Spring详细教程
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class User {
@Override
public String toString() {
return “User [id=” + id + “, name=” + name + “]”;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int id;
private String name;
}
2.编写Spring配置文件,类型为xml,文件名可以自定义
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
>
<bean id="User" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="jayjay"></property>
</bean>
beans>
3.利用Spring容器创建托管对象User
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User u = (User)context.getBean("User"); System.out.println(u);
三、Bean的配置深入
1.bean引用其他bean
实体类示例:
package test.Spring.helloworld;
public class HelloWorld {
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloWorld [name=" + name + ", user=" + user + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private String name;
private User user;
public HelloWorld(){
}
public HelloWorld(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
配置示例:
<bean id="HelloWorld" class="test.Spring.helloworld.HelloWorld">
<constructor-arg value="spring2" type="java.lang.String">constructor-arg>
<property name="user">
<ref bean="User"/>
property>
bean>
调用方法依然是根据bean中的id
2.集合bean配置
实体类示例:
package test.Spring.helloworld;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class User {
public Map
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map
this.map = map;
}
public List
return list;
}
public void setList(List
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return “User [id=” + id + “, name=” + name + “, list=” + list
+ “, map=” + map + “]”;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int id;
private String name;
private List
private Map
}
配置示例:
<bean id="testList" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User">
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1value>
<value>list2value>
<value>list3value>
list>
property>
bean>
<!-- configure the map -->
<bean id="testMap" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User">
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="first" value="1"></entry>
<entry key="second" value="2"></entry>
<entry key="third" value="3"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
3.Properties类型的bean
实体类示例:
package test.Spring.helloworld;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DataSource {
@Override
public String toString() {
return “Properties [properties=” + properties + “]”;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
private Properties properties;
}
配置示例:
<bean id="dataSource1" class="test.Spring.helloworld.DataSource">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="user">rootprop>
<prop key="password">1234prop>
<prop key="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql:///testprop>
<prop key="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driverprop>
props>
property>
bean>
4.使用Util定义引用其他bean的公共集合
需要先在xml导入命名空间
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
>
beans>
集合以及调用的xml配置
<util:list id="users">
<ref bean="User"/>
<ref bean="User"/>
<ref bean="User"/>
util:list>
<bean id="Users" class="test.Spring.helloworld.Users">
<property name="list">
<ref bean="users"/>
</property>
</bean>
5.使用p简化bean的属性赋值
首先,导入p的命名空间
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
实体类实例:
package test.Spring.helloworld;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class User {
@Override
public String toString() {
return “User [id=” + id + “, name=” + name + “]”;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int id;
private String name;
}
配置示例:
<bean id="User1" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User" p:id="2" p:name="jayjay2" />
6.abstract模板bean
设置abstract=true表明此bean是模板bean,为其他bean提供属性值模板
<bean abstract="true" id="template" p:id="50" p:name="fromTemplate">bean>
<bean id="User2" parent="template" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User">bean>
7.单例bean和原型bean
<bean id="User3" parent="template" scope="singleton" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User">bean>
<bean id="User4" parent="template" scope="prototype" class="test.Spring.helloworld.User">bean>
singleton:此bean为单例,在context创建时已经创建,并且只有一个实例。
prototype:当需要时创建实例。
8.静态工厂方法配置bean
静态工厂类示例:
package test.Spring.FactoryBean;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class StaticFactoryMethod {
public static Map
static {
map.put("first", new Person(1,"jayjay1"));
map.put("second", new Person(2,"jayjay2"));
}
public static Person getPerson(String key){
return map.get(key);
}
}
配置示例:
<bean id="person" factory-method="getPerson" class="test.Spring.FactoryBean.StaticFactoryMethod">
<constructor-arg value="first" type="java.lang.String">constructor-arg>
bean>
9.实例工厂方法配置bean
工厂类示例:
package test.Spring.FactoryBean;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class InstanceFactoryMethod {
public static Map
static {
map.put("first", new Person(1,"jayjay1"));
map.put("second", new Person(2,"jayjay2"));
}
public Person getPerson(String key){
return map.get(key);
}
}
配置示例:
<bean id="InstanceFactoryMethod" class="test.Spring.FactoryBean.InstanceFactoryMethod">bean>
<bean id="person1" factory-bean="InstanceFactoryMethod" factory-method="getPerson">
<constructor-arg value="second">constructor-arg>
bean>
10.通过实现FactoryBean完成bean的配置
需要对FactoryBean接口的3个方法进行适当重写
PersonFactoryBean类示例:
package test.Spring.FactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
public class PersonFactoryBean implements FactoryBean
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int id;
private String name;
@Override
public Person getObject() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Person(id,name);
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Person.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}
配置示例:
<bean id="person2" class="test.Spring.FactoryBean.PersonFactoryBean">
<property name="id" value="3">property>
<property name="name" value="FactoryBean">property>
bean>
四、通过注解配置bean
加上注解的类会被Spring容器管理
@Component
标注于通用实体类
@Controller
标注于Controller/Action
@Service
标注于Service
@Respository
标注于RespositoryImpl/DaoImlp
@Autowired
依据类型自动装配
@Qualifier
指定自动装载的bean的name
1.在Spring配置文件中导入context命名空间,并加入
<context:component-scan base-package="test.Spring.Annotation">context:component-scan>
表示Spring将扫描test.Spring.Annotation及其子包中所有java文件,并将带有注解的类加入Spring容器进行管理。
例如:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context">
<context:component-scan base-package="test.Spring.Annotation">context:component-scan>
beans>
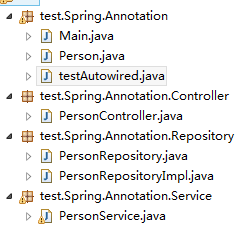
2.模拟三层,并用Spring注解方式注入
项目结构:
Person实体类
package test.Spring.Annotation; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Person {
@Override
public String toString() {
return “Person [id=” + id + “, name=” + name + “]”;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int id;
private String name;
}
PersonController
package test.Spring.Annotation.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class PersonController {
public void excute(){
System.out.println(“PersonController.excute()…”);
}
}
PersonService
package test.Spring.Annotation.Service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class PersonService {
public void add(){
System.out.println(“PersonService.add()…”);
}
}
PersonRepository接口
package test.Spring.Annotation.Repository;
public interface PersonRepository {
void add();
}
PersonRepositoryImpl接口实现类
package test.Spring.Annotation.Repository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class PersonRepositoryImpl implements PersonRepository {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("PersonRepositoryImpl.add()...");
}
}
Main类中测试
package test.Spring.Annotation;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import test.Spring.Annotation.Controller.PersonController;
import test.Spring.Annotation.Repository.PersonRepository;
import test.Spring.Annotation.Service.PersonService;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContextForAnnotation.xml”);
//inject the common bean
System.out.println(context.getBean("testAutowired"));
//inject the repository
PersonRepository pr = (PersonRepository)context.getBean("personRepositoryImpl");
pr.add();
//inject the controller
PersonController pc = (PersonController)context.getBean("personController");
pc.excute();
//inject the service
PersonService ps = (PersonService)context.getBean("personService");
ps.add();
}
}
3.泛型三层的注入
Spring配置文件
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
>
<context:component-scan base-package="test.Spring.Generic.di">context:component-scan>
beans>
BaseRespository
package test.Spring.Generic.di;
public class BaseRepository
public void save() {
System.out.println("repository.save()...");
}
}
PersonRepository
package test.Spring.Generic.di;
public interface PersonRespository {
void save();
}
PersonRepositoryImpl
