安装依赖
- cuda(安过)
- cudnn(安过)
- cuBLAS(在cuda toolkit里)
- pybind11(放到/home/user/下):git clone -b v2.2.3 https://github.com/pybind/pybind11.git
- Pillow:pip3 install Pillow
- pycuda:pip3 install ‘pycuda>=2017.1.1’
- numpy:pip3 install numpy
- argparse:pip3 install argparse
运行过程
- cd /your/TensorRT/path/samples/python/fc_plugin_caffe_mnist
- mkdir build & pushd build
- cmake ..
- make
- popd
- sudo python3 sample.py -d /home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT/data/

代码解析
# 限定使用的最小cmake版本
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.2 FATAL_ERROR)
# 项目名称:FCPlugin 编程语言:CXX和C(如果不指定LANGUAGES即为CXX和C)
project(FCPlugin LANGUAGES CXX C)
# 设置一个宏set_ifndef,当变量var没找到时,将其设定为val
macro(set_ifndef var val)
if(NOT ${var})
set(${var} ${val})
endif()
message(STATUS "Configurable variable ${var} set to ${${var}}")
endmacro()
# -------- 配置 --------
# 设置模块的名称为fcplugin,这个名称必须与pyFullyConnected.cpp中的名称一致
set_ifndef(PY_MODULE_NAME fcplugin)
# 设置C++标准为C++11
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
# pybind11默认支持C++14,我们使用C++11标准
set(PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD -std=c++11)
# $ENV{HOME}代表环境变量HOME,调用宏set_ifndef把它的下属文件夹pybind11赋值给变量PYBIND11_DIR
set_ifndef(PYBIND11_DIR $ENV{HOME}/pybind11/)
# 下面这些set_ifndef也是一些变量值的设置
set_ifndef(CUDA_VERSION 10.0)
set_ifndef(CUDA_ROOT /usr/local/cuda-${CUDA_VERSION})
set_ifndef(CUDNN_ROOT ${CUDA_ROOT})
set_ifndef(PYTHON_ROOT /usr/include)
set_ifndef(TRT_LIB_DIR /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(TRT_INC_DIR /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu)
# 输出提示信息:以下变量的值如果不显式提供,则从已得到的变量中派生得到
message("\nThe following variables are derived from the values of the previous variables unless provided explicitly:\n")
# 查找包含cuda_runtime_api.h的路径,将该路径赋值给变量_CUDA_INC_DIR
# HINTS ${CUDA_ROOT} 指定${CUDA_ROOT}为额外的搜索路径
# PATH_SUFFIXES include 指定额外要搜索的子目录include
find_path(_CUDA_INC_DIR cuda_runtime_api.h HINTS ${CUDA_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES include)
set_ifndef(CUDA_INC_DIR ${_CUDA_INC_DIR})
find_library(_CUDA_LIB cudart HINTS ${CUDA_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64)
set_ifndef(CUDA_LIB ${_CUDA_LIB})
find_library(_CUBLAS_LIB cublas HINTS ${CUDA_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64)
set_ifndef(CUBLAS_LIB ${_CUBLAS_LIB})
find_path(_CUDNN_INC_DIR cudnn.h HINTS ${CUDNN_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES include x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(CUDNN_INC_DIR ${_CUDNN_INC_DIR})
find_library(_CUDNN_LIB cudnn HINTS ${CUDNN_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64 x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(CUDNN_LIB ${_CUDNN_LIB})
find_library(_TRT_INC_DIR NvInfer.h HINTS ${TRT_INC_DIR} PATH_SUFFIXES include x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(TRT_INC_DIR ${_TRT_INC_DIR})
find_library(_NVINFER_LIB nvinfer HINTS ${TRT_LIB_DIR} PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64 x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(NVINFER_LIB ${_NVINFER_LIB})
find_library(_NVPARSERS_LIB nvparsers HINTS ${TRT_LIB_DIR} PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64 x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(NVPARSERS_LIB ${_NVPARSERS_LIB})
find_library(_NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB nvinfer_plugin HINTS ${TRT_LIB_DIR} PATH_SUFFIXES lib lib64 x86_64-linux-gnu)
set_ifndef(NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB ${_NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB})
find_path(_PYTHON2_INC_DIR Python.h HINTS ${PYTHON_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES python2.7)
