本文翻译自TopCoder上的一篇文章: Dynamic Programming: From novice to advanced ,并非严格逐字逐句翻译,其中加入了自己的一些理解。水平有限,还望指摘。
前言
我们遇到的问题中,有很大一部分可以用动态规划(简称DP)来解。 解决这类问题可以很大地提升你的能力与技巧,我会试着帮助你理解如何使用DP来解题。 这篇文章是基于实例展开来讲的,因为干巴巴的理论实在不好理解。
注意:如果你对于其中某一节已经了解并且不想阅读它,没关系,直接跳过它即可。
简介(入门)
什么是动态规划,我们要如何描述它?
动态规划算法通常基于一个递推公式及一个或多个初始状态。 当前子问题的解将由上一次子问题的解推出。使用动态规划来解题只需要多项式时间复杂度, 因此它比回溯法、暴力法等要快许多。
现在让我们通过一个例子来了解一下DP的基本原理。
首先,我们要找到某个状态的最优解,然后在它的帮助下,找到下一个状态的最优解。
“状态”代表什么及如何找到它?
“状态”用来描述该问题的子问题的解。原文中有两段作者阐述得不太清楚,跳过直接上例子。
如果我们有面值为1元、3元和5元的硬币若干枚,如何用最少的硬币凑够11元? (表面上这道题可以用贪心算法,但贪心算法无法保证可以求出解,比如1元换成2元的时候)首先我们思考一个问题,如何用最少的硬币凑够i元(i<11)?为什么要这么问呢? 两个原因:
- 当我们遇到一个大问题时,总是习惯把问题的规模变小,这样便于分析讨论。
- 这个规模变小后的问题和原来的问题是同质的,除了规模变小,其它的都是一样的, 本质上它还是同一个问题(规模变小后的问题其实是原问题的子问题)。
好了,让我们从最小的i开始吧。当i=0,即我们需要多少个硬币来凑够0元。 由于1,3,5都大于0,即没有比0小的币值,因此凑够0元我们最少需要0个硬币。 (这个分析很傻是不是?别着急,这个思路有利于我们理清动态规划究竟在做些什么。) 这时候我们发现用一个标记来表示这句“凑够0元我们最少需要0个硬币。”会比较方便, 如果一直用纯文字来表述,不出一会儿你就会觉得很绕了。那么, 我们用d(i)=j来表示凑够i元最少需要j个硬币。于是我们已经得到了d(0)=0, 表示凑够0元最小需要0个硬币。当i=1时,只有面值为1元的硬币可用, 因此我们拿起一个面值为1的硬币,接下来只需要凑够0元即可,而这个是已经知道答案的, 即d(0)=0。所以,d(1)=d(1-1)+1=d(0)+1=0+1=1。当i=2时, 仍然只有面值为1的硬币可用,于是我拿起一个面值为1的硬币, 接下来我只需要再凑够2-1=1元即可(记得要用最小的硬币数量),而这个答案也已经知道了。 所以d(2)=d(2-1)+1=d(1)+1=1+1=2。一直到这里,你都可能会觉得,好无聊, 感觉像做小学生的题目似的。因为我们一直都只能操作面值为1的硬币!耐心点, 让我们看看i=3时的情况。当i=3时,我们能用的硬币就有两种了:1元的和3元的( 5元的仍然没用,因为你需要凑的数目是3元!5元太多了亲)。 既然能用的硬币有两种,我就有两种方案。如果我拿了一个1元的硬币,我的目标就变为了: 凑够3-1=2元需要的最少硬币数量。即d(3)=d(3-1)+1=d(2)+1=2+1=3。 这个方案说的是,我拿3个1元的硬币;第二种方案是我拿起一个3元的硬币, 我的目标就变成:凑够3-3=0元需要的最少硬币数量。即d(3)=d(3-3)+1=d(0)+1=0+1=1. 这个方案说的是,我拿1个3元的硬币。好了,这两种方案哪种更优呢? 记得我们可是要用最少的硬币数量来凑够3元的。所以, 选择d(3)=1,怎么来的呢?具体是这样得到的:d(3)=min{d(3-1)+1, d(3-3)+1}。
OK,码了这么多字讲具体的东西,让我们来点抽象的。从以上的文字中, 我们要抽出动态规划里非常重要的两个概念:状态和状态转移方程。
上文中d(i)表示凑够i元需要的最少硬币数量,我们将它定义为该问题的”状态”, 这个状态是怎么找出来的呢?我在另一篇文章 动态规划之背包问题(一)中写过: 根据子问题定义状态。你找到子问题,状态也就浮出水面了。 最终我们要求解的问题,可以用这个状态来表示:d(11),即凑够11元最少需要多少个硬币。 那状态转移方程是什么呢?既然我们用d(i)表示状态,那么状态转移方程自然包含d(i), 上文中包含状态d(i)的方程是:d(3)=min{d(3-1)+1, d(3-3)+1}。没错, 它就是状态转移方程,描述状态之间是如何转移的。当然,我们要对它抽象一下,
d(i)=min{ d(i-vj)+1 },其中i-vj>=0,vj表示第j个硬币的面值;
有了状态和状态转移方程,这个问题基本上也就解决了。当然了,Talk is cheap,show me the code!
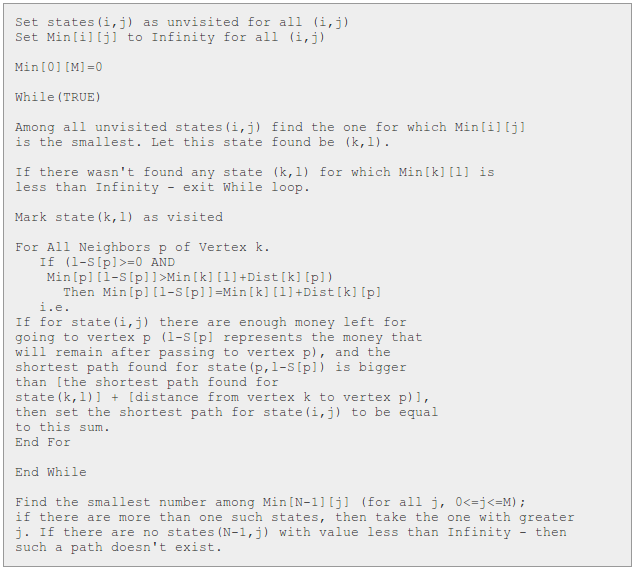
伪代码如下:
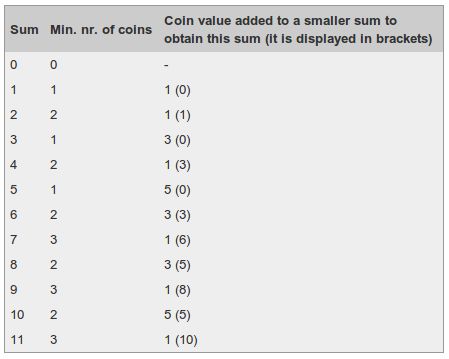
下图是当i从0到11时的解:
从上图可以得出,要凑够11元至少需要3枚硬币。
此外,通过追踪我们是如何从前一个状态值得到当前状态值的, 可以找到每一次我们用的是什么面值的硬币。比如,从上面的图我们可以看出, 最终结果d(11)=d(10)+1(面值为1),而d(10)=d(5)+1(面值为5),最后d(5)=d(0)+1 (面值为5)。所以我们凑够11元最少需要的3枚硬币是:1元、5元、5元。
注意:原文中这里本来还有一段的,但我反反复复读了几遍, 大概的意思我已经在上文从i=0到i=3的分析中有所体现了。作者本来想讲的通俗一些, 结果没写好,反而更不好懂,所以这段不翻译了。
初级
上面讨论了一个非常简单的例子。现在让我们来看看对于更复杂的问题, 如何找到状态之间的转移方式(即找到状态转移方程)。 为此我们要引入一个新词叫递推关系来将状态联系起来(说的还是状态转移方程)
OK,上例子,看看它是如何工作的。
一个序列有N个数:A[1],A[2],…,A[N],求出最长非降子序列的长度。 (讲DP基本都会讲到的一个问题LIS:longest increasing subsequence)
正如上面我们讲的,面对这样一个问题,我们首先要定义一个“状态”来代表它的子问题, 并且找到它的解。注意,大部分情况下,某个状态只与它前面出现的状态有关, 而独立于后面的状态。
让我们沿用“入门”一节里那道简单题的思路来一步步找到“状态”和“状态转移方程”。 假如我们考虑求A[1],A[2],…,A[i]的最长非降子序列的长度,其中i
5,3,4,8,6,7
根据上面找到的状态,我们可以得到:(下文的最长非降子序列都用LIS表示)
前1个数的LIS长度d(1)=1(序列:5)
前2个数的LIS长度d(2)=1(序列:3;3前面没有比3小的)
前3个数的LIS长度d(3)=2(序列:3,4;4前面有个比它小的3,所以d(3)=d(2)+1)
前4个数的LIS长度d(4)=3(序列:3,4,8;8前面比它小的有3个数,所以 d(4)=max{d(1),d(2),d(3)}+1=3)
OK,分析到这,我觉得状态转移方程已经很明显了,如果我们已经求出了d(1)到d(i-1), 那么d(i)可以用下面的状态转移方程得到:
d(i) = max{1, d(j)+1},其中j用大白话解释就是,想要求d(i),就把i前面的各个子序列中, 最后一个数不大于A[i]的序列长度加1,然后取出最大的长度即为d(i)。 当然了,有可能i前面的各个子序列中最后一个数都大于A[i],那么d(i)=1, 即它自身成为一个长度为1的子序列。
分析完了,上图:(第二列表示前i个数中LIS的长度, 第三列表示,LIS中到达当前这个数的上一个数的下标,根据这个可以求出LIS序列)
Talk is cheap, show me the code:
#include
using namespace std;
int lis(int A[], int n){
int *d = new int[n];
int len = 1;
for(int i=0; id[i])
d[i] = d[j] + 1;
if(d[i]>len) len = d[i];
}
delete[] d;
return len;
}
int main(){
int A[] = {
5, 3, 4, 8, 6, 7
};
cout< 该算法的时间复杂度是O(n^2 ),并不是最优的解法。 还有一种很巧妙的算法可以将时间复杂度降到O(nlogn),网上已经有各种文章介绍它, 这里就不再赘述。传送门: LIS的O(nlogn)解法。 此题还可以用“排序+LCS”来解,感兴趣的话可自行Google。
练习题
无向图G有N个结点(1
尝试解决以下来自topcoder竞赛的问题:
ZigZag - 2003 TCCC Semifinals 3
BadNeighbors - 2004 TCCC Round 4
FlowerGarden - 2004 TCCC Round 1
中级
接下来,让我们来看看如何解决二维的DP问题。
平面上有N*M个格子,每个格子中放着一定数量的苹果。你从左上角的格子开始, 每一步只能向下走或是向右走,每次走到一个格子上就把格子里的苹果收集起来, 这样下去,你最多能收集到多少个苹果。
解这个问题与解其它的DP问题几乎没有什么两样。第一步找到问题的“状态”, 第二步找到“状态转移方程”,然后基本上问题就解决了。
