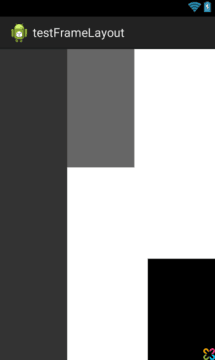Android Layout 布局属性全解
Android Layout 布局属性全解
android:descendantFocusability
开发中很常见的一个问题,项目中的listview不仅仅是简单的文字,常常需要自己定义listview,自己的Adapter去继承BaseAdapter,在adapter中按照需求进行编写,问题就出现了,可能会发生点击每一个item的时候没有反应,无法获取的焦点。原因多半是由于在你自己定义的Item中存在诸如ImageButton,Button,CheckBox等子控件(也可以说是Button或者Checkable的子类控件),此时这些子控件会将焦点获取到,所以常常当点击item时变化的是子控件,item本身的点击没有响应。
这时候就可以使用descendantFocusability来解决啦,API描述如下:
android:descendantFocusability
Defines the relationship between the ViewGroup and its descendants when looking for a View to take focus.
Must be one of the following constant values.
该属性是当一个为view获取焦点时,定义viewGroup和其子控件两者之间的关系。
属性的值有三种:
beforeDescendants:viewgroup会优先其子类控件而获取到焦点
afterDescendants:viewgroup只有当其子类控件不需要获取焦点时才获取焦点
blocksDescendants:viewgroup会覆盖子类控件而直接获得焦点
通常我们用到的是第三种,即在Item布局的根布局加上android:descendantFocusability=”blocksDescendants”的属性就好了
android:layoutMode
Defines the layout mode of this ViewGroup.
Must be one of the following constant values.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
clipBounds |
0 | Use the children's clip bounds when laying out this container.铺设这种容器时,使用子控件剪辑边界。 |
opticalBounds |
1 | Use the children's optical bounds when laying out this container.铺设这种容器时,使用子控件光纤边界界。 |
This corresponds to the global attribute resource symbol layoutMode.
Related Methods
- setLayoutMode(int)
android:paddingstart
Android 4.1(Jelly Bean) 在 TextView 和 EditText 元素里对“双向文字顺序”提供了有限的功能支持,允许应用程序在编辑和显示字符的时候,能够同时支持从左到右(LTR)以及从右到左(RTL)的排列格式。Android 4.2目前已经对“从右到左”的文字排列顺序给予了原生级别的全面支持,包括提供了一个布局镜面工具,使得开发者把能够将优质的用户体验带给每一位用户,不管该用户的书写顺序是从左到右,还是从右到左。
Android 4.2保证了该新特性不会影响到目前已经存在程序,如果之前的程序代码不修改,其应用的外观将维持现状。如果你想要修改程序,那么仅仅需要很小的改动,应用就可以自动地被“镜面反射”,这样就能轻易地将系统语言设置为从右到左的书写格式(阿拉伯语,希伯来语和波斯语都采用这种格式)。例如,下面的截图就展示了上述的设置效果:
从左到右的布局方式从右到左的布局方式
要实现RTL(从右到左)的布局镜面反射,仅仅需要遵循下列步骤就可以做到:
1. 在你的应用程序声明文件(manifest)里声明开启RTL mirroring的支持。具体做法是:在manifest.xml声明文件的
2. 修改应用程序中所有的“left/right”布局属性,改为对应的”start/end”布局
1)如果你的应用程序是针对Android 4.2目标平台(应用的targetSdkVersion或者minSdkVersion是17或者更高), 那么你就应当用“start”和“end”替换原来的“left”和“right”。例如,android:paddingLeft应当被替换为android:paddingStart。
2) 如果你想让你的应用程序与Android 4.2之前的版本保持兼容(也就是与targetSdkVersion或者minSdkVersion为16或者更早的版本),那么你应当既加上“start”和“end”,又加上“left”和“right”。例如,你应当同时写上:adnroid:paddingLeft和android:paddingStart。
为了更精确地控制应用程序在UI上的文字书写顺序(从左到右,或者从右到左),Android 4.2 引入了如下的API:
android:layoutDirection —该属性设置组件的布局排列方向
android:textDirection — 该属性设置组件的文字排列方向
android:textAlignment — 该属性设置文字的对齐方式
getLayoutDirectionFromLocale() —该方法用于获取指定地区的惯用布局方式
在使用从右到左的排列方式时,你甚至创建自定义的布局方式,可绘制对象,以及其他资源。仅仅是简单地使用资源匹配器“ldrtl”对你的资源进行一下标识,你就可以把资源定义为“从右到左方向的资源”。在调试和优化从右到左的布局方面,HierarchyViewer目前支持对start/end属性,布局方向,文字方向,文字对齐方式等所有信息的层次化显示。
那么现在是时候为所有的用户开发优美的Android应用程序了,无论用户的文字语言习惯是从左到右,还是从右到左。我们非常期待看到这些优美应用的产生!
android:foreground
- android:foreground 设置布局的前景图,前景图不会被子元素覆盖
- android:foregroundGravity 设置布局前景图的位置
对于FrameLayout.LayoutParams,这里仅有android:layout_gravity属性,可以查看前面文章
http://isux.tencent.com/learn-android-from-zero-session3.html
我们可以实践一下:
新建一个Android项目,然后在layout文件夹找到布局xml文件并写入以下布局
android:measureAllChildren
viewFlipper中的item如何动态设置高度?
