增强学习 学习笔记一基本原理
参考:Reinforcement Learning:An Introduction
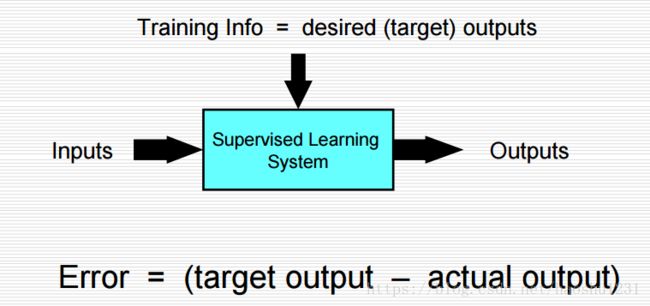
监督学习:
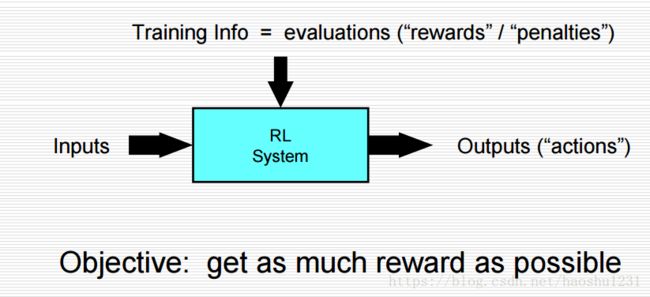
增强学习(RL):
RL的主要特征:
1)学习器不被告知要采取的行动
2)试错法搜索
3)延迟的reward(牺牲短期获得长期收益)
4)explore(new) and exploit(old)
5)代理与环境的交互作用
完整流程:
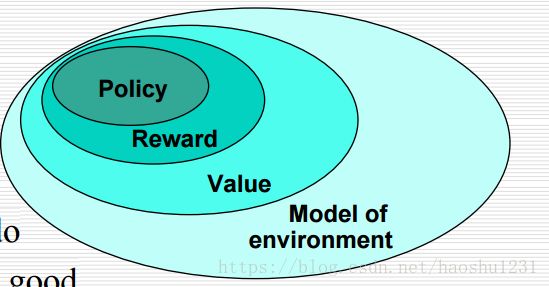
RL的元素:
1)Policy: what to do
2)Reward: what is good
3) Value: what is good because it predicts reward
4)Model: what follows what
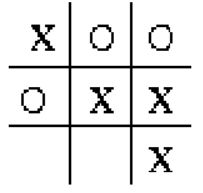
基础RL使用实例-tic toc toe游戏
双人对战游戏,一方在横,竖或对角连成三个即为胜利。
解决策略:
1.Model:明确模型每一种状态
2.Value:在每一种状态下的获胜的最新的估计概率
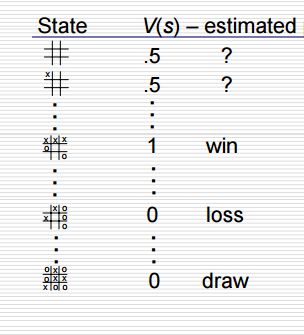
用如下表格表示步骤1,2:(其中V(s)是估计概率)
在这个游戏里,每个玩家有自己对应的V(s),他们的V(s)有反比的关系,例如当State(i)表示p1玩家获胜的情况,则p1.V(s)=1,p2.V(s)=0,反之亦然。初始时,对于所有可能处于的状态,除了必胜和必输,V(s)均置为0.5。
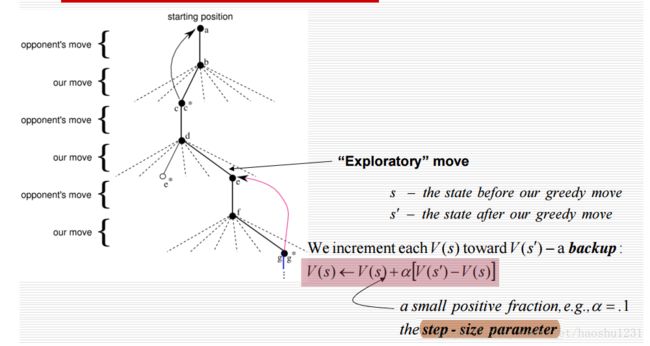
3.重复进行很多很多次游戏训练学习器。每一次游戏中玩家下一步采取的行动或选取可能达到状态中具有最大V(s)的状态(exploit),或偶尔的随机选取可能达到的状态之一(explore),该过程如下图所示。
4.你在每一次游戏结束后,根据比赛结果返回p1,p2的reward,并分别根据上面的更新公式,从后到前,更新每一个状态下的估计值V(s)。
上述过程可以用如下代码描述:
#######################################################################
# Copyright (C) #
# 2016 Shangtong Zhang([email protected]) #
# 2016 Jan Hakenberg([email protected]) #
# 2016 Tian Jun([email protected]) #
# 2016 Kenta Shimada([email protected]) #
# Permission given to modify the code as long as you keep this #
# declaration at the top #
#######################################################################
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import pickle
BOARD_ROWS = 3
BOARD_COLS = 3
BOARD_SIZE = BOARD_ROWS * BOARD_COLS
class State:
def __init__(self):
# the board is represented by a n * n array,
# 1 represents chessman of the player who moves first,
# -1 represents chessman of another player
# 0 represents empty position
self.data = np.zeros((BOARD_ROWS, BOARD_COLS))
self.winner = None
self.hashVal = None
self.end = None
# calculate the hash value for one state, it's unique
def getHash(self):
if self.hashVal is None:
self.hashVal = 0
for i in self.data.reshape(BOARD_ROWS * BOARD_COLS):
if i == -1:
i = 2
self.hashVal = self.hashVal * 3 + i
return int(self.hashVal)
# determine whether a player has won the game, or it's a tie
def isEnd(self):
if self.end is not None:
return self.end
results = []
# check row
for i in range(0, BOARD_ROWS):
results.append(np.sum(self.data[i, :]))
# check columns
for i in range(0, BOARD_COLS):
results.append(np.sum(self.data[:, i]))
# check diagonals
results.append(0)
for i in range(0, BOARD_ROWS):
results[-1] += self.data[i, i]
results.append(0)
for i in range(0, BOARD_ROWS):
results[-1] += self.data[i, BOARD_ROWS - 1 - i]
for result in results:
if result == 3:
self.winner = 1
self.end = True
return self.end
if result == -3:
self.winner = -1
self.end = True
return self.end
# whether it's a tie
sum = np.sum(np.abs(self.data))
if sum == BOARD_ROWS * BOARD_COLS:
self.winner = 0
self.end = True
return self.end
# game is still going on
self.end = False
return self.end
# @symbol 1 or -1
# put chessman symbol in position (i, j)
def nextState(self, i, j, symbol):
newState = State()
newState.data = np.copy(self.data)
newState.data[i, j] = symbol
return newState
# print the board
def show(self):
for i in range(0, BOARD_ROWS):
