android线程管理五(ActivityThread与ApplicationThread)
前言
android中
App
第一次启动时,会创建一个进程,在这个进程中可以启动各个组件(如
Activity、BroadcastReceiver、Service),这些组件都是在同一个进程中运行的,
而
负责它们执行的是该进程中的UI线程。本篇主要介绍
ActivityThread、ApplicationThread。
转载请注明出处:小石头的博客
http://blog.csdn.net/lu1024188315/article/details/74518599
一 ActivityThread
1 几个重要的成员变量
(1)ApplicationThread
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
说明,ApplicationThread是ActivityThread的内部类,ActivityThread与启动Activity有关,那么
ApplicationThread就与启动Application有关了。
(2)H
final H mH = new H();
H#源码如下:
private class H extends Handler { ......//声明的一些常量 ...... public void handleMessage(Message msg) { ...... switch (msg.what) { //针对不同的常量,做不同的业务处理 case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: { ......//启动一个Activity handleLaunchActivity(r, null, "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY"); ...... } break; case RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY: { ...... handleRelaunchActivity(r); ...... } break; case PAUSE_ACTIVITY: { ...... handlePauseActivity((IBinder) args.arg1, false, (args.argi1 & USER_LEAVING) != 0, args.argi2, (args.argi1 & DONT_REPORT) != 0, args.argi3); maybeSnapshot(); ...... } break; ...... } ...... } private void maybeSnapshot() { ......//这个方法主要统计snapshot } }
说明,H继承与Handle,重写了handleMessage的方法,这个类主要作用就是根据不同的情况处理各种业务,而且处理业务的方法一般是以handle开头,handleXXX的格式,如下:
handleActivityConfigurationChanged() handleBindApplication() handleBindService() handleCancelVisibleBehind() handleConfigurationChanged() handleCreateService() handleDestroyActivity() handleDispatchPackageBroadcast() handleLaunchActivity() handleLowMemory() handleMessage() handleNewIntent() handlePauseActivity() handleReceiver() handleRelaunchActivity() handleResumeActivity() handleSendResult() handleServiceArgs() handleStopActivity() handleStopService()
而这些函数有的又会调用到如下的performXXX系列函数完成最终的事件处理:
performDestroyActivity() performDestroyActivity() performLaunchActivity() performNewIntents() performPauseActivity() performPauseActivity() performRestartActivity() performResumeActivity() performStopActivity() performStopActivityInner() performUserLeavingActivity()
例如当msg.what == LAUNCH_ACTIVITY就是调用handleLaunchActivity方法启动一个Activity,Activity#
handleLaunchActivity源码如下:
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) { ......//调用performLaunchActivity方法完成Activity的启动 Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent); ...... }
说明,在
handleLaunchActivity中又调用了performLaunchActivity方法来创建一个Activity实例,完成Activity的启动。
(3)
mActivities
final ArrayMap<IBinder, ActivityClientRecord> mActivities = new ArrayMap<>();
说明,mActivities包含了当前进程的所有的activity,注意不是简单的把activity做了数据集合,而是封装成了ActivityClientRecord,
ActivityClientRecord是ActivityThread的内部类,那么
ActivityClientRecord是个神马鬼?源码如下:
static final class ActivityClientRecord { IBinder token;//Activity的token 每一个Activity对应一个token int ident; Intent intent;//保存启动Activity的意图 String referrer; //这个是IPC接口,aidl文件,会被VoiceInteractor回调 IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor; Bundle state; PersistableBundle persistentState; //被创建的Activity将会被保存在这里 Activity activity; //保存该activity中的窗口 Window window; //该Activity的父组件 Activity parent; String embeddedID; Activity.NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances; //true 说明该Activity 处于暂停状态 即调用了onPause boolean paused; //true 说明该Activity结束了 boolean stopped; //true 说明该Activity不可见 boolean hideForNow; Configuration newConfig; Configuration createdConfig; Configuration overrideConfig; // Used for consolidating configs before sending on to Activity. private Configuration tmpConfig = new Configuration(); ActivityClientRecord nextIdle; ProfilerInfo profilerInfo; //保存该Activity相关信息 ActivityInfo activityInfo; CompatibilityInfo compatInfo; //保存apk加载相关信息 LoadedApk packageInfo; //ResultInfo类保存了应用程序相关信息 