继承BaseRepository就不需要再写一次save方法,且同时实现了PersonRepository接口
package test.Spring.Generic.di;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import test.Spring.Annotation.Person;
@Repository
public class PersonRespositoryImpl extends BaseRepository
}
BaseService对Dao进行自动装配,子类继承后装配的是子类Respository
package test.Spring.Generic.di;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class BaseService
@Autowired
protected BaseRepository<T> baseRespository;
public void save(){
System.out.println("service.save()...");
System.out.println(baseRespository);
}
}
PersonService继承了BaseService,就不需要再写实现save方法,定义Repository字段了
package test.Spring.Generic.di;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import test.Spring.Annotation.Person;
@Service
public class PersonService extends BaseService
}
Main类中调用
package test.Spring.Generic.di;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContextForGeneric.xml”);
PersonService ps = (PersonService)context.getBean(“personService”);
ps.save();
}
}
输出为
第二句说明调用的是继承BaseService的PersonService拿到的Respository是PersonRepositoryImpl,说明泛型注入成功。
十、使用SpringAOP完成简单的程序
1.导入SpringAOP所需jar包
2.编写spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd " xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" > <!-- configure the package for spring to scan --> <context:component-scan base-package="test.Spring.AOP" /> <!-- make the aspectj annotation to be used --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>xsi:schemaLocation
beans>
3.创建一个HelloWord接口以及它的实现类HelloWordImpl
public interface HelloWord { public int sayHello(int num); }
@Component public class HelloWordImpl implements HelloWord{ public int sayHello(int num){ System.out.println("hello word"); return 100/num; } }
4.SpringAOP注释的类型有5种
@Before 前置通知 在方法执行前执行
@After 后置通知 在方法执行后执行
@AfterThrowing 异常通知 在方法抛出异常之后执行
@AfterReturning 返回通知 在方法返回结果之后执行
@Around 环绕通知 环绕着方法执行
5.创建一个切面类(包含@Before @After @AfterThrowing @AfterReturning)
@Component @Aspect public class HelloWordAspect {@Before(value="execution(* test.Spring.AOP.HelloWord.sayHello(..))") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint jp){ String methodName = jp.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println(methodName); System.out.println("before method execute,args are "+Arrays.toString(jp.getArgs())); } @After("execution(* test.Spring.AOP.HelloWord.sayHello(..))") public void afterMethod(JoinPoint jp){ System.out.println("after method execute,args are "+Arrays.toString(jp.getArgs())); } @AfterThrowing(value="execution(* test.Spring.AOP.HelloWord.sayHello(..))",throwing="ex") public void afterThrow(Exception ex){ System.out.println("afterThrow"+ex.getMessage()); } @AfterReturning(value="execution(* test.Spring.AOP.HelloWord.sayHello(..))",returning="result") public void afterReturn(Object result){ System.out.println("the result is "+result); }
}
6.在主函数调用
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextForAOP.xml");HelloWord hw = (HelloWord) context.getBean("helloWordImpl"); hw.sayHello(10); }
}
7.调用结果
结果说明,在sayHello方法是被Spring代理执行了,执行前后加上了一些切面类中定义的信息。
8.使用Around环绕通知切面类实现类似效果
@Component @Aspect public class HelloWordAspectAround { @Around(value="execution(* test.Spring.AOP.HelloWord.sayHello(..)))") public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){ Object result = null; String methodName = pjp.getSignature().getName(); try { result = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("the result is "+result); } catch (Throwable e) { System.out.println("Exception occurs : "+e.getMessage()); throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println(methodName+" end");return result; }
}
十一、SpringAOP整合Hibernate并使用事务(模拟买书的过程)
1.内容准备
①.编写实体类
Book
public class Book { public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } private int id; private String name; private int price; private int count; }
Customer
public class Customer { public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(int balance) { this.balance = balance; } private int id; private String name; private int balance; }
②.编写实体类映射文件
<hibernate-mapping package="springaop.model"> <class name="Book" table="t_book"> <id name="id" type="int" column="id" > <generator class="native">generator> id> <property name="name" type="string" column="name"/> <property name="price" type="int" column="price"/> <property name="count" type="int" column="count"/></class>
hibernate-mapping>