首先,我们要找到这个问题中的“状态”是什么?我们必须注意到的一点是, 到达一个格子的方式最多只有两种:从左边来的(除了第一列)和从上边来的(除了第一行)。 因此为了求出到达当前格子后最多能收集到多少个苹果, 我们就要先去考察那些能到达当前这个格子的格子,到达它们最多能收集到多少个苹果。 (是不是有点绕,但这句话的本质其实是DP的关键:欲求问题的解,先要去求子问题的解)
经过上面的分析,很容易可以得出问题的状态和状态转移方程。 状态S[i][j]表示我们走到(i, j)这个格子时,最多能收集到多少个苹果。那么, 状态转移方程如下:
S[i][j]=A[i][j] + max(S[i-1][j], if i>0 ; S[i][j-1], if j>0)
其中i代表行,j代表列,下标均从0开始;A[i][j]代表格子(i, j)处的苹果数量。
S[i][j]有两种计算方式:1.对于每一行,从左向右计算,然后从上到下逐行处理;2. 对于每一列,从上到下计算,然后从左向右逐列处理。 这样做的目的是为了在计算S[i][j]时,S[i-1][j]和S[i][j-1]都已经计算出来了。
伪代码如下:
以下两道题来自topcoder,练习用的。
AvoidRoads - 2003 TCO Semifinals 4
ChessMetric - 2003 TCCC Round 4
中高级
这一节要讨论的是带有额外条件的DP问题。
以下的这个问题是个很好的例子。
无向图G有N个结点,它的边上带有正的权重值。
你从结点1开始走,并且一开始的时候你身上带有M元钱。如果你经过结点i, 那么你就要花掉S[i]元(可以把这想象为收过路费)。如果你没有足够的钱, 就不能从那个结点经过。在这样的限制条件下,找到从结点1到结点N的最短路径。 或者输出该路径不存在。如果存在多条最短路径,那么输出花钱数量最少的那条。 限制:1
下面有几道topcoder上的题以供练习:
Jewelry - 2003 TCO Online Round 4
StripePainter - SRM 150 Div 1
QuickSums - SRM 197 Div 2
ShortPalindromes - SRM 165 Div 2
高级
以下问题需要仔细的揣摩才能将其规约为可用DP解的问题。
问题:StarAdventure - SRM 208 Div 1:
给定一个M行N列的矩阵(M*N个格子),每个格子中放着一定数量的苹果。 你从左上角的格子开始,只能向下或向右走,目的地是右下角的格子。 你每走过一个格子,就把格子上的苹果都收集起来。然后你从右下角走回左上角的格子, 每次只能向左或是向上走,同样的,走过一个格子就把里面的苹果都收集起来。 最后,你再一次从左上角走到右下角,每过一个格子同样要收集起里面的苹果 (如果格子里的苹果数为0,就不用收集)。求你最多能收集到多少苹果。
注意:当你经过一个格子时,你要一次性把格子里的苹果都拿走。
限制条件:1 < N, M <= 50;每个格子里的苹果数量是0到1000(包含0和1000)。
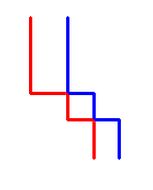
如果我们只需要从左上角的格子走到右下角的格子一次,并且收集最大数量的苹果, 那么问题就退化为“中级”一节里的那个问题。将这里的问题规约为“中级”里的简单题, 这样一来会比较好解。让我们来分析一下这个问题,要如何规约或是修改才能用上DP。 首先,对于第二次从右下角走到左上角得出的这条路径, 我们可以将它视为从左上角走到右下角得出的路径,没有任何的差别。 (即从B走到A的最优路径和从A走到B的最优路径是一样的)通过这种方式, 我们得到了三条从顶走到底的路径。对于这一点的理解可以稍微减小问题的难度。 于是,我们可以将这3条路径记为左,中,右路径。对于两条相交路径(如下图):
在不影响结果的情况下,我们可以将它们视为两条不相交的路径:
这样一来,我们将得到左,中,右3条路径。此外,如果我们要得到最优解, 路径之间不能相交(除了左上角和右下角必然会相交的格子)。因此对于每一行y( 除了第一行和最后一行),三条路径对应的x坐标要满足:x1[y] < x2[y] < x3[y]。 经过这一步的分析,问题的DP解法就进一步地清晰了。让我们考虑行y, 对于每一个x1[y-1],x2[y-1]和x3[y-1],我们已经找到了能收集到最多苹果数量的路径。 根据它们,我们能求出行y的最优解。现在我们要做的就是找到从一行移动到下一行的方式。 令Max[i][j][k]表示到第y-1行为止收集到苹果的最大数量, 其中3条路径分别止于第i,j,k列。对于下一行y,对每个Max[i][j][k] 都加上格子(y,i),(y,j)和(y,k)内的苹果数量。因此,每一步我们都向下移动。 我们做了这一步移动之后,还要考虑到,一条路径是有可能向右移动的。 (对于每一个格子,我们有可能是从它上面向下移动到它, 也可能是从它左边向右移动到它)。为了保证3条路径互不相交, 我们首先要考虑左边的路径向右移动的情况,然后是中间,最后是右边的路径。 为了更好的理解,让我们来考虑左边的路径向右移动的情况,对于每一个可能的j,k对(j
