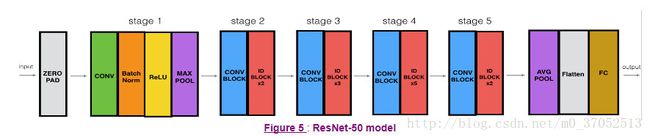
deeplearning.ai 第四课第二周 resnet 50层神经网络实现
1、导入函数库:
import numpy as np
from keras import layers
from keras.layers import Input, Add, Dense, Activation, ZeroPadding2D, BatchNormalization, Flatten, Conv2D, AveragePooling2D, MaxPooling2D, GlobalMaxPooling2D
from keras.models import Model, load_model
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.utils import layer_utils
from keras.utils.data_utils import get_file
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
import pydot
from IPython.display import SVG
from keras.utils.vis_utils import model_to_dot
from keras.utils import plot_model
from resnets_utils import *
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
import scipy.misc
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
%matplotlib inline
import keras.backend as K
K.set_image_data_format('channels_last')
K.set_learning_phase(1)2、定义一个identity_block,该block的特质是其在一个block内,四层的矩阵维度都没有变化
block如下图所示:

# GRADED FUNCTION: identity_block
def identity_block(X, f, filters, stage, block):
"""
Implementation of the identity block as defined in Figure 3
Arguments:
X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path
filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path
stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
Returns:
X -- output of the identity block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C)
"""
# defining name basis
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
# Retrieve Filters
F1, F2, F3 = filters
# Save the input value. You'll need this later to add back to the main path.
X_shortcut = X
# First component of main path
X = Conv2D(filters = F1, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
### START CODE HERE ###
# Second component of main path (≈3 lines)
X = Conv2D(filters=F2,kernel_size=(f,f),strides=(1,1),padding='same',name=conv_name_base+'2b',kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# Third component of main path (≈2 lines)
X = Conv2D(filters=F3,kernel_size=(1,1),strides=(1,1),padding='valid',name=conv_name_base+'2c',kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base+'2c')(X)
# Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation (≈2 lines)
X = Add()([X,X_shortcut])
X = Activation('relu')(X)
### END CODE HERE ###
return X3、定义convolution_block 该定义是,该block跳跃两层,总共有四层,且中间传输数据维度有变化。图片如下
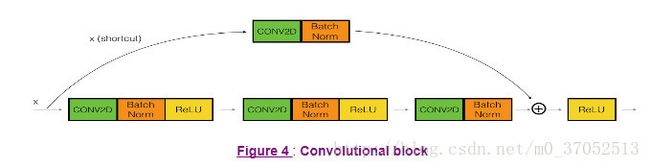
def convolutional_block(X, f, filters, stage, block, s = 2):
"""
Implementation of the convolutional block as defined in Figure 4
Arguments:
X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path
filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path
stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
s -- Integer, specifying the stride to be used
Returns:
X -- output of the convolutional block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C)
"""
# defining name basis
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
# Retrieve Filters
F1, F2, F3 = filters
# Save the input value
X_shortcut = X
##### MAIN PATH #####
# First component of main path
X = Conv2D(F1, (1, 1), strides = (s,s), name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
### START CODE HERE ###
# Second component of main path (≈3 lines)
X = Conv2D(F2,(f,f),strides=(1,1),name=conv_name_base+'2b',padding='same',kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base+'2b')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# Third component of main path (≈2 lines)
X = Conv2D(F3,(1,1),strides=(1,1),name=conv_name_base+'2c',padding='valid',kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base+'2c')(X)
##### SHORTCUT PATH #### (≈2 lines)
X_shortcut = Conv2D(F3,(1,1),strides=(s,s),name=conv_name_base+'1',padding='valid',kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_shortcut)
X_shortcut = BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base+'1')(X_shortcut)
# Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation (≈2 lines)
X = Add()([X,X_shortcut])
X = Activation('relu')(X)
### END CODE HERE ###
return X# GRADED FUNCTION: ResNet50
def ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6):
"""
Implementation of the popular ResNet50 the following architecture:
CONV2D -> BATCHNORM -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*3
-> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*5 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> AVGPOOL -> TOPLAYER
Arguments:
input_shape -- shape of the images of the dataset
classes -- integer, number of classes
Returns:
model -- a Model() instance in Keras
"""
# Define the input as a tensor with shape input_shape
X_input = Input(input_shape)
# Zero-Padding
X = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input)
# Stage 1
X = Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides = (2, 2), name = 'conv1', kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = 'bn_conv1')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
X = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(X)
# Stage 2
X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [64, 64, 256], stage = 2, block='a', s = 1)
X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
### START CODE HERE ###
# Stage 3 (≈4 lines)
X = convolutional_block(X,f=3,filters=[128,128,512],stage=3,block='a',s=2)
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[128,128,512],stage=3,block='b')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[128,128,512],stage=3,block='c')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[128,128,512],stage=3,block='d')
# Stage 4 (≈6 lines)
X = convolutional_block(X,f = 3, filters=[256,256,1024],stage=4,block='a',s=2)
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[256,256,1024],stage=4,block='b')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[256,256,1024],stage=4,block='c')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[256,256,1024],stage=4,block='d')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[256,256,1024],stage=4,block='e')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[256,256,1024],stage=4,block='f')
# Stage 5 (≈3 lines)
X = convolutional_block(X,f=3,filters=[512,512,2048],stage=5,block='a',s=2)
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[512,512,2048],stage=5,block='b')
X = identity_block(X,f=3,filters=[512,512,2048],stage=5,block='c')
# AVGPOOL (≈1 line). Use "X = AveragePooling2D(...)(X)"
X = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2,2),strides=(1,1),padding='valid')(X)
### END CODE HERE ###
# output layer
X = Flatten()(X)
X = Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='fc' + str(classes), kernel_initializer = glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
# Create model
model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='ResNet50')
return model5、模型实体化:
model = ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6)6、定义模型训练过程及相应超参 (compile)
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])7、训练数据载入:
X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()
# Normalize image vectors
X_train = X_train_orig/255.
X_test = X_test_orig/255.
# Convert training and test labels to one hot matrices
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6).T
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6).T
print ("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[0]))
print ("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[0]))
print ("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape))
print ("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape))
print ("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape))
print ("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape))8、模型训练:
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs = 100, batch_size = 32)9、模型评估:
preds = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test)
print ("Loss = " + str(preds[0]))
print ("Test Accuracy = " + str(preds[1]))