spark-core_15:sparkContext初始化源码分析
这幅图是网友提供的,非常感谢
/**
* Main entry point for Sparkfunctionality. A SparkContext represents the connection to a Spark cluster, andcan be used to create RDDs, accumulators and broadcast variables on thatcluster.
*
* Only one SparkContext may be activeper JVM. You must `stop()` the active SparkContext before creating a new one. This limitation may eventually be removed;see SPARK-2243 for more details.
*
* @param config a Spark Configobject describing the application configuration. Any settings in this configoverrides the default configs as well as system properties.
*
* SparkContext是spark功能的主入口,代表着集群的联接,可以用它在集群中创建rdds,累加器和广播变量
* 每个jvm只能有一个SparkContext,再创建新的SparkContext之前需要先stop()当前活动的SparkContext,不过这种限制可能会在将来被移除,看SPARK-2243
* 它的构造参数是SparkConf是当前app的配制。这个配置会覆盖默认的配置以及系统属性
*
* SparkContext的初始化步骤:
* 1.创建Spark执行环境SparkEnv;
* 2.创建并且初始化Spark UI;
* 3.hadoop相关配置以及Executor环境变量的设置;
* 4.创建任务调度TaskScheduler;
* 5.创建和启动DAGScheduler;
* 6.TaskScheduler的启动;
* 7.初始化管理器BlockManager(BlockManager是存储体系的主要组件之一)
* 8.启动测量系统MetricsSystem;
* 9.创建和启动Executor分配管理器ExecutorAllocationManager;
* 10.ContextCleaner的启动和创建。
* 11.Spark环境更新
* 12.创建DAGSchedulerSource和BlockManagerSource;
* 13.将SparkContext标记激活
*/
class SparkContext(config: SparkConf) extends Logging withExecutorAllocationClient {
/**The call site where this SparkContext was constructed.spark
* 这个CallSite是一个case class
* 在sparkPi例子中,获得的CallSite数据如下:(该方法不单单在SparkContext被调用,在RDD或广播时等地都会被调用,每一次调用结果都是不一样的)
* shortForm:最短栈:SparkContext at SparkPi.scala:29
* longForm:最长栈: org.apache.spark.SparkContext.
*org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi$.main(SparkPi.scala:29)
*org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi.main(SparkPi.scala) */
private val creationSite: CallSite = Utils.getCallSite()
1、先查看一下Uitls.getCallSite()它的作用就是用于打印执行过程中的堆栈信息.
/** * When called inside a class in the spark package, returns the name of the user code class * (outside the spark package) that called into Spark, as well as which Spark method they called. * This is used, for example, to tell users where in their code each RDD got created. * 返回spark调用代码对应类的名称和方法,如选择用户每个RDD的调用过程 过滤掉非用户编写的代码 * @param skipClass Function that is used to exclude non-user-code classes. * * 功能描述:获取当前SparkContext的当前调用栈,将栈中最靠近栈底的属于Spark或者Scala核心的类压入callStack的栈顶, 并将此类的方法存入lastSparkMethod; * 将栈里最靠近栈顶的用户类放入callStack,将此类的行号存入firstUserline,类名 * 存入firstUserFile,最终返回的样例类CallSite存储了最短栈和长度默认为20的最长栈的样例类。 * 在sparkPi例子中,获得的数据如下:(该方法不单单在SparkContext被调用,在RDD或广播时都会被调用,每一次调用结果都是不一样的) * shortForm:最短栈:SparkContext at SparkPi.scala:29 * longForm:最长栈: org.apache.spark.SparkContext.(SparkContext.scala:82) org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi$.main(SparkPi.scala:29) org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi.main(SparkPi.scala) */ def getCallSite(skipClass: String => Boolean = sparkInternalExclusionFunction): CallSite = { //会一直跟踪到spark代码,会将用户调用的Rdd转换等信息都取出;跟踪最后一个(最浅的)连续的Spark方法。
这可能是一个RDD转换,一个SparkContext函数(例如parallelize),或者其他导致RDD实例化的东西。
var lastSparkMethod= "
var insideSpark= true
var callStack = new ArrayBuffer[String]() :+ "
// getStackTrace()方法返回,StackTraceElement[]栈帧集合,每个元素都是一个栈帧,除了最顶部栈帧,都是一个方法的调用。
// 堆栈顶部的帧表示生成堆栈跟踪的执行点
Thread.currentThread.getStackTrace().foreach {ste: StackTraceElement =>
// When running under some profilers, the current stacktrace might contain some bogus
// frames. This is intended to ensurethat we don't crash in these situations by
// ignoring any frames that we can'texamine.
