前言
当我们自己去写SQL代码的时候有时候会因为不熟练会导致效率低,再之后要进行许多的优化,并且操作也较为繁琐。因此ORM框架就能够解决上面的问题,它能根据自身的一些规则来帮助开发者去生成SQL代码。按性能上看虽然直接去写SQL语句会比ORM框架生成的效率高,但实际上每一个开发者的SQL代码程度都参差不齐,因此框架在这里就起到了一个统一的作用。
ORM框架(SQLAlchemy)
作用:提供简单的规则,去自动转换成SQL语句
安装:
pip install SQLAlchemy;
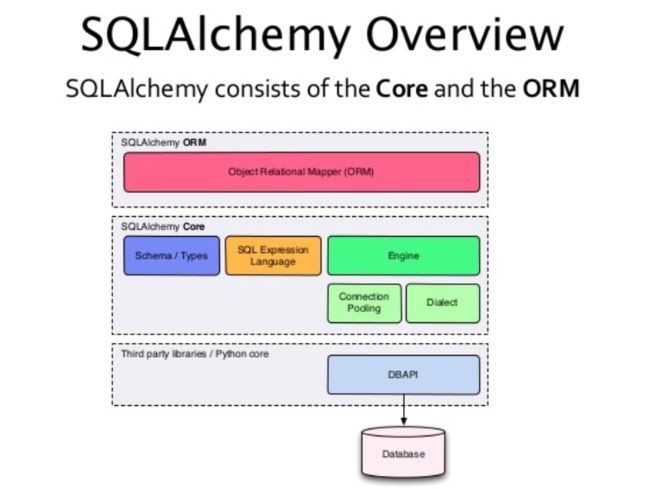
系统架构:
SQLAlchemy主要分为SQLAlchemy ORM和SQLAlchemy Core两个部分,这里的DBAPI指的是像mysqldb、pymysql、cx_Oracle...用来连接数据库的模块。因此这里的DBAPI和SQLAchemy是没有直接的关系的,SQLAlchemy主要就是负责将对象和类转换为SQL语句。在使用SQLAlchemy去创建数据库中之前,要把pymysql给安装才能实现相关的功能。
Object Relational Mapper(ORM)为关系对象映射,简单来说就是对象和类
Schema/Types和SQL Expression Language主要帮助上面的ORM转换为SQL语句
Engine为引擎,用于操作配置文件、Connection Pooling为连接池用于保持多少个和数据库相连的连接、Dialect用于选择去连接Mysql、SQLSever、Oracle等数据库去选择
连接其他数据库的方法:
1.Oracle + cx_oracle oracle+cx_oracle://user:pass@host:port/dbname[?key=value&key=value...] 2.SQLite + pysqlite sqlite+pysqlite:///file_path 3.SQLite + pysqlcipher sqlite+pysqlcipher://:passphrase/file_path[?kdf_iter=] 4.Mysql + pymysql mysql+pymysql:// : @ / [? ] 5.Mysql + Oursql mysql+oursql:// : @ [: ]/
参考网站:https://www.sqlalchemy.org/
ORM分为两类(DB first、Code first)
DB first:手动创建数据以及表->通过ORM框架去自动生成类
Code first:手动创建类和数据库->通过ORM框架创建表。
创建一个表(前提先创建一个数据库):
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column,Integer,String from sqlalchemy import create_engine Base = declarative_base() #创建表 class Users(Base): __tablename__ = 'users' #定义数据库的表名,id,name,email表示这张表会生成三列 id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True,autoincrement = True) name = Column(String(32)) email = Column(String(16)) engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) #root后面可以写登录密码,max_overflow表示最多和数据库建立5个连接 Base.metadata.create_all(engine) #找到py文件中的这个类在数据库中创建表
完成表的创建:
那如果要删除这些创建的表:
Base.metadata.drop_all(engine)
创建两张表之间的关系员工和部门表:
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Column,Integer,String,ForeignKey,UniqueConstraint,Index from sqlalchemy import create_engine Base = declarative_base() #创建部门表 class Department(Base): __tablename__ = 'department' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True,nullable=False) depart = Column(String(32),nullable=False) #创建员工表 class Employee(Base): __tablename__ = 'employee' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True,nullable=False) name = Column(String(32),nullable=False,index=True) #开启索引 age = Column(Integer,default=20) #默认年龄为20 email = Column(String(32),unique=True) #创建唯一索引 employee_depart_id = Column(Integer,ForeignKey('department.id')) #创建外键'employee_depart_id' __table_args__ = ( UniqueConstraint('id','name','email',name = 'uindex_i_n_e'), #创建联合唯一索引'uindex_i_n_e' Index('index_name_email','name','email') #创建联合普通索引'index_name_email' ) engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
完成表的创建:
将删除表和创建表封装为两个不同的函数,方便之后的操作:
def create_db(): engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Base.metadata.create_all(engine) def drop_db(): engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8', max_overflow = 5) Base.metadata.drop_all(engine)
代码中String表示了Char和Varchar,若只需要用Char或Varchar可以在import后面不写String单写Varchar或Char就好
操作数据行
增
增加部门表的数据
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8', max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() #获取一个连接去进行操作 #增加部门表数据 objs = [ Department(depart = '保安'), #一张表代表了一个类,对象代指的是数据行 Department(depart = '程序员'), Department(depart = 'DBA'), Department(depart = 'BOSS') ] session.add_all(objs) session.commit() session.close()
增加员工表的数据
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8', max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() #增加员工表数据 objs = [ Employee(name='aaa1',age=21,email='[email protected]',employee_depart_id=1), Employee(name='aaa2',email='[email protected]',employee_depart_id=2), Employee(name='aaa3',age=23,email='[email protected]',employee_depart_id=3), Employee(name='aaa4',age=31,email='[email protected]',employee_depart_id=4), Employee(name='aaa5',email='[email protected]',employee_depart_id=3), Employee(name='aaa6',age=51,email='[email protected]',employee_depart_id=3) ] session.add_all(objs) session.commit() session.close()
删
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8', max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() employee_list = session.query(Employee).filter(Department.id == 6).delete() session.commit() session.close()
改
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8', max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() employee_list = session.query(Employee.name).filter(Employee.id > 0).update({'name': 'abc'}) #全改 employee_list = session.query(Employee.name).filter(Employee.id > 0).update({Employee.name:Employee.name + '777'},synchronize_session=False) employee_list = session.query(Employee.name).filter(Employee.id > 0).update({'name':Employee.age + 1},synchronize_session='evaluate') session.commit() session.close()
