Opencv调用深度学习模型
OpenCv 从V3.3版本开始支持调用深度学习模型,例如Caffe, Tensorflow, darknet等.详细见下图,具体的使用方法,可以参考官网:
https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.1/d6/d0f/group__dnn.html
目前Opencv可以支持的网络有GoogLeNet, ResNet-50,MobileNet-SSD from Caffe等,具体的可以参考:https://github.com/opencv/opencv/wiki/ChangeLog,里面有对dnn模块的详细介绍.
在github上,Opencv也有关于dnn模块的使用例子:https://github.com/opencv/opencv/tree/3.4.1/samples/dnn
这里只使用Python接口的Opencv 对Yolo V2(目前Opencv还不支持Yolo V3, 期待下一个版本支持)和Tensorflow训练出来的ssd_inception_v2_coco模型进行说明.
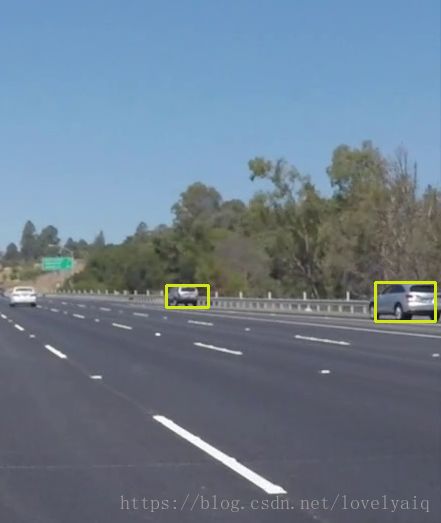
Yolo V2模型:
import cv2
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('solidYellowLeft.mp4')
def read_cfg_model():
model_path = '/home/scyang/TiRan/WorkSpace/others/darknet/cfg/yolov2.weights'
cfg_path = '/home/scyang/TiRan/WorkSpace/others/darknet/cfg/yolov2.cfg'
yolo_net = cv2.dnn.readNet(model_path, cfg_path, 'darknet')
while True:
flag, img = cap.read()
if flag:
yolo_net.setInput(cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1.0/127.5, (416, 416), (127.5, 127.5, 127.5), False, False))
cvOut = yolo_net.forward()
for detection in cvOut:
confidence = np.max(detection[5:])
if confidence > 0:
classIndex = np.argwhere(detection == confidence)[0][0] - 5
x_center = detection[0] * cols
y_center = detection[1] * rows
width = detection[2] * cols
height = detection[3] * rows
start = (int(x_center - width/2), int(y_center - height/2))
end = (int(x_center + width/2), int(y_center + height/2))
cv2.rectangle(img,start, end , (23, 230, 210), thickness=2)
else:
break
cv2.imshow('show', img)
cv2.waitKey(10) 这里需要对cvOut的结果说明一下:cvOut的前4个表示检测到的矩形框信息,第5位表示背景,从第6位开始代表检测到的目标置信度及目标属于那个类。
因此,下面两处的作用是,从5位开始获取结果中目标的置信度及目标属于那个类。
confidence = np.max(detection[5:])
classIndex = np.argwhere(detection == confidence)[0][0] - 5Tensorflow模型
cvNet = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow('model/ssd_inception_v2_coco_2017_11_17.pb','model/ssd_inception_v2_coco_2017_11_17.pbtxt')
while True:
flag, img = cap.read()
if flag:
rows = img.shape[0]
cols = img.shape[1]
width = height = 300
image = cv2.resize(img, ((int(cols * height / rows), width)))
img = image[0:height, image.shape[1] - width:image.shape[1]]
cvNet.setInput(cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1.0/127.5, (300, 300), (127.5, 127.5, 127.5), swapRB=True, crop=False))
cvOut = cvNet.forward()
# Network produces output blob with a shape 1x1xNx7 where N is a number of
# detections and an every detection is a vector of values
# [batchId, classId, confidence, left, top, right, bottom]
for detection in cvOut[0,0,:,:]:
score = float(detection[2])
if score > 0.3:
rows = cols = 300
# print(detection)
left = detection[3] * cols
top = detection[4] * rows
right = detection[5] * cols
bottom = detection[6] * rows
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), (23, 230, 210), thickness=2)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.waitKey(10)
else:
break效果如下:
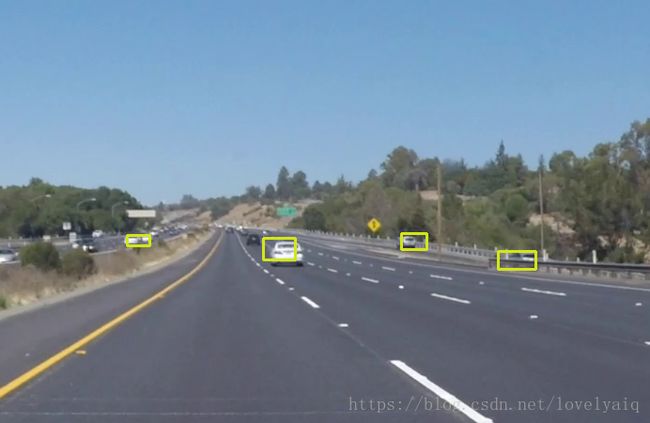

使用方法和Yolo的类似,从最终的效果可以看出,ssd_inception_v2模型要比V2好。
注:blobFromImage的详细介绍及使用方法,可以参考某大神的博客:https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2017/11/06/deep-learning-opencvs-blobfromimage-works/。这里就不在多述了,要学会站在巨人的肩膀上。