print('-------------')
out = '| '
for j in range(0, BOARD_COLS):
if self.data[i, j] == 1:
token = '*'
if self.data[i, j] == 0:
token = '0'
if self.data[i, j] == -1:
token = 'x'
out += token + ' | '
print(out)
print('-------------')
def getAllStatesImpl(currentState, currentSymbol, allStates):
for i in range(0, BOARD_ROWS):
for j in range(0, BOARD_COLS):
if currentState.data[i][j] == 0:
newState = currentState.nextState(i, j, currentSymbol)
newHash = newState.getHash()
if newHash not in allStates.keys():
isEnd = newState.isEnd()
allStates[newHash] = (newState, isEnd)
if not isEnd:
getAllStatesImpl(newState, -currentSymbol, allStates)
def getAllStates():
currentSymbol = 1
currentState = State()
allStates = dict()
allStates[currentState.getHash()] = (currentState, currentState.isEnd())
getAllStatesImpl(currentState, currentSymbol, allStates)
return allStates
# all possible board configurations
allStates = getAllStates()
print('allStates',len(allStates))
class Judger:
# @player1: player who will move first, its chessman will be 1
# @player2: another player with chessman -1
# @feedback: if True, both players will receive rewards when game is end
def __init__(self, player1, player2, feedback=True):
self.p1 = player1
self.p2 = player2
self.feedback = feedback
self.currentPlayer = None
self.p1Symbol = 1
self.p2Symbol = -1
self.p1.setSymbol(self.p1Symbol)
self.p2.setSymbol(self.p2Symbol)
self.currentState = State()
self.allStates = allStates
# give reward to two players
def giveReward(self):
if self.currentState.winner == self.p1Symbol:
self.p1.feedReward(1)
self.p2.feedReward(0)
elif self.currentState.winner == self.p2Symbol:
self.p1.feedReward(0)
self.p2.feedReward(1)
else:
self.p1.feedReward(0.1)
self.p2.feedReward(0.5)
def feedCurrentState(self):
self.p1.feedState(self.currentState)
self.p2.feedState(self.currentState)
def reset(self):
self.p1.reset()
self.p2.reset()
self.currentState = State()
self.currentPlayer = None
# @show: if True, print each board during the game
def play(self, show=False):
self.reset()
self.feedCurrentState()
while True:
# set current player
if self.currentPlayer == self.p1:
self.currentPlayer = self.p2
else:
self.currentPlayer = self.p1
if show:
self.currentState.show()
[i, j, symbol] = self.currentPlayer.takeAction()
self.currentState = self.currentState.nextState(i, j, symbol)
hashValue = self.currentState.getHash()
self.currentState, isEnd = self.allStates[hashValue]
self.feedCurrentState()
if isEnd:
if self.feedback:
self.giveReward()
return self.currentState.winner
# AI player
class Player:
# @stepSize: step size to update estimations
# @exploreRate: possibility to explore
def __init__(self, stepSize = 0.1, exploreRate=0.1):
self.allStates = allStates
self.estimations = dict()
self.stepSize = stepSize
self.exploreRate = exploreRate
self.states = []
def reset(self):
self.states = []
def setSymbol(self, symbol):
self.symbol = symbol
for hash in self.allStates.keys():
(state, isEnd) = self.allStates[hash]
if isEnd:
if state.winner == self.symbol:
self.estimations[hash] = 1.0
else:
self.estimations[hash] = 0
else:
self.estimations[hash] = 0.5
# accept a state
def feedState(self, state):
self.states.append(state)