MiniPaint - SRM 178 Div 1
其它
当阅读一个题目并且开始尝试解决它时,首先看一下它的限制。 如果要求在多项式时间内解决,那么该问题就很可能要用DP来解。遇到这种情况, 最重要的就是找到问题的“状态”和“状态转移方程”。(状态不是随便定义的, 一般定义完状态,你要找到当前状态是如何从前面的状态得到的, 即找到状态转移方程)如果看起来是个DP问题,但你却无法定义出状态, 那么试着将问题规约到一个已知的DP问题(正如“高级”一节中的例子一样)。
解题思路
第一步: 找出递归方法
本质:递归
原问题(N) ->子问题(N-1)->原问题(N)
最优子结构
.子问题最优决策可导出原问题最优决策
.无后效性
第二步: 自底向上, 进行剪枝
重叠子问题
.去冗余
.空间换时间
套路
最优, 最大,最小, 最长, 计数
基本步骤:
1.设计暴力算法,找到冗余
2.设计并存储状态
3.递归式
4.自底向上计算最优解
例题:
leetcode198
1.暴力法 必会
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector& nums) {
return solve(nums, nums.size()-1);
}
int max(int a, int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int solve(vector&nums, int idx)
{
if (idx<0){
return 0;
}
return max(nums[idx] + solve(nums, idx-2), solve(nums, idx-1));
}
};
2.0-1背包
int search(int idx, int S)
{
if (S>W)
return 0;
if(idx>=n)
return 0;
return max(search(idx+1, S+w[idx])+ v[idx], search(idx+1, S));
}
最长子公共序列
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1010;
int dp[MAXN][MAXN];
int getcls(string s)
{
string s2(s);
reverse(s2.begin(), s2.end());
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i> str;
memset(dp, 0, MAXN*MAXN*sizeof(int));
cout << str.size() - getcls(str) << endl;
}
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100;
double data[MAXN];
double dp[MAXN+10][MAXN + 10];
double func(double data[], int n)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
dp[0][j] = 1.0;
} //用memset double出错-
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] * (1 - data[i]);
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = (dp[i - 1][j - 1] * data[i]+ dp[i - 1][j] * (1 - data[i])) ;
}
dp[i][i] = dp[i - 1][i- 1] * data[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
{
cout << dp[i][j]<< " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int index = (n + 1) / 2;
