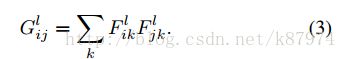使用CNN做图像风格转化+代码实现
18/6/13更新:
由于评论区很多说效果不明显,这是因为之前使用的是Squeezenet,且并没有经过任何预训练,所以效果不是很好。
在这里补上一个效果更好的、使用VGG19并经过了Imagenet预训练的一个结构,其代码下载地址:vgg19_transfer
相应的权重文件可在百度网盘下载:vgg19.npy
论文来源:Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks
图像风格转化,即将我们的原始图片,转换成我们想要的特定风格的图片。这是一个比较好玩的东西,可以用来合成许多有意思的图片。下图为论文中给出的结果图。
简单来说,就是我们给定两幅图片,其中我们想要提取出风格的图片为我们的style image,另一个想要提取出内容的图片为我们的content image。
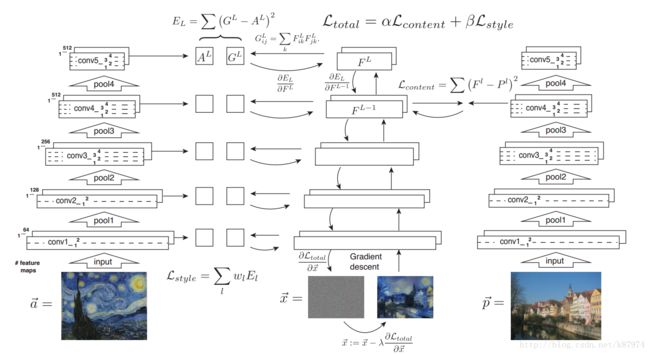
我们搭建三个卷积神经网络,其中之一用于提取style image的特征,其二用于提取content image的特征,最后一个神经网络初始化一个随机噪声图像,通过对图像做梯度下降来不断迭代更新我们的图像,来生成我们的最终结果图。
下图为论文作者给出的content image 和style image在神经网络(VGG19)架构中不同层次中的可视化表示,其结果表明在神经网络低层次中,content image的可视化重建与原图几乎没什么差别。
简单来说,就是我们给定两幅图片,其中我们想要提取出风格的图片为我们的style image,另一个想要提取出内容的图片为我们的content image。
下图所示为论文的具体实现过程,原作者使用的神经网络架构为VGG19网络。
content representation
A layer with Nl distinct filters has Nl feature maps each of size Ml, where Ml is the height times the width of the feature map. So the responses in a layer l can be stored in a matrix F l ∈ RNl×Ml where F l
ij is the activation of the ith filter at position j in layer l.简单来说Fl 就是第l层的特征表示。用![]() 和
和![]() 分别表示生成图和原图,Fl和Pl分别为其特征表示。然后定义一个平方差loss函数。
分别表示生成图和原图,Fl和Pl分别为其特征表示。然后定义一个平方差loss函数。
通过上述公式,我们可以使用梯度下降方法来使我们的生成图像在对应的卷积层生成与原图相同的特征表示。这样这完成了我们风格转化中内容图像的转化。
style representation
feature correlations are given by the Gram matrix Gl ∈ RNl×Nl, where Gl ij is the inner product between the vectorised feature maps i and j in layer l:
简单来说,Gl ij 表示第l层不同feature map之间的内在点积。令![]() 为我们的style image,则可以定义一个loss:
为我们的style image,则可以定义一个loss:
则总的style loss 就可以表示为: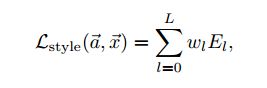 ,其中,wl为不同卷积层所占的权重。其导数计算如下:
,其中,wl为不同卷积层所占的权重。其导数计算如下:
最后,总的loss如上图中所示。
其代码实现,我们使用SqueezeNet,squeezeNet为AlexNet的精简版,在达到AlexNet在imageNet上分类正确率的同事,减少了50X的参数量。简单来讲,就是性能不变,速度更快了。比较适合我这种电脑比较渣的人。
使用tensorflow的实现如下:
def content_loss(content_weight, content_current, content_original):
"""
Compute the content loss for style transfer.
Inputs:
- content_weight: scalar constant we multiply the content_loss by.
- content_current: features of the current image, Tensor with shape [1, height, width, channels]
- content_target: features of the content image, Tensor with shape [1, height, width, channels]
Returns:
- scalar content loss
"""
# tf.shape outputs a tensor containing the size of each axis.
shapes = tf.shape(content_current)
F_l = tf.reshape(content_current, [shapes[1], shapes[2]*shapes[3]])
P_l = tf.reshape(content_original,[shapes[1], shapes[2]*shapes[3]])
loss = content_weight * (tf.reduce_sum((F_l - P_l)**2))
return loss在定义style loss之前,先定义Gram 矩阵:
def gram_matrix(features, normalize=True):
"""
Compute the Gram matrix from features.
Inputs:
- features: Tensor of shape (1, H, W, C) giving features for
a single image.
- normalize: optional, whether to normalize the Gram matrix
If True, divide the Gram matrix by the number of neurons (H * W * C)
Returns:
- gram: Tensor of shape (C, C) giving the (optionally normalized)
Gram matrices for the input image.
"""
shapes = tf.shape(features)
# Reshape feature map from [1, H, W, C] to [H*W, C].
F_l = tf.reshape(features, shape=[shapes[1]*shapes[2],shapes[3]])
# Gram calculation is just a matrix multiply of F_l and F_l transpose to get [C, C] output shape.
gram = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(F_l),F_l)
if normalize == True:
gram /= tf.cast(shapes[1]*shapes[2]*shapes[3],tf.float32)
return gram接下来完成style loss:
def style_loss(feats, style_layers, style_targets, style_weights):
"""
Computes the style loss at a set of layers.
