiguration, modelWeights)
self.net.setPreferableBackend(cv.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
self.net.setPreferableTarget(cv.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
def getOutputsNames(self,net):
'''
Get the names of the output layers
:param net:
:return:
'''
# Get the names of all the layers in the network
layersNames = net.getLayerNames()
# Get the names of the output layers, i.e. the layers with unconnected outputs
return [layersNames[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
def drawPred(self,frame,classes,classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):
'''
Draw the predicted bounding box
:param frame:
:param classes:
:param classId:
:param conf:
:param left:
:param top:
:param right:
:param bottom:
:return:
'''
# Draw a bounding box.
cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (255, 178, 50), 3)
label = '%.2f' % conf
# Get the label for the class name and its confidence
if classes:
assert (classId < len(classes))
label = '%s:%s' % (classes[classId], label)
# Display the label at the top of the bounding box
labelSize, baseLine = cv.getTextSize(label, cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
top = max(top, labelSize[1])
cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize[1])), (left + round(1.5 * labelSize[0]), top + baseLine),
(255, 255, 255), cv.FILLED)
cv.putText(frame, label, (left, top), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (0, 0, 0), 1)
def postprocess(self,frame, classes,outs):
'''
Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence using non-maxima suppression
:param frame:
:param classes:
:return: outs:[507*85 =(13*13*3)*(5+80),
2028*85=(26*26*3)*(5+80),
8112*85=(52*52*3)*(5+80)]
outs中每一行是一个预测值:[x,y,w,h,confs,class_probs_0,class_probs_1,..,class_probs_78,class_probs_79]
:return:
'''
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
# Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the
# ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class with the highest score.
classIds = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for out in outs:
for detection in out:
scores = detection[5:]
classId = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classId]
if confidence > self.confThreshold:
center_x = int(detection[0] * frameWidth)
center_y = int(detection[1] * frameHeight)
width = int(detection[2] * frameWidth)
height = int(detection[3] * frameHeight)
left = int(center_x - width / 2)
top = int(center_y - height / 2)
classIds.append(classId)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
# Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
# lower confidences.
indices = cv.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold)
for i in indices:
i = i[0]
box = boxes[i]
left = box[0]
top = box[1]
width = box[2]
height = box[3]
self.drawPred(frame,classes,classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)
def cv_dnn_forward(self,frame):
'''
:param frame:
:return: outs:[507*85 =13*13*3*(5+80),
2028*85=26*26*3*(5+80),
8112*85=52*52*3*(5+80)]
'''
# Create a 4D blob from a frame.
blob = cv.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255, (self.net_width, self.net_height), [0, 0, 0], 1, crop=False)
# Sets the input to the network
self.net.setInput(blob)
# Runs the forward pass to get output of the output layers
outs = self.net.forward(self.getOutputsNames(self.net))
# Put efficiency information. The function getPerfProfile returns the overall time for inference(t) and the timings for each of the layers(in layersTimes)
runtime, _ = self.net.getPerfProfile()
return outs,runtime
def yolov3_predict(self,image_path):
'''
:param image_path:
:return:
'''
# Process inputs
winName = 'Deep learning object detection in OpenCV'
cv.namedWindow(winName, cv.WINDOW_NORMAL)
frame=cv.imread(image_path)
outs,runtime=self.cv_dnn_forward(frame)
# Remove the bounding boxes with low confidence
self.postprocess(frame, self.classes, outs)
label = 'Inference time: %.2f ms' % (runtime * 1000.0 / cv.getTickFrequency())
cv.putText(frame, label, (0, 15), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255))
cv.imshow(winName, frame)
cv.waitKey(0)
if __name__=="__main__":
confThreshold = 0.5 # Confidence threshold
nmsThreshold = 0.5 # Non-maximum suppression threshold
net_input_width = 416 # Width of network's input image
net_input_height = 416 # Height of network's input image
image_path = "./data/demo_data/dog.jpg"
# anchors_path = './data/coco_anchors.txt'
classesFile = './data/coco.names'
modelConfiguration = "model/yolov3.cfg";
modelWeights = "model/yolov3.weights";
cv_model=cv_yolov3(classesFile,net_input_width,net_input_height,confThreshold,nmsThreshold)
cv_model.cv_dnn_init(modelConfiguration,modelWeights)
cv_model.yolov3_predict(image_path)
3、YOLO的缺点
- YOLO对相互靠的很近的物体,还有很小的群体 检测效果不好,这是因为一个网格中只预测了两个框,并且只属于一类。
- 对测试图像中,同一类物体出现的新的不常见的长宽比和其他情况是。泛化能力偏弱。
- 由于损失函数的问题,定位误差是影响检测效果的主要原因。尤其是大小物体的处理上,还有待加强。
4、参考资料:
[1].《论文阅读笔记:You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection》https://blog.csdn.net/tangwei2014/article/details/50915317
[2]. https://blog.csdn.net/xiaohu2022/article/details/79211732
[3]. https://blog.csdn.net/u014380165/article/details/72616238