// 在某些profiler下运行时,当前堆栈跟踪可能包含一些假frames。
// 这是为了确保我们在这些情况下不会忽略任何我们不能检查的框架。
if (ste!= null && ste.getMethodName != null
&& !ste.getMethodName.contains("getStackTrace")) {
if (insideSpark){
if (skipClass(ste.getClassName)){ //如果是spark或scala内部类则将spark的方法名给lastSparkMethod
//如果栈帧的方法名是
//它的方法名是
lastSparkMethod = if (ste.getMethodName== "
// Spark method is a constructor; get its class name
//得到的类名是SparkContext,在RDD调用时,也会调用这个方法,然后得到的MapPartitionsRDD
ste.getClassName.substring(ste.getClassName.lastIndexOf('.') + 1)
} else {
ste.getMethodName
}
//将最后的spark方法的的堆栈信息放ArrayBuffer最上面
callStack(0) = ste.toString // Put last Spark method on top of the stack trace.
} else{
//出spark内部代码时,将第一个用户调用代码的栈帧方法对应的行号,文件名取出,再栈信息加到callStack:ArrayBuffer中
firstUserLine = ste.getLineNumber
firstUserFile = ste.getFileName
callStack += ste.toString
insideSpark = false //因为先从spark代码开始的,如果调用到用户代码时,就说明出了spark内部代码,则将insideSpark设置成false
}
} else {
//将用户代码的所有堆栈信息都取出来加到callStack:ArrayBuffer中
callStack += ste.toString
}
}
}
===》分析一下带名参数getCallSite(skipClass: String => Boolean= sparkInternalExclusionFunction)
/** Defaultfiltering function for finding call sites using `getCallSite`.
* 过滤掉非用户编写的代码,即将spark、scala自身的代码过滤掉
* */
private def sparkInternalExclusionFunction(className: String): Boolean = {
// A regular expression to match classes of the internalSpark API's
// that we want to skip when findingthe call site of a method.
val SPARK_CORE_CLASS_REGEX=
"""^org\.apache\.spark(\.api\.java)?(\.util)?(\.rdd)?(\.broadcast)?\.[A-Z]""".r
val SPARK_SQL_CLASS_REGEX= """^org\.apache\.spark\.sql.*""".r
val SCALA_CORE_CLASS_PREFIX= "scala"
//使用正则表达式将sparkCore,sql,scala的代码过滤掉
val isSparkClass= SPARK_CORE_CLASS_REGEX.findFirstIn(className).isDefined ||
SPARK_SQL_CLASS_REGEX.findFirstIn(className).isDefined
val isScalaClass= className.startsWith(SCALA_CORE_CLASS_PREFIX)
// If the class is a Spark internal class or a Scalaclass, then exclude.
isSparkClass || isScalaClass
}
===>再回到sparkContext初始化代码:
2,可以看出当前版本默认只能有一个活跃的SparkContext在jvm中,否则多个活跃SparkContext会抛异常
// If true, logwarnings instead of throwing exceptions when multiple SparkContexts are active
// 如果设置为true log日志里将会抛出多个SparkContext处于活动状态的异常
private val allowMultipleContexts: Boolean =
config.getBoolean("spark.driver.allowMultipleContexts", false)
// In order to prevent multipleSparkContexts from being active at the same time, mark this
// context as having started construction.
