python 战棋游戏代码实现(2):六边形地图寻路和显示
python 战棋游戏代码实现(2):六边形地图寻路和显示
- 六边形地图介绍
- 代码介绍
- 地图六边形显示
- A*算法的六边形寻路修改
- 判断某个点在哪个六边形中
- 完整代码
- 编译运行
六边形地图介绍
之前的文章 生物行走和攻击选择 实现了简单的方格地图,战棋游戏一般是使用六边形地图,六边形地图的显示和寻路会更加复杂些,所以这边自己尝试增加了六边形地图的实现。
图1 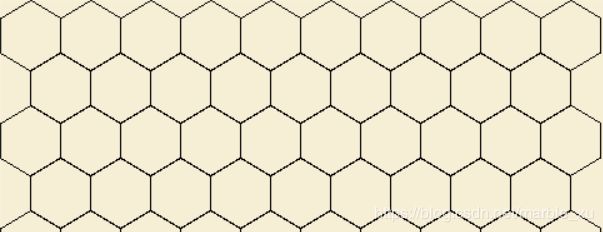
六边形地图有2种形式,这里采用上面图1的形式。
地图的坐标还是采用二维数组,如下面图2所示,六边形里面的(x, y) 表示在地图数组中的坐标。
注意一点:奇数行的六边形数会比偶数行少一,比如图2中第0行有10个六边形,第1行有9个六边形。
图2 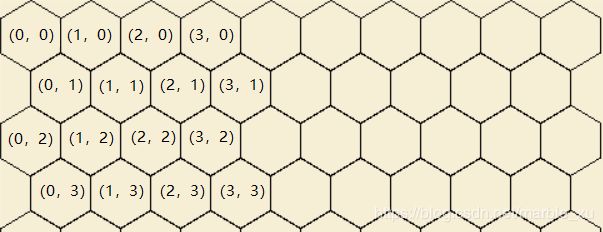
生物的行走范围如图3所示,图3 中的步兵行走范围属性值是4,表示可以走4个六边形,图中背景是深蓝色的方格就是该步兵可以走的格子,可以一步走到相邻的6个格子。
图3 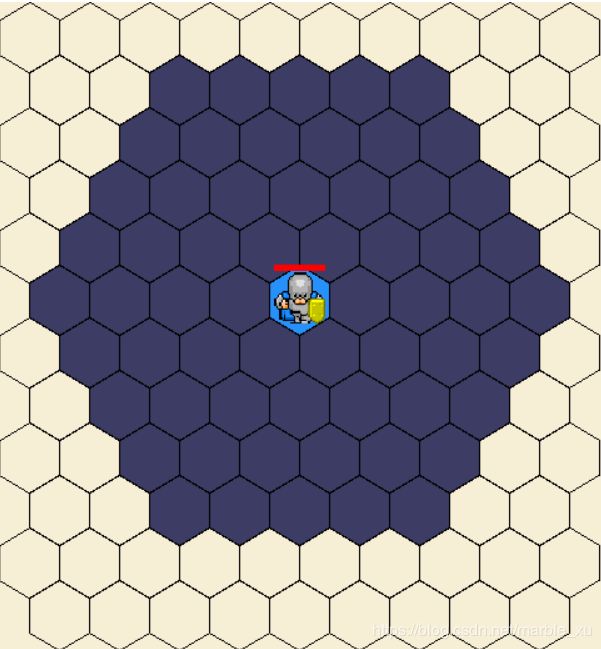
游戏截图如下:
图4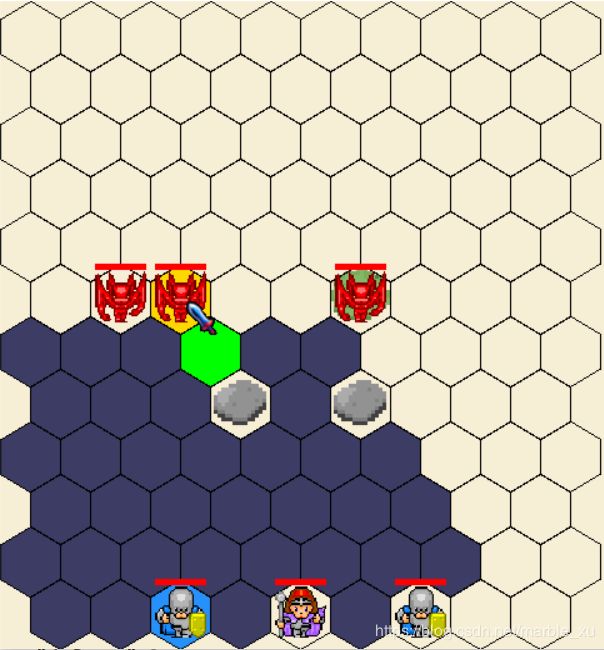
图4中,目前轮到行动的生物是我方的左下角背景为浅蓝色的步兵,可以看到背景为深蓝色的六边形为步兵可以行走的范围。背景为绿色的六边形为目前选定要行走到得方格。鼠标指向敌方生物,如果敌方生物背景六边形颜色变成黄色,表示可以攻击。图中还有石块,表示不能移动到的格子。
代码介绍
地图六边形显示
看下如何在代码中实现图1的六边形显示,这边使用的pygame的绘制多边形的函数pygame.draw.polygon() 来设置六边形的背景色,绘制连续线段的函数pygame.draw.lines() 来画六边形的黑色边。
pygame.draw.polygon()
draw a polygon
polygon(surface, color, points) -> Rect
points (tuple(coordinate) or list(coordinate)):
-- a sequence of 3 or more (x, y)
pygame.draw.lines()
draw multiple contiguous straight line segments
lines(surface, color, closed, points) -> Rect
points的使用可以看下面drawBackgroundHex函数中的例子,points 列表保存了六边形六个顶点的坐标。
图5 
如图5所示,红色长方形里面的六边形,先根据该六边形的坐标计算出左上角红点的值(base_x, base_y),HEX_X_SIZE 和 HEX_Y_SIZE 分别表示红色长方形的宽度和长度。
getHexMapPos函数计算出给定坐标的左上角红点的值,可以看到奇数行相对偶数行的x值会有X_LEN的偏移(即长方形的宽度的一半)。计算y值时也是按照奇数行或偶数行分别计算。
HEX_Y_SIZE = 56
HEX_X_SIZE = 48
def getHexMapPos(x, y):
X_LEN = c.HEX_X_SIZE // 2
Y_LEN = c.HEX_Y_SIZE // 2
if y % 2 == 0:
base_x = X_LEN * 2 * x
base_y = Y_LEN * 3 * (y//2)
else:
base_x = X_LEN * 2 * x + X_LEN
base_y = Y_LEN * 3 * (y//2) + Y_LEN//2 + Y_LEN
return (base_x, base_y)