set_ifndef(PYTHON2_INC_DIR ${_PYTHON2_INC_DIR})
find_path(_PYTHON3_INC_DIR Python.h HINTS ${PYTHON_ROOT} PATH_SUFFIXES python3.7 python3.6 python3.5 python3.4)
set_ifndef(PYTHON3_INC_DIR ${_PYTHON3_INC_DIR})
# -------- 构建 --------
# 添加include文件夹
include_directories(${TRT_INC_DIR} ${CUDA_INC_DIR} ${CUDNN_INC_DIR} ${PYBIND11_DIR}/include/)
# 添加子目录,使我们可以检索pybind11_add_module
add_subdirectory(${PYBIND11_DIR} ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/pybind11)
# GLOB会遍历指定目录下的文件,将符合的组成一个列表,赋值给变量
# GLOB_RECURSE会遍历${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/plugin/目录和其子目录下的所有.cpp文件,将他们组成一个列表,赋值给变量SOURCE_FILES
file(GLOB_RECURSE SOURCE_FILES ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/plugin/*.cpp)
# Bindings library. The module name MUST MATCH the module name specified in the .cpp
if(PYTHON3_INC_DIR AND NOT (${PYTHON3_INC_DIR} STREQUAL "None"))
pybind11_add_module(${PY_MODULE_NAME} SHARED THIN_LTO ${SOURCE_FILES})
target_include_directories(${PY_MODULE_NAME} BEFORE PUBLIC ${PYTHON3_INC_DIR})
target_link_libraries(${PY_MODULE_NAME} PRIVATE ${CUDNN_LIB} ${CUDA_LIB} ${CUBLAS_LIB} ${NVINFER_LIB} ${NVPARSERS_LIB} ${NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB})
endif()
if(PYTHON2_INC_DIR AND NOT (${PYTHON2_INC_DIR} STREQUAL "None"))
# Suffix the cmake target name with a 2 to differentiate from the Python 3 bindings target.
pybind11_add_module(${PY_MODULE_NAME}2 SHARED THIN_LTO ${SOURCE_FILES})
target_include_directories(${PY_MODULE_NAME}2 BEFORE PUBLIC ${PYTHON2_INC_DIR})
target_link_libraries(${PY_MODULE_NAME}2 PRIVATE ${CUDNN_LIB} ${CUDA_LIB} ${CUBLAS_LIB} ${NVINFER_LIB} ${NVPARSERS_LIB} ${NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB})
# Rename to remove the .cpython-35... extension.
set_target_properties(${PY_MODULE_NAME}2 PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME ${PY_MODULE_NAME} SUFFIX ".so")
# Python 2 requires an empty __init__ file to be able to import.
file(WRITE ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/__init__.py "")
endif()
#ifndef _FULLY_CONNECTED_H_
#define _FULLY_CONNECTED_H_
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "NvCaffeParser.h"
#define CHECK(status) { if (status != 0) throw std::runtime_error(__FILE__ + __LINE__ + std::string{"CUDA Error: "} + std::to_string(status)); }
// Helpers to move data to/from the GPU.
nvinfer1::Weights copyToDevice(const void* hostData, int count)
{
void* deviceData;
CHECK(cudaMalloc(&deviceData, count * sizeof(float)));
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(deviceData, hostData, count * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
return nvinfer1::Weights{nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, deviceData, count};
}
int copyFromDevice(char* hostBuffer, nvinfer1::Weights deviceWeights)
{
*reinterpret_cast(hostBuffer) = deviceWeights.count;
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(hostBuffer + sizeof(int), deviceWeights.values, deviceWeights.count * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
return sizeof(int) + deviceWeights.count * sizeof(float);
}
class FCPlugin: public nvinfer1::IPluginExt
{
public:
// In this simple case we're going to infer the number of output channels from the bias weights.
// The knowledge that the kernel weights are weights[0] and the bias weights are weights[1] was
// divined from the caffe innards
FCPlugin(const nvinfer1::Weights* weights, int nbWeights)
{
assert(nbWeights == 2);
mKernelWeights = copyToDevice(weights[0].values, weights[0].count);
mBiasWeights = copyToDevice(weights[1].values, weights[1].count);
}
// Create the plugin at runtime from a byte stream.
