数据结构与算法(十一)Trie字典树
本文主要包括以下内容:
- Trie字典树的基本概念
- Trie字典树的基本操作
- 插入
- 查找
- 前缀查询
- 删除
- 基于链表的Trie字典树
- 基于Trie的Set性能对比
- LeetCode相关线段树的问题
- LeetCode第208号问题
- LeetCode第211号问题
- LeetCode第677号问题
Trie字典树的基本概念
上一篇我们介绍了 线段树(Segment Tree),本文主要介绍Trie字典树。
通过前面的介绍我们知道一个线性表的顺序查找的时间复杂度为O(n);二分搜索树的查找为O(log n),它们都和数据结构中的元素个数相关。关于线性表和二分搜索树的时间复杂度分析有需要的可以查看 Set集合和BinarySearchTree的时间复杂度分析
本文介绍的Trie字典树(主要用于存储字符串)查找速度主要和它的元素(字符串)的长度相关[O(w)]。
Trie字典树主要用于存储字符串,Trie 的每个 Node 保存一个字符。用链表来描述的话,就是一个字符串就是一个链表。每个Node都保存了它的所有子节点。
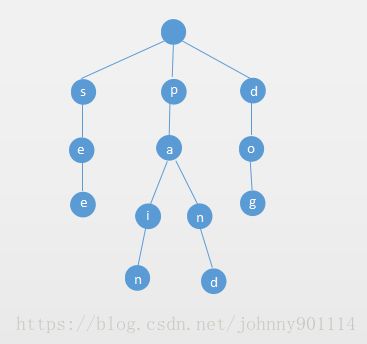
例如我们往字典树中插入see、pain、paint三个单词,Trie字典树如下所示:
也就是说如果只考虑小写的26个字母,那么Trie字典树的每个节点都可能有26个子节点。
Trie字典树的基本操作
插入
本文是使用链表来实现Trie字典树,字符串的每个字符作为一个Node节点,Node主要有两部分组成:
- 是否是单词 (boolean isWord)
- 节点所有的子节点,用map来保存 (Map next)
例如插入一个paint单词,如果用户查询pain,尽管 paint 包含了 pain,但是Trie中仍然不包含 pain 这个单词,所以如果往Trie中插入一个单词,需要把该单词的最后一个字符的节点的 isWord 设置为 true。所以为什么Node需要存储 是否是单词 这个属性。
节点的所有子节点,通过一个Map来存储,key是当前子节点对应的字符,value是子节点。
实现的伪代码如下:
public void add(String word) {
Node current = root;
char[] cs = word.toCharArray();
for (char c : cs) {
Node next = current.next.get(c);
if (next == null) {
//一个字符对应一个Node节点
current.next.put(c, new Node());
}
current = current.next.get(c);
}
//current就是word的最后一个字符的Node
//如果当前的node已经是一个word,则不需要添加
if (!current.isWord) {
size++;
current.isWord = true;
}
}
查找
Trie查找操作就比较简单了,遍历带查找的字符串的字符,如果每个节点都存在,并且待查找字符串的最后一个字符对应的Node的 isWord 属性为 true ,则表示该单词存在,伪代码如下:
public boolean contains(String word) {
Node current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
Node node = current.next.get(c);
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
current = node;
}
//current就是word的最后一个字符的Node
return current.isWord;
}
前缀查询
前缀查询和上面的查询操作基本类似,就是不需要判断 isWord 了
public boolean containsPrefix(String prefix) {
Node current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
Node node = current.next.get(c);
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
current = node;
}
return true;
}
删除
Trie的删除操作就稍微复杂一些,主要分为以下3种情况:
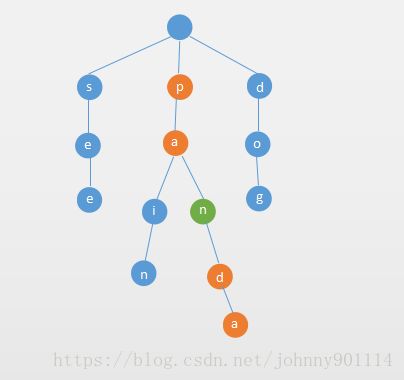
如果单词是另一个单词的前缀
如果待删除的单词是另一个单词的前缀,只需要把该单词的最后一个节点的 isWord 的改成false
比如Trie中存在 panda 和 pan 这两个单词,删除 pan ,只需要把字符 n 对应的节点的 isWord 改成 false 即可
如下图所示
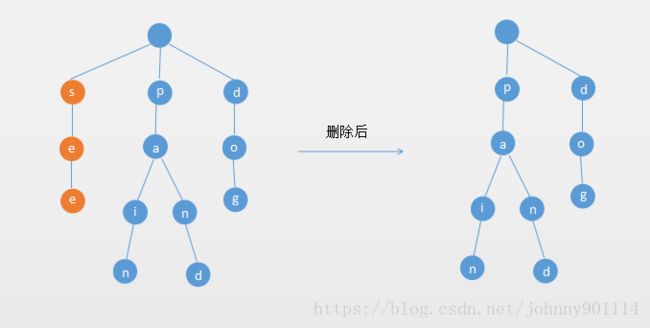
如果单词的所有字母的都没有多个分支,删除整个单词
如果单词的所有字母的都没有多个分支(也就是说该单词所有的字符对应的Node都只有一个子节点),则删除整个单词
例如要删除如下图的see单词,如下图所示:
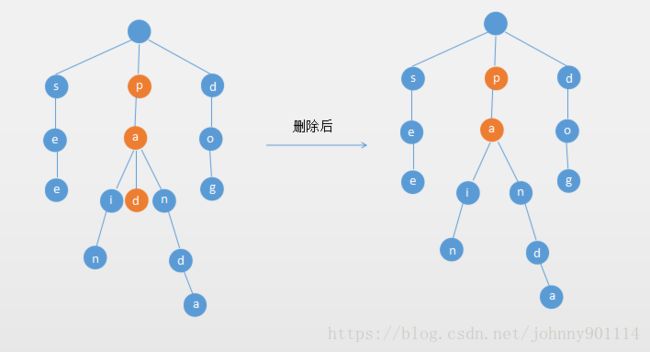
如果单词的除了最后一个字母,其他的字母有多个分支
基于链表的Trie字典树
public class Trie {
private Node root;
private int size;
private static class Node {
public boolean isWord;
public Map next;
public Node() {
next = new TreeMap<>();
}
public Node(boolean isWord) {
this();
this.isWord = isWord;
}
}
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* 插入操作
*
* @param word 单词
*/
public void add(String word) {
Node current = root;
char[] cs = word.toCharArray();