drawBackgroundHex 函数计算出六边形所在长方形的左上角顶点值 (base_x, base_y) 后,就可以根据固定的偏移量,计算出六边形六个顶点的值, 具体的偏移量可以按照图5上的示例算出来。
def drawBackgroundHex(self, surface):
Y_LEN = c.HEX_Y_SIZE // 2
X_LEN = c.HEX_X_SIZE // 2
pg.draw.rect(surface, c.LIGHTYELLOW, pg.Rect(0, 0, c.MAP_WIDTH, c.MAP_HEIGHT))
for y in range(self.height):
for x in range(self.width):
if self.bg_map[y][x] == c.BG_EMPTY:
color = c.LIGHTYELLOW
elif self.bg_map[y][x] == c.BG_ACTIVE:
color = c.SKY_BLUE
elif self.bg_map[y][x] == c.BG_RANGE:
color = c.NAVYBLUE
elif self.bg_map[y][x] == c.BG_SELECT:
color = c.GREEN
elif self.bg_map[y][x] == c.BG_ATTACK:
color = c.GOLD
base_x, base_y = tool.getHexMapPos(x, y)
points = [(base_x, base_y + Y_LEN//2 + Y_LEN), (base_x, base_y + Y_LEN//2),
(base_x + X_LEN, base_y), (base_x + X_LEN * 2, base_y + Y_LEN//2),
(base_x + X_LEN * 2, base_y + Y_LEN//2 + Y_LEN), (base_x + X_LEN, base_y + Y_LEN*2)]
pg.draw.polygon(surface, color, points)
surface.blit(self.map_image, self.rect)
for y in range(self.height):
for x in range(self.width):
if y % 2 == 1 and x == self.width - 1:
continue
base_x, base_y = tool.getHexMapPos(x, y)
points = [(base_x, base_y + Y_LEN//2 + Y_LEN), (base_x, base_y + Y_LEN//2),
(base_x + X_LEN, base_y), (base_x + X_LEN * 2, base_y + Y_LEN//2),
(base_x + X_LEN * 2, base_y + Y_LEN//2 + Y_LEN), (base_x + X_LEN, base_y + Y_LEN*2)]
pg.draw.lines(surface, c.BLACK, True, points)
A*算法的六边形寻路修改
A* 算法的代码实现可以看我之前的一篇文章 A*算法实现
针对六边形地图的实现修改比较简单,就修改2个函数。
getMovePositions函数获取当前位置可以移动的格子,从 图2 可以看到奇数行和偶数行格子的相邻坐标是不一样的。
def getMovePositions(x, y):
if c.MAP_HEXAGON:
if y % 2 == 0:
offsets = [(-1, 0), (-1, -1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 1)]
else:
offsets = [(-1, 0), (0, -1), (1, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)]
calHeuristicDistance函数用来估计两个坐标之前的位置,注意两个坐标间X轴的距离计算:如果X轴距离小于Y轴距离的一半,就可以忽略,否则需要减去Y轴距离一半的值。
def calHeuristicDistance(self, x1, y1, x2, y2):
if c.MAP_HEXAGON:
dis_y = abs(y1 - y2)
dis_x = abs(x1 - x2)
half_y = dis_y // 2
if dis_y >= dis_x:
dis_x = 0
else:
dis_x -= half_y
return (dis_y + dis_x)
如图6所示举两个计算距离的例子,
- 从坐标A(0,0) 到坐标B(1,3) 的距离, 在图中可以看到按照红色线移动的距离是3 。两点间X轴距离是1,Y轴距离是3,X轴距离小于Y轴距离的一半,所以X轴距离可以忽略。
- 从坐标A(0,0) 到坐标C(3,3) 的距离,在图中可以看到是两条红色线条相加,距离是5。两点间X轴距离是3,Y轴距离是3,X轴距离大于Y轴距离的一半(3/2=1),所以X轴距离修正为2(3 - 1)。
图6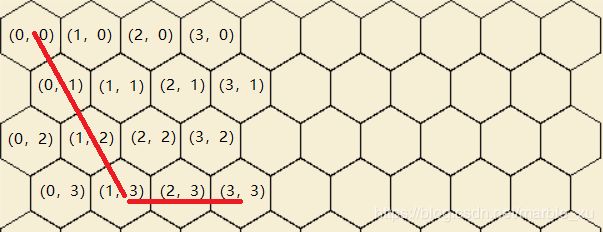
判断某个点在哪个六边形中
如何切分地图的六边形,可以有多种方式,图7中红色长方形是我采用的切分方式,长方形的宽度是六边形的宽度 (HEX_X_SIZE),长方形的长度是六边形长度的1.5倍(HEX_Y_SIZE/2 * 3)
图7 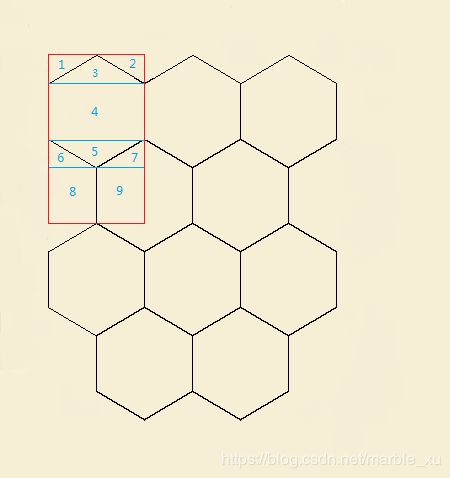
从图7出看到红色长方形里面有分成9个小的三角形或长方形区域。假设 编号3,4,5所在六边形的坐标为(map_x, map_y), 那么按照图2上的坐标可以算出:
- 编号1所在六边形的坐标为(map_x-1, map_y-1)
- 编号2所在六边形的坐标为(map_x, map_y-1)
- 编号6,8所在六边形的坐标为(map_x-1, map_y+1)
- 编号7,9所在六边形的坐标为(map_x, map_y+1)
getHexMapIndex函数就是具体的实现,根据Y轴的offset先分成三个区域(编号1,2,3, 4), (编号5,6,7)和(编号8,9)。先判断在哪个区域内,如果区域内有三角形,就调用isInTriangle函数判断是否在某个三角形中。
def getHexMapIndex(x, y):
X_LEN = c.HEX_X_SIZE // 2
Y_LEN = c.HEX_Y_SIZE // 2
tmp_x, offset_x = divmod(x, c.HEX_X_SIZE)
tmp_y, offset_y = divmod(y, Y_LEN * 3)
map_x, map_y = 0, 0
if offset_y <= (Y_LEN + Y_LEN//2):
if offset_y >= Y_LEN//2:
map_x, map_y = tmp_x, tmp_y * 2
else:
triangle_list = [(0, 0, 0, Y_LEN//2, X_LEN, 0),
(0, Y_LEN//2, X_LEN, 0, c.HEX_X_SIZE, Y_LEN//2),
(X_LEN, 0, c.HEX_X_SIZE, 0, c.HEX_X_SIZE, Y_LEN//2)]
map_list = [(tmp_x - 1, tmp_y * 2 -1), (tmp_x, tmp_y * 2), (tmp_x, tmp_y * 2 -1)]
for i, data in enumerate(triangle_list):