# update estimation according to reward
def feedReward(self, reward):
if len(self.states) == 0:
return
self.states = [state.getHash() for state in self.states]
target = reward
for latestState in reversed(self.states):
value = self.estimations[latestState] + self.stepSize * (target - self.estimations[latestState])
self.estimations[latestState] = value
target = value
self.states = []
# determine next action
def takeAction(self):
state = self.states[-1]
nextStates = []
nextPositions = []
for i in range(BOARD_ROWS):
for j in range(BOARD_COLS):
if state.data[i, j] == 0:
nextPositions.append([i, j])
nextStates.append(state.nextState(i, j, self.symbol).getHash())
if np.random.binomial(1, self.exploreRate):
np.random.shuffle(nextPositions)
# Not sure if truncating is the best way to deal with exploratory step
# Maybe it's better to only skip this step rather than forget all the history
self.states = []
action = nextPositions[0]
action.append(self.symbol)
return action
values = []
for hash, pos in zip(nextStates, nextPositions):
values.append((self.estimations[hash], pos))
np.random.shuffle(values)
values.sort(key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True)
action = values[0][1]
action.append(self.symbol)
return action
def savePolicy(self):
fw = open('optimal_policy_' + str(self.symbol), 'wb')
pickle.dump(self.estimations, fw)
fw.close()
def loadPolicy(self):
fr = open('optimal_policy_' + str(self.symbol),'rb')
self.estimations = pickle.load(fr)
fr.close()
# human interface
# input a number to put a chessman
# | 1 | 2 | 3 |
# | 4 | 5 | 6 |
# | 7 | 8 | 9 |
class HumanPlayer:
def __init__(self, stepSize = 0.1, exploreRate=0.1):
self.symbol = None
self.currentState = None
return
def reset(self):
return
def setSymbol(self, symbol):
self.symbol = symbol
return
def feedState(self, state):
self.currentState = state
return
def feedReward(self, reward):
return
def takeAction(self):
data = int(input("Input your position:"))
data -= 1
i = data // int(BOARD_COLS)
j = data % BOARD_COLS
if self.currentState.data[i, j] != 0:
return self.takeAction()
return (i, j, self.symbol)
def train(epochs=20000):
player1 = Player()
player2 = Player()
judger = Judger(player1, player2)
player1Win = 0.0
player2Win = 0.0
for i in range(0, epochs):
print("Epoch", i)
winner = judger.play()
if winner == 1:
player1Win += 1
if winner == -1:
player2Win += 1
judger.reset()
print(player1Win / epochs)
print(player2Win / epochs)
player1.savePolicy()
player2.savePolicy()
def compete(turns=500):
player1 = Player(exploreRate=0)
player2 = Player(exploreRate=0)
judger = Judger(player1, player2, False)
player1.loadPolicy()
player2.loadPolicy()
player1Win = 0.0
player2Win = 0.0
for i in range(0, turns):
print("Epoch", i)
winner = judger.play()
if winner == 1:
player1Win += 1
if winner == -1:
player2Win += 1
judger.reset()
print(player1Win / turns)
print(player2Win / turns)
def play():
while True:
player1 = Player(exploreRate=0)
player2 = HumanPlayer()
judger = Judger(player1, player2, False)
player1.loadPolicy()
winner = judger.play(True)
if winner == player2.symbol:
print("Win!")
elif winner == player1.symbol:
print("Lose!")
else:
print("Tie!")
train()
compete()
play()