Spring Boot 2 使用配置汇总
- Spring Boot 配置汇总
- 导入Spring boot 方式
- 导入web支持
- 编写程序入口类
- 编写控制器类
- Jackson设置日期的显示格式
- 使用fastjson处理返回的json
- web相关配置属性
- banner.txt
- 访问页面中的小图标
- Application.properties
- 代码热加载(防止频繁重启)
- 自动热加载(spring loader)
- 自动重启(spring boot devtools)(推荐使用)
- 数据库相关配置
- 关系型数据库
- Mysql
- H2
- HSQL
- Derby
- 数据库连接池
- Durid
- HiKariCP:号称最快的连接池。
- Tomcat pooling:
- Commons DBCP2:
- 持久层框架
- hibernate
- Mybatis
- 基于xml
- 基于注解的方式
- PageHelper
- Spring Data
- 面向对象数据库
- Mongodb
- 缓存配置
- Redis
- Spring Cache
- 缓存配置
- redis缓存配置
- 配置Session共享
- 关系型数据库
Spring Boot 配置汇总
导入Spring boot 方式
创建一个普通的Maven项目
使用标签进行导入
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>- 通过配置依赖项导入
<properties>
<springboot.version>2.0.0.RELEASEspringboot.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>${springboot.version}version>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>importscope>
dependency>
dependencies>spring-boot-starter 列表
其它需要导入内容
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<version>${springboot.version}version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>导入web支持
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
<version>${springboot.version}version>
dependency>编写程序入口类
/**
* 使用@SpringBootApplication注解标记的类会被spring boot进行加载;
* 默认会扫描当前类所在包和子包所有配置了spring注解的所有类。也可以通过scanBasePackages设置扫描的包
*
* @author xudl
*
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}编写控制器类
package org.demo.xudl.springboot2.web;
import java.util.Date;
import org.demo.xudl.springboot2.entity.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @RestController 和 @Controller的区别在@RestController返回JSON数据时,不需要指定@ResponseBody
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/getuser")
public User getUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("xudl");
user.setAge(30);
user.setCreateDate(new Date());
return user;
}
}访问该路径,可以直接获得JSON格式的数据。但日期的格式不太符合预期。需要进行配置和才能按照希望的方式进行显示;
Jackson设置日期的显示格式
package org.demo.xudl.springboot2.config;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
@Configuration
public class CustomerConfig {
/**
* 制定jsckson工具转换时对日期格式的处理
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ObjectMapper getObjectMapper() {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
return mapper;
}
}
再次访问上面的路径,返回的日期已经按照指定的格式进行返回了。Srping boot默认使用Jackson来进行序列化和返序列化。也可以配置使用其他开源工具进行转换。例如fastjson。
使用fastjson处理返回的json
- 导入依赖包(注意导入版本)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.46version>
dependency>- 添加转换器
-
- 继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter(已不推荐使用)
@SpringBootApplication
public class App extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List> converters) {
//定义一个转换消息的对象
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
//添加fastjson的配置信息 比如 :是否要格式化返回的json数据
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat);
List fastMediaTypes = new ArrayList();
// 处理中文乱码问题
fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8);
fastConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(fastMediaTypes);
//在转换器中添加配置信息
fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
//将转换器添加到converters中
converters.add(fastConverter);
} -
- @Bean方式
/**
* 添加fastjson的转换
*/
@Configuration
public class FastjsonConverter {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters customConverters() {
// 定义一个转换消息的对象
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
// 添加fastjson的配置信息 比如 :是否要格式化返回的json数据
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat);
List fastMediaTypes = new ArrayList();
// 处理中文乱码问题
fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8);
fastConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(fastMediaTypes);
// 在转换器中添加配置信息
fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
// 将转换器添加到converters中
return new HttpMessageConverters(fastConverter);
}
} - 实体类设置