List<ResultInfo> pendingResults; List<ReferrerIntent> pendingIntents; boolean startsNotResumed; boolean isForward; int pendingConfigChanges; boolean onlyLocalRequest; //当该Activity销毁的时候,会把上面提到window保存这个变量里面,以备该Activity再此启动的时候使用 Window mPendingRemoveWindow; //当该Activity销毁的时候,会WindowManager保存这个变量里面,以备该Activity再此启动的时候使用 WindowManager mPendingRemoveWindowManager; boolean mPreserveWindow; // Set for relaunch requests, indicates the order number of the relaunch operation, so it // can be compared with other lifecycle operations. int relaunchSeq = 0; // Can only be accessed from the UI thread. This represents the latest processed message // that is related to lifecycle events/ int lastProcessedSeq = 0; //构造函数 ActivityClientRecord() { parent = null; embeddedID = null; paused = false; stopped = false; hideForNow = false; nextIdle = null; } //判断android版本 大于 android 3.0 返回 false 否则返回true public boolean isPreHoneycomb() { if (activity != null) { return activity.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB; } return false; } //判断该Activity是否能被重启 public boolean isPersistable() { return activityInfo.persistableMode == ActivityInfo.PERSIST_ACROSS_REBOOTS; } ...... }
说明,从上述代码不难看出
ActivityClientRecord不仅仅保存了Activity本身
及其相关的信息
,还会保存与该Activity有关的成员(例如window、windowManager等),接下来看看它是如何往里面添加内容的:
ActivityThread#performLaunchActivity:
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) { ...... Activity activity = null; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader(); //创建一个Activity实例,mInstrumentation为Instrumentation类型, //用来监控系统组件与应用的交互过程,里面有很多方法供回调 activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity( cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent); ...... } catch (Exception e) { ...... } try { //获取一个Application实例 Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation); ...... if (activity != null) { //创建一个上下 Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity); //获取标题 CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager()); ...... Window window = null; if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) { //如果r.mPendingRemoveWindow 不为null,就是直接拿来使用 window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow; //重置r.mPendingRemoveWindow,r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager为null r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null; r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null; } //在这个方法中将会绑定上下文,创建一个窗口实例,获取窗口管理器等 activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config, r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window); ...... activity.mStartedActivity = false; //activity主题资源id int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource(); if (theme != 0) { activity.setTheme(theme); } activity.mCalled = false; if (r.isPersistable()) {//调用Activity的OnCreate方法 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state); } ...... //保存刚刚创建的Activity实例到r.activity中 r.activity = activity; r.stopped = true; if (!r.activity.mFinished) { //在这个方法中最终会调用Activity的onStart函数,当然是通过Instrumentation调用的 activity.performStart(); r.stopped = false; } if (!r.activity.mFinished) { if (r.isPersistable()) { if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) { //通过Instrumentation调用Activity的performRestoreInstanceState函数 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } } else if (r.state != null) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state); } } if (!r.activity.mFinished) { activity.mCalled = false; if (r.isPersistable()) { //通过Instrumentation调用Activity的onPostCreate函数 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state); } ...... } } r.paused = true; //关键的来了,在这里把ActivityClientRecord的对象引用放置到mActivities中 mActivities.put(r.token, r); } catch (SuperNotCalledException e) { ...... } catch (Exception e) { ...... } //返回刚刚创建的Activity实例 return activity; }