double result = 0.0;
for (int j = index; j <= n; j++)
{
result += dp[n][j];
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n)
{
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(data));
** for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)**
{
cin >>data[i];
data[i] =data[i]/100;
}
double result = func(data, n);
printf("%.5lf", result);
}
}
0-1背包
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 200002 ;
int need[MAXN];
int value[MAXN];
int dp[MAXN];
int dpfunc(int* need, int* value, int n, int V)
{
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = V; j >= need[i]; j--)
dp[j] = std::max(dp[j - need[i]] + value[i], dp[j]);
}
return dp[V];
}
int main()
{
int n, V;
while (cin >> n >> V)
{
memset(need, 0, sizeof(need));
memset(value, 0, sizeof(value));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> need[i] >> value[i];
}
cout << dpfunc(need, value, n, V);
}
return 0;
}
完全背包
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 200002 ;
int need[MAXN];
int value[MAXN];
int dp[MAXN];
int dpfunc(int* need, int* value, int n, int V)
{
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = need[i]; j <=V; j++)
dp[j] = std::max(dp[j - need[i]] + value[i], dp[j]);
}
return dp[V];
}
int main()
{
int n, V;
while (cin >> n >> V)
{
memset(need, 0, sizeof(need));
memset(value, 0, sizeof(value));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> need[i] >> value[i];
}
cout << dpfunc(need, value, n, V);
}
return 0;
}
leetocde494.Target Sum
You are given a list of non-negative integers, a1, a2, ..., an, and a target, S. Now you have 2 symbols +
and -
. For each integer, you should choose one from +
and -
as its new symbol.
Find out how many ways to assign symbols to make sum of integers equal to target S.
Example 1:
Input: nums is [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S is 3. Output: 5Explanation: -1+1+1+1+1 = 3+1-1+1+1+1 = 3+1+1-1+1+1 = 3+1+1+1-1+1 = 3+1+1+1+1-1 = 3There are 5 ways to assign symbols to make the sum of nums be target 3.