查
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8', max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() employee_list = session.query(Employee) print(employee_list) #这里表示的是SQL查询语句 employee_list = session.query(Employee).all() #查询表内的数据 for i in employee_list: print(type(i),i,i.name,i.age,i.email) #<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F1EF98> aaa1 21 [email protected] #<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F1EEF0> aaa2 20 [email protected] #<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F4E0F0> aaa3 23 [email protected] #<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F4E6D8> aaa4 31 [email protected] #<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F4E2E8> aaa5 20 [email protected] #<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F4E160> aaa6 51 [email protected] employee_list = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id > 2) #类似于使用where条件语句进行数据筛选 for i in employee_list: print(i.id,i.name) # 3 aaa3 # 4 aaa4 # 5 aaa5 # 6 aaa6 employee_list = session.query(Employee.name,Employee.email).filter(Employee.id > 2) #表示只取这张表的哪几列 for i in employee_list: print(i.name) # aaa3 # aaa4 # aaa5 # aaa6 session.commit() session.close()
其他操作
员工表:
1.分组
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() from sqlalchemy.sql import func ret1 = session.query(func.max(Employee.id),func.min(Employee.id),func.sum(Employee.id),func.avg(Employee.id)).group_by(Employee.name).all() ret2 = session.query(func.max(Employee.id)).group_by(Employee.name).having(func.min(Employee.id) > 2).all() session.commit() session.close()
2.排序
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() ret1 = session.query(Employee).order_by(Employee.name.desc(),Employee.age.asc(),Employee.email.desc()).all() for i in ret1: print(i.id, i.name, i.email) # 6 52 [email protected] # # 4 32 [email protected] # # 3 24 [email protected] # # 1 22 [email protected] # # 5 21 [email protected] # # 2 21 [email protected] session.commit() session.close()
3.连表
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() ret1 = session.query(Employee,Department).filter(Employee.employee_depart_id == Department.id).all() ret2 = session.query(Employee).join(Department).all() #这里会自动找到外键将两张表进行连接,这里相当于inner join ret3 = session.query(Employee).join(Department,isouter=True).all() #这里相当于left join,这里开False也是inner join session.commit() session.close()
4.通配符
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() ret1 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.name.like('2_')).all() for i in ret1: print(i.id, i.name, i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] # 1 22 [email protected] # 3 24 [email protected] ret2 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.name.like('%2')).all() for i in ret2: print(i.id, i.name, i.email) # 1 22 [email protected] # 4 32 [email protected] # 6 52 [email protected] ret3 = session.query(Employee).filter(~Employee.name.like('%2')).all() for i in ret3: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 3 24 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] session.commit() session.close()
5.子查询
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() #1.select * from b where id in (select id from tb); ret1 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id.in_(session.query(Employee.id).filter_by(name = '21'))).all() for i in ret1: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] #2.select * from (select * from tb) as T; q1 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id > 2).subquery() ret2 = session.query(q1).all() for i in ret2: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 3 24 [email protected] # 4 32 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] # 6 52 [email protected] #3.select id,(select * from tb where a.type_id == b.id) from b; ret3 = session.query(Department.id,session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id == Department.id).as_scalar()) session.commit() session.close()
6.limit(限制)
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() ret1 = session.query(Employee)[3:6] for i in ret1: print(i.id, i.name, i.email) # 4 32 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] # 6 52 [email protected] session.commit() session.close()
7.union(组合)
