CTE 递归查询全解
在TSQL脚本中,也能实现递归查询,SQL Server提供CTE(Common Table Expression),只需要编写少量的代码,就能实现递归查询,本文详细介绍CTE递归调用的特性和使用示例,递归查询主要用于层次结构的查询,从叶级(Leaf Level)向顶层(Root Level)查询,或从顶层向叶级查询,或递归的路径(Path)。
一,递归查询原理
CTE的递归查询必须满足三个条件:初始条件,递归调用表达式,终止条件,CTE 递归查询的伪代码如下:
WITH cte_name ( column_name [,...n] ) AS ( --Anchor member is defined CTE_query_definition UNION ALL --Recursive member is defined referencing cte_name CTE_query_definition ) -- Statement using the CTE SELECT * FROM cte_name
1,递归查询至少包含两个子查询:
- 第一个子查询称作定点(Anchor)子查询:定点查询只是一个返回有效表的查询,用于设置递归的初始值;
- 第二个子查询称作递归子查询:该子查询调用CTE名称,触发递归查询,实际上是递归子查询调用递归子查询;
- 两个子查询使用union all,求并集;
2,CTE的递归终止条件
递归查询没有显式的递归终止条件,只有当递归子查询返回空结果集(没有数据行返回)或是超出了递归次数的最大限制时,才停止递归。
默认的递归查询次数是100,可以使用查询提示(hint):MAXRECURSION 控制递归的最大次数:OPTION( MAXRECURSION 16);如果允许无限制的递归次数,使用查询提示:option(maxrecursion 0);当递归查询达到指定或默认的 MAXRECURSION 数量限制时,SQL Server将结束查询并返回错误,如下:
The statement terminated. The maximum recursion 10 has been exhausted before statement completion.
事务执行失败,该事务包含的所有操作都被回滚。在产品环境中,慎用maxrecursion 查询提示,推荐通过 where 条件限制递归的次数。
3,递归步骤
step1:定点子查询设置CTE的初始值,即CTE的初始值Set0;
递归调用的子查询过程:递归子查询调用递归子查询;
step2:递归子查询第一次调用CTE名称,CTE名称是指CTE的初始值Set0,第一次执行递归子查询之后,CTE名称是指结果集Set1;
step3:递归子查询第二次调用CTE名称,CTE名称是指Set1,第二次执行递归子查询之后,CTE名称是指结果集Set2;
step4:在第N次执行递归子查询时,CTE名称是指Set(N-1),递归子查询都引用前一个递归子查询的结果集;
Step5:如果递归子查询返回空数据行,或超出递归次数的最大限制,停止递归;
二,递归查询示例(员工职称)
1,创建测试数据
ManagerID是UserID的父节点,这是一个非常简单的层次结构模型。
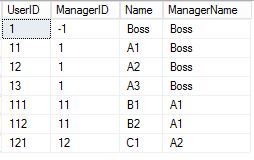
use tempdb go create table dbo.dt_user ( UserID int, ManagerID int, Name Nvarchar(10) ) insert into dbo.dt_user select 1,-1,N'Boss' union all select 11,1,N'A1' union all select 12,1,N'A2' union all select 13,1,N'A3' union all select 111,11,N'B1' union all select 112,11,N'B2' union all select 121,12,N'C1'
2,查询每个User的的直接上级Manager
;with cte as ( select UserID,ManagerID,name,name as ManagerName from dbo.dt_user where ManagerID=-1 union all select c.UserID,c.ManagerID,c.Name,p.name as ManagerName from cte P inner join dbo.dt_user c on p.UserID=c.ManagerID ) select UserID,ManagerID,Name,ManagerName from cte order by UserID
step1:查询ManagerID=-1,作为root node,这是递归查询的起始点。
step2:迭代公式是 union all 下面的查询语句。在查询语句中调用中cte,而查询语句就是cte的组成部分,即 “自己调用自己”,这就是递归的真谛所在。
所谓迭代,是指每一次递归都要调用上一次查询的结果集,Union ALL是指每次都把结果集并在一起。