public class UserVo implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String userName;
// 配置不转换JSON时忽略该属性
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private String password;
private String name;
private int age;
// 定义日期的格式化方法
@JSONField(format = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date crateDate;
// 省略getter和setter方法
}web相关配置属性
banner.txt
该文件配置了在启动时在控制台输出的内容。直接放在resources目录下即可覆盖默认的设置。在文件的信息也可以在application.properties文件中进行配置。
访问页面中的小图标
- 先将图片上传到resources/static/images目录中
- 在页面中添加标签:
Application.properties
Spring boot 默认通过resources目录下的Application.properties来设置配置信息。直接在目录中创建该文件。
#==================================
# 启动显示信息 相关配置
#----------------------------------
#spring.banner.charset=utf-8
#spring.banner.location=classpath:banner.txt
#spring.banner.image.location=classpath:static/images/canvas.png
#spring.banner.image.width=50
#spring.banner.image.height=50
#spring.banner.image.margin=10
#==================================
# servlet 相关配置
#----------------------------------
# 设置项目路径。默认是“/”
server.servlet.context-path=/xudl
# 设置session超时时间。单位为秒
server.servlet.session.timeout=1800
#==================================
# 日志 相关配置
#----------------------------------
# 日志配置方式。配置总体的日志级别和对应包的日志级别.使用logging.level开头即可
logging.level.root=INFO
logging.level.org.springframework.web=ERROR
logging.level.org.demo.xudl=debugSSS代码热加载(防止频繁重启)
- 开发工具要设置
-
- eclipse勾选设置(Project –> Build Automatically)
自动热加载(spring loader)
- 即代码修改后立即生效,不会重启。但这种情况下新增方法或删除方式后必须重启才会生效;
- 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>springloadedartifactId>
<version>1.2.8.RELEASEversion>
dependency>- 启动方式
- 1.添加VM参数:-javaagent:G:/software/springloaded-1.2.8.RELEASE.jar -noverify (将jar文件放在文件系统中方便不同项目使用)
-
- mvn spring-boot:run 会导致重启的时候报端口已被占用。必须手动关闭进程。(不推荐使用)
自动重启(spring boot devtools)(推荐使用)
- 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>- 上面的配置就可以实现代码修改后自动重启了。(Spring boot 重启只会重启自己编译的代码,导入的第三方包不需要重新加载,所以速度会比较快)
- 重启方式实践:
-
-
- Eclipse中每次修改都会导致自动重启,此时可以先取消自动编译,完成后打开编译即可重启;
-
-
-
- 配置一个监听文件,只有当这个文件修改后,才会触发重启;重启相关配置:
-
-
-
- 自动重启相关参数配置。Application.properties
-
#==================================
# devtools 相关设置
#----------------------------------
# 关闭日志记录中显示自动配置的项目修改
spring.devtools.restart.log-condition-evaluation-delta=false
# 默认的不自动重启目录有(修改后会自动加载):/META-INF/maven, /META-INF/resources, /resources, /static, /public, or /templates
# 如果想保留默认配置,只添加新目录。
#spring.devtools.restart.additional-exclude=html/*
# 覆盖默认配置
#spring.devtools.restart.exclude=static/**,public/**
# 配置类路径以外的文件修改后自动重启
#spring.devtools.restart.additional-paths=c:\restart.txt
# 配置特点文件的修改后,才自动重启
#spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file=
# 是否禁用重启功能。即使设置为false,仍然会初始化restart类加载器。通过java设置系统属性来禁止初始化restart
spring.devtools.restart.enabled=truepublic static void main(String[] args) {
// 完全禁止自动重启和初始化restart类加载器
System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled", "false");
SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args);
}数据库相关配置
Spring boot会根据导入的相关配置信息。来自动识别数据库。
关系型数据库
Mysql
- 导入驱动包
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>6.0.6version>
dependency>- application.properties
#==================================
# 数据库 相关设置
#----------------------------------
# datasource后面如果不接连接池配置,则是公共的配置;加上连接池名称可以设置连接池的特有配置
# 建议省略数据库驱动类,spring boot可以根据url判断出数据库类型
# spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.74.10:3306/xudl?characterEncoding=utf8&autoReConnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=xudl
spring.datasource.password=123456H2
HSQL
Derby
数据库连接池
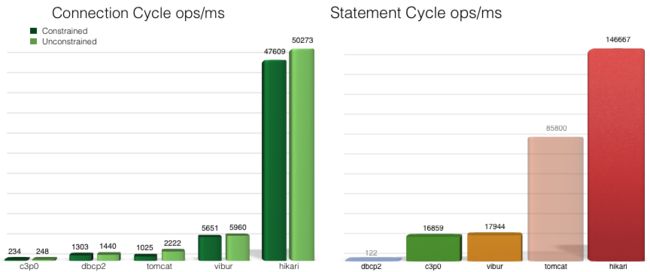
Spring boot默认的数据库连接池顺序:HiKariCP,Tomcat poolin, Commons DBCP2
Durid
- 依赖导入
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.9version>
dependency>- 配置application.properties
HiKariCP:号称最快的连接池。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zaxxergroupId>