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() q1 = session.query(Employee.name).filter(Employee.id > 3) q2 = session.query(Department.depart).filter(Department.id > 1) u1 = q1.union(q2).all() #去重 u2 = q1.union_all(q2).all() #不去重 session.commit() session.close()
8.条件
filter_by里面穿的是参数,filter里面传的是表达式,filter_by内部会调用filter
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() ret1 = session.query(Employee).filter_by(name = '22').all() for i in ret1: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) #1 22 [email protected] ret2 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id > 1,Employee.name == '21').all() #这里默认使用AND for i in ret2: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] ret3 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id.between(2,4),Employee.name == '24').all() for i in ret3: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 3 24 [email protected] ret4 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id.in_([1,2,6])).all() for i in ret4: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 1 22 [email protected] # 2 21 [email protected] # 6 52 [email protected] ret5 = session.query(Employee).filter(~Employee.id.in_([1,2,6])).all() for i in ret5: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 3 24 [email protected] # 4 32 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] ret6 = session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.id.in_(session.query(Employee.id).filter_by(name = '21'))).all() #临时表 for i in ret6: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] from sqlalchemy import and_,or_ ret7 = session.query(Employee).filter(and_(Employee.id > 4,Employee.name == '21')).all() #这里默认使用AND for i in ret7: print(i.id,i.name,i.email) # 5 21 [email protected] ret8 = session.query(Employee).filter(or_(Employee.id > 4,Employee.name == '21')).all() for i in ret8: print(i.id, i.name, i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] # 6 52 [email protected] ret9 = session.query(Employee).filter( or_( Employee.id > 2, and_( Employee.age > 20,Employee.email == "[email protected]" ), Employee.name == '21' ) ).all() for i in ret9: print(i.id, i.name, i.email) # 2 21 [email protected] # 3 24 [email protected] # 4 32 [email protected] # 5 21 [email protected] # 6 52 [email protected] session.commit() session.close()
9.原生SQL
建立Relationship
一般情况下我们要去获取员工信息以及与它关联的员工类型名称(正向操作)
写法一:
ret = session.query(Employee,Department).join(Department,isouter=True) print(ret) for row in ret: print(row[0].id,row[0].name,row[0].age,row[0].email,row[0].employee_depart_id,row[1].depart)
写法二:
ret = session.query(Employee.name,Department.depart).join(Department,isouter=True) print(ret) for row in ret: print(row[0],row[1]) #两种写法都一样 print(row.name,row.depart)
在query()后面不加上all()拿ret就相当于一个迭代器,加上all()就相当于fetchall()把所有的数据都拿回来了
那除了用以上的方法之外我们还可以在Employee表中加上关系:
depart_relation = relationship('Department')
在此之前要import relation模块
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
执行代码:
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:@127.0.0.1:3306/db3?charset=utf8',max_overflow = 5) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) session = Session() ret = session.query(Employee) for row in ret: print(row.id,row.name,row.age,row.email,row.depart_relation.depart) # 1 22 21 [email protected] 保安 # 2 21 20 [email protected] 程序员 # 3 24 23 [email protected] DBA # 4 32 31 [email protected] BOSS # 5 21 20 [email protected] DBA # 6 52 51 [email protected] DBA session.commit() session.close()
那如果要获取用户的数据类型(反向操作)该怎么写?
一般写法:
ret = session.query(Department) for row in ret: print(row.id,row.depart,session.query(Employee).filter(Employee.employee_depart_id == row.id).all()) # 1 保安 [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F67358>] # 2 程序员 [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F674A8>] # 3 DBA [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F675F8>, <__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F47F28>, <__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F47CF8>] # 4 BOSS [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F67588>]
将添加的关系语句后加上:
depart_relation = relationship('Department',backref = 'relatvar') #这里的backref是给Department用的
执行代码:
ret = session.query(Department) for row in ret: print(row.id,row.depart,row.relatvar) # 1 保安 [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F66BE0>] # 2 程序员 [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F66C88>] # 3 DBA [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F66DD8>, <__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F66E48>, <__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F66EB8>] # 4 BOSS [<__main__.Employee object at 0x0000000003F87048>]
relationship一般写在有外键的那张表上