for (char c : cs) {
Node next = current.next.get(c);
if (next == null) {
current.next.put(c, new Node());
}
current = current.next.get(c);
}
//如果当前的node已经是一个word,则不需要添加
if (!current.isWord) {
size++;
current.isWord = true;
}
}
/**
* 是否包含某个单词
*
* @param word 单词
* @return 存在返回true,反之false
*/
public boolean contains(String word) {
Node current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
Node node = current.next.get(c);
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
current = node;
}
//如果只存在 panda这个词,查询 pan,虽然有这3个字母,但是并不存在该单词
return current.isWord;
}
/**
* Trie是否包含某个前缀
*
* @param prefix 前缀
* @return
*/
public boolean containsPrefix(String prefix) {
Node current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
Node node = current.next.get(c);
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
current = node;
}
return true;
}
/*
* 1,如果单词是另一个单词的前缀,只需要把该word的最后一个节点的isWord的改成false
* 2,如果单词的所有字母的都没有多个分支,删除整个单词
* 3,如果单词的除了最后一个字母,其他的字母有多个分支,
*/
/**
* 删除操作
*
* @param word
* @return
*/
public boolean remove(String word) {
Node multiChildNode = null;
int multiChildNodeIndex = -1;
Node current = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
Node child = current.next.get(word.charAt(i));
//如果Trie中没有这个单词
if (child == null) {
return false;
}
//当前节点的子节点大于1个
if (child.next.size() > 1) {
multiChildNodeIndex = i;
multiChildNode = child;
}
current = child;
}
//如果单词后面还有子节点
if (current.next.size() > 0) {
if (current.isWord) {
current.isWord = false;
size--;
return true;
}
//不存在该单词,该单词只是前缀
return false;
}
//如果单词的所有字母的都没有多个分支,删除整个单词
if (multiChildNodeIndex == -1) {
root.next.remove(word.charAt(0));
size--;
return true;
}
//如果单词的除了最后一个字母,其他的字母有分支
if (multiChildNodeIndex != word.length() - 1) {
multiChildNode.next.remove(word.charAt(multiChildNodeIndex + 1));
size--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
基于Trie的Set性能对比
在前面的Set集合和BinarySearchTree的时间复杂度分析中我们分别使用了基于链表和基于二分搜索树实现的Set,对两本英文原著进行简单的词频统计。
现在使用Trie实现下Set集合,然后三者性能做一个比较,还是以傲慢与偏见、双城记、战争与和平三本原著作为数据源。
傲慢与偏见(Pride and Prejudice)的性能对比
Pride and Prejudice
Total words: 125901
Total different words: 6530
TrieSet Time: 0.099788784
BSTSet Time: 0.339963625
LinkedListSet Time: 3.554973381
从中可以看出傲慢与偏见不同的单词只有6000左右,阅读难度不是很大。
双城记(A Tale of Two Cities)的性能对比
A Tale of Two Cities
Total words: 141489
Total different words: 9944
TrieSet Time: 0.119505174
BSTSet Time: 0.331334495
LinkedListSet Time: 5.26063235
战争与和平(War and peace)的性能对比
War and Peace
Total words: 602359
Total different words: 16725
TrieSet Time: 0.09750872
BSTSet Time: 0.233328074
以上关于原著词汇的统计只是简单的对比单词是否一致,并没有考虑一个单词的过去式、进行时等时态,只要字符串不一致都把它当作不同的单词。
更多关于Trie的话题
上面实现的Trie中,我们是使用TreeMap来保存节点的所有的子节点,也可以使用HashMap来保存所有的子节点,效率更高:
public Node() {
next = new HashMap<>();
}
当然我们也可以使用一个定长的数组来存储所有的子节点,效率比HashMap更高,因为不需要使用hash函数:
public Node(boolean isWord){
this.isWord = isWord;
next = new Node[26];//只能存储26个小写字母
}
Trie查询效率非常高,但是对空间的消耗还是挺大的,这也是典型的空间换时间。
可以使用 压缩字典树(Compressed Trie) ,但是维护相对来说复杂一些。
如果我们不止存储英文单词,还有其他特殊字符,那么维护子节点的集合可能会更多。
可以对Trie字典树做些限制,比如每个节点只能有3个子节点,左边的节点是小于父节点的,中间的节点是等于父节点的,右边的子节点是大于父节点的,这就是三分搜索Trie字典树(Ternary Search Trie)。
LeetCode相关线段树的问题
LeetCode第208号问题
问题描述:
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个操作。
示例:
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // 返回 true
trie.search("app"); // 返回 false
trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // 返回 true
问题说明:
你可以假设所有的输入都是由小写字母 a-z 构成的。
保证所有输入均为非空字符串。
这个问题在我们实现的 Trie字典树 中已经实现了这个功能了,add()就是对应的insert(),contains()就是对应的search(),starcontainsPrefix()就是对应的startsWith(),这里就不贴代码了。
LeetCode第211号问题
问题描述:
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
void addWord(word)
bool search(word)
search(word)
可以搜索文字或正则表达式字符串,字符串只包含字母 . 或 a-z 。 . 可以表示任何一个字母。
示例:
addWord("bad")
addWord("dad")
addWord("mad")
search("pad") -> false
search("bad") -> true
search(".ad") -> true
search("b..") -> true
问题说明:
你可以假设所有单词都是由小写字母 a-z 组成的。
这个问题就是上一个问题的基础上加上 . 的处理,稍微复杂点。
如果下一个字符是 . ,那么需要遍历该节点的所有子节点,对所有子节点的处理就是一个递归程序:
public boolean searchByWildCard(String express) {
return search(root, express, 0);
}
private boolean search(Node node, String express, int index) {
//如果已经到了待查询字符串的尾端了
if (index == express.length()) {
return node.isWord;
}
char c = express.charAt(index);
if (c != '.') {
Node nextChar = node.next.get(c);
if (nextChar == null) {
return false;
}
return search(nextChar, express, index + 1);
} else {//如果是通配符
Map nextNodes = node.next;
//遍历所有的子节点
for (Map.Entry entry : nextNodes.entrySet()) {
if (search(entry.getValue(), express, index + 1)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
LeetCode第677号问题
问题描述:
实现一个 MapSum 类里的两个方法,insert 和 sum。
对于方法 insert,你将得到一对(字符串,整数)的键值对。字符串表示键,整数表示值。如果键已经存在,那么原来的键值对将被替代成新的键值对。
对于方法 sum,你将得到一个表示前缀的字符串,你需要返回所有以该前缀开头的键的值的总和。
示例 1:
输入: insert("apple", 3), 输出: Null
输入: sum("ap"), 输出: 3
输入: insert("app", 2), 输出: Null
输入: sum("ap"), 输出: 5
总结一句话就是,求出所有符合该前缀的字符串的键值的总和。
节点需要保存一个键值,用于求和。节点Node不需要维护 isWord 这个属性了,因为不关注是不是一个单词。
class Node {
public int value;
public Map next;
}
public int sum(String prefix) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
Node node = cur.next.get(c);
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
cur = node;
}
//cur指向prefix的最后一个字符的Node
//对每个以prefix为前缀的node进行累加
return countValue(cur);
}
private int countValue(Node node) {
int result = node.value;
for (char c : node.next.keySet()) {
result += countValue(node.next.get(c));
}
return result;
}
上面三个LeetCode的问题答案,都可以在我的github上查看
Reference
本文主要内容和大纲是学习了慕课网 liuyubobobo 老师的视频《算法大神带你玩转数据结构 从入门到精通》
有需要的同学可以看看, 真心不错. 墙裂推荐… 最好能加上自己的思考和理解.
下面是我的公众号,干货文章不错过,有需要的可以关注下,有任何问题可以联系我:
文本相关源代码github