python 微服务方案
介绍
使用python做web开发面临的一个最大的问题就是性能,在解决C10K问题上显的有点吃力。有些异步框架Tornado、Twisted、Gevent 等就是为了解决性能问题。这些框架在性能上有些提升,但是也出现了各种古怪的问题难以解决。
在python3.6中,官方的异步协程库asyncio正式成为标准。在保留便捷性的同时对性能有了很大的提升,已经出现许多的异步框架使用asyncio。
使用较早的异步框架是aiohttp,它提供了server端和client端,对asyncio做了很好的封装。但是开发方式和最流行的微框架flask不同,flask开发简单,轻量,高效。正是结合这些优点, 以Sanic为基础,集成多个流行的库来搭建微服务。 Sanic框架是和Flask相似的异步协程框架,简单轻量,并且性能很高。本项目就是以Sanic为基础搭建的python微服务框架。(思想适用于其他语言)
微服务设计原则个人总结:
X 轴 :指的是水平复制,很好理解,就是讲单体系统多运行几个实例,做个集群加负载均衡的模式。
Z 轴 :是基于类似的数据分区,比如一个互联网打车应用突然或了,用户量激增,集群模式撑不住了,那就按照用户请求的地区进行数据分区,北京、上海、四川等多建几个集群。简单理解数据库拆分,比如分库分表
Y 轴 :就是我们所说的微服务的拆分模式,就是基于不同的业务拆分。
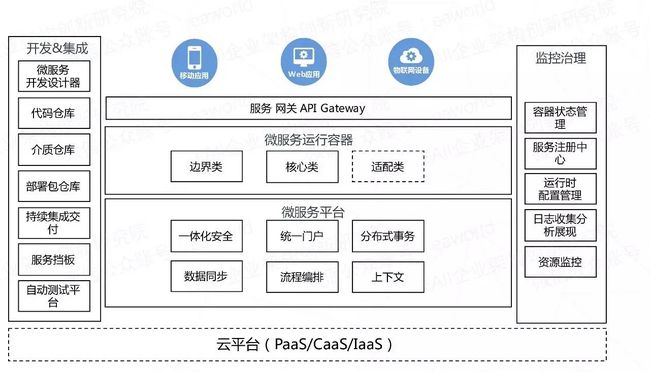
特点
- 使用sanic异步框架,简单,轻量,高效。
- 使用uvloop为核心引擎,使sanic在很多情况下单机并发甚至不亚于Golang。
- 使用asyncpg为数据库驱动,进行数据库连接,执行sql语句执行。
- 使用aiohttp为Client,对其他微服务进行访问。
- 使用peewee为ORM,但是只是用来做模型设计和migration。
- 使用opentracing为分布式追踪系统。
- 使用unittest做单元测试,并且使用mock来避免访问其他微服务。
- 使用swagger做API标准,能自动生成API文档。
服务端
使用sanic异步框架,有较高的性能,但是使用不当会造成blocking, 对于有IO请求的都要选用异步库。 添加库要慎重。
sanic使用uvloop异步驱动,uvloop基于libuv使用Cython编写,性能比nodejs还要高。
功能说明:
启动前
@app.listener('before_server_start')
async def before_srver_start(app, loop):
queue = asyncio.Queue()
app.queue = queue
loop.create_task(consume(queue, app.config.ZIPKIN_SERVER))
reporter = AioReporter(queue=queue)
tracer = BasicTracer(recorder=reporter)
tracer.register_required_propagators()
opentracing.tracer = tracer
app.db = await ConnectionPool(loop=loop).init(DB_CONFIG)- 创建DB连接池
- 创建Client连接
- 创建queue, 消耗span,用于日志追踪
- 创建opentracing.tracer进行日志追踪
中间件
@app.middleware('request')
async def cros(request):
if request.method == 'POST' or request.method == 'PUT':
request['data'] = request.json
span = before_request(request)
request['span'] = span
@app.middleware('response')
async def cors_res(request, response):
span = request['span'] if 'span' in request else None
if response is None:
return response
result = {'code': 0}
if not isinstance(response, HTTPResponse):
if isinstance(response, tuple) and len(response) == 2:
result.update({
'data': response[0],
'pagination': response[1]
})
else:
result.update({'data': response})
response = json(result)
if span:
span.set_tag('http.status_code', "200")
if span:
span.set_tag('component', request.app.name)
span.finish()
return response- 创建span, 用于日志追踪
- 对response进行封装,统一格式
异常处理
对抛出的异常进行处理,返回统一格式
任务
创建task消费queue中对span,用于日志追踪
异步处理
由于使用的是异步框架,可以将一些IO请求并行处理
Example:
async def async_request(datas):
# async handler request
results = await asyncio.gather(*[data[2] for data in datas])
for index, obj in enumerate(results):
data = datas[index]
data[0][data[1]] = results[index]
@user_bp.get('/')
@doc.summary("get user info")
@doc.description("get user info by id")
@doc.produces(Users)
async def get_users_list(request, id):
async with request.app.db.acquire(request) as cur:
record = await cur.fetch(
""" SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = $1 """, id)
datas = [
[record, 'city_id', get_city_by_id(request, record['city_id'])]
[record, 'role_id', get_role_by_id(request, record['role_id'])]
]
await async_request(datas)
return recordget_city_by_id, get_role_by_id是并行处理。
相关连接
sanic
模型设计 & ORM
Peewee is a simple and small ORM. It has few (but expressive) concepts, making it easy to learn and intuitive to use。ORM使用peewee, 只是用来做模型设计和migration, 数据库操作使用asyncpg。