这道题学习一下如何把负数转换为正数;
分析:
sum(P) - sum(N) = target
sum(P) - sum(N) = target + sum(P) + sum(N)
2 * sum(P) = target + sum(nums)
So the original problem has been converted to a subset sum problem as follows:Find a subset P
of nums
such that sum(P) = (target + sum(nums)) / 2
class Solution {
public:
int findTargetSumWays(std::vector& nums, int S) {
int sum = std::accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
return sum < S || (S + sum) & 1 ? 0 : subsetSum(nums, (S+sum) >> 1);
}
int subsetSum(std::vector& nums, int s) {
int dp[s+1];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(int)*(s+1));
dp[0] = 1;
for(int n: nums) {
for (int i = s; i >= n; --i) {
dp[i] += dp[i-n];
}
}
return dp[s];
}
};
LeetCode 638. Shopping Offers
In LeetCode Store, there are some kinds of items to sell. Each item has a price.
However, there are some special offers, and a special offer consists of one or more different kinds of items with a sale price.
You are given the each item's price, a set of special offers, and the number we need to buy for each item. The job is to output the lowest price you have to pay for exactly certain items as given, where you could make optimal use of the special offers.
Each special offer is represented in the form of an array, the last number represents the price you need to pay for this special offer, other numbers represents how many specific items you could get if you buy this offer.
You could use any of special offers as many times as you want.
Example 1:
Input: [2,5], [[3,0,5],[1,2,10]], [3,2]Output: 14Explanation: There are two kinds of items, A and B. Their prices are $2 and $5 respectively. In special offer 1, you can pay $5 for 3A and 0BIn special offer 2, you can pay $10 for 1A and 2B. You need to buy 3A and 2B, so you may pay $10 for 1A and 2B (special offer #2), and $4 for 2A.
Example 2:
Input: [2,3,4], [[1,1,0,4],[2,2,1,9]], [1,2,1]Output: 11Explanation: The price of A is $2, and $3 for B, $4 for C. You may pay $4 for 1A and 1B, and $9 for 2A ,2B and 1C. You need to buy 1A ,2B and 1C, so you may pay $4 for 1A and 1B (special offer #1), and $3 for 1B, $4 for 1C. You cannot add more items, though only $9 for 2A ,2B and 1C.
这道题还是背包问题, 而且是多重背包,只是维度增加了,不再只是V这一个维度
分析:
d[a1][a2][a3][a4][a5] 表示第 1 个物品买 a1 个,第 2 个物品买 a2 个,第 3 个物品买 a3 个,第 4 个物品买 a4 个,第 5 个物品买 a5 个的最小值。d[a1][a2][a3][a4][a5]=min(d[a1-b1][ a2-b2][ a3-b3][ a4-b4][ a5-b5] + reduce[i] );
b1、b2、b3、b4、b5 表示按照某打折方式各个物品需要要买的物品数目。
p[i][j] 表示第 i 个打折方式,所需要购买物品 j 的数量(j是那个物品的号码)
//20170812 两个钟,多重背包, 多维
class Solution {
public:
int shoppingOffers(vector& price, vector>& special, vector& needs) {
while (price.size() < 6) {
price.push_back(0);
}
while(needs.size() < 6) {
needs.push_back(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < special.size(); i++) {
vector& temp = special[i];
int tail = temp.back();
temp.pop_back();
while (temp.size() < 6) {
temp.push_back(0);
}
temp.push_back(tail);
}
for(int a0 = 0; a0 <=needs[0]; a0++) {
for (int a1 = 0; a1 <= needs[1]; a1++) {
for (int a2 = 0; a2 <= needs[2]; a2++) { //a2写成了a1,卡了很久
for (int a3 = 0; a3 <= needs[3]; a3++) {
for (int a4 = 0; a4 <= needs[4]; a4++) {
for (int a5 = 0; a5 <= needs[5]; a5++) {
dp[a0][a1][a2][a3][a4][a5] = price[0] * a0 + price[1] * a1 + price[2] * a2 + price[3]*a3 + price[4] * a4 + price[5] * a5;
}
}
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < special.size(); i++) {
for(int a0 = special[i][0]; a0 <=needs[0]; a0++) {
for (int a1 = special[i][1]; a1 <= needs[1]; a1++) {
for (int a2 = special[i][2]; a2 <= needs[2]; a2++) {
for (int a3 = special[i][3]; a3 <= needs[3]; a3++) {
for (int a4 = special[i][4]; a4 <= needs[4]; a4++) {
for (int a5 = special[i][5]; a5 <= needs[5]; a5++) {
int b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5;
b0 = a0 - special[i][0];
b1 = a1 - special[i][1];
b2 = a2 - special[i][2];
b3 = a3 - special[i][3];
b4 = a4 - special[i][4];
b5 = a5 - special[i][5];
if (b0 >=0 && b1 >= 0 && b2 >= 0 && b3 >= 0 && b4 >=0 && b5 >= 0) {
dp[a0][a1][a2][a3][a4][a5] =
std::min(dp[a0][a1][a2][a3][a4][a5],
dp[a0 - special[i][0]][a1- special[i][1]]
[a2- special[i][2]][a3- special[i][3]]
[a4- special[i][4]][a5- special[i][5]] + special[i][6]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[needs[0]][needs[1]][needs[2]][needs[3]][needs[4]][needs[5]];
}
int dp[7][7][7][7][7][7];
};
leetcode 72. Edit Distance
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to convert word1 to word2. (each operation is counted as 1 step.)
