Hibernate缓存机制
hibernate缓存机制是hibernate中很重要的一个内容,我们来看下hibernate的缓存机制。
hibernate缓存分为:一级缓存、二级缓存、查询缓存
1、一级缓存
又称为session缓存,生命周期相同,周期较短。也称为事务级别的缓存。
通过项目案例来简单了解下,项目结构如下:
Book实体类
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private double price;
private String author;
private Date pubDate;
public Book() {
}
public Book(String name, double price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price
+ ", author=" + author + ", pubDate=" + pubDate + "]";
}
//省略get/set
}
hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql:///hibernatetest
root
root
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
true
update
public class HibernateUtil {
private static Configuration cfg=null;
private static SessionFactory factory=null;
private static Session session=null;
static{
cfg=new Configuration().configure();
factory=cfg.buildSessionFactory(new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.applySettings(cfg.getProperties()).build());
}
public static Session getSession(){
if(factory!=null)
return session=factory.openSession();
factory=cfg.buildSessionFactory(new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.applySettings(cfg.getProperties()).build());
return session=factory.openSession();
}
public static void closeSession(){
if(session!=null && session.isOpen())
session.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testCreateDB(){
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
SchemaExport se=new SchemaExport(cfg);
se.create(true, true);
}向数据库表插入数据
@Test
public void testSave(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=new Book();
book.setName("读者");
book.setPrice(21.5);
book.setAuthor("读者出版传媒有限公司");
book.setPubDate(new Date());
Book book1=new Book();
book1.setName("蓝血人");
book1.setPrice(50);
book1.setAuthor("卫斯理");
book1.setPubDate(new Date());
Book book2=new Book();
book2.setName("傲慢与偏见");
book2.setPrice(80);
book2.setAuthor("简.奥斯丁");
book2.setPubDate(new Date());
Book book3=new Book();
book3.setName("中国历史");
book3.setPrice(21.5);
book3.setAuthor("人民");
book3.setPubDate(new Date());
session.save(book);
session.save(book1);
session.save(book2);
session.save(book3);
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}接下来就是各种查询的缓存问题
1)get方法
@Test
public void testGet(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
//发出sql语句取数据
System.out.println(book.getName());
System.out.println("============");
book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
System.out.println(book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_, book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
读者
============
读者get使用了一级缓存,用get查询时,首先检查缓存中是否有该数据,如果有直接从缓存中取数据,如果没有再查询数据库,并且将数据放入缓存中。
2)load方法
@Test
public void testLoad(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=(Book) session.load(Book.class, 1);
//发出sql语句取数据
System.out.println(book.getName());
System.out.println("============");
book=(Book) session.load(Book.class, 1);
System.out.println(book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
读者
============
读者总结:
load方法使用了一级缓存,用load查数据时,首先检查缓存中是否有该数据,
如果有,直接从缓存中获取数据;如果没有,再去数据库查数据,然后将数据放入缓存中。load还支持lazy
3)先get,后load
@Test
public void testGetLoad(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
//发出sql语句取数据
System.out.println(book.getName());
System.out.println("============");
book=(Book) session.load(Book.class, 1);
System.out.println(book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
读者
============
读者总结:
先用get,再用load,load同样从一级缓存中查找数据,如果有数据,直接取不用到数据库查询。
4)list方法
@Test
public void testList(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
List list=session.createQuery("from Book").list();
System.out.println("条数:"+list.size());
System.out.println("=========");
list=session.createQuery("from Book").list();
System.out.println("条数:"+list.size());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_
条数:4
=========
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_
条数:4list查数据不去缓存中查数据,但是list查出来的‘实体对象’数据,会放入缓存中。
5)先list,再get
@Test
public void testList(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
List list=session.createQuery("from Book").list();
System.out.println("条数:"+list.size());
System.out.println("=========");
Book book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 2);
System.out.println("书名:"+book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
} 控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_
条数:4
=========
书名:蓝血人总结:
先用list查询,list查出来的实体对象数据,放入缓存中。然后用get直接从缓存中取数据。
6)先list,后uniqueResult
@Test
public void testListUniqueResult(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
List list=session.createQuery("select name from Book").list();
System.out.println("条数:"+list.size());
System.out.println("=========");
Object bookName=session.createQuery("select name from Book where id=:id")
.setInteger("id", 2).uniqueResult();
System.out.println("书名:"+bookName);
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
} 控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.name as col_0_0_ from book book0_
条数:4
=========
Hibernate: select book0_.name as col_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
书名:蓝血人这里list查询出来的不是实体对象,所以这些数据不会存入缓存中(只有当list查询出的是实体对象时,才会被存入缓存中)
7)uniqueResult测试
@Test
public void testUnique(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=(Book) session.createQuery("from Book where id=:id")
.setInteger("id", 2).uniqueResult();
System.out.println("书名:"+book.getName());
System.out.println("=========");
book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 2);
System.out.println("书名:"+book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
书名:蓝血人
=========
书名:蓝血人总结:
unique查数据不去缓存中查数据。
8)先list,再iterate
@Test
public void testListIterate(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
List list=session.createQuery("from Book").list();
System.out.println("条数:"+list.size());
System.out.println("=========");
Iterator iter=session.createQuery("from Book").iterate();
for(;iter.hasNext();){
Book book=iter.next();
System.out.println("书名:"+book.getName());
}
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
} 控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_
条数:4
=========
Hibernate: select book0_.id as col_0_0_ from book book0_
书名:读者
书名:蓝血人
书名:傲慢与偏见
书名:中国历史从上面示例可以看出iterate只查询了id,并没有查询实体类。iterate使用了缓存。
9)iterate
@Test
public void testIterate(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Iterator iter=session.createQuery("from Book").iterate();
for(;iter.hasNext();){
System.out.println("书名:"+iter.next().getName());
}
System.out.println("=========");
iter=session.createQuery("from Book").iterate();
for(;iter.hasNext();){
Book book=iter.next();
System.out.println("书名:"+book.getName());
}
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}
Hibernate: select book0_.id as col_0_0_ from book book0_
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
书名:读者
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
书名:蓝血人
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
书名:傲慢与偏见
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
书名:中国历史
=========
Hibernate: select book0_.id as col_0_0_ from book book0_
书名:读者
书名:蓝血人
书名:傲慢与偏见
书名:中国历史总结:
iterate会执行查询id的操作,当查询对象时,会检查缓存中是否存在。如果存在从缓存中取数据。iterate查询出来的对象也会放入缓存中。
管理一级缓存
flush():强制将数据存入数据库表中;
clear():清除缓存;
evict():将对象从当前session中清除;
一级缓存很难管理,我们不一定知道什么时候该用flush,clear,evict,如果需要实时性很强的数据一般不用hibernate。
flush代码
@Test
public void testSaveBatch(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
Book book=new Book();
book.setName("测试"+i);
book.setPrice(21.5);
book.setAuthor("读者出版传媒有限公司");
book.setPubDate(new Date());
if(i%50==0)session.flush();
session.save(book);
}
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}evict代码与clear效果相同
@Test
public void testEvict(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
System.out.println(book.getName());
//将book对象从session中清除(等同于session.clear())
session.evict(book);
//清除缓存
//session.clear();
System.out.println("----------");
book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
System.out.println(book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
读者
----------
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
读者2、二级缓存
SessionFactory:进程级别的缓存,支持集群。
使用步骤:
1)在hibernate.cfg.xml中配置(默认是开启的)
true
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory
3)导入ehcache的jar包
ehcache的jar包的地址是 hibernate-release-4.3.11.Final\lib\optional\ehcache
如图:
4)将ehcache的配置文件包放到src下
ehcache的配置文件的地址是 hibernate-release-4.3.11.Final\project\etc
如图:
ehcache.xml中部分属性的含义
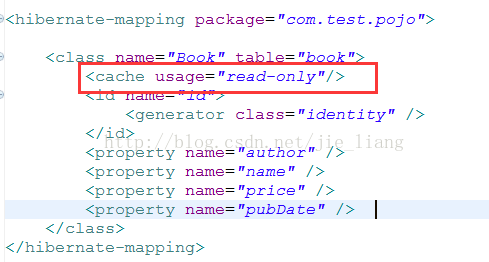
5)在*.hbm.xml或在hibernate.cfg.xml中指定要使用二级缓存的类(推荐使用在hibernate.cfg.xml中指定)
在Book.hbm.xml中指定
在hibernate.cfg.xml中指定
6)测试
@Test
public void testGet(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
Book book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
//发出sql语句取数据
System.out.println(book.getName());
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
System.out.println("============");
book=(Book) session.get(Book.class, 1);
System.out.println(book.getName());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
}控制台打印信息如下
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.id=?
读者
============
读者虽然我们关闭了session,又重新获得了一个session,但是获取第二个数据时,并没有去数据库查数据,说明二级缓存起作用了。
3、查询缓存
查询缓存是在二级缓存的基础上设置的,也就是说要使用查询缓存,我们需要先把二级缓存配置好,然后配置查询缓存
1)配置查询缓存
测试
@Test
public void testQueryCache(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
List list=session.createQuery("from Book")
.setCacheable(true) //使用查询缓存
.list();
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println("-------");
list=session.createQuery("from Book")
.setCacheable(true) //使用查询缓存
.list();
System.out.println(list.size());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
} 控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_
4
-------
4将session关闭,再重新打开仍然可以从二级缓存中使用查询缓存取出数据。
测试代码:
@Test
public void testQueryCache(){
Session session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
Transaction tx=session.beginTransaction();
List list=session.createQuery("from Book")
.setCacheable(true) //使用查询缓存
.list();
System.out.println(list.size());
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
session=HibernateUtil.getSession();
System.out.println("-------");
list=session.createQuery("from Book")
.setCacheable(true) //使用查询缓存
.list();
System.out.println(list.size());
tx.commit();
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
} 控制台打印信息如下:
Hibernate: select book0_.id as id1_0_, book0_.author as author2_0_, book0_.name as name3_0_,
book0_.price as price4_0_, book0_.pubDate as pubDate5_0_ from book book0_
4
-------
4说明数据存在二级缓存中,关闭session并不影响查询数据。