<hibernate-mapping package="springaop.model"> <class name="Customer" table="t_customer"> <id name="id" type="int" column="id" > <generator class="native">generator> id> <property name="name" type="string" column="name"/> <property name="balance" type="int" column="balance"/></class>
hibernate-mapping>
③.编写dao及daoImpl
public interface ShopRepository { public int findBookPriceByBookName(String name); public void updateBookCount(String name); public void updateUserBalance(String name,int price); }
@Repository public class ShopRepositoryImpl implements ShopRepository{@Autowired private SessionFactory sessionFactory; private Session getSession(){ return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession(); } @Override public int findBookPriceByBookName(String name) { String sql = "select b.price from Book b where b.name=?"; Query query = getSession().createQuery(sql).setString(0, name); return (Integer)query.uniqueResult(); } @Override public void updateBookCount(String name) { String sql1 = "select b.count from Book b where b.name=?"; Query query = getSession().createQuery(sql1).setString(0,name); int count = (int)query.uniqueResult(); if(count<=0){ throw new RuntimeException("库存不足"); } String sql2 = "update Book b set b.count=b.count-1 where b.name=?"; getSession().createQuery(sql2).setString(0,name).executeUpdate(); } @Override public void updateUserBalance(String name, int price) { String sql1 = "select c.balance from Customer c where c.name=?"; Query query = getSession().createQuery(sql1).setString(0,name); int count = (int)query.uniqueResult(); if(count-price<0){ throw new RuntimeException("余额不足"); } String sql2 = "update Customer c set c.balance=c.balance-? where c.name=?"; getSession().createQuery(sql2).setInteger(0, price).setString(1,name).executeUpdate(); }
}
④.编写service及serviceImpl
public interface ShopService { public void shop(String bookName,String username); }
@Service public class ShopServiceImpl implements ShopService{@Autowired private ShopRepository sr; @Override public void shop(String bookName, String username) { int price = sr.findBookPriceByBookName(bookName); sr.updateUserBalance(username, price); sr.updateBookCount(bookName); }
}
2.加入Hibernate
①.添加hibernate必须的jar包
②.添加hibernate.cfg.xml
<hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialectproperty> <property name="show_sql">trueproperty> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">updateproperty><!-- 配置hibernate二级缓存相关 --> </session-factory>
hibernate-configuration>
3.加入Spring
①.导入Spring必须的jar包
②.配置Spring的applicationContext.xml及db.properties文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd " xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" ><!-- 配置Spring扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="springaop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <!-- 导入资源文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property> <property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initialPoolSize}"></property> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置Hibernete的SessionFactory实例 --> <!-- 通过配置Spring提供的LcalSessionFactory --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml"></property> <property name="mappingLocations" value="classpath:springaop/model/*.hbm.xml"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置Spring的声明式事务 --> <!-- 1.配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property> </bean> <!-- 2.配置事务属性 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 3.配置事务切点,并把切点和事务关联起来, --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* springaop.service.*.*(..))" id="txPointcut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/> </aop:config>
beans>
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=1234
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///test
jdbc.initialPoolSize=5
jdbc.maxPoolSize=10
4.运行测试
public class test { private ApplicationContext context = null;private ShopService ss = null; { context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ss= context.getBean(ShopService.class); } @Test public void test() throws SQLException{ DataSource ds = context.getBean(DataSource.class); System.out.println(ds.getConnection()); } @Test public void test1(){ ss.shop("Java", "jayjay"); } @Test public void test3(){ ss.shop("C", "jayjay"); }
}
当钱不够的时候,会抛出异常“余额不足”,并且事务回滚;当钱足够时,正常执行。
源码下载:SpringAOP整合Hibernate并使用事务(模拟买书的过程)-源码
转自:Spring详细教程