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
a) Insert a characterb) Delete a characterc) Replace a character
思路:
如果我们用 i 表示当前字符串 A 的下标,j 表示当前字符串 B 的下标。 如果我们用d[i, j] 来表示A[1, ... , i] B[1, ... , j] 之间的最少编辑操作数。那么我们会有以下发现:
- d[0, j] = j;
- d[i, 0] = i;
- d[i, j] = d[i-1, j - 1] if A[i] == B[j]
- d[i, j] = min(d[i-1, j - 1], d[i, j - 1], d[i-1, j]) + 1 if A[i] != B[j]
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
vector> dp(word1.size() + 1, vector(word2.size() + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= word2.size(); j++) {
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= word2.size(); j++) {
if (word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i -1][j - 1];
} else {
int rpl = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
int del = std::min(dp[i][j - 1] + 1, dp[i - 1][j] + 1);
dp[i][j] = std::min(del, rpl);
}
}
}
return dp[word1.size()][word2.size()];
}
};
leetcode 87. Scramble String
Given a string s1, we may represent it as a binary tree by partitioning it to two non-empty substrings recursively.
Below is one possible representation of s1 = "great"
:
great / \ gr eat / \ / \g r e at / \ a t
To scramble the string, we may choose any non-leaf node and swap its two children.
For example, if we choose the node "gr"
and swap its two children, it produces a scrambled string "rgeat"
.
rgeat / \ rg eat / \ / \r g e at / \ a t
We say that "rgeat"
is a scrambled string of "great"
.
Similarly, if we continue to swap the children of nodes "eat"
and "at"
, it produces a scrambled string "rgtae"
.
rgtae / \ rg tae / \ / \r g ta e / \ t a
We say that "rgtae"
is a scrambled string of "great"
.
Given two strings s1 and s2 of the same length, determine if s2 is a scrambled string of s1.
分析:这道题太难了,一开始都没啥思路首先想到的是递归(即深搜),对两个string进行分割,然后比较四对字符串。代码虽然简单,但是复杂度比较高。有两种加速策略,一种是剪枝,提前返回;一种是加缓存,缓存中间结果,即memorization(翻译为记忆化搜索)。
剪枝可以五花八门,要充分观察,充分利用信息,找到能让节点提前返回的条件。例如,判断两个字符串是否互为scamble,至少要求每个字符在两个字符串中出现的次数要相等,如果不相等则返回false。
加缓存,可以用数组或HashMap。本题维数较高,用HashMap,{map}和{unordered_map}均可。
既然可以用记忆化搜索,这题也一定可以用动规。设状态为{f[n][i][j]},表示长度为$n$,起点为{s1[i]}和起点为{s2[j]}两个字符串是否互为scramble
//20170827 太难了,网上找的
public class Solution {
public boolean isScramble(String s1, String s2) {
if (s1.length() != s2.length()) return false;
if (s1.equals(s2)) return true;
boolean[][][] dp = new boolean[s1.length()][s2.length()][s1.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < s2.length(); j++) {
dp[i][j][1] = s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j);
}
}
for (int len = 2; len <= s1.length(); len++) {
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length() - len + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < s2.length() - len + 1; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k < len; k++) {
dp[i][j][len] |= dp[i][j][k] && dp[i + k][j + k][len - k] || dp[i][j + len - k][k] && dp[i + k][j][len - k];
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][s1.length()];
}
}
参考资料
1.http://www.hawstein.com/posts/dp-novice-to-advanced.html
- 算法导论