kmcuda: GPU加速 Kmeans
文章目录
- 1、kmcuda简介
- 2、安装
- 1. 查询gcc版本
- 2. 查询GPU算力
- 3. 配置GPU路径
- 3、完整安装命令
- 4、安装遇到的问题
- 1. 使用pip安装
- 2. 未指定GPU算力或使用默认值
- 5、Python测试用例
- 1. K-means, L2 (Euclidean) distance
- 2. K-means, angular (cosine) distance + average
- 6、Python API
- 1. kmeans_cuda()
- 2. knn_cuda()
- 最近项目使用到Kmeans算法,考虑到CPU实现速度上的限制,需要使用GPU加速,因此查到
libKMCUDA库。- 记录安装使用过程中遇到的一些问题。
1、kmcuda简介
项目地址:kmcuda
项目内容:Large scale K-means and K-nn implementation on NVIDIA GPU / CUDA
该项目具体的介绍可参照github上的说明。
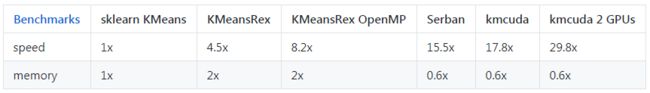
性能如下:
从技术上来讲,该项目是一个共享库,可导出kmcuda.h中定义的两个函数:kmeasn_cuda和knn_cuda。它具有内置的Python3和R语言本机扩展支持,因此可以从libKMCUDA导入kmeans_cuda或dyn.load("libKMCUDA.so")。
2、安装
Github上给出的安装命令:
git clone https://github.com/src-d/kmcuda
cd src
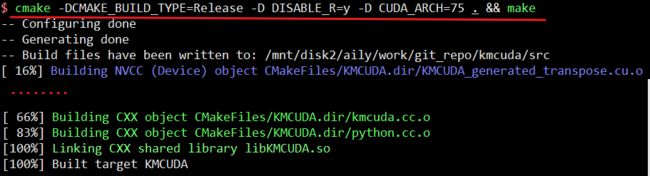
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release . && make
有几个参数需要注意一下:
-
-D DISABLE_PYTHON: 如果不想编译Python支持模块,将该项值为y,即增加-D DISABLE_PYTHON=y -
-D DISABLE_R: 如果不想编译R支持模块,增加-D DISABLE_R=y -
-D CUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR=/usr/local/cuda-10.0(修改为自己的路径):如果CUDA无法自动找到,则增加该项 -
-D CUDA_ARCH=52:指定当前机器的CUDA计算能力(GPU Compute Capability) -
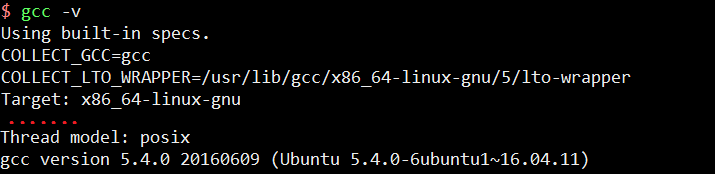
gcc:有文章提到,低版本的gcc编译器不支持,我当前版本是5.4,可满足需求。
1. 查询gcc版本
若版本过低,可安装gcc-5.4,具体安装参考如下博文:
linux下安装gcc详解
2. 查询GPU算力
通过NVIDIA官网查询自己GPU服务器的GPU算力,地址如下:
CUDA GPUs | NVIDIA Developer
我当前使用的服务器是GeForce RTX 2070,对应的算力是7.5。
因此,CUDA_ARCH设置为75, -D CUDA_ARCH=75
3. 配置GPU路径
为了能够自动查找相关库的路径,将cuda的路径配置到配置文件中。当前系统使用的shell为zsh:
在~/.zshrc中增加如下项:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/cuda/bin
export LD_LIBRARAY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export CUDA_TOOLKIT_ROOT_DIR=/usr/local/cuda:$CUDA_TOOLKIT_BOOT_DIR
export CUDA_INCLUDE_DIRS=/usr/local/cuda/include
激活生效:
source ~/.zshrc
3、完整安装命令
当前设备参数:
- gcc: 版本 5.4
- GPU算力: 7.5
- 仅需要Python版本支持
完整安装命令:
git clone https://github.com/src-d/kmcuda
cd src
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -D DISABLE_R-y -D CUDA_ARCH=75 . && make
4、安装遇到的问题
1. 使用pip安装
安装命令如下:
CUDA_ARCH=75 pip install libKMCUDA
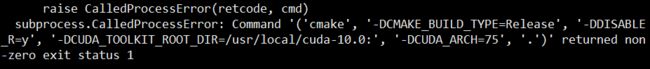
出现错误:
2. 未指定GPU算力或使用默认值
-
使用pip安装源文件
安装命令:
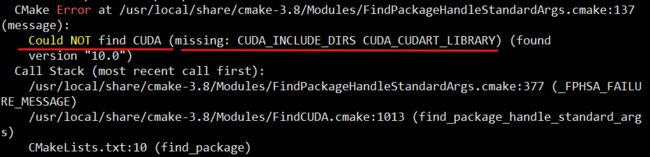
pip install git+https://github.com/src-d/kmcuda.git#subdirectory=src出现如下错误:
由此错误可见,使用该方式安装,默认使用使用的
-DCUDA_ARCH为61,与当前实际不符。 -
未指定GPU算力
安装命令:
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -D DISABLE_R=y . && make
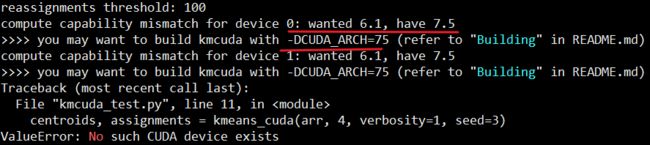
在进行测试的时候,会出现如下错误:
提示计算能力与设备不匹配。
5、Python测试用例
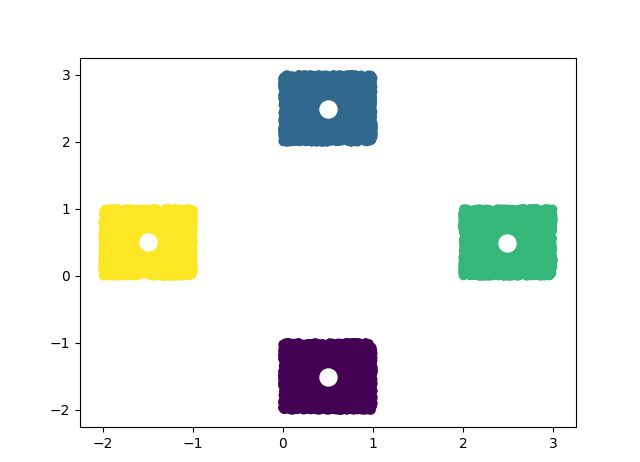
1. K-means, L2 (Euclidean) distance
import numpy
from matplotlib import pyplot
from libKMCUDA import kmeans_cuda
numpy.random.seed(0)
arr = numpy.empty((10000, 2), dtype=numpy.float32)
arr[:2500] = numpy.random.rand(2500, 2) + [0, 2]
arr[2500:5000] = numpy.random.rand(2500, 2) - [0, 2]
arr[5000:7500] = numpy.random.rand(2500, 2) + [2, 0]
arr[7500:] = numpy.random.rand(2500, 2) - [2, 0]
centroids, assignments = kmeans_cuda(arr, 4, verbosity=1, seed=3)
print(centroids)
pyplot.scatter(arr[:, 0], arr[:, 1], c=assignments)
pyplot.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1], c="white", s=150)
pyplot.show()
2. K-means, angular (cosine) distance + average
import numpy
from matplotlib import pyplot
from libKMCUDA import kmeans_cuda
numpy.random.seed(0)
arr = numpy.empty((10000, 2), dtype=numpy.float32)
angs = numpy.random.rand(10000) * 2 * numpy.pi
for i in range(10000):
arr[i] = numpy.sin(angs[i]), numpy.cos(angs[i])
centroids, assignments, avg_distance = kmeans_cuda(
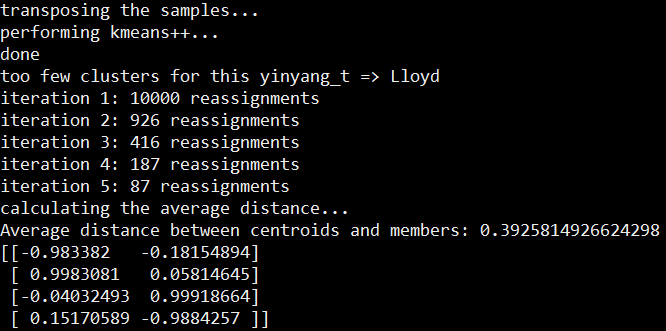
arr, 4, metric="cos", verbosity=1, seed=3, average_distance=True)
print("Average distance between centroids and members:", avg_distance)
print(centroids)
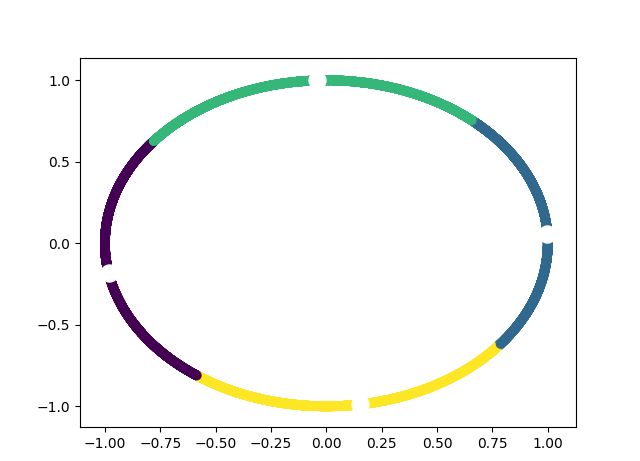
pyplot.scatter(arr[:, 0], arr[:, 1], c=assignments)
pyplot.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1], c="white", s=150)
pyplot.show()
结果如下:
6、Python API
1. kmeans_cuda()
def kmeans_cuda(samples, clusters, tolerance=0.01, init="k-means++",
yinyang_t=0.1, metric="L2", average_distance=False,
seed=time(), device=0, verbosity=0)
参数:
samples:shape为[样本数,特征数]的numpy数组,或者元组(raw device pointer (int), device index (int)clusters:int类型,聚类簇的数目tolerance:float类型,如果相对重新分配数量下降到该值以下,则算法停止。init:string或numpy数组,设置质心初始化方法,可以是k-means++,afk-mc2,random或指定shape的numpy数组[cluster, 特征数],类型必须是float32yinynag_t:float类型,通常设置为0.1metric:str类型,使用的距离度量名称。默认为Duclidean(L2),可以改为cos。请注意,后一种情况下,样本必须归一化。average_distance:boolean类型,该值表示是否计算类内元素与相应质心之间的平均距离,对于寻找最优K有用,作为第三个元组元素返回。seed:int类型,随机生成器种子用于再现结果。device:int类型,CUDA设备索引,如1表示第一个设备,2表示第二个,3表示使用第一个和第二个。指定为0表示启用所有设备,默认为0.verbosity:int类型,0意味着完全无输出,1表示仅记录进度,2表示大量输出。
返回值:元组(centroids, assignments, [average_distance])。
如果samples是numpy数组偶主机指针元组,则类型是numpy数组,否则,原始指针(整数)分配在同一设备上。
如果samples是float16,则返回的质心也是float16。
2. knn_cuda()
def knn_cuda(k, samples, centroids, assignments, metric="L2", device=0, verbosity=0)
参数:
-
k: integer, the number of neighbors to search for each sample. Must be ≤ 116.
-
samples: numpy array of shape [number of samples, number of features] or tuple(raw device pointer (int), device index (int), shape (tuple(number of samples, number of features[, fp16x2 marker]))). In the latter case, negative device index means host pointer. Optionally, the tuple can be 1 item longer with the preallocated device pointer for neighbors. dtype must be either float16 or convertible to float32.
-
centroids: numpy array with precalculated clusters’ centroids (e.g., using K-means/kmcuda/kmeans_cuda()). dtype must match samples. If samples is a tuple then centroids must be a length-2 tuple, the first element is the pointer and the second is the number of clusters. The shape is (number of clusters, number of features).
-
assignments: numpy array with sample-cluster associations. dtype is expected to be compatible with uint32. If samples is a tuple then assignments is a pointer. The shape is (number of samples,).
-
metric: str, the name of the distance metric to use. The default is Euclidean (L2), it can be changed to “cos” to change the algorithm to Spherical K-means with the angular distance. Please note that samples must be normalized in the latter case.
-
device: integer, bitwise OR-ed CUDA device indices, e.g. 1 means first device, 2 means second device, 3 means using first and second device. Special value 0 enables all available devices. The default is 0.
-
verbosity: integer, 0 means complete silence, 1 means mere progress logging, 2 means lots of output.
返回值: neighbor indices. If samples was a numpy array or a host pointer tuple, the return type is numpy array, otherwise, a raw pointer (integer) allocated on the same device. The shape is (number of samples, k).