例如:
<ViewFlipper android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="bottom"> <include layout="@layout/layoutone"/> <include layout="@layout/layouttwo"/> <include layout="@layout/layoutthree"/> ViewFlipper>
假如想做成一个layoutone是50dp,layouttwo是50dp,layoutthree是80dp高度的话,你会发现在子布局中设置高度后,ViewFlipper切换时总是以子view中高度最大的值为其高度值,也就是80dp。但是又不想让layoutone和layouttwo太高,开始的时候想通过LayoutParams动态设置吧,可惜不行(把viewflipper单独出来才行),然后找到需要设置android:measureAllChildren="false",或者代码调用setMeasureAllChildren(false);即可,因为默认情况下measureAllChildren=true。设置后各个view的高度就不同了。该属性也适合FrameLayout等。
原因:参见FrameLayout#onMeasure(int, int)的源码,android:measureAllChildren="true"时,将所有children加入到mMeasureAllChildren的链表中,然后再重新measure下。
效果图
看到这个图时你可以先想想如果是你,你怎么实现这个效果。马上想到用RelativeLayout?NO,NO,NO,,,
二、实现代码
< LinearLayout xmlns:android ="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width ="match_parent"
android:layout_height ="match_parent"
android:clipChildren ="false"
android:orientation ="vertical" >
< android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
android:id ="@+id/view_pager"
android:layout_width ="match_parent"
android:layout_height ="0dip"
android:layout_weight ="1.0" />
< LinearLayout
android:layout_width ="match_parent"
android:layout_height ="48dip"
android:background ="#B0C4DE"
android:orientation ="horizontal" >
< ImageView
android:layout_width ="0dip"
android:layout_height ="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight ="1.0"
android:scaleType ="fitCenter"
android:src ="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
< ImageView
android:layout_width ="0dip"
android:layout_height ="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight ="1.0"
android:scaleType ="fitCenter"
android:src ="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
< ImageView
android:layout_width ="0dip"
android:layout_height ="64dip"
android:layout_gravity ="bottom"
android:layout_weight ="1.0"
android:scaleType ="fitCenter"
android:src ="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
< ImageView
android:layout_width ="0dip"
android:layout_height ="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight ="1.0"
android:scaleType ="fitCenter"
android:src ="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
< ImageView
android:layout_width ="0dip"
android:layout_height ="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight ="1.0"
android:scaleType ="fitCenter"
android:src ="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
LinearLayout >
LinearLayout >
代码说明:
1、只需在根节点设置android:clipChildren为false即可,默认为true
2、可以通过android:layout_gravity控制超出的部分如何显示。
3、android:clipChildren的意思:是否限制子View在其范围内
翻文档找到下面介绍
android:clipChildren setClipChildren(boolean) Defines whether a child is limited to draw inside of its bounds or not.
android:clipToPadding setClipToPadding(boolean)Defines whether the ViewGroup will clip its drawing surface so as to exclude the padding area.
2. clipToPadding用来定义ViewGroup是否允许在padding中绘制。默认情况下,cliptopadding被设置为ture, 也就是把padding中的值都进行裁切了。1.clipChild用来定义他的子控件是否要在他应有的边界内进行绘制。 默认情况下,clipChild被设置为true。 也就是不允许进行扩展绘制。
还有该功能是android第一个版本就已经提供的方法。 所有可以跨任意android版本使用。
这两个属性联合起来能干什么呢? 哈, 用来做一些类似于心形放大等点击特效非常合适啊。 不用去更改布局, 只需加入这两个属相,并引入动画效果就完成了。
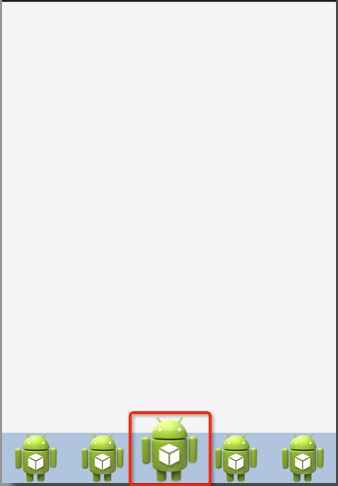
按照上面的思路,做个demo吧。
先看看最后的效果吧, 点击第三个机器人就会播放一个变大的效果(类似于心变大的效果)
废话不多说,上关键代码:
1. 布局代码(核心)
主要看设的两个关键属性android:clipChildren和android:clipToPadding均为false。 这就让点击第三个小人时,可以跨边界进行绘制,并且允许其在padding区域内绘制。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:clipChildren="false" android:clipToPadding="false"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img3" android:onClick="AA" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="@android:color/black" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img5" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img6" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> LinearLayout>
2. 其他辅助代码,如动画和act等内容
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<scale
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:fromYScale="1.0"
android:toXScale="3.0"
android:toYScale="3.0"
android:duration="2000"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
>
scale>
package com.example.clipchildren; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.View; import android.view.animation.Animation; import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils; import android.widget.ImageView; import android.widget.Toast; public class MainActivity extends Activity { //只对第三个小人做放大动作 ImageView image3 =null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); image3 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.img3); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true; } public void AA(View view) { Toast.makeText(this, "aa", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); Animation an = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(getApplicationContext(), R.anim.anims); image3.startAnimation(an); } }
3. 除了这种应用,网上还有其他人对这两个属性的妙用:
用viewPaper来实现一个Gallery效果:http://www.iteye.com/topic/1129898