说明,注意红色的部分,把
封装好的ActivityClientRecord保存到
mActivities
中,而这个方法的主要作用就是(1)创建一个Activity实例(2)获取一个Application实例(3)创建一个Context实例(4)保存该Activity相关信息到
mActivities
(5)调用attach实现Activity、Context之间的绑定及窗口、WMS的创建
。
(4)mServices
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
说明,
mActivities是储存当前进程所用的Activity实例,那么
mServices就是
储存
当前进程所用的Service实例。
ActivityThread#handleCreateService:
rivate void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) { ...... LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck( data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo); Service service = null; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); //通过类加载器创建一个service实例 service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { ...... } try { ...... ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo); context.setOuterContext(service); Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation); service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()); service.onCreate(); //保存Service到mServices中 mServices.put(data.token, service); try { ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting( data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0); } catch (RemoteException e) { ...... } } catch (Exception e) { ...... } }
说明,这块代码和
ActivityThread#performLaunchActivity的代码类似就不累述了。
(5)其他成员变量
//很明显这个集合就是为了保存Application实例的,一个APP应用中使用一个类继承Application,子类的onCreate只被调用一次, //这里为什么使用集合了呢 //在LoadedAPK的makeApplication方法也能体现这一点,mApplication为null就创建一个Application实例,否则就返回它。 //但是其下面还有一行代码:mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);在这里把刚刚创建Application实例到 //mAllApplications中保存起来了,那只有LoadedAPK角度分析,会发现在handleReceiver、handleCreateService方法 //都有创建LoadedAPK实例,也调用了 makeApplication方法当然这个时候也会创建一个Application实例, //所以不要单纯地以为只有启动Activity的时候才使用Application。 final ArrayList<Application> mAllApplications = new ArrayList<Application>(); //这个集合是为了保存LoadedApk实例,进一步证明了Application实例可不只会被创建一个 final ArrayMap<String, WeakReference<LoadedApk>> mPackages = new ArrayMap<String, WeakReference<LoadedApk>>(); //下面这两个集合都为Provider,只是方式不一样 final ArrayMap<ProviderKey,ProviderClientRecord> mProviderMap = new ArrayMap<ProviderKey,ProviderClientRecord>(); final ArrayMap<IBinder,ProviderClientRecord> mLocalProviders = new ArrayMap<IBinder ProviderClientRecord>();
2 内部类
static final class BindServiceData //用来封装使用bindeservice启动的时候的service的信息. static final class ReceiverData //用来封装和广播处理相关的一些信息. final class ProviderClientRecord //用来封装和Provider交互的一些信息 static final class AppBindData //用来封装和Application交互时的一些信息
3 main函数分析
ActivityThread的入口函数如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { ...... //启动性能统计器 SamplingProfilerIntegration.start(); //关闭CloseGuard CloseGuard.setEnabled(false); //初始化用户环境 Environment.initForCurrentUser(); ...... // 获取用户配置文件目录 final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId()); //设置配置文件存储默认目录 TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir); //Change this process's argv[0] parameter. This can be useful to show //more descriptive information in things like the 'ps' command. Process.setArgV0("" ); //初始当前线程为Looper线程 Looper.prepareMainLooper(); //创建一个ActivityThread实例 ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); //绑定应用,attach是一个非常重要的函数 这个过程下文详细介绍 thread.attach(false); //获取Handle实例,其实获取的是Handle子类H对象引用,在H中添加了处理各种消息的业务 if (sMainThreadHandler == null) { sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(); } ...... //开始循环 Looper.loop(); //异常退出,将抛出异常 throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); }
说明,在这个函数中做许多的事情,例如启动性能统计器、设置默认的配置文件目录、实例化当前线程为looper线程等,这也说明平时所说的Activity中UI线程其实就是一个looper线程,这是系统自动处理好的,在这里还进行了应用的绑定,下文详细分析绑定过程。
二 ApplicationThread
1 ActivityThread的内部类
ApplicationThread是ActivityThread的内部类,也是一个Binder对象。在此处它是作为IApplicationThread对象的server端等待client端的请求然后进行处理,最大的client就是AMS.