if isInTriangle(*data, offset_x, offset_y):
map_x, map_y = map_list[i]
break
elif offset_y >= c.HEX_Y_SIZE:
if offset_x <= X_LEN:
map_x, map_y = tmp_x - 1, tmp_y * 2 + 1
else:
map_x, map_y = tmp_x, tmp_y *2 + 1
else:
triangle_list = [(0, Y_LEN + Y_LEN//2, 0, c.HEX_Y_SIZE, X_LEN, c.HEX_Y_SIZE),
(0, Y_LEN + Y_LEN//2, X_LEN, c.HEX_Y_SIZE, c.HEX_X_SIZE, Y_LEN + Y_LEN//2),
(X_LEN, c.HEX_Y_SIZE, c.HEX_X_SIZE, Y_LEN + Y_LEN//2, c.HEX_X_SIZE, c.HEX_Y_SIZE)]
map_list = [(tmp_x - 1, tmp_y * 2 + 1), (tmp_x, tmp_y * 2), (tmp_x, tmp_y *2 + 1)]
for i, data in enumerate(triangle_list):
if isInTriangle(*data, offset_x, offset_y):
map_x, map_y = map_list[i]
break
if map_x == 0 and map_y == 0:
print('pos[%d, %d](%d, %d) base[%d, %d] off[%d, %d] ' % (map_x, map_y, x, y, tmp_x, tmp_y, offset_x, offset_y))
return (map_x, map_y)
isInTriangle函数的参数是三角形的三个顶点坐标和目标坐标,通过计算顶点和目标坐标的向量乘积来判断某个点是否在三角形中。
class Vector2d():
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def minus(self, vec):
return Vector2d(self.x - vec.x, self.y - vec.y)
def crossProduct(self, vec):
return (self.x * vec.y - self.y * vec.x)
def isInTriangle(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x, y):
A = Vector2d(x1, y1)
B = Vector2d(x2, y2)
C = Vector2d(x3, y3)
P = Vector2d(x, y)
PA = A.minus(P)
PB = B.minus(P)
PC = C.minus(P)
t1 = PA.crossProduct(PB)
t2 = PB.crossProduct(PC)
t3 = PC.crossProduct(PA)
if (t1 * t2 >= 0) and (t1 * t3 >= 0):
return True
return False
完整代码
游戏默认是使用方块地图,如果要改成六边形地图,需要修改 source\constants.py 中的参数MAP_HEXAGON 为True
MAP_HEXAGON = True
游戏实现代码的github链接 战棋游戏
这边是csdn的下载链接 六边形战棋游戏
编译运行
1.编译环境
python3.7 + pygame1.9
2.运行
直接运行根目录下的 main.py
$ python main.py