step3-N,迭代公式利用上一次查询返回的结果集执行特定的查询,直到CTE返回null 或达到最大的迭代次数,默认值是32。最终的结果集是迭代公式返回的各个结果集的并集,求并集是由Union All 子句定义的,并且只能使用Union ALL。
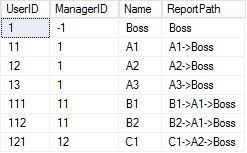
3,查询路径,在层次结构中查询子节点到父节点的path
;with cte as ( select UserID,ManagerID,name,cast(name as nvarchar(max)) as ReportPath from dbo.dt_user where ManagerID=-1 union all select c.UserID,c.ManagerID,c.Name,c.name+'->'+p.ReportPath as ReportPath from cte P inner join dbo.dt_user c on p.UserID=c.ManagerID ) select UserID,ManagerID,Name,ReportPath from cte order by UserID
查询结果如下截图:
三,递归查询示例(行政区划)
1,需求模拟
在TSQL中实现层次结构,例如有这样一种数据结构,省,市,县,乡,村,如何使用一张表表示这种数据结构,并且允许是不对称的,例如,上海市是个直辖市,没有省份。
create table dbo.hierarchy ( ID int not null primary key, --type int not null, ParentID int not null, name varchar(100) not null )
type表示类型,可以设置:省,Type是1;市,type是2,以此类推。
ParentID标识的是父级ID,例如信阳市的ParentID是河南省的ID。
2,插入测试数据
测试数据格式说明了归属关系,博主懒,去掉type字段。
insert into dbo.hierarchy values(1,0,'河南省') ,(2,1,'信阳市'),(3,2,'淮滨县'),(4,3,'芦集乡'),(12,3,'邓湾乡'),(13,3,'台头乡'),(14,3,'谷堆乡') ,(8,2,'固始县'),(9,8,'李店乡') ,(10,2,'息县'),(11,10,'关店乡') ,(5,1,'安阳市'),(6,5,'滑县'),(7,6,'老庙乡') ,(15,1,'南阳市'),(16,15,'方城县') ,(17,1,'驻马店市'),(18,17,'正阳县') select * from dbo.hierarchy order by ParentID
3,实现由父级向子级的查询
由于实际的数据可能有很多,所以,要想获取河南省下的所有市,县,乡,村等信息,必须使用递归查询
;with cte(Id,ParentID,Name) as ( select * from dbo.hierarchy where id=1 union all select h.* from dbo.hierarchy h inner join cte c on h.ParentID=c.id --where c.id!=h.ID ) select * from cte order by ParentID
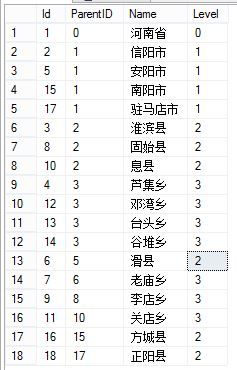
如果要查看向内递归到多少level,可以使用派生列,level=0是省level,level=1是市level,依次类推。
;with cte(Id,ParentID,Name,Level) as ( select ID,ParentID,Name,0 as Level from dbo.hierarchy where id=1 union all select h.ID,h.ParentID,h.Name,c.Level+1 as Level from dbo.hierarchy h inner join cte c on h.ParentID=c.id --where c.id!=h.ID ) select * from cte order by ParentID
查询结果如图:
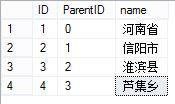
4,由子级向父级的递归查询
;with cte as ( select ID,ParentID,name from dbo.hierarchy where id=4 --芦集乡的ID union all select h.ID,h.ParentID,h.name from dbo.hierarchy h inner join cte c on h.id=c.ParentID ) select ID,ParentID,name from cte order by ParentID
查询结果如图:
参考文档:
Recursive Queries Using Common Table Expressions
WITH common_table_expression (Transact-SQL)
--欢迎转载,转载请注明出处--