FCPlugin(const void* data, size_t length)
{
const char* d = reinterpret_cast(data);
const char* check = d;
// Deserialize kernel.
const int kernelCount = reinterpret_cast(d)[0];
mKernelWeights = copyToDevice(d + sizeof(int), kernelCount);
d += sizeof(int) + mKernelWeights.count * sizeof(float);
// Deserialize bias.
const int biasCount = reinterpret_cast(d)[0];
mBiasWeights = copyToDevice(d + sizeof(int), biasCount);
d += sizeof(int) + mBiasWeights.count * sizeof(float);
// Check that the sizes are what we expected.
assert(d == check + length);
}
virtual int getNbOutputs() const override { return 1; }
virtual nvinfer1::Dims getOutputDimensions(int index, const nvinfer1::Dims* inputs, int nbInputDims) override
{
assert(index == 0 && nbInputDims == 1 && inputs[0].nbDims == 3);
return nvinfer1::DimsCHW{static_cast(mBiasWeights.count), 1, 1};
}
virtual int initialize() override
{
CHECK(cudnnCreate(&mCudnn));
CHECK(cublasCreate(&mCublas));
// Create cudnn tensor descriptors for bias addition.
CHECK(cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&mSrcDescriptor));
CHECK(cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&mDstDescriptor));
return 0;
}
virtual void terminate() override
{
CHECK(cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(mSrcDescriptor));
CHECK(cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(mDstDescriptor));
CHECK(cublasDestroy(mCublas));
CHECK(cudnnDestroy(mCudnn));
}
// This plugin requires no workspace memory during build time.
virtual size_t getWorkspaceSize(int maxBatchSize) const override { return 0; }
virtual int enqueue(int batchSize, const void* const* inputs, void** outputs, void* workspace, cudaStream_t stream) override
{
int nbOutputChannels = mBiasWeights.count;
int nbInputChannels = mKernelWeights.count / nbOutputChannels;
constexpr float kONE = 1.0f, kZERO = 0.0f;
// Do matrix multiplication.
cublasSetStream(mCublas, stream);
cudnnSetStream(mCudnn, stream);
CHECK(cublasSgemm(mCublas, CUBLAS_OP_T, CUBLAS_OP_N, nbOutputChannels, batchSize, nbInputChannels, &kONE,
reinterpret_cast(mKernelWeights.values), nbInputChannels,
reinterpret_cast(inputs[0]), nbInputChannels, &kZERO,
reinterpret_cast(outputs[0]), nbOutputChannels));
// Add bias.
CHECK(cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(mSrcDescriptor, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, 1, nbOutputChannels, 1, 1));
CHECK(cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(mDstDescriptor, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, batchSize, nbOutputChannels, 1, 1));
CHECK(cudnnAddTensor(mCudnn, &kONE, mSrcDescriptor, mBiasWeights.values, &kONE, mDstDescriptor, outputs[0]));
return 0;
}
// For this sample, we'll only support float32 with NCHW.
virtual bool supportsFormat(nvinfer1::DataType type, nvinfer1::PluginFormat format) const override
{
return (type == nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT && format == nvinfer1::PluginFormat::kNCHW);
}
void configureWithFormat(const nvinfer1::Dims* inputDims, int nbInputs, const nvinfer1::Dims* outputDims, int nbOutputs, nvinfer1::DataType type, nvinfer1::PluginFormat format, int maxBatchSize)
{
assert(nbInputs == 1 && inputDims[0].d[1] == 1 && inputDims[0].d[2] == 1);
assert(nbOutputs == 1 && outputDims[0].d[1] == 1 && outputDims[0].d[2] == 1);
assert(mKernelWeights.count == inputDims[0].d[0] * inputDims[0].d[1] * inputDims[0].d[2] * mBiasWeights.count);
}
virtual size_t getSerializationSize() override
{
return sizeof(int) * 2 + mKernelWeights.count * sizeof(float) + mBiasWeights.count * sizeof(float);
}
virtual void serialize(void* buffer) override
{
char* d = reinterpret_cast(buffer);
const char* check = d;
d += copyFromDevice(d, mKernelWeights);
d += copyFromDevice(d, mBiasWeights);
assert(d == check + getSerializationSize());
}
// Free buffers.
virtual ~FCPlugin()
{
cudaFree(const_cast(mKernelWeights.values));
mKernelWeights.values = nullptr;
cudaFree(const_cast(mBiasWeights.values));
mBiasWeights.values = nullptr;
}
private:
cudnnHandle_t mCudnn;
cublasHandle_t mCublas;
nvinfer1::Weights mKernelWeights{nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr}, mBiasWeights{nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr};
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t mSrcDescriptor, mDstDescriptor;
};
class FCPluginFactory : public nvcaffeparser1::IPluginFactoryExt, public nvinfer1::IPluginFactory
{
public:
bool isPlugin(const char* name) override { return isPluginExt(name); }
bool isPluginExt(const char* name) override { return !strcmp(name, "ip2"); }
// Create a plugin using provided weights.
