Android N的Audio系统(五)
- AudioFlinger 回放录制线程
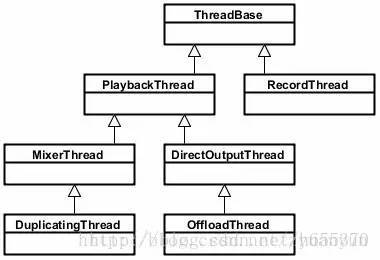
AndioFlinger 作为 Android 的音频系统引擎,重任之一是负责输入输出流设备的管理及音频流数据的处理传输,这是由回放线程(PlaybackThread 及其派生的子类)和录制线程(RecordThread)进行的,我们简单看看回放线程和录制线程类关系:
ThreadBase:PlaybackThread 和 RecordThread 的基类
RecordThread:录制线程类,由 ThreadBase 派生
PlaybackThread:回放线程基类,同由 ThreadBase 派生
MixerThread:混音回放线程类,由 PlaybackThread 派生,负责处理标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY、AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_FAST、AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DEEP_BUFFER 的音频流,MixerThread 可以把多个音轨的数据混音后再输出
DirectOutputThread:直输回放线程类,由 PlaybackThread 派生,负责处理标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT 的音频流,这种音频流数据不需要软件混音,直接输出到音频设备即可
DuplicatingThread:复制回放线程类,由 MixerThread 派生,负责复制音频流数据到其他输出设备,使用场景如主声卡设备、蓝牙耳机设备、USB 声卡设备同时输出
OffloadThread:硬解回放线程类,由 DirectOutputThread 派生,负责处理标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD 的音频流,这种音频流未经软件解码的(一般是 MP3、AAC 等格式的数据),需要输出到硬件解码器,由硬件解码器解码成 PCM 数据
PlaybackThread 中有个极为重要的函数 threadLoop(),当 PlaybackThread 被强引用时,threadLoop() 会真正运行起来进入循环主体,处理音频流数据相关事务,threadLoop() 大致流程如下(以 MixerThread 为例):
bool AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::threadLoop()
{
Vector< spthreadLoop() 循环的条件是 exitPending() 返回 false,如果想要 PlaybackThread 结束循环,则可以调用 requestExit() 来请求退出;
processConfigEvents_l() :处理配置事件;当有配置改变的事件发生时,需要调用 sendConfigEvent_l() 来通知 PlaybackThread,这样 PlaybackThread 才能及时处理配置事件;常见的配置事件是切换音频通路;
检查此时此刻是否符合 standby 条件,比如当前并没有 ACTIVE 状态的 Track(mActiveTracks.size() = 0),那么调用 threadLoop_standby() 关闭音频硬件设备以节省能耗;
prepareTracks_l(): 准备音频流和混音器,该函数非常复杂,这里不详细分析了,仅列一下流程要点:
遍历 mActiveTracks,逐个处理 mActiveTracks 上的 Track,检查该 Track 是否为 ACTIVE 状态;
如果 Track 设置是 ACTIVE 状态,则再检查该 Track 的数据是否准备就绪了;
根据音频流的音量值、格式、声道数、音轨的采样率、硬件设备的采样率,配置好混音器参数;
如果 Track 的状态是 PAUSED 或 STOPPED,则把该 Track 添加到 tracksToRemove 向量中;
threadLoop_mix():读取所有置了 ACTIVE 状态的音频流数据,混音器开始处理这些数据;
threadLoop_write(): 把混音器处理后的数据写到输出流设备;
threadLoop_removeTracks(): 把 tracksToRemove 上的所有 Track 从 mActiveTracks 中移除出来;这样下一次循环时就不会处理这些 Track 了。
这里说说 PlaybackThread 与输出流设备的关系:PlaybackThread 实例与输出流设备是一一对应的,比方说 OffloadThread 只会将音频数据输出到 compress_offload 设备中,MixerThread(with FastMixer) 只会将音频数据输出到 low_latency 设备中。
从 Audio HAL 中,我们通常看到如下 4 种输出流设备,分别对应着不同的播放场景:
primary_out:主输出流设备,用于铃声类声音输出,对应着标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY 的音频流和一个 MixerThread 回放线程实例
low_latency:低延迟输出流设备,用于按键音、游戏背景音等对时延要求高的声音输出,对应着标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_FAST 的音频流和一个 MixerThread 回放线程实例