Inputs:
- feats: list of the features at every layer of the current image, as produced by
the extract_features function.
- style_layers: List of layer indices into feats giving the layers to include in the
style loss.
- style_targets: List of the same length as style_layers, where style_targets[i] is
a Tensor giving the Gram matrix the source style image computed at
layer style_layers[i].
- style_weights: List of the same length as style_layers, where style_weights[i]
is a scalar giving the weight for the style loss at layer style_layers[i].
Returns:
- style_loss: A Tensor contataining the scalar style loss.
"""
# Hint: you can do this with one for loop over the style layers, and should
# not be very much code (~5 lines). You will need to use your gram_matrix function.
# Initialise style loss to 0.0 (this makes it a float)
style_loss = tf.constant(0.0)
# Compute style loss for each desired feature layer and then sum.
for i in range(len(style_layers)):
current_im_gram = gram_matrix(feats[style_layers[i]])
style_loss += style_weights[i] * tf.reduce_sum((current_im_gram - style_targets[i])**2)
return style_loss我们可以通过添加一个total-variation regularization来减少像素值中的摆动或“总体变化”。
def tv_loss(img, tv_weight):
"""
Compute total variation loss.
Inputs:
- img: Tensor of shape (1, H, W, 3) holding an input image.
- tv_weight: Scalar giving the weight w_t to use for the TV loss.
Returns:
- loss: Tensor holding a scalar giving the total variation loss
for img weighted by tv_weight.
"""
# Your implementation should be vectorized and not require any loops!
w_variance = tf.reduce_sum((img[:,:,1:,:] - img[:,:,:-1,:])**2)
h_variance = tf.reduce_sum((img[:,1:,:,:] - img[:,:-1,:,:])**2)
loss = tv_weight * (w_variance + h_variance)
return loss接下来,完成风格转化的函数:
def style_transfer(content_image, style_image, image_size, style_size, content_layer, content_weight,
style_layers, style_weights, tv_weight, init_random = False):
"""Run style transfer!
Inputs:
- content_image: filename of content image
- style_image: filename of style image
- image_size: size of smallest image dimension (used for content loss and generated image)
- style_size: size of smallest style image dimension
- content_layer: layer to use for content loss
- content_weight: weighting on content loss
- style_layers: list of layers to use for style loss
- style_weights: list of weights to use for each layer in style_layers
- tv_weight: weight of total variation regularization term
- init_random: initialize the starting image to uniform random noise
"""
# Extract features from the content image
content_img = preprocess_image(load_image(content_image, size=image_size))
feats = model.extract_features(model.image)
content_target = sess.run(feats[content_layer],
{model.image: content_img[None]})
# Extract features from the style image
style_img = preprocess_image(load_image(style_image, size=style_size))
style_feat_vars = [feats[idx] for idx in style_layers]
style_target_vars = []
# Compute list of TensorFlow Gram matrices
for style_feat_var in style_feat_vars:
style_target_vars.append(gram_matrix(style_feat_var))
# Compute list of NumPy Gram matrices by evaluating the TensorFlow graph on the style image
style_targets = sess.run(style_target_vars, {model.image: style_img[None]})
# Initialize generated image to content image
if init_random:
img_var = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform(content_img[None].shape, 0, 1), name="image")
else:
img_var = tf.Variable(content_img[None], name="image")
# Extract features on generated image
feats = model.extract_features(img_var)
# Compute loss
c_loss = content_loss(content_weight, feats[content_layer], content_target)
s_loss = style_loss(feats, style_layers, style_targets, style_weights)
t_loss = tv_loss(img_var, tv_weight)
loss = c_loss + s_loss + t_loss
# Set up optimization hyperparameters
initial_lr = 3.0
decayed_lr = 0.1
decay_lr_at = 180
max_iter = 200
# Create and initialize the Adam optimizer
lr_var = tf.Variable(initial_lr, name="lr")
# Create train_op that updates the generated image when run
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer") as opt_scope:
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr_var).minimize(loss, var_list=[img_var])
# Initialize the generated image and optimization variables
opt_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES, scope=opt_scope.name)
sess.run(tf.variables_initializer([lr_var, img_var] + opt_vars))
# Create an op that will clamp the image values when run
clamp_image_op = tf.assign(img_var, tf.clip_by_value(img_var, -1.5, 1.5))
f, axarr = plt.subplots(1,2)
axarr[0].axis('off')
axarr[1].axis('off')
axarr[0].set_title('Content Source Img.')
axarr[1].set_title('Style Source Img.')
axarr[0].imshow(deprocess_image(content_img))
axarr[1].imshow(deprocess_image(style_img))
plt.show()
plt.figure()
# Hardcoded handcrafted
for t in range(max_iter):
# Take an optimization step to update img_var
sess.run(train_op)
if t < decay_lr_at:
sess.run(clamp_image_op)
if t == decay_lr_at:
sess.run(tf.assign(lr_var, decayed_lr))
if t % 100 == 0:
print('Iteration {}'.format(t))
img = sess.run(img_var)
plt.imshow(deprocess_image(img[0], rescale=True))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
print('Iteration {}'.format(t))
img = sess.run(img_var)
plt.imshow(deprocess_image(img[0], rescale=True))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()其中的一个结果如下:
文章中比较重要的两个参数就是α与β,这决定了你生成的图像所占的艺术比重以及内容比重,下图为作者所示的不同比重的结果:
图像风格转化是一个典型的卷积神经网络的应用,欢迎各位在评论区探讨。
代码下载地址如下:Style-transfer
如果你觉得有用,帮忙扫个红包支持一下吧: