sklearn线性回归,支持向量机SVR回归,随机森林回归,神经网络回归参数解释及示例
1.sklearn线性回归
线性回归,其中目标值 y 是输入变量 x 的线性组合。 在数学概念中,如果 是预测值。
在整个模块中,我们定义向量 作为 coef_ ,定义 作为 intercept_ ,是它的截距。
LinearRegression 拟合一个带有系数 的线性模型,使得数据集实际观测数据和预测数据(估计值)之间的残差平方和最小。其数学表达式为:
class sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True, normalize=False, copy_X=True, n_jobs=1)
fit_intercept=True, 默认存在截距 normalize=False,默认不进行标准化处理 copy_X=True,If True, X will be copied; else, it may be overwritten.
from sklearn import linear_model
reg = linear_model.LinearRegression()
a=[[1,2], [2,3], [3,4],[1,5]]
b=[6,9,12,12]
reg.fit (a, b)
w_dt=reg.coef_
re=reg.predict(([[4,4]]))
print(w_dt)
print(reg.intercept_)
print(re)
[1. 2.]
1.0000000000000018
[13.]2.支持向量机回归SVR
C : float, optional (default=1.0)
误差项的惩罚参数,一般取值为10的n次幂,如10的-5次幂,10的-4次幂。。。。10的0次幂,10,1000,1000,在python中可以使用pow(10,n) n=-5~inf
C越大,相当于希望松弛变量接近0,即对误分类的惩罚增大,趋向于对训练集全分对的情况,这样会出现训练集测试时准确率很高,但泛化能力弱。
C值小,对误分类的惩罚减小,容错能力增强,泛化能力较强。kernel : string, optional (default=’rbf’)
svc中指定的kernel类型。
可以是: ‘linear’, ‘poly’, ‘rbf’, ‘sigmoid’, ‘precomputed’ 或者自己指定。 默认使用‘rbf’ 。degree : int, optional (default=3)
当指定kernel为 ‘poly’时,表示选择的多项式的最高次数,默认为三次多项式。
若指定kernel不是‘poly’,则忽略,即该参数只对‘poly’有作用。gamma : float, optional (default=’auto’)
当kernel为‘rbf’, ‘poly’或‘sigmoid’时的kernel系数。
如果不设置,默认为 ‘auto’ ,此时,kernel系数设置为:1/n_featurescoef0 : float, optional (default=0.0)
kernel函数的常数项。
只有在 kernel为‘poly’或‘sigmoid’时有效,默认为0。probability : boolean, optional (default=False)
是否采用概率估计。
必须在fit()方法前使用,该方法的使用会降低运算速度,默认为False。 shrinking : boolean, optional (default=True)
如果能预知哪些变量对应着支持向量,则只要在这些样本上训练就够了,其他样本可不予考虑,这不影响训练结果,但降低了问题的规模并有助于迅速求解。进一步,如果能预知哪些变量在边界上(即a=C),则这些变量可保持不动,只对其他变量进行优化,从而使问题的规模更小,训练时间大大降低。这就是Shrinking技术。
Shrinking技术基于这样一个事实:支持向量只占训练样本的少部分,并且大多数支持向量的拉格朗日乘子等于C。tol : float, optional (default=1e-3)
误差项达到指定值时则停止训练,默认为1e-3,即0.001。cache_size : float, optional
指定内核缓存的大小,默认为200M。class_weight : {dict, ‘balanced’}, optional
权重设置。如果不设置,则默认所有类权重值相同。
以字典形式传入。
Set the parameter C of class i to class_weight[i]*C for SVC. If not given, all classes are supposed to have weight one. The “balanced” mode uses the values of y to automatically adjust weights inversely proportional to class frequencies in the input data as n_samples / (n_classes * np.bincount(y))verbose : bool, default: False
是否启用详细输出。
多线程时可能不会如预期的那样工作。默认为False。max_iter : int, optional (default=-1)
默认设置为-1,表示无穷大迭代次数。
Hard limit on iterations within solver, or -1 for no limit.decision_function_shape : ‘ovo’, ‘ovr’, default=’ovr’
Whether to return a one-vs-rest (‘ovr’) decision function of shape (n_samples, n_classes) as all other classifiers, or the original one-vs-one (‘ovo’) decision function of libsvm which has shape (n_samples, n_classes * (n_classes - 1) / 2).
Changed in version 0.19: decision_function_shape is ‘ovr’ by default.
New in version 0.17: decision_function_shape=’ovr’ is recommended.
Changed in version 0.17: Deprecated decision_function_shape=’ovo’ and None.random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, optional (default=None)
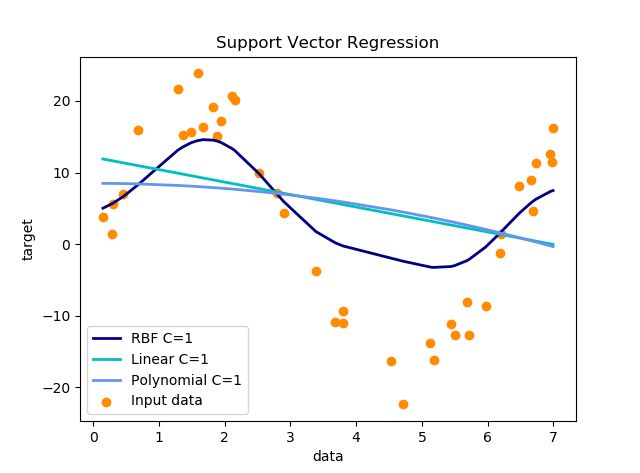
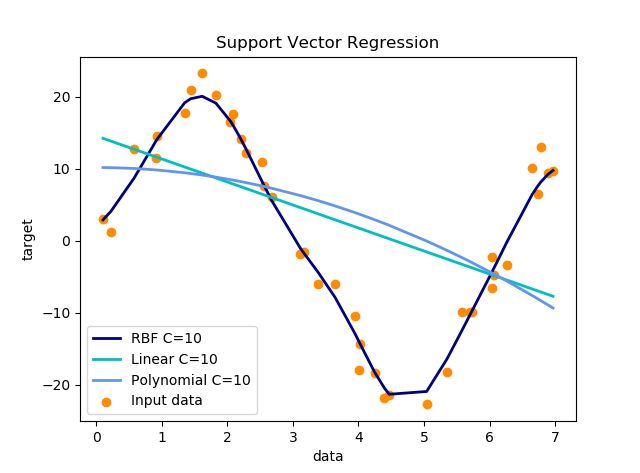
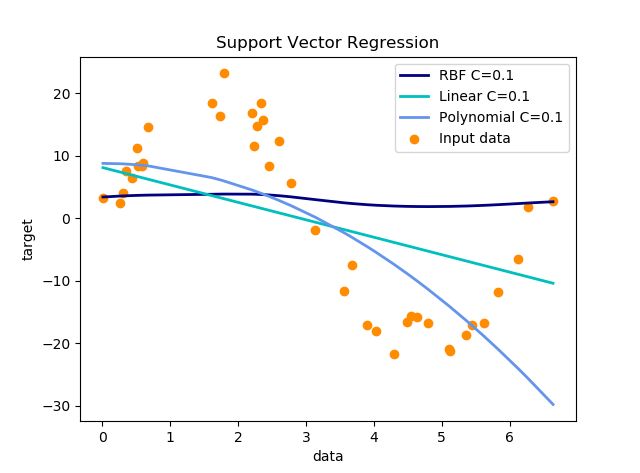
伪随机数使用数据。 import numpy as np from sklearn.svm import SVR import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # ############################################################################# # Generate sample data X = np.sort(7 * np.random.rand(40, 1), axis=0) y = np.sin(X).ravel()*20 # ############################################################################# # Add noise to targets noise= 9 * (0.5 - np.random.rand(40)) y_noise=y+noise # ############################################################################# # Fit regression model svr_rbf = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=1) svr_lin = SVR(kernel='linear', C=1) svr_poly = SVR(kernel='poly', C=1, degree=2) y_rbf = svr_rbf.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X) y_lin = svr_lin.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X) y_poly = svr_poly.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X) # ############################################################################# # Look at the results lw = 2 plt.scatter(X, y_noise, color='darkorange', label='Input data') plt.plot(X, y_rbf, color='navy', lw=lw, label='RBF C=1 ') plt.plot(X, y_lin, color='c', lw=lw, label='Linear C=1') plt.plot(X, y_poly, color='cornflowerblue', lw=lw, label='Polynomial C=1') plt.xlabel('data') plt.ylabel('target') plt.title('Support Vector Regression') plt.legend() plt.show()
参数设置:C取1,其他都为默认值
- 参数设置:C取10,其他都为默认值
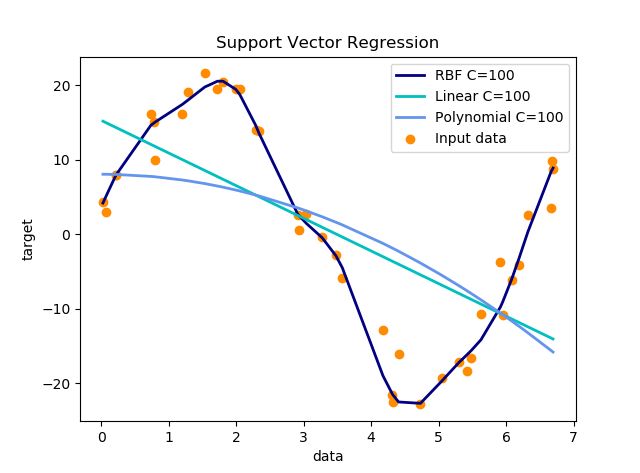
- 参数设置:C取100,其他都为默认值
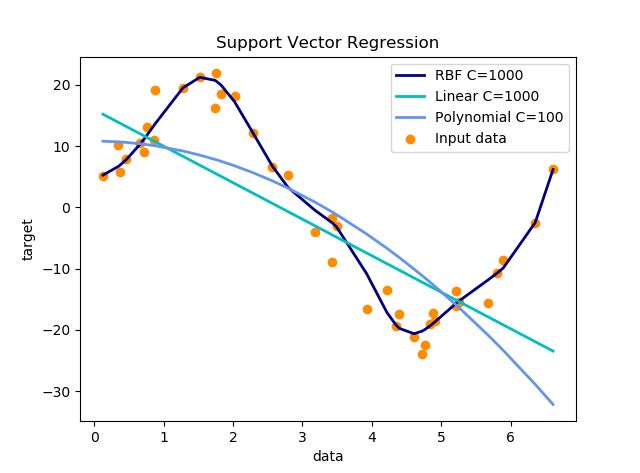
- 参数设置:C取1000,其他都为默认值
- 参数设置:C取0.1,其他都为默认值
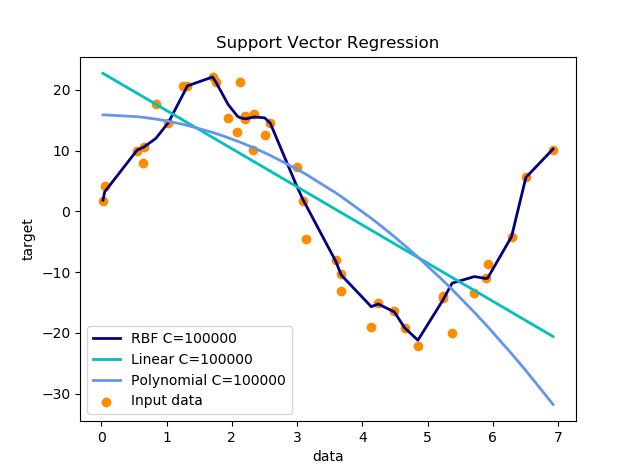
- 参数设置:C取10000,其他都为默认值
3.随机森林回归
随机森林的生成
从样本集中通过重采样的方式产生n个样本。假设样本特征数目为a,对n个样本选择a中的k个特征,用建立决策树的方式获得最佳分割点。
重复m次,产生m棵决策树。
多数投票机制进行预测。随机森林中的随机是什么意思?
随机森林中的随机性主要体现在两个方面:
随机采样:随机森林在计算每棵树时,从全部训练样本(样本数为n)中选取一个可能有重复的、大小同样为n的数据集进行训练(即booststrap采样)。
特征选取的随机性:在每个节点随机选取所有特征的一个子集,用来计算最佳分割方式。
随机森林的优点:
表现性能好,与其他算法相比有着很大优势。随机森林能处理很高维度的数据(也就是很多特征的数据),并且不用做特征选择。
在训练完之后,随机森林能给出哪些特征比较重要。
训练速度快,容易做成并行化方法(训练时,树与树之间是相互独立的)。
在训练过程中,能够检测到feature之间的影响。
对于不平衡数据集来说,随机森林可以平衡误差。当存在分类不平衡的情况时,随机森林能提供平衡数据集误差的有效方法。
如果有很大一部分的特征遗失,用RF算法仍然可以维持准确度。
随机森林算法有很强的抗干扰能力(具体体现在6,7点)。所以当数据存在大量的数据缺失,用RF也是不错的。
随机森林抗过拟合能力比较强(虽然理论上说随机森林不会产生过拟合现象,但是在现实中噪声是不能忽略的,增加树虽然能够减小过拟合,但没有办法完全消除过拟合,无论怎么增加树都不行,再说树的数目也不可能无限增加的。)
随机森林能够解决分类与回归两种类型的问题,并在这两方面都有相当好的估计表现。(虽然RF能做回归问题,但通常都用RF来解决分类问题)。
在创建随机森林时候,对generlization error(泛化误差)使用的是无偏估计模型,泛化能力强。
随机森林在Python的实现
#Import Library
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
#use RandomForestRegressor for regression problem
#Assumed you have, X (predictor) and Y (target) for training data set and x_test(predictor) of test_dataset
# Create Random Forest object
model= RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=1000)
# Train the model using the training sets and check score
model.fit(X, y) #Predict Output
predicted= model.predict(x_test)
随机森林在sklearn-RandomForest参数
RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=10, //树的棵数
criterion='gini', //分类标准
max_depth=None, //最大深度
min_samples_split=2, //最少分裂几个子节点
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
max_leaf_nodes=None,
bootstrap=True,
n_jobs=1, //指定并行使用的进程数
random_state=None,
verbose=0,
warm_start=False,
class_weight=None //类别权重,样本不均衡时很重要
)from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
import numpy as np
rf = RandomForestRegressor()
a=[[1,2], [2,3], [3,4],[1,5]]
b=np.array([[6],[9],[12],[12]])
rf.fit (a, b.ravel())
re=rf.predict([[4,4]])
print(re)
c=[[1,2], [2,3], [3,4],[1,5]]
d=np.array([[7],[11],[15],[10]])
rf.fit (c, d.ravel())
re=rf.predict([[4,4]])
print(re)
[11.4]
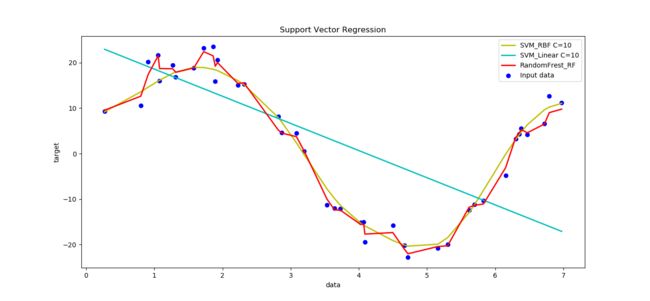
[13.7]随机森林回归与支持向量机回归比较
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.svm import SVR
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# #############################################################################
# Generate sample data
X = np.sort(7 * np.random.rand(40, 1), axis=0)
y = np.sin(X).ravel() * 20
# #############################################################################
# Add noise to targets
noise = 9 * (0.5 - np.random.rand(40))
y_noise = y + noise
# #############################################################################
# Fit regression model
svr_rbf = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=10)
svr_lin = SVR(kernel='linear', C=10)
rf=RandomForestRegressor()
y_SVM_rbf = svr_rbf.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X)
y_SVM_lin = svr_lin.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X)
y_RF_rf = rf.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X)
# #############################################################################
# Look at the results
lw = 2
plt.scatter(X, y_noise, color='b', label='Input data')
plt.plot(X, y_SVM_rbf, color='y', lw=lw, label='SVM_RBF C=10 ')
plt.plot(X,y_SVM_lin, color='c', lw=lw, label='SVM_Linear C=10')
plt.plot(X, y_RF_rf, color='r', lw=lw, label='RandomFrest_RF')
plt.xlabel('data')
plt.ylabel('target')
plt.title('Support Vector Regression')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
4.神经网络回归
mlp=MLPClassifier(solver=’sgd’,activation=’relu’,alpha=1e-4,hidden_layer_sizes=(50,50), random_state=1,max_iter=10,verbose=10,learning_rate_init=.1)
参数说明:
1. hidden_layer_sizes :例如hidden_layer_sizes=(50, 50),表示有两层隐藏层,第一层隐藏层有50个神经元,第二层也有50个神经元。
2. activation :激活函数,{‘identity’, ‘logistic’, ‘tanh’, ‘relu’}, 默认relu- identity:f(x) = x
- logistic:其实就是sigmod,f(x) = 1 / (1 + exp(-x)).
- tanh:f(x) = tanh(x).
- relu:f(x) = max(0, x)
3. solver: {‘lbfgs’, ‘sgd’, ‘adam’}, 默认adam,用来优化权重- lbfgs:quasi-Newton方法的优化器
- sgd:随机梯度下降
- adam: Kingma, Diederik, and Jimmy Ba提出的机遇随机梯度的优化器
注意:默认solver ‘adam’在相对较大的数据集上效果比较好(几千个样本或者更多),对小数据集来说,lbfgs收敛更快效果也更好。
4. alpha :float,可选的,默认0.0001,正则化项参数
5. batch_size : int , 可选的,默认’auto’,随机优化的minibatches的大小batch_size=min(200,n_samples),如果solver是’lbfgs’,分类器将不使用minibatch
6. learning_rate :学习率,用于权重更新,只有当solver为’sgd’时使用,{‘constant’,’invscaling’, ‘adaptive’},默认constant- ‘constant’: 有’learning_rate_init’给定的恒定学习率
- ‘incscaling’:随着时间t使用’power_t’的逆标度指数不断降低学习率learning_rate_ ,effective_learning_rate = learning_rate_init / pow(t, power_t)
- ‘adaptive’:只要训练损耗在下降,就保持学习率为’learning_rate_init’不变,当连续两次不能降低训练损耗或验证分数停止升高至少tol时,将当前学习率除以5.
7. power_t: double, 可选, default 0.5,只有solver=’sgd’时使用,是逆扩展学习率的指数.当learning_rate=’invscaling’,用来更新有效学习率。
8. max_iter: int,可选,默认200,最大迭代次数。
9. random_state:int 或RandomState,可选,默认None,随机数生成器的状态或种子。
10. shuffle: bool,可选,默认True,只有当solver=’sgd’或者‘adam’时使用,判断是否在每次迭代时对样本进行清洗。
11. tol:float, 可选,默认1e-4,优化的容忍度
12. learning_rate_int:double,可选,默认0.001,初始学习率,控制更新权重的补偿,只有当solver=’sgd’ 或’adam’时使用。
14. verbose : bool, 可选, 默认False,是否将过程打印到stdout
15. warm_start : bool, 可选, 默认False,当设置成True,使用之前的解决方法作为初始拟合,否则释放之前的解决方法。
16. momentum : float, 默认 0.9,动量梯度下降更新,设置的范围应该0.0-1.0. 只有solver=’sgd’时使用.
17. nesterovs_momentum : boolean, 默认True, Whether to use Nesterov’s momentum. 只有solver=’sgd’并且momentum > 0使用.
18. early_stopping : bool, 默认False,只有solver=’sgd’或者’adam’时有效,判断当验证效果不再改善的时候是否终止训练,当为True时,自动选出10%的训练数据用于验证并在两步连续迭代改善,低于tol时终止训练。
19. validation_fraction : float, 可选, 默认 0.1,用作早期停止验证的预留训练数据集的比例,早0-1之间,只当early_stopping=True有用
20. beta_1 : float, 可选, 默认0.9,只有solver=’adam’时使用,估计一阶矩向量的指数衰减速率,[0,1)之间
21. beta_2 : float, 可选, 默认0.999,只有solver=’adam’时使用估计二阶矩向量的指数衰减速率[0,1)之间
22. epsilon : float, 可选, 默认1e-8,只有solver=’adam’时使用数值稳定值。
属性说明:- classes_:每个输出的类标签
- loss_:损失函数计算出来的当前损失值
- coefs_:列表中的第i个元素表示i层的权重矩阵
- intercepts_:列表中第i个元素代表i+1层的偏差向量
- n_iter_ :迭代次数
- n_layers_:层数
- n_outputs_:输出的个数
- out_activation_:输出激活函数的名称。
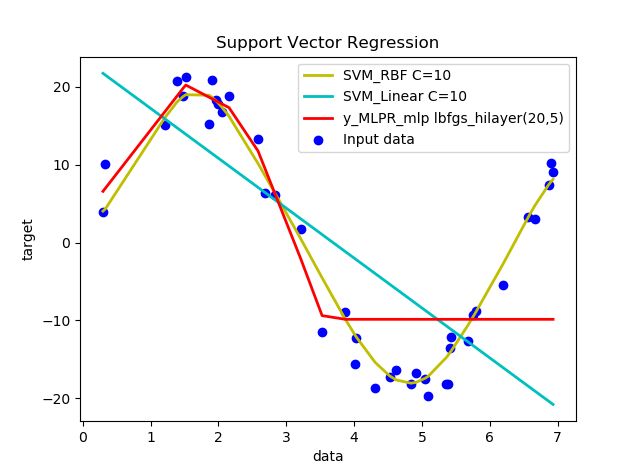
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# #############################################################################
# Generate sample data
X = np.sort(7 * np.random.rand(40, 1), axis=0)
y = np.sin(X).ravel() * 20
# #############################################################################
# Add noise to targets
noise = 9 * (0.5 - np.random.rand(40))
y_noise = y + noise
# #############################################################################
# Fit regression model
svr_rbf = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=10)
svr_lin = SVR(kernel='linear', C=10)
mlp=MLPRegressor(solver='lbfgs',hidden_layer_sizes=(5,2))
y_SVM_rbf = svr_rbf.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X)
y_SVM_lin = svr_lin.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X)
y_MLPR_mlp = mlp.fit(X, y_noise).predict(X)
# #############################################################################
# Look at the results
lw = 2
plt.scatter(X, y_noise, color='b', label='Input data')
plt.plot(X, y_SVM_rbf, color='y', lw=lw, label='SVM_RBF C=10 ')
plt.plot(X,y_SVM_lin, color='c', lw=lw, label='SVM_Linear C=10')
plt.plot(X, y_MLPR_mlp, color='r', lw=lw, label='y_MLPR_mlp lbfgs_hilayer(5,2)')
plt.xlabel('data')
plt.ylabel('target')
plt.title('Support Vector Regression')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
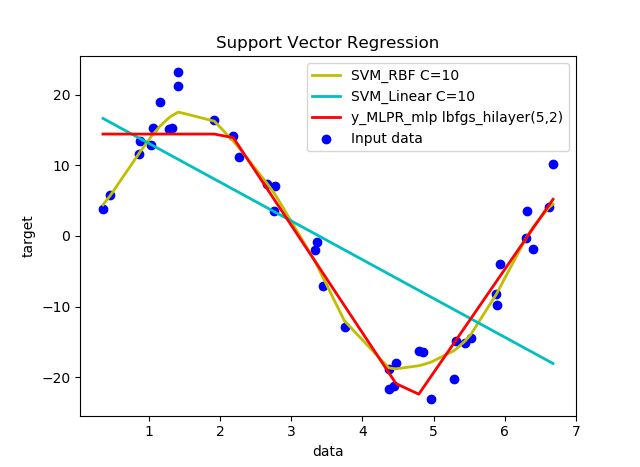
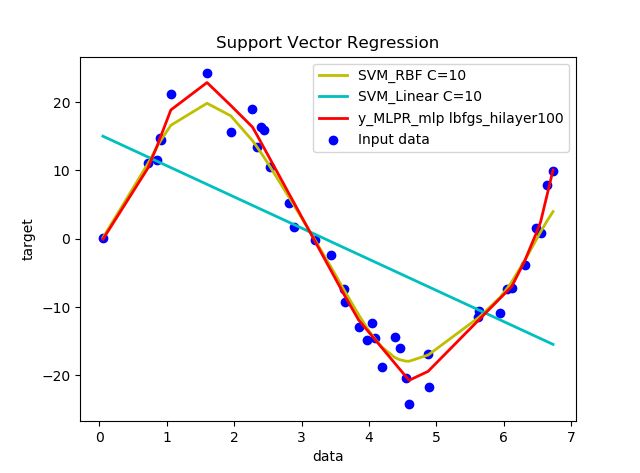
上图两层隐含层,隐层1有5个神经元,隐层2有2个神经元
上图两层隐含层,隐层1有20个神经元,隐层2有5个神经元
上图一层隐含层,隐层100个神经元
引用:
https://blog.csdn.net/suibianshen2012/article/details/51502797
https://blog.csdn.net/a819825294/article/details/51177435?locationNum=6
https://blog.csdn.net/zhongjunlang/article/details/79488955
https://blog.csdn.net/u011311291/article/details/78743393