deep_buffer:音乐音轨输出流设备,用于音乐等对时延要求不高的声音输出,对应着标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DEEP_BUFFER 的音频流和一个 MixerThread 回放线程实例
compress_offload:硬解输出流设备,用于需要硬件解码的数据输出,对应着标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD 的音频流和一个 OffloadThread 回放线程实例
其中 primary_out 设备是必须声明支持的,而且系统启动时就已经打开 primary_out 设备并创建好对应的 MixerThread 实例。其他类型的输出流设备并非必须声明支持的,主要是看硬件上有无这个能力。
可能有人产生这样的疑问:既然 primary_out 设备一直保持打开,那么能耗岂不是很大?这里阐释一个概念:输出流设备属于逻辑设备,并不是硬件设备。所以即使输出流设备一直保持打开,只要硬件设备不工作,那么就不会影响能耗。那么硬件设备什么时候才会打开呢?答案是 PlaybackThread 将音频数据写入到输出流设备时。
下图简单描述 AudioTrack、PlaybackThread、输出流设备三者的对应关系:
我们可以这么说:输出流设备决定了它对应的 PlaybackThread 是什么类型。怎么理解呢?意思是说:只有支持了该类型的输出流设备,那么该类型的 PlaybackThread 才有可能被创建。举个例子:只有硬件上具备硬件解码器,系统才建立 compress_offload 设备,然后播放 mp3 格式的音乐文件时,才会创建 OffloadThread 把数据输出到 compress_offload 设备上;反之,如果硬件上并不具备硬件解码器,系统则不应该建立 compress_offload 设备,那么播放 mp3 格式的音乐文件时,通过 MixerThread 把数据输出到其他输出流设备上。
那么有无可能出现这种情况:底层并不支持 compress_offload 设备,但偏偏有个标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD 的音频流送到 AudioFlinger 了呢?这是不可能的。系统启动时,会检查并保存输入输出流设备的支持信息;播放器在播放 mp3 文件时,首先看 compress_offload 设备是否支持了,如果支持,那么不进行软件解码,直接把数据标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD;如果不支持,那么先进行软件解码,然后把解码好的数据标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DEEP_BUFFER,前提是 deep_buffer 设备是支持了的;如果 deep_buffer 设备也不支持,那么把数据标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY。
系统启动时,就已经打开 primary_out、low_latency、deep_buffer 这三种输出流设备,并创建对应的 MixerThread 了;而此时 DirectOutputThread 与 OffloadThread 不会被创建,直到标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT/AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD 的音频流需要输出时,才开始创建 DirectOutputThread/OffloadThread 和打开 direct_out/compress_offload 设备。这一点请参考如下代码,注释非常清晰:
AudioPolicyManager::AudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface)
:
#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
Thread(false),
#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
mLimitRingtoneVolume(false), mLastVoiceVolume(-1.0f),
mA2dpSuspended(false),
mAudioPortGeneration(1),
mBeaconMuteRefCount(0),
mBeaconPlayingRefCount(0),
mBeaconMuted(false),
mTtsOutputAvailable(false),
mMasterMono(false)
{
mUidCached = getuid();
mpClientInterface = clientInterface;
// TODO: remove when legacy conf file is removed. true on devices that use DRC on the
// DEVICE_CATEGORY_SPEAKER path to boost soft sounds, used to adjust volume curves accordingly.