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative { public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) { ...... } public final void scheduleStopActivity(IBinder token, boolean showWindow, int configChanges) { ...... } public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<ReferrerIntent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) { ...... } ...... }
可以看出来它继承了ApplicationThreadNative的,并且它内部有非常多的scheduleXXX的方法.以后看到thread调用这个方法 就可以往这边找。我们先说一下这些方法,这些方法由外部的ActivityThread的binder远程代理对象调用最终走到这里.这些 schedulexxx的方法会进一步的通过往外发送消息给mH这个消息队列.来做处理.比如:
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<ReferrerIntent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) { ...... }
说明,这个用来启动一个Activity的,当然还有其他比较重要的schedulexxx方法:
schedulePauseActivity() scheduleStopActivity() scheduleResumeActivity() scheduleSendResult() scheduleLaunchActivity() scheduleNewIntent() scheduleDestroyActivity() scheduleReceiver() scheduleCreateService() scheduleBindService() scheduleUnbindService() scheduleServiceArgs() scheduleStopService() bindApplication() scheduleConfigurationChanged() scheduleRegisteredReceiver() scheduleInstallProvider()
2 ApplicationThreadNative
接下来我们再看看ApplicationThreadNative,其源码如下:
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder implements IApplicationThread { //根据传入的不同参数决定返回不同的值. static public IApplicationThread asInterface(IBinder obj) { if (obj == null) { return null; } IApplicationThread in = (IApplicationThread)obj.queryLocalInterface(descriptor); if (in != null) { return in; } return new ApplicationThreadProxy(obj); } public ApplicationThreadNative() { attachInterface(this, descriptor); } @Override public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException { switch (code) { ...... } } public IBinder asBinder(){ return this; } }
说明:
该类实现业务接口IApplicationThread,非常标准的Binder模板.IApplicationThread extends IInterface
它里面就是定义了非常多的通信的业务接口,也都是schedulexxx理解上对应到ApplicationThread那些方法。
该类
首先是提供了一个静态的方法asInterface()用来获取IApplicationThread的Binder对象或者Binder代理对象,其它进程跨进
程调用时候当传入的是BinderProxy那么就会返回一个ApplicationThreadProxy对象并把BinderProxy传入它的构造,而一般在
本进程中调用的时候,就直接返回当前IApplicationThread对象,然后就是onTransact()函数了,里面通过不同的code对应到不
同的case,进而调用不同的schedulexxx的方法,最终调用ApplicationThread中的schedulexxx方法。
ApplicationThread这样就完成了作为服务端的构架,接下来就就是代理端的分析了.前面我们知道跨进程调用asInterface的
时候返回的是ApplicationThreadProxy对象,该类位于ApplicationThreadNative.java文件当中,是其内部类。
3 ApplicationThreadProxy
ApplicationThreadNative#源码:
class ApplicationThreadProxy implements IApplicationThread { private final IBinder mRemote; public ApplicationThreadProxy(IBinder remote) { mRemote = remote; } public final IBinder asBinder() { return mRemote; } public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished, boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) throws RemoteException { Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(); data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor); data.writeStrongBinder(token); data.writeInt(finished ? 1 : 0); data.writeInt(userLeaving ? 1 :0); data.writeInt(configChanges); data.writeInt(dontReport ? 1 : 0); mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null, IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY); data.recycle(); } public final void scheduleStopActivity(IBinder token, boolean showWindow, int configChanges) throws RemoteException { ...... } ......//一些列的schedulexxx }
说明,也是代理端的标准实现,实现了IApplicationThread 接口,然后实现接口中定义的
业务方法,在每个方法中最终调用到了服务端的对应的schedulexxx方法中。当然这个过程是通过Binder通信调用的,例如上面通过mRemote变量和驱动去交互进而调用到server端, mRemote是一个BinderProxy对象.
关于IApplicationThread的Binder相关实现,有个需要注意的它没有趣ServiceManager中注册,走的是一个匿名的binder的方法,其实对于驱动来说都一样.暂时发现的是别的地方如AMS用的时候通过ActivityThread的接口获得到ApplicationThread的对象,然后传入到asInterface(),获取对应的IApplicationThread对象进行跨进程调用。
三 Instrumentation
在android.app包下有Instrumentation这个类,这个类没有继承和实现其它的任何类,也没被其它的类继承。看看它的英文注释:
/**
* Base class for implementing application instrumentation code. When running
* with instrumentation turned on, this class will be instantiated for you
* before any of the application code, allowing you to monitor all of the
* interaction the system has with the application. An Instrumentation
* implementation is described to the system through an AndroidManifest.xml's
* <instrumentation> tag.