virtual nvinfer1::IPlugin* createPlugin(const char* layerName, const nvinfer1::Weights* weights, int nbWeights) override
{
assert(isPluginExt(layerName) && nbWeights == 2);
assert(mPlugin == nullptr);
// This plugin will need to be manually destroyed after parsing the network, by calling destroyPlugin.
mPlugin = new FCPlugin{weights, nbWeights};
return mPlugin;
}
// Create a plugin from serialized data.
virtual nvinfer1::IPlugin* createPlugin(const char* layerName, const void* serialData, size_t serialLength) override
{
assert(isPlugin(layerName));
// This will be automatically destroyed when the engine is destroyed.
return new FCPlugin{serialData, serialLength};
}
// User application destroys plugin when it is safe to do so.
// Should be done after consumers of plugin (like ICudaEngine) are destroyed.
void destroyPlugin() { delete mPlugin; }
FCPlugin* mPlugin{ nullptr };
};
#endif //_FULLY_CONNECTED_H
#include "FullyConnected.h"
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "NvCaffeParser.h"
#include
PYBIND11_MODULE(fcplugin, m)
{
namespace py = pybind11;
// This allows us to use the bindings exposed by the tensorrt module.
py::module::import("tensorrt");
// Note that we only need to bind the constructors manually. Since all other methods override IPlugin functionality, they will be automatically available in the python bindings.
// The `std::unique_ptr` specifies that Python is not responsible for destroying the object. This is required because the destructor is private.
py::class_>(m, "FCPlugin")
// Bind the normal constructor as well as the one which deserializes the plugin
.def(py::init())
.def(py::init())
;
// Our custom plugin factory derives from both nvcaffeparser1::IPluginFactoryExt and nvinfer1::IPluginFactory
py::class_(m, "FCPluginFactory")
// Bind the default constructor.
.def(py::init<>())
// The destroy_plugin function does not override either of the base classes, so we must bind it explicitly.
.def("destroy_plugin", &FCPluginFactory::destroyPlugin)
;
}
# This sample uses a Caffe model along with a custom plugin to create a TensorRT engine.
from random import randint
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import tempfile
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
import tensorrt as trt
try:
from build import fcplugin
except ImportError as err:
raise ImportError("""ERROR: Failed to import module ({})
Please build the FullyConnected sample plugin.
For more information, see the included README.md
Note that Python 2 requires the presence of `__init__.py` in the build folder""".format(err))
# Allows us to import from common.
import sys, os
sys.path.insert(1, os.path.join(sys.path[0], ".."))
import common
# You can set the logger severity higher to suppress messages (or lower to display more messages).
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
# Define some global constants about the model.
class ModelData(object):
INPUT_NAME = "input"
INPUT_SHAPE = (1, 28, 28)
OUTPUT_NAME = "prob"
OUTPUT_SHAPE = (10, )
DTYPE = trt.float32
# Uses a parser to retrieve mean data from a binary_proto.
def retrieve_mean(mean_proto):
with trt.CaffeParser() as parser:
return parser.parse_binary_proto(mean_proto)
# Create the parser's plugin factory. The factory is global because it has
# to be destroyed after the engine is destroyed.
fc_factory = fcplugin.FCPluginFactory()
# For more information on TRT basics, refer to the introductory parser samples.
def build_engine(deploy_file, model_file):
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, builder.create_network() as network, trt.CaffeParser() as parser:
builder.max_workspace_size = common.GiB(1)
# Set the parser's plugin factory. Note that we bind the factory to a reference so
# that we can destroy it later. (parser.plugin_factory_ext is a write-only attribute)
parser.plugin_factory_ext = fc_factory
# Parse the model and build the engine.
model_tensors = parser.parse(deploy=deploy_file, model=model_file, network=network, dtype=ModelData.DTYPE)
network.mark_output(model_tensors.find(ModelData.OUTPUT_NAME))
return builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
# Tries to load an engine from the provided engine_path, or builds and saves an engine to the engine_path.
def get_engine(deploy_file, model_file, engine_path):
try:
with open(engine_path, "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) as runtime:
# Note that we have to provide the plugin factory when deserializing an engine built with an IPlugin or IPluginExt.
return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read(), fc_factory)
except:
# Fallback to building an engine if the engine cannot be loaded for any reason.
engine = build_engine(deploy_file, model_file)
with open(engine_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())
return engine
# Loads a test case into the provided pagelocked_buffer.
def load_normalized_test_case(data_path, mean):
case_num = randint(0, 9)
test_case_path = os.path.join(data_path, str(case_num) + ".pgm")