// Note: remove also speaker_drc_enabled from global configuration of XML config file.
bool speakerDrcEnabled = false;
#ifdef USE_XML_AUDIO_POLICY_CONF
mVolumeCurves = new VolumeCurvesCollection();
AudioPolicyConfig config(mHwModules, mAvailableOutputDevices, mAvailableInputDevices,
mDefaultOutputDevice, speakerDrcEnabled,
static_cast<VolumeCurvesCollection *>(mVolumeCurves));
PolicySerializer serializer;
if (serializer.deserialize(AUDIO_POLICY_XML_CONFIG_FILE, config) != NO_ERROR) {
#else
mVolumeCurves = new StreamDescriptorCollection();
AudioPolicyConfig config(mHwModules, mAvailableOutputDevices, mAvailableInputDevices,
mDefaultOutputDevice, speakerDrcEnabled);
if ((ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_VENDOR_CONFIG_FILE, config) != NO_ERROR) &&
(ConfigParsingUtils::loadConfig(AUDIO_POLICY_CONFIG_FILE, config) != NO_ERROR)) {
#endif
ALOGE("could not load audio policy configuration file, setting defaults");
config.setDefault();
}
// must be done after reading the policy (since conditionned by Speaker Drc Enabling)
mVolumeCurves->initializeVolumeCurves(speakerDrcEnabled);
// Once policy config has been parsed, retrieve an instance of the engine and initialize it.
audio_policy::EngineInstance *engineInstance = audio_policy::EngineInstance::getInstance();
if (!engineInstance) {
ALOGE("%s: Could not get an instance of policy engine", __FUNCTION__);
return;
}
// Retrieve the Policy Manager Interface
mEngine = engineInstance->queryInterface<AudioPolicyManagerInterface>();
if (mEngine == NULL) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to get Policy Engine Interface", __FUNCTION__);
return;
}
mEngine->setObserver(this);
status_t status = mEngine->initCheck();
(void) status;
ALOG_ASSERT(status == NO_ERROR, "Policy engine not initialized(err=%d)", status);
// mAvailableOutputDevices and mAvailableInputDevices now contain all attached devices
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
audio_devices_t outputDeviceTypes = mAvailableOutputDevices.types();
audio_devices_t inputDeviceTypes = mAvailableInputDevices.types() & ~AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN;
for (size_t i = 0; i < mHwModules.size(); i++) {
mHwModules[i]->mHandle = mpClientInterface->loadHwModule(mHwModules[i]->getName());
if (mHwModules[i]->mHandle == 0) {
ALOGW("could not open HW module %s", mHwModules[i]->getName());
continue;
}
// open all output streams needed to access attached devices
// except for direct output streams that are only opened when they are actually
// required by an app.
// This also validates mAvailableOutputDevices list
for (size_t j = 0; j < mHwModules[i]->mOutputProfiles.size(); j++)
{
const sp<IOProfile> outProfile = mHwModules[i]->mOutputProfiles[j];
if (!outProfile->hasSupportedDevices()) {
ALOGW("Output profile contains no device on module %s", mHwModules[i]->getName());
continue;
}
if ((outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_TTS) != 0) {
mTtsOutputAvailable = true;
}
if ((outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT) != 0) {
continue;
}
audio_devices_t profileType = outProfile->getSupportedDevicesType();
if ((profileType & mDefaultOutputDevice->type()) != AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {
profileType = mDefaultOutputDevice->type();
} else {
// chose first device present in profile's SupportedDevices also part of
// outputDeviceTypes
profileType = outProfile->getSupportedDeviceForType(outputDeviceTypes);
}
if ((profileType & outputDeviceTypes) == 0) {
continue;
}
sp<SwAudioOutputDescriptor> outputDesc = new SwAudioOutputDescriptor(outProfile,
mpClientInterface);
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = outProfile->getSupportedDevices();
const DeviceVector &devicesForType = supportedDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