// NOTE: this must be placed at the beginning of the SparkContext constructor.
// 为了预防多SparkContexts同一时间处于活动状态,如果出现多个活跃的SparkContext则会报错,如果spark.driver.allowMultipleContexts值为true就会有警告日志
// 注:这placed必须要开始的sparkcontextconstructor。
SparkContext.markPartiallyConstructed(this, allowMultipleContexts)
// 得到系统的当前时间
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
//使用Atomic原子类来确保stopped变量原子性
private[spark] val stopped: AtomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean(false)
3,查看SparkContext主构造器
/**
* Alternative constructor that allowssetting common Spark properties directly
* 替代构造函数,允许直接设置常用的Spark属性
*master对应集群的URL
* @param master Cluster URL toconnect to (e.g. mesos://host:port, spark://host:port, local[4]).
* @param appName A name for yourapplication, to display on the cluster web UI
* @param conf a [[org.apache.spark.SparkConf]] objectspecifying other Spark parameters
*/
def this(master: String, appName: String, conf: SparkConf) =
this(SparkContext.updatedConf(conf, master, appName))
…
/**
* Alternative constructor that allowssetting common Spark properties directly
* 替代构造函数,允许直接设置常用的Spark属性
* @param master Cluster URL toconnect to (e.g. mesos://host:port, spark://host:port, local[4]).
* @param appName A name for yourapplication, to display on the cluster web UI.
*/
private[spark] def this(master: String, appName: String) =
this(master, appName, null, Nil, Map())
===》顺便看一下SparkContext.updatedConf(conf, master, appName)方法
/**
* Creates a modified version of aSparkConf with the parameters that can be passed separately
* to SparkContext, to make it easier towrite SparkContext's constructors. This ignores
* parameters that are passed as thedefault value of null, instead of throwing an exception
* like SparkConf would.
* 通过参数修改sparkConf的内容
*/
private[spark] def updatedConf(
conf: SparkConf,
master: String,
appName: String,
sparkHome: String= null,
jars: Seq[String] = Nil, //Nil表示空元素的list()
environment: Map[String, String] = Map()): SparkConf =
{
val res= conf.clone()
res.setMaster(master)
res.setAppName(appName)
if (sparkHome!= null) {
res.setSparkHome(sparkHome)
}
//会将上传的jar发送到每个节点,然后存在到SparkConf下面的ConcurrentHashMap中。它的key是spark.jars,value是按jars每个元素按逗号分开的串 if (jars != null && !jars.isEmpty) { res.setJars(jars) } //将由seq每个元素对应的key指定的环境变量值添加到Executor进程。 然后在Executor进来取出来使用 // 如:存在到SparkConf下面的ConcurrentHashMap中key:spark.executorEnv.VAR_NAME(是当前environment的key),value:当前environment的value res.setExecutorEnv(environment.toSeq) res }
4,初始化生成LiveListenerBus
/**Anasynchronous listener bus for Spark events
* a,它和StreamingListenerBus有相同的父类AsynchronousListenerBus , 使用相同的监听器StreamingListener
* b,异步将SparkListenerEvents事件注册到SparkListeners, 在调用start()之前,所有发布的事件仅被缓存。
* 只有在此LiveListenerBus启动后,事件才会实际传播给所有连接的SparkListener。
* 该LiveListenerBus在接收到使用stop()发布的SparkListenerShutdown事件时停止。
*/
private[spark] val listenerBus= new LiveListenerBus
。。。
// Used to store a URLfor each static file/jar together with the file's local timestamp
//用于将每个静态文件/ jar的URL与文件的本地时间戳一起存储
private[spark] val addedFiles= HashMap[String,Long]()
private[spark] val addedJars = HashMap[String, Long]()
// Keeps track of all persisted RDDs,保持跟踪所有存储的RDD
private[spark] val persistentRdds= new TimeStampedWeakValueHashMap[Int, RDD[_]]
。。。
// Environmentvariables to pass to our executors. 设置环境变化给executor使用
private[spark] val executorEnvs= HashMap[String, String]()
// Set SPARK_USER for user who is runningSparkContext. 返回当前环境的机器名:luyl
val sparkUser = Utils.getCurrentUserName()
5,初始化ThreadLocal及它的子类InheritableThreadLocal
// Thread Localvariable that can be used by users to pass information down the stack
//可以使用ThreadLocal传递的线程的变量
//它和ThreadLocal的区别:
//a,ThreadLocal只有在当前线程中,线程变量值有效,如果是当前线程的子线程,线程值就不一样了。
//b,InheritableThreadLocal可以解决在当前线程的子线程取父线程的值,同时它多了一个childValue方法,
// 这个方法可以从父线程中得到父线程中set或第一次get是初始化initialValue的值,然后可以对这个值进行重写
protected[spark] val localProperties= new InheritableThreadLocal[Properties]{
override protected def childValue(parent:Properties): Properties = {
// Note: make a clone such that changes in the parentproperties aren't reflected in
// the those of the children threads,which has confusing semantics (SPARK-10563).
SerializationUtils.clone(parent).asInstanceOf[Properties]
}
override protected def initialValue(): Properties = new Properties()
}
。。。。。
6,检查SparkConf的必要属性,并对相应属性做解析将相应的值赋给SparkContext成员
try {
//config就是主构造参数传进来的SparkConf,里面没有master或appName会报错
_conf =config.clone()
_conf.validateSettings()
if (!_conf.contains("spark.master")) {
throw new SparkException("A masterURL must be set in your configuration")
}
if (!_conf.contains("spark.app.name")) {
throw new SparkException("Anapplication name must be set in your configuration")
}
// System property spark.yarn.app.id must be set if usercode ran by AM on a YARN cluster
// yarn-standalone is deprecated, butstill supported
if ((master== "yarn-cluster" || master == "yarn-standalone") &&
!_conf.contains("spark.yarn.app.id")) {
throw new SparkException("Detectedyarn-cluster mode, but isn't running on a cluster. " + "Deployment to YARN is not supported directly by SparkContext. Pleaseuse spark-submit.")
}
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.logConf", false)) {
logInfo("Spark configuration:\n"+ _conf.toDebugString)
}
// Set Spark driver host and port system properties
//如果conf中没有host,port属性,会设置host就是本机域名 port是0
_conf.setIfMissing("spark.driver.host", Utils.localHostName())
_conf.setIfMissing("spark.driver.port", "0")
//DRIVER_IDENTIFIER的值就是driver,可见driver也是一个executor
_conf.set("spark.executor.id", SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER)
//spark.jars就是SparkSubmit解析val (childArgs, childClasspath,sysProps, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
//在sparkSubmit的606行sysProps.put("spark.jars",jars.mkString(",")),这些默认参数会在sparkConf初始化时加进去
//这边把jars的串,按逗号分隔成一个集合串
_jars = _conf.getOption("spark.jars").map(_.split(",")).map(_.filter(_.size != 0)).toSeq.flatten
//是通过--files传进来的,放在每个executor的工作目录的。也是按逗号分开的
_files = _conf.getOption("spark.files").map(_.split(",")).map(_.filter(_.size != 0))
.toSeq.flatten
7,将spark的事件日志目录及压缩日志的类提取出来
/**
* 如果spark.eventLog.enabled为true,默认是false,如果设置成true则记录Spark事件的根目录。在这个根目录中,
* Spark为每个应用程序创建一个子目录,并在该目录中记录特定于应用程序的事件。
* 可以设置它成hdfs目录,以便历史记录服务器可以读取历史文件。
* spark.eventLog.dir:默认值是/tmp/spark-events ,即在hdfs中会变成Some(URI(http://192.168.1.150:50070/tmp/spark-events))
* 本地文件:Some(URI(file:///tmp/spark-events))
spark.eventLog.dir、spark.eventLog.enabled,这两个属性在Spark_home/conf/spark-defaults.conf也可以配制
*/
_eventLogDir =
if (isEventLogEnabled){ //isEventLogEnabled : 默认是false,对应spark.eventLog.enabled配制
val unresolvedDir= conf.get("spark.eventLog.dir", EventLoggingListener.DEFAULT_LOG_DIR)
.stripSuffix("/") //该方法会把串中后面带有“/”去掉
//unresolvedDir得到的是如:/tmp/spark-events
//为用户输入字符串描述的文件返回格式正确的网络URI路径。如:file:/tmp/spark-events
Some(Utils.resolveURI(unresolvedDir))
} else {
None
}
/**
* spark.eventLog.compress是否压缩事件日志,默认false
*/
_eventLogCodec = {
val compress= _conf.getBoolean("spark.eventLog.compress", false)
if (compress&& isEventLogEnabled) { //isEventLogEnabled: 默认是false,对应spark.eventLog.enabled
//默认是Some("snappy").map("snappy"),返回Some("snappy")
Some(CompressionCodec.getCodecName(_conf)).map(CompressionCodec.getShortName)
} else {
None
}
}
//给外部block存储的目录,生成一个随机的名称,在这个名称后缀上加上timestamp,得到的是spark-cf14b6b5-baff-44dc-a434-429f251cb505
_conf.set("spark.externalBlockStore.folderName", externalBlockStoreFolderName)
if (master == "yarn-client") System.setProperty("SPARK_YARN_MODE", "true")
//给外部block存储的目录,生成一个随机的名称,在这个名称后缀上加上timestamp,得到的是spark-cf14b6b5-baff-44dc-a434-429f251cb505
_conf.set("spark.externalBlockStore.folderName", externalBlockStoreFolderName)
8,初始化JobProgressLIstener(sparkConf),并加到LiveListenerBus中
// "_jobProgressListener"should be set up before creating SparkEnv because when creating
// "SparkEnv", some messages will be posted to"listenerBus" and we should not miss them.
//创建SparkEnv之前应该设置“jobProgressListener”,因为在创建“SparkEnv”时,一些消息将被发布到“listenerBus”
_jobProgressListener= new JobProgressListener(_conf) //跟踪要在UI中显示的任务级别信息。
listenerBus.addListener(jobProgressListener)
1, 初始化SparkEnv(查看:spark-core_16:初始化Driver的SparkEnv)
* SparkEnv的构造步骤如下:
* 1.创建安全管理器SecurityManager
* 2.创建给予AKKa的分布式消息系统ActorSystem; --未来版本会被移除
* 3.创建Map任务输出跟踪器mapOutputTracker;
* 4.实例化ShuffleManager;
* 5.创建块传输服务BlockTransferService;
* 6.创建BlockManagerMaster;
* 7.创建块管理器BlockManager;
* 8.创建广播管理器BroadcastManager;
* 9.创建缓存管理器CacheManager;
* 10.创建HTTP文件服务器HttpFileServer;
* 11.创建测量系统MetricsSystem;
* 12.创建输出提交控制器OutputCommitCoordinator;
* 13.创建SparkEnv;
// Create the Sparkexecution environment (cache, map output tracker, etc)
//SparkContext初始化时,将SparkEnv初始化出来
_env = createSparkEnv(_conf, isLocal, listenerBus)
SparkEnv.set(_env)
// This functionallows components created by SparkEnv to be mocked in unit tests: 可以在单元测试中可以调用这个方法创建SparkEnv
//SparkContext初始化时,将SparkEnv初始化出来
//SparkContext.numDriverCores(master):如果master是local模式会将driver对应节点cpu的线程数取出来,如果是集群模式则返回0
private[spark] def createSparkEnv(
conf: SparkConf,
isLocal: Boolean,
listenerBus: LiveListenerBus): SparkEnv = {
SparkEnv.createDriverEnv(conf, isLocal, listenerBus, SparkContext.numDriverCores(master))
}
9、启动jettyServer,跟踪job相关的信息然后在web展示出来
//实例化出来的SparkEnv,通过SparkEnv.set(),将sparkEnv实例,设置到伴生对象的成员变量中
SparkEnv.set(_env)
//运行一个定时器定期清理原数据,如旧文件或hashTable实例kv,前提是设置spark.cleaner.ttl的值才会定时清理
_metadataCleaner = new MetadataCleaner(MetadataCleanerType.SPARK_CONTEXT, this.cleanup, _conf)
//用于监控Job和Stage进度的低级状态报告API
_statusTracker = new SparkStatusTracker(this)
_progressBar =
if (_conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.showConsoleProgress", true) && !log.isInfoEnabled) {
Some(new ConsoleProgressBar(this))
} else {
None
}
//初始化EnvironmentListener,StorageStatusListener,ExecutorsListener,RDDOperationGraphListener,放到LisvListenerBus中,
// 然后将SparkUI初始化出来,即4040对应的页面
_ui =
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.ui.enabled", true)) {
//_jobProgressListener跟踪要在UI中显示的任务级别信息,startTime就是SparkContext的初始时的系统时间 返回SparkUI,它的父类是WebUI,和MasterWebUI是一个级别的
Some(SparkUI.createLiveUI(this, _conf, listenerBus, _jobProgressListener,
_env.securityManager, appName, startTime = startTime))
} else {
// For tests, do not enable the UI
None
}
// Bind the UI before starting the taskscheduler to communicate
// the bound port to the cluster manager properly
//调用SparkUI的bind()方法,就是启动jetty Server
//在启动任务调度程序之前绑定用户界面,以便将绑定的端口正确地与集群管理器进行通信
_ui.foreach(_.bind())
//返回Hadoop的Configuration()实例
_hadoopConfiguration= SparkHadoopUtil.get.newConfiguration(_conf)
10,将sparkSubmit的--jars和--files发布到HttpBasedFileServer对应的jettyServer的路径下
// Add each JAR giventhrough the constructor.为SparkContext上执行的所有任务添加JAR依赖项。
if (jars != null) {
//每个jar路径是jars集合的元素,会被HttpBasedFileServer对应的jettyServer发布网络上
/*如果传递进来的是/data/path/aa.jar,getScheme得到的是file,jettyServer提供一个文件服务*/
jars.foreach(addJar)
}
if (files != null) {
//是通过--files传进来的,放在每个节点的HttpBasedFileServer对应的jettyServer发布网络上。也是按逗号分开的
//目前只支持hadoop协议的上的数据,并且必须把路径写全,如:写成hdfs://ns1/examples/src/main/resources/people.json
//否则会报错
files.foreach(addFile)
}
//每个执行程序进程使用的内存量,默认是1G,System.getenv是从spark-env.sh中得到的(SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY、SPARK_MEM),
// 或提交参数时指定:--executor-memory
//默认是取的1024
_executorMemory = _conf.getOption("spark.executor.memory")
.orElse(Option(System.getenv("SPARK_EXECUTOR_MEMORY")))
.orElse(Option(System.getenv("SPARK_MEM"))
.map(warnSparkMem))
.map(Utils.memoryStringToMb)
.getOrElse(1024)
11,每分钟检测一下Executor的心跳
// We need to register"HeartbeatReceiver" before "createTaskScheduler" becauseExecutor will retrieve "HeartbeatReceiver" in the constructor.(SPARK-6640)
//我们需要在“createTaskScheduler”之前注册“HeartbeatReceiver”,因为Executor将在构造函数中检索“HeartbeatReceiver”
//创建一个HeartbeatReceiver 的RpcEndpoint注册到RpcEnv中,每分钟给自己发送ExpireDeadHosts,去检测Executor是否存在心跳, 如果当前时间减去最一次心跳时间,大于1分钟,就会用CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend将Executor杀死
_heartbeatReceiver = env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(
HeartbeatReceiver.ENDPOINT_NAME, new HeartbeatReceiver(this))
===》进入HeartbeatReceiver(this),即是一个RepEndPoint也是一个SparkListener监听器
/**
* Lives in the driver to receiveheartbeats from executors..
* driver接收所有executor的心跳,混入SparkListener,说明它是一个监听器
*/
private[spark] class HeartbeatReceiver(sc:SparkContext, clock: Clock)
extends ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint withSparkListener with Logging {
def this(sc: SparkContext) {
this(sc, new SystemClock)
}
sc.addSparkListener(this)
override val rpcEnv:RpcEnv = sc.env.rpcEnv
private[spark]var scheduler: TaskScheduler = null
// executor ID -> timestamp of when the last heartbeatfrom this executor was received
//executor ID - >接收到来自该执行者的最后一次心跳的时间戳
private val executorLastSeen = new mutable.HashMap[String,Long]
// "spark.network.timeout" uses"seconds", while `spark.storage.blockManagerSlaveTimeoutMs` uses"milliseconds"
//“spark.network.timeout”使用“秒”,而`spark.storage.blockManagerSlaveTimeoutMs`使用“毫秒”
private val slaveTimeoutMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsMs("spark.storage.blockManagerSlaveTimeoutMs", "120s")
//executorTimeoutMs是120秒
private val executorTimeoutMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsSeconds("spark.network.timeout", s"${slaveTimeoutMs}ms") * 1000
// "spark.network.timeoutInterval" uses"seconds", while
//"spark.storage.blockManagerTimeoutIntervalMs" uses"milliseconds"
private val timeoutIntervalMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsMs("spark.storage.blockManagerTimeoutIntervalMs", "60s")
private val checkTimeoutIntervalMs =
sc.conf.getTimeAsSeconds("spark.network.timeoutInterval", s"${timeoutIntervalMs}ms") * 1000
private var timeoutCheckingTask: ScheduledFuture[_] = null
// "eventLoopThread" is used to run some prettyfast actions. The actions running in it should not
// block the thread for a long time.
//“eventLoopThread”用于运行一些相当快的动作。 在其中运行的动作不应该长时间阻塞线程。生成一个单线程的调度池
private val eventLoopThread =
ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadScheduledExecutor("heartbeat-receiver-event-loop-thread")
private val killExecutorThread = ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadExecutor("kill-executor-thread")
override def onStart(): Unit = {
//每分钟给自己发送ExpireDeadHosts
timeoutCheckingTask = eventLoopThread.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
Option(self).foreach(_.ask[Boolean](ExpireDeadHosts))
}
}, 0, checkTimeoutIntervalMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
===》onStart()方法每分钟执行一下心跳检测:
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
// Messages sent and received locally
。。。
case ExpireDeadHosts=>
expireDeadHosts()
context.reply(true)
===》expireDeadHosts会在比对Executor最后一次心跳时间,超过1分钟的,调用ExecutorSchedulerBackEnd清除Executor
private def expireDeadHosts(): Unit= {
logTrace("Checking for hosts with no recent heartbeats inHeartbeatReceiver.")
val now= clock.getTimeMillis() //值就是currentTimeMillis
//executorLastSeen:HashMap[String,Long]必须有Executor注册才会有值,Long值是executor最后一个心跳时间
for ((executorId, lastSeenMs) <- executorLastSeen) {
//当前时间减去lastSeenMs(executor最后一个心跳时间)大于60s则移除Executor
if (now- lastSeenMs > executorTimeoutMs) {
logWarning(s"Removing executor $executorId with no recent heartbeats: " +
s"${now - lastSeenMs} ms exceeds timeout $executorTimeoutMs ms")
//scheduler得有消息发到TaskSchedulerIsSet才会有值
scheduler.executorLost(executorId, SlaveLost("Executorheartbeat " +
s"timed out after ${now- lastSeenMs} ms"))
// Asynchronously kill the executor to avoid blocking thecurrent thread
// 异步杀死executor避免阻塞当前线程
killExecutorThread.submit(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.tryLogNonFatalError {
// Note: we want to get an executor back after expiringthis one,
// so do not simply call`sc.killExecutor` here (SPARK-8119)
sc.killAndReplaceExecutor(executorId)
}
})
executorLastSeen.remove(executorId)
}
}
}
===>再回到SparkContext中
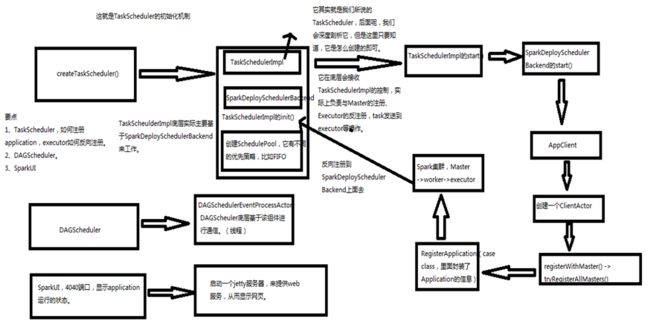
12、创建TaskSchdulerImpl和SparkDeploySchedulerBackend,在createTaskScheduler()。TaskSchdulerImpl.initialize()会被调用,同时将SparkDeploySchedulerBackend,,赋给TaskSchdulerImpl成员上
查看(spark-core_22: SparkDeploySchedulerBackend,TaskSchedulerImpl的初始化源码分析)和
(spark-core_23: TaskSchedulerImpl.start()、SparkDeploySchedulerBackend.start()、CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.start()、AppClient.start()源码分析)
// Create and startthe scheduler,这个master是在sparkSubmit.Main方法得到:spark://luyl152:7077,luyl153:7077,luyl154:7077
//如果集群管理器是standalone模式:该方法返回(SparkDeploySchedulerBackend,TaskSchedulerImpl)
val (sched, ts)= SparkContext.createTaskScheduler(this, master)
_schedulerBackend = sched //SparkDeploySchedulerBackend
_taskScheduler = ts //TaskSchedulerImpl
(查看spark-core_27:DAGScheduler的初始化源码分析)
_dagScheduler = new DAGScheduler(this) //DAGScheduler初始化时会将自己设置到TaskSchedulerImpl中
_heartbeatReceiver.ask[Boolean](TaskSchedulerIsSet)//向HeartbeatReceiver发出询问,将TaskSchedulerImpl赋给TaskSchedulerIsSet.scheduler成员
// start TaskScheduler after taskScheduler sets DAGScheduler reference inDAGScheduler's constructor
在TaskSchedulerImpl在DAGScheduler的构造函数中设置DAGScheduler引用后启动TaskScheduler
_taskScheduler.start()
13,从sparkDeploySchdulerBackend中取得appId给sparkContext的_applicationId赋值
同时调用BlockManager.initialized()
_applicationId = _taskScheduler.applicationId() //在sparkDeploySchedulerBackend中的AppClient的start()往master注册得到的值: app-20180404172558-0000
//如果集群管理器支持多次尝试,则获取此运行的尝试标识。 在客户端模式下运行的应用程序不会有尝试ID。
_applicationAttemptId= taskScheduler.applicationAttemptId()
_conf.set("spark.app.id", _applicationId)
_ui.foreach(_.setAppId(_applicationId))//给sparkUI设置的
查看(spark-core_29:Executor初始化过程env.blockManager.initialize(conf.getAppId)源码分析)driver的blockManager.initialize也是类似的
_env.blockManager.initialize(_applicationId) //Executor在初始化时调用一次,driver在SparkContext初始化也调用