# Flatten the image into a 1D array, and normalize.
img = np.array(Image.open(test_case_path)).ravel() - mean
return img, case_num
def main():
# Get data files for the model.
data_path, [deploy_file, model_file, mean_proto] = common.find_sample_data(description="Runs an MNIST network using a Caffe model file", subfolder="mnist", find_files=["mnist.prototxt", "mnist.caffemodel", "mnist_mean.binaryproto"])
# Cache the engine in a temporary directory.
engine_path = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), "mnist.engine")
with get_engine(deploy_file, model_file, engine_path) as engine, engine.create_execution_context() as context:
# Build an engine, allocate buffers and create a stream.
# For more information on buffer allocation, refer to the introductory samples.
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = common.allocate_buffers(engine)
mean = retrieve_mean(mean_proto)
# For more information on performing inference, refer to the introductory samples.
inputs[0].host, case_num = load_normalized_test_case(data_path, mean)
# The common.do_inference function will return a list of outputs - we only have one in this case.
[output] = common.do_inference(context, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)
pred = np.argmax(output)
print("Test Case: " + str(case_num))
print("Prediction: " + str(pred))
# After the engine is destroyed, we destroy the plugin. This function is exposed through the binding code in plugin/pyFullyConnected.cpp.
fc_factory.destroy_plugin()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
遇到的问题
- 在cmake时出现variables NOTFOUND,如下图所示:
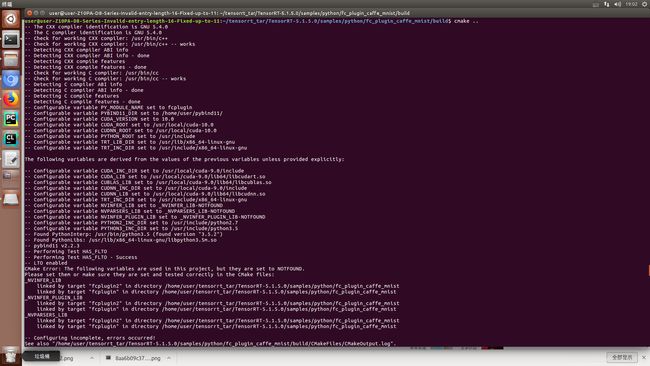 解决办法:在cmake时对他们的目录进行指定
解决办法:在cmake时对他们的目录进行指定
指令:cmake .. -DNVINFER_LIB=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/lib/libnvinfer.so
-D_NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/lib/
-D_NVPARSERS_LIB=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/lib/
- 在make的时候出现fatal error: NvInfer.h: No such file or directory,如下图所示:
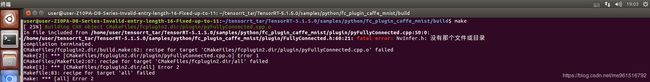 解决办法:在cmake时指定TRT_INC_DIR的目录
解决办法:在cmake时指定TRT_INC_DIR的目录
指令:cmake .. -DNVINFER_LIB=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/lib/libnvinfer.so
-D_NVINFER_PLUGIN_LIB=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/lib/
-D_NVPARSERS_LIB=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/lib/
-DTRT_INC_DIR=/home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/include/
- 在python sample.py时出现/usr/src/tensorrt/data/mnist does not exist,如下图:
 解决办法:指定data目录
解决办法:指定data目录
指令:sudo python3 sample.py -d /home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/data/
- 在python sample.py时出现段错误
解决方法:重启电脑
- ImportError: libnvonnxparser.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
解决办法:将这个文件从TensorRT的lib目录中拷贝至/usr/lib
指令:sudo cp /home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/targets/x86_64-linux-gnu/lib/libnvonnxparser.so.0 /usr/lib/
- ImportError: libnvonnxparser_runtime.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
解决方法:同上
指令:sudo cp /home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/targets/x86_64-linux-gnu/lib/libnvonnxparser_runtime.so.0 /usr/lib/
- ImportError: libnvinfer_plugin.so.5: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
解决方法:同上
指令:sudo cp /home/user/tensorrt_tar/TensorRT-5.1.5.0/targets/x86_64-linux-gnu/lib/libnvinfer_plugin.so.5 /usr/lib/

 解决办法:在cmake时对他们的目录进行指定
解决办法:在cmake时对他们的目录进行指定 解决办法:在cmake时指定TRT_INC_DIR的目录
解决办法:在cmake时指定TRT_INC_DIR的目录 解决办法:指定data目录
解决办法:指定data目录