String8 address = devicesForType.size() > 0 ? devicesForType.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
outputDesc->mDevice = profileType;
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
config.sample_rate = outputDesc->mSamplingRate;
config.channel_mask = outputDesc->mChannelMask;
config.format = outputDesc->mFormat;
audio_io_handle_t output = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
status_t status = mpClientInterface->openOutput(outProfile->getModuleHandle(),
&output,
&config,
&outputDesc->mDevice,
address,
&outputDesc->mLatency,
outputDesc->mFlags);
if (status != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGW("Cannot open output stream for device %08x on hw module %s",
outputDesc->mDevice,
mHwModules[i]->getName());
} else {
outputDesc->mSamplingRate = config.sample_rate;
outputDesc->mChannelMask = config.channel_mask;
outputDesc->mFormat = config.format;
for (size_t k = 0; k < supportedDevices.size(); k++) {
ssize_t index = mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(supportedDevices[k]);
// give a valid ID to an attached device once confirmed it is reachable
if (index >= 0 && !mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->isAttached()) {
mAvailableOutputDevices[index]->attach(mHwModules[i]);
}
}
if (mPrimaryOutput == 0 &&
outProfile->getFlags() & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY) {
mPrimaryOutput = outputDesc;
}
addOutput(output, outputDesc);
setOutputDevice(outputDesc,
outputDesc->mDevice,
true,
0,
NULL,
address.string());
}
}
// open input streams needed to access attached devices to validate
// mAvailableInputDevices list
for (size_t j = 0; j < mHwModules[i]->mInputProfiles.size(); j++)
{
const sp<IOProfile> inProfile = mHwModules[i]->mInputProfiles[j];
if (!inProfile->hasSupportedDevices()) {
ALOGW("Input profile contains no device on module %s", mHwModules[i]->getName());
continue;
}
// chose first device present in profile's SupportedDevices also part of
// inputDeviceTypes
audio_devices_t profileType = inProfile->getSupportedDeviceForType(inputDeviceTypes);
if ((profileType & inputDeviceTypes) == 0) {
continue;
}
sp<AudioInputDescriptor> inputDesc =
new AudioInputDescriptor(inProfile);
inputDesc->mDevice = profileType;
// find the address
DeviceVector inputDevices = mAvailableInputDevices.getDevicesFromType(profileType);
// the inputs vector must be of size 1, but we don't want to crash here
String8 address = inputDevices.size() > 0 ? inputDevices.itemAt(0)->mAddress
: String8("");
ALOGV(" for input device 0x%x using address %s", profileType, address.string());
ALOGE_IF(inputDevices.size() == 0, "Input device list is empty!");
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
config.sample_rate = inputDesc->mSamplingRate;
config.channel_mask = inputDesc->mChannelMask;
config.format = inputDesc->mFormat;
audio_io_handle_t input = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
status_t status = mpClientInterface->openInput(inProfile->getModuleHandle(),
&input,
&config,
&inputDesc->mDevice,
address,
AUDIO_SOURCE_MIC,
AUDIO_INPUT_FLAG_NONE);
if (status == NO_ERROR) {
const DeviceVector &supportedDevices = inProfile->getSupportedDevices();
for (size_t k = 0; k < supportedDevices.size(); k++) {
ssize_t index = mAvailableInputDevices.indexOf(supportedDevices[k]);
// give a valid ID to an attached device once confirmed it is reachable
if (index >= 0) {
sp<DeviceDescriptor> devDesc = mAvailableInputDevices[index];
if (!devDesc->isAttached()) {
devDesc->attach(mHwModules[i]);
devDesc->importAudioPort(inProfile);
}
}
}
mpClientInterface->closeInput(input);
} else {
ALOGW("Cannot open input stream for device %08x on hw module %s",
inputDesc->mDevice,
mHwModules[i]->getName());
}
}
}
// make sure all attached devices have been allocated a unique ID
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableOutputDevices.size();) {