<artifactId>HikariCPartifactId>
<version>2.7.8version>
dependency>- application.properties
#==================================
# HiKariCP连接池 相关设置
#----------------------------------
# hikari连接池的参数。(Tomcat pooling使用tomcat,dbcp2使用dbcp2)
# 定义获取连接的超时时间。最小250ms,默认30s
spring.datasource.hikari.connectionTimeout=10000
# 定义连接空闲时间。最小10s,默认10m
spring.datasource.hikari.idleTimeout=50000
# 定义最小的空闲连接数。推荐不设置。或与最大连接数一致;保持固定的连接数目
spring.datasource.hikari.minimumIdle=100
# 定义最大的连接数。默认10
spring.datasource.hikari.maximumPoolSize=100
# 定义连接的最大生命周期。推荐设置该属性。最小30s,默认30m
# spring.datasource.hikari.maxLifeTime=600000
# 从连接池获取到连接后,进行检查的查询语句。推荐设置该属性。默认值为none
spring.datasource.hikari.connectionTestQuery=select 1Tomcat pooling:
Commons DBCP2:
持久层框架
hibernate
Mybatis
- 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.3.1version>
dependency>基于xml
- (xml配置可以使用比较复杂的组合)
- mybatis-config.xml 放入到resources目录中
<configuration>
<mappers>
<package name="org.xudl.demo.spring.boot2.dao"/>
mappers>
configuration>- 编写CityMapper接口类(添加@Mapper注解),对应的映射文件,放在同一目录中
-
- CityMapper.java
package org.xudl.demo.spring.boot2.dao.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.demo.springboot2.commons.City;
@Mapper
public interface CityMapper {
City findByState(String state);
}-
- CityMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="org.xudl.demo.spring.boot2.dao.mapper.CityMapper">
<select
id="findByState"
resultType="org.demo.springboot2.commons.City">
SELECT id, name, state, country,create_time as createTime FROM city WHERE state = #{state}
select>
mapper>基于注解的方式
- 在类启动的地方配置@MapperScan并设置扫描的包;例如:@MapperScan(basePackages = “org.xudl.demo.spring.boot2.dao.mybatis.mapper”)
- 在上面的包和子包中添加接口类即可;
- 也可以将比较复杂的,或者不能通过注解实现的查询,使用xml进行编写;
注意:两种方式可以同时使用,使用注解时,也可以省略mybatis-config.xml文件;
PageHelper
- 提供分页的插件。项目地址
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.2.3version>
dependencySpring Data
面向对象数据库
Mongodb
缓存配置
Redis
使用Spring Data Redis来进行redis的访问,支持使用Jedis,lettuce来访问Redis。
- Spring Data Redis 官方文档
- 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>- application.properties配置相关信息
#==================================
# Redis 相关设置
#----------------------------------
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址。如果配置了集群,则集群的配置会覆盖host设置的地址
#spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.1.72:7001,192.168.1.72:7002,192.168.1.72:7003,192.168.1.72:7004,192.168.1.72:7005,192.168.1.72:7006
spring.redis.host=192.168.74.10
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
#spring.redis.password=
#------哨兵配置----------------------------------
# 设置哨兵配置中设置的监控名称
#spring.redis.sentinel.master=mymaster
# 启动的哨兵服务器端口。哨兵通常配置为奇数个
# 配置了哨兵模式,就不需要配置直接连接的redis端口信息了
#spring.redis.sentinel.nodes=192.168.1.72:7001,192.168.1.72:7002,192.168.1.72:7003
#------连接池配置----------------------------------
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=100
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=1000
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=100
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=100
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=1000- 在需要使用redis的类中注入StringRedisTemplate,通过调用其ops系列方法来获取操作接口;例如:strRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(“springdataredis”, “20180314”);
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate strRedisTemplate;
// 操作redis的方式
strRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("springdataredis", "20180314111222");
// 原子增操作
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("size", 1);
// Hashes 操作
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user", "name", "xudl2018");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().get("user", "name");
// 有序集合的操作
