聊聊CatBoost
CatBoost(categorical boosting)是由Yandex公司(Yandex公司服务范围有搜索、新闻、地图、百科、电子信箱、电子商务、互联网广告等,Yandex在俄罗斯本地搜索引擎的市场份额非常大)在机器学习顶级会议NIPS 2017(Neural Information Processing Systems)提出的一种能够很好地处理类别型特征的梯度提升算法库。该库中的学习算法基于GPU实现,打分算法基于CPU实现。
所谓类别型特征,即为这类特征不是数值型特征,而是离散的集合,比如省份名(山东,山西,河北等),城市名(北京,上海,南京等),学历(高中,本科,硕士等)。在梯度提升算法中,最常用的是将这些类别型特征转为数值型来处理,一般类别型特征会转化为一个或多个数值型特征。如果某个类别型特征基数比较低,即该特征的所有值去重后构成的集合元素个数比较少,一般利用one-hot编码方法将特征转为数值型。
将类别型特征转为数值型特征也可以基于统计来做,比如,首先统计该特征中某个取值c1对应的类别标签的总和SumY,然后用该总和SumY除以该特征取值为c1的样本数n1,进而可以将类别型特征转为数值型特征。这种做法容易过拟合,比如取值为c1的样本只有一个的情形。为了避免过拟合,可以将样本集分成两部分,一部分用来统计,另一部分用来训练,这样就减少了训练的样本量,用来统计的样本量也会有所不足。
为了将所有样本用于训练,CatBoost给出了一种解决方案,即首先对所有样本进行随机排序,然后针对类别型特征中的某个取值,每个样本的该特征转为数值型时都是基于排在该样本之前的类别标签取均值,同时加入了优先级和优先级的权重系数。公式示例如下
这种做法可以降低类别特征中低频次特征带来的噪声。
在回归问题中,计算优先级一般通过对标签值取平均得到。针对二分类问题,优先级一般基于正类样本的先验概率得到。
针对类别型特征,也可以将两个类别型特征组合起来,在CatBoost中,第一次分割时不考虑类别型特征的组合,下面的分割中将所有类别型特征之间的组合考虑进来,组合后的特征就会变成数值型的。CatBoost也会把分割得到的两组值作为类别型特征参与后面的组合。
在GBDT中,构建下一棵树包含两步,即选择树的结构以及树结构固定之后设置叶子节点的值。在CatBoost中,对于每个样本Sample,都单独构建一个利用该样本之前的样本点的梯度估计得到的模型Model,针对这些模型Model,估计该样本Sample的梯度,然后利用新模型Model_new重新对样本Sample打分。
算法伪代码示例如下:
容易看出,上面的模型依赖于样本的排序,那么利用多种样本排序可以训练得到多种模型,这样可以减少过拟合现象。
CatBoost具有两大优势,其一,它在训练过程中处理类别型特征,而不是在特征预处理阶段处理类别型特征;其二,选择树结构时,计算叶子节点的算法可以避免过拟合。
另外,在CatBoost中,将浮点型特征,统计值以及one-hot编码的特征二值化,所有这些二值化特征放入向量中,然后在打分过程中利用二值化的特征计算模型的输出。
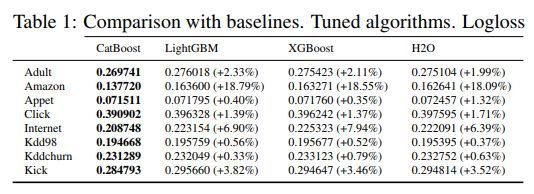
实验结果如下
实验结果是五次实验的平均值,实验结果显示CatBoost优于LightGBM,XGBoost以及H2O。
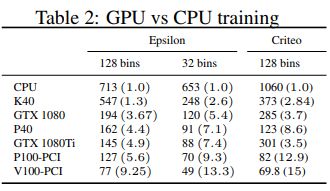
下面是训练过程中基于GPU和基于CPU的对比,容易看出,GPU可以大大加速训练过程。
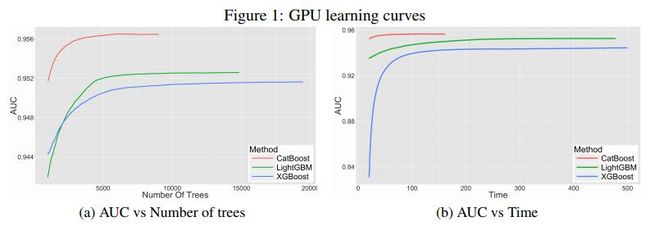
下面是各个算法训练效果的对比。
下面是各个算法的打分过程耗时对比,容易看出,CatBoost相对XGBoost和LightGBM在打分速度上可以提升很多。
示例代码,
二分类示例代码(python):
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
# Initialize data
cat_features = [0,1,2] train_data = [["a","b",1,4,5,6],["a","b",4,5,6,7],["c","d",30,40,50,60]] train_labels = [1,1,-1] test_data = [["a","b",2,4,6,8],["a","d",1,4,50,60]]
# Initialize CatBoostClassifier
model = CatBoostClassifier(
iterations=2,
learning_rate=1,
depth=2, loss_function='Logloss')
# Fit model
model.fit(train_data, train_labels, cat_features)
# Get predicted classes
preds_class = model.predict(test_data)
# Get predicted probabilities for each class
preds_proba = model.predict_proba(test_data)
# Get predicted RawFormulaVal
preds_raw = model.predict(test_data, prediction_type='RawFormulaVal')
