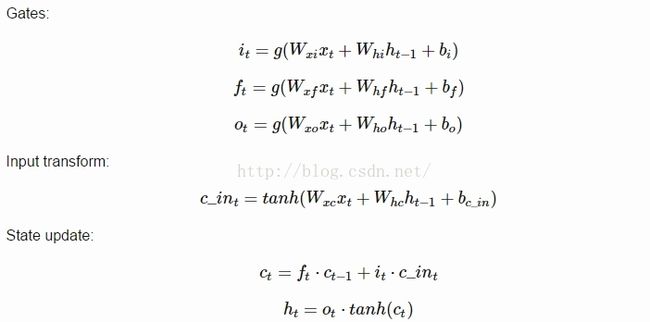Lua实现LSTM 前向传播
LSTM本身不是一个完整的模型,LSTM是对RNN隐藏层的改进。一般所称的LSTM网络应该称为使用了LSTM单元的RNN网络。如下图所示,LSTM网络,只是将RNN的隐层神经元换成了LSTM单元。本博文翻译自https://apaszke.github.io/lstm-explained.html。
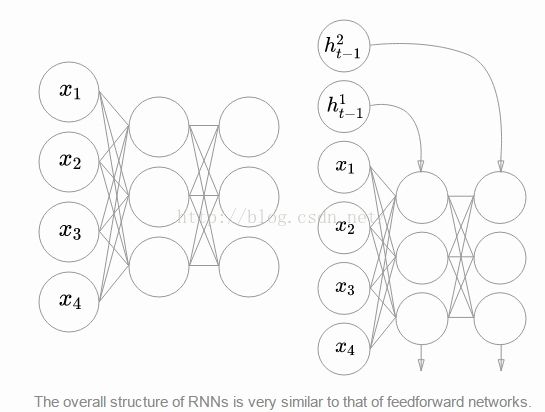
1、RNN其实和前馈网络没很大差异,RNN也可以层级堆叠。只是说前一时刻的隐藏层的输出要继续作为当前时刻的输入。
2、Lua实现LSTM前馈传播单元。深度学习网络都是可以模块化的,包括前向传播过程和BP反向传播过程。整个复杂的网络都是可以按照模块进行组装在一起的。本文,我们只实现了LSTM的前向传播模块。
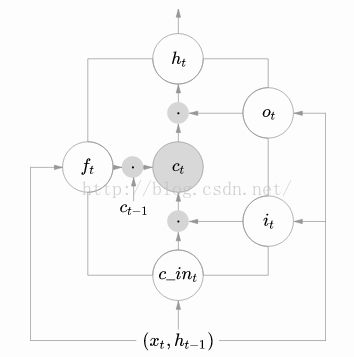
LSTM的模块示意图如下:该模块的输入(x(t),h(t-1),c(t-1)),该模块的输出(h(t),c(t)) 。
整个LSTM模块前向传播的算法如下:
具体Lua的实现步骤,可以参照该博客:
整个LSTM模块前向传播的lua代码如下:
require 'nn'
require 'nngraph'
local LSTM = {}
function LSTM.create(input_size, rnn_size)
--------------------- input structure ---------------------
local inputs = {}
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- network input
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- c at time t-1
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- h at time t-1
local input = inputs[1]
local prev_c = inputs[2]
local prev_h = inputs[3]
--------------------- preactivations ----------------------
local i2h = nn.Linear(input_size, 4 * rnn_size)(input) -- input to hidden
local h2h = nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size)(prev_h) -- hidden to hidden
local preactivations = nn.CAddTable()({i2h, h2h}) -- i2h + h2h
------------------ non-linear transforms ------------------
-- gates
local pre_sigmoid_chunk = nn.Narrow(2, 1, 3 * rnn_size)(preactivations)
local all_gates = nn.Sigmoid()(pre_sigmoid_chunk)
-- input
local in_chunk = nn.Narrow(2, 3 * rnn_size + 1, rnn_size)(preactivations)
local in_transform = nn.Tanh()(in_chunk)
---------------------- gate narrows -----------------------
local in_gate = nn.Narrow(2, 1, rnn_size)(all_gates)
local forget_gate = nn.Narrow(2, rnn_size + 1, rnn_size)(all_gates)
local out_gate = nn.Narrow(2, 2 * rnn_size + 1, rnn_size)(all_gates)
--------------------- next cell state ---------------------
local c_forget = nn.CMulTable()({forget_gate, prev_c}) -- previous cell state contribution
local c_input = nn.CMulTable()({in_gate, in_transform}) -- input contribution
local next_c = nn.CAddTable()({
c_forget,
c_input
})
-------------------- next hidden state --------------------
local c_transform = nn.Tanh()(next_c)
local next_h = nn.CMulTable()({out_gate, c_transform})
--------------------- output structure --------------------
outputs = {}
table.insert(outputs, next_c)
table.insert(outputs, next_h)
-- packs the graph into a convenient module with standard API (:forward(), :backward())
return nn.gModule(inputs, outputs)
end
return LSTM当然,LSTM也是可以跟传统的CNN一样,几个模块堆起来,前一个模块隐层的输出作为下一个模块的输入。所以,通过堆叠三个LSTM单元,得到LSTM深度网络的代码如下:
require 'nn'
require 'nngraph'
LSTM = require 'LSTM.lua'
-- 3-layer LSTM network (input and output have 3 dimensions)
network = {LSTM.create(3, 4), LSTM.create(4, 4), LSTM.create(4, 3)}
-- network input
local x = torch.randn(1, 3)
local previous_state = {
{torch.zeros(1, 4), torch.zeros(1,4)},
{torch.zeros(1, 4), torch.zeros(1,4)},
{torch.zeros(1, 3), torch.zeros(1,3)}
}
-- network output
output = nil
next_state = {}
-- forward pass
local layer_input = {x, table.unpack(previous_state[1])}
for l = 1, #network do
-- forward the input
local layer_output = network[l]:forward(layer_input)
-- save output state for next iteration
table.insert(next_state, layer_output)
-- extract hidden state from output
local layer_h = layer_output[2]
-- prepare next layer's input or set the output
if l < #network then
layer_input = {layer_h, table.unpack(previous_state[l + 1])}
else
output = layer_h
end
end
print(next_state)
print(output)