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("chinese_score", "xiaoming", 99.8);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("chinese_score", "mijs", 10.8);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("chinese_score", "wangfeng", 50.8);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("chinese_score", "xudl", 30.8);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().range("chinese_score", 0, 2);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRange("chinese_score", 0, 2);Spring Cache
Spring Cache 是Spring对缓存的抽象。用统一的方式来提供缓存的功能;这样替换具体的缓存方案时,代码不需要做调整;Spring本事提供了很多的缓存管理器:
- SimpleCacheManager
- EhCacheCacheManager
- CaffeineCacheManager
- GuavaCacheManager
- CompositeCacheManager
Spring boot 中通过@EnableCaching注解来提供缓存的功能;默认按下面的顺序来查找缓存提供者:
- Generic
- JCache (JSR-107)
- EhCache 2.x
- Hazelcast
- Infinispan
- Redis
- Guava
- Simple
缓存配置
- 添加@EnableCaching注解;通常在程序入口处添加;
- 在需要缓存的接口或实行类上面添加@CacheConfig注解,并配置一个缓存名称;例如:@CacheConfig(cacheNames = “city”)
- 在需要缓存的方法上添加@Cacheable(key = “#state”)。表示取参数state的值作为key,方法返回值作为value进行缓存;
- 在需要更新缓存的地方添加@CacheEvict(key = “#state”)。表示清除缓存;
注解说明:
- @Cacheable 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
- @CachePut 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用
- @CachEvict 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
属性含义:
1. value (也可使用 cacheNames) : 可看做命名空间,和key属性值共同组成redis的key。
2. key : 表示命名空间下缓存唯一key,使用Spring Expression Language(简称SpEL)生成。
3. condition : 表示在哪种情况下才缓存结果(对应的还有unless,哪种情况不缓存),同样使用SpEL。
4. allEntries: 标记是否删除命名空间下所有缓存,默认为false
使用示例:
缓存属性的常见用法:
@CachePut(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")
@Cacheable(value="accountCache",key="#accountName.concat(#password)")
@Cacheable(value="accountCache",condition="#accountName.length() <= 4")
@CachePut(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")
@CacheEvict(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")
@CacheEvict(value="accountCache",allEntries=true)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "query_user_", key = "'user_name_'+#name")redis缓存配置
- 通过上面的配置,不需要进行额外的配置。只要项目中配置了redis,就会使用redis缓存;
- 在application.properties中可以配置的缓存项目:
#==================================
# Spring Cache 相关设置
#----------------------------------
# 配置redis cache
# 配置缓存的前缀。如果不配置,则会使用@CacheConfig中的cacheNames+冒号+配置的key的值作为redis的key
# @Cacheable中配置的cacheNames会覆盖@CacheConfig中的cacheNames
spring.cache.redis.key-prefix=spring_cache_
# 配置缓存的失效时间。单位秒
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=36000Java中的写法。@CacheConfig和@Cacheable中,至少有一个指定cacheNames属性。
package org.demo.xudl.springboot2.dao;
import org.demo.xudl.springboot2.entity.User;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user")
public interface UserDao {
@Cacheable(key = "'user_name_'+#name")
User queryUserByName(String name);
}
还可以直接实现一个keyGenerator来设置缓存的key。配置和设置的key属性将不会生效。(配置后,该配置未生效,后续补充原因)
/**
* 定义自动缓存时,key的生成方式
*/
@Bean
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
// 设置key的格式为:"spring_case_"+类名+方法名称+参数值
// 此方式不利于更新缓存时指定某个key
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("springcase_");
sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
sb.append(method.getName());
for (Object obj : params) {
sb.append(obj.toString());
}
return sb.toString();
}
};
}配置Session共享
- 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.sessiongroupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>- 在application中配置
# 使用redis实现session共享
spring.session.store-type=redis
# 定义写入redis的时机
spring.session.redis.flush-mode=IMMEDIATE
spring.session.redis.namespace=spring:session
# 定义session的超时时间
server.servlet.session.timeout=1200- 添加注解@EnableRedisHttpSession启用session共享
@EnableRedisHttpSession(maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds = 86400 * 30)会覆盖server.servlet.session.timeout属性的值,不建议配置;
此时所有放入session的内容就会放入到redis中。档项目进行负载均衡时,当用户访问到不同的服务器时,就可以根据传入的sessionid获取该session对应的信息,实现共享;