多分类示例代码(Python):
from catboost import Pool, CatBoostClassifier TRAIN_FILE = '../data/cloudness_small/train_small'
TEST_FILE = '../data/cloudness_small/test_small'
CD_FILE = '../data/cloudness_small/train.cd'
# Load data from files to Pool
train_pool = Pool(TRAIN_FILE, column_description=CD_FILE) test_pool = Pool(TEST_FILE, column_description=CD_FILE)
# Initialize CatBoostClassifier
model = CatBoostClassifier(
iterations=2,
learning_rate=1,
depth=2,
loss_function='MultiClass')
# Fit model
model.fit(train_pool)
# Get predicted classes
preds_class = model.predict(test_pool)
# Get predicted probabilities for each class
preds_proba = model.predict_proba(test_pool)
# Get predicted RawFormulaVal
preds_raw = model.predict(test_pool, prediction_type='RawFormulaVal')
R中使用示例:
library(catboost) train_path = system.file("extdata", "adult_train.1000", package="catboost") test_path = system.file("extdata", "adult_test.1000", package="catboost") column_description_vector = rep('numeric', 15) cat_features <- c(3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 15)
for (i in cat_features) column_description_vector[i] <- 'factor'
train <- read.table(train_path, head = F, sep = "\t", colClasses = column_description_vector, na.strings='NAN') test <- read.table(test_path, head = F, sep = "\t", colClasses = column_description_vector, na.strings='NAN') target <- c(1) train_pool <- catboost.load_pool(
data=train[,-target], label = train[,target]) test_pool <- catboost.load_pool(
data=test[,-target], label = test[,target]) head(train_pool, 1)[[1]] head(test_pool, 1)[[1]]
fit_params <- list(
iterations = 100, thread_count = 10, loss_function = 'Logloss:Border=0.5', ignored_features = c(4,9), border_count = 32, depth = 5, learning_rate = 0.03, l2_leaf_reg = 3.5, train_dir = 'train_dir') model <- catboost.train(pool, test_pool, fit_params)
prediction <- catboost.predict(model, pool, prediction_type = 'RawFormulaVal')
参考资料
https://github.com/Microsoft/LightGBM
http://docs.h2o.ai/h2o/latest-stable/h2o-docs/data-science/gbm.html
https://github.com/catboost/catboost
http://learningsys.org/nips17/assets/papers/paper_11.pdf
https://tech.yandex.com/catboost/doc/dg/concepts/python-usages-examples-docpage/
https://tech.yandex.com/catboost/doc/dg/concepts/about-docpage/