if (!mAvailableOutputDevices[i]->isAttached()) {
ALOGW("Output device %08x unreachable", mAvailableOutputDevices[i]->type());
mAvailableOutputDevices.remove(mAvailableOutputDevices[i]);
continue;
}
// The device is now validated and can be appended to the available devices of the engine
mEngine->setDeviceConnectionState(mAvailableOutputDevices[i],
AUDIO_POLICY_DEVICE_STATE_AVAILABLE);
i++;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < mAvailableInputDevices.size();) {
if (!mAvailableInputDevices[i]->isAttached()) {
ALOGW("Input device %08x unreachable", mAvailableInputDevices[i]->type());
mAvailableInputDevices.remove(mAvailableInputDevices[i]);
continue;
}
// The device is now validated and can be appended to the available devices of the engine
mEngine->setDeviceConnectionState(mAvailableInputDevices[i],
AUDIO_POLICY_DEVICE_STATE_AVAILABLE);
i++;
}
// make sure default device is reachable
if (mDefaultOutputDevice == 0 || mAvailableOutputDevices.indexOf(mDefaultOutputDevice) < 0) {
ALOGE("Default device %08x is unreachable", mDefaultOutputDevice->type());
}
ALOGE_IF((mPrimaryOutput == 0), "Failed to open primary output");
updateDevicesAndOutputs();
#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
if (mPrimaryOutput != 0) {
AudioParameter outputCmd = AudioParameter();
outputCmd.addInt(String8("set_id"), 0);
mpClientInterface->setParameters(mPrimaryOutput->mIoHandle, outputCmd.toString());
mTestDevice = AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER;
mTestSamplingRate = 44100;
mTestFormat = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT;
mTestChannels = AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO;
mTestLatencyMs = 0;
mCurOutput = 0;
mDirectOutput = false;
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_TEST_OUTPUTS; i++) {
mTestOutputs[i] = 0;
}
const size_t SIZE = 256;
char buffer[SIZE];
snprintf(buffer, SIZE, "AudioPolicyManagerTest");
run(buffer, ANDROID_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST
}其中 mpClientInterface->openOutput() 最终会调用到 AudioFlinger::openOutput():打开输出流设备,并创建 PlaybackThread 对象:
AudioFlinger OffloadThread
系统启动时,就已经打开 primary_out、low_latency、deep_buffer 这三种输出流设备,并创建对应的 MixerThread 了;而此时 DirectOutputThread 与 OffloadThread 不会被创建,直到标识为 AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT/AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD 的音频流需要输出时,才开始创建 DirectOutputThread/OffloadThread 和打开 direct_out/compress_offload 设备。
这里不知大家有无疑问:为什么 DirectOutputThread 与 OffloadThread 会被单独对待?DirectOuputThread 使用率较低,尚可以理解,但 OffloadThread 的使用率还是很高的,为什么不让 OffloadThread/compress_offload 设备也进入待命状态呢?
要回答这个问题:我们首先得明白 compress_offload 设备是什么东东,与其他输出流设备有什么不同。先看个图:
红色的是 Offload 音频流,它与其他音频流有什么本质的不同?Offload 音频流是未经 NuPlayerDecoder 进行解码的(NuPlayerDecoder 设置了 Passthrough 模式),所以必须把这些音频流数据送到 DSP,让 DSP 对其解码,解码后的 PCM 数据再送到 Codec 输出。
compress_offload 设备,说白了,就是驱动 DSP 解码数据、Codec 输出声音。 而 DSP 要解码数据,首先得知道数据的编码信息,如编码器 codec_id、采样率 sample_rate、声道数 channel_mask、比特率 bit_rate 等信息,由于 DSP 并没有实现 DataSource/Parser 部件,不能自己解析数据的编码信息,所以得有“人”告诉它,这个“人”无疑是 compress_offload 设备。
AudioTrack 构造函数有个 offloadInfo 的参数,参数原型定义如下:
NuPlayer DataSource/Parser 解析 mp3、flac 等文件得到数据编码信息,并在构造 AudioTrack 实例时作为参数传入,AudioFlinger 将基于这些编码信息打开 compress_offload 设备。
到这里,大家明白了吗?每个 mp3/flac 文件的编码信息可能是不一样的,比如 a.mp3 文件的编码信息是 mp3&44.1KHZ&16bit… ,而 b.flac 文件的编码信息是 flac&48KHz&24bit…; 播放 a.mp3 时,AudioFlinger 打开一个配置为 mp3&44.1KHz&16bit… 的 compress_offload 设备,接着播放 b.flac,就需要关闭之前的 compress_offload 设备,重新打开一个配置为 flac&48KHz&24bit… 的 compress_offload 设备。所以系统不会提前打开 compress_offload 设备,只有等到播放 mp3、flac 时取到明确的数据编码信息,才基于这些编码信息打开 compress_offload 设备。
编码信息包含很多条目,切换音源时,是否编码信息有一点点不一样,都需要重新打开 compress_offload 设备呢?不能运行时更新信息到 DSP 吗?其实 stagefright 和 compress_offload 是支持运行期更新某些信息的,也就是无缝切换,至于是哪些信息,依赖于 DSP 算法实现;有兴趣深入的可以参考 sendMetaDataToHal() 和 compress_set_gapless_metadata()。