*/
这句话大致意思:它会在应用的任何
代码执行前被实列化,用来监控系统组件与应用的交互过程,还可以在配置文件中使用
Instrumentation
对
Android组件单元测试。
每一个应用进程中只有唯一的Instrumentation, 在ActivityThread中成员变量Instrumentation mInstrumentation,通过方法
public Instrumentation getInstrumentation()来获得该对象实例。
小编对
Instrumentation
也做了些总结想了解更多点击查看《
Instrumentation
》。
四 应用程序绑定过程分析
最后,回到ActivityThread的
attach方法上,
这个方法在ActivityThread的入口函数main中被调用了,它在systemMain()当中也被调用了,并且
传
入的参数是true,接下来看看这个方法:
ActivityThread#
attach
private void attach(boolean system) { sCurrentActivityThread = this; //true守护线程 false 用户线程 守护线程是为用户线程服务的,一般业务逻辑的处理都写在守护线程里面 mSystemThread = system; if (!system) { ...... //获取代表类ActivityManagerProxy实例 final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault(); try { //调用ActivityManagerProxy的attachApplication实施绑定,最终会调用远程类AMS的attachApplication完成绑定
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } ...... } else { ...... try { mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation(); ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext( this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo); mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null); //调用application onCreate函数 mInitialApplication.onCreate(); } catch (Exception e) { ...... } } ...... ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(new ComponentCallbacks2() { @Override public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) { synchronized (mResourcesManager) { ...... } } @Override public void onLowMemory() { } @Override public void onTrimMemory(int level) { } }); }
说明,
在这里
调用
远程接口涉及到了ActivityManager框架的问题,有兴趣的可以参考这篇《
ActivityManager框架之简要
》文章,这个不是本文焦点就不多介绍啦
,直接
AMS的方法attachApplication:
@Override public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) { synchronized (this) { //调用native函数获取当前进程的Id int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid(); //重置当前线程的IPC的id final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid); Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); } }
说明, 获得了正在Binder通信的客户端的当前线程的id,然后和ApplicationThread对象作为参数传入到AMS的attachApplicationLocked,
AMS#attachApplicationLocked源码如下:
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread, int pid) { // Find the application record that is being attached... either via // the pid if we are running in multiple processes, or just pull the // next app record if we are emulating process with anonymous threads. ProcessRecord app; if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) { synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) { app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);//在整个启动进程的流程中在前面已经push进入 } } else { app = null; } if (app == null) { ...... return false;//为null的时候直接返回. } //正常第一次开启时此时还是null if (app.thread != null) { handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true); } ...... final String processName = app.processName; ...... // 用来时例化ProcessRecord的thread变量.它是一个IApplicationThread对象. app.makeActive(thread, mProcessStats);//在这里实现的附着! app.curAdj = app.setAdj = -100; app.curSchedGroup = app.setSchedGroup = Process.THREAD_GROUP_DEFAULT; app.forcingToForeground = null; updateProcessForegroundLocked(app, false, false); app.hasShownUi = false; app.debugging = false; app.cached = false; app.killedByAm = false; mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app); boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info); List<ProviderInfo> providers = normalMode ? generateApplicationProvidersLocked(app) : null; ...... try { ...... // 这是一个远程调用,但最终会调用ApplicationThread的bindApplication函数完成绑定过程 thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass, profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher, app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode, enableOpenGlTrace, isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent, new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat, getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated), mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked()); updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null); app.lastRequestedGc = app.lastLowMemory = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); } catch (Exception e) { ...... return false; } // Remove this record from the list of starting applications. mPersistentStartingProcesses.remove(app); if (DEBUG_PROCESSES && mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) Slog.v(TAG, "Attach application locked removing on hold: " + app); mProcessesOnHold.remove(app); boolean badApp = false; boolean didSomething = false; // See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process... if (normalMode) { ..... } // Find any services that should be running in this process... if (!badApp) { ...... } // Check if a next-broadcast receiver is in this process... if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) { ...... } // Check whether the next backup agent is in this process... if (!badApp && mBackupTarget != null && mBackupTarget.appInfo.uid == app.uid) { ...... } if (badApp) { ...... } if (!didSomething) { ...... } return true; }
说明,
thread是ApplicationThreadProxy的对象引用,它是代理对象,先调用
ApplicationThreadProxy的
bindApplication方法,接着在这个方法中又调用
ApplicationThreadNative的函数
onTransact,然后
函数
onTransact中根据code找到对应的case,
最终会调用ApplicationThread的bindApplication方法,
接下来看看函数
bindApplication
,源码如下:
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo, List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs, IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher, IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode, boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation, boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map<String, IBinder> services, Bundle coreSettings) { if (services != null) {//初始化缓存 // Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services); } setCoreSettings(coreSettings); //保存Bind数据 AppBindData data = new AppBindData(); data.processName = processName; data.appInfo = appInfo; data.providers = providers; data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName; data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs; data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher; data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection; data.debugMode = debugMode; data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking; data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation; data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode; data.persistent = persistent; data.config = config; data.compatInfo = compatInfo; data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo; //发送信息 sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data); }
说明,在这里,bindApplication方法通过向ActivityThread的消息队列发送BIND_APPLICATION消息,消息的处理调用handleBindApplication方法,
handleBindApplication方法比较重要的是会调用如下方法
:
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
说明,callApplicationOnCreate即调用应用程序Application的onCreate()方法,说明Application的onCreate()方法会比所有activity的onCreate()方法先调用。
五 小结
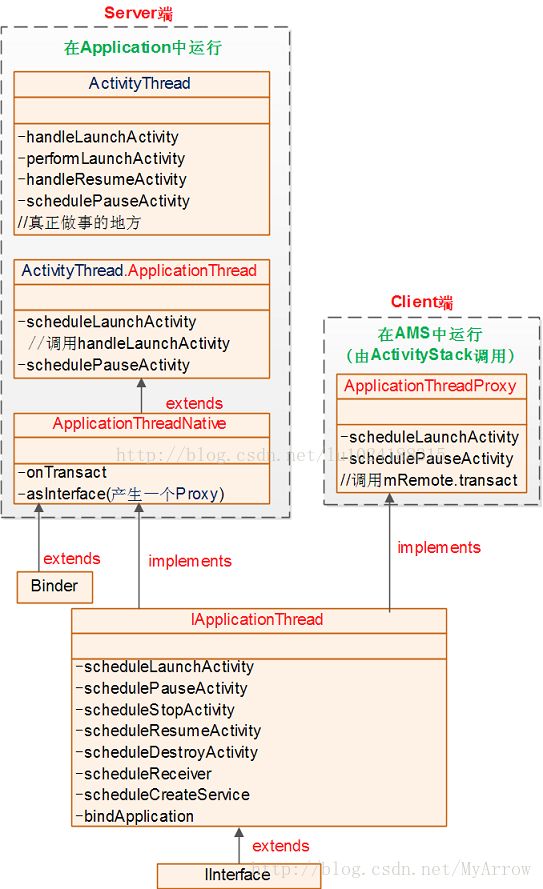
最后,借用猿友的一幅图来描述今天的东西:
说明,整个ActivityThread框架是基于Binder通信的C/S结构,从图可知Server端是ActivityThread、ApplicationThread,Client是AMS(ActivityManagerService),而
ApplicationThreadProxy可以看作AMS中Server
代表。
本篇到此结束。
参考:
1《ActivityThread与ApplicationThread简析》
2《ActivityThread绑定ApplicationThread的过程》
3《UI线程简介》
4《CloseGuard》
5《
SamplingProfilerIntegration
》
6《ActivityInfo、ApplicationInfo、PagerInfo》