Example:
# models.py
class Users(Model):
id = PrimaryKeyField()
create_time = DateTimeField(verbose_name='create time',
default=datetime.datetime.utcnow)
name = CharField(max_length=128, verbose_name="user's name")
age = IntegerField(null=False, verbose_name="user's age")
sex = CharField(max_length=32, verbose_name="user's sex")
city_id = IntegerField(verbose_name='city for user', help_text=CityApi)
role_id = IntegerField(verbose_name='role for user', help_text=RoleApi)
class Meta:
db_table = 'users'
# migrations.py
from sanic_ms.migrations import MigrationModel, info, db
class UserMigration(MigrationModel):
_model = Users
# @info(version="v1")
# def migrate_v1(self):
# migrate(self.add_column('sex'))
def migrations():
try:
um = UserMigration()
with db.transaction():
um.auto_migrate()
print("Success Migration")
except Exception as e:
raise e
if __name__ == '__main__':
migrations()- 运行命令 python migrations.py
- migrate_v1函数添加字段sex, 在BaseModel中要先添加name字段
- info装饰器会创建表migrate_record来记录migrate,version每个model中必须唯一,使用version来记录是否执行过,还可以记录author,datetime
- migrate函数必须以migrate_开头
相关连接
peewee
数据库操作
asyncpg is the fastest driver among common Python, NodeJS and Go implementations使用asyncpg为数据库驱动, 对数据库连接进行封装, 执行数据库操作。
不使用ORM做数据库操作,一个原因是性能,ORM会有性能的损耗,并且无法使用asyncpg高性能库。另一个是单个微服务是很简单的,表结构不会很复杂,简单的SQL语句就可以处理来,没必要引入ORM。使用peewee只是做模型设计
Example:
sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE name=$1"
name = "test"
async with request.app.db.acquire(request) as cur:
data = await cur.fetchrow(sql, name)
async with request.app.db.transaction(request) as cur:
data = await cur.fetchrow(sql, name)- acquire() 函数为非事务, 对于只涉及到查询的使用非事务,可以提高查询效率
- tansaction() 函数为事务操作,对于增删改必须使用事务操作
- 传入request参数是为了获取到span,用于日志追踪
- TODO 数据库读写分离
相关连接
asyncpg
benchmarks
客户端
使用aiohttp中的client,对客户端进行了简单的封装,用于微服务之间访问。Don’t create a session per request. Most likely you need a session per application which performs all requests altogether.
A session contains a connection pool inside, connection reusage and keep-alives (both are on by default) may speed up total performance.
Example:
@app.listener('before_server_start')
async def before_srver_start(app, loop):
app.client = Client(loop, url='http://host:port')
async def get_role_by_id(request, id):
cli = request.app.client.cli(request)
async with cli.get('/cities/{}'.format(id)) as res:
return await res.json()
@app.listener('before_server_stop')
async def before_server_stop(app, loop):
app.client.close()
对于访问不同的微服务可以创建多个不同的client,这样每个client都会keep-alives
日志 & 分布式追踪系统
装饰器logger
@logger(type='method', category='test', detail='detail', description="des", tracing=True, level=logging.INFO)
async def get_city_by_id(request, id):
cli = request.app.client.cli(request)- type: 日志类型,如 method, route
- category: 日志类别,默认为app的name
- detail: 日志详细信息
- description: 日志描述,默认为函数的注释
- tracing: 日志追踪,默认为True
- level: 日志级别,默认为INFO
分布式追踪系统
- OpenTracing是以Dapper,Zipkin等分布式追踪系统为依据, 建立了统一的标准。
- Opentracing跟踪每一个请求,记录请求所经过的每一个微服务,以链条的方式串联起来,对分析微服务的性能瓶颈至关重要。
- 使用opentracing框架,但是在输出时转换成zipkin格式。 因为大多数分布式追踪系统考虑到性能问题,都是使用的thrift进行通信的,本着简单,Restful风格的精神,没有使用RPC通信。以日志的方式输出, 可以使用fluentd, logstash等日志收集再输入到Zipkin。Zipkin是支持HTTP输入的。
- 生成的span先无阻塞的放入queue中,在task中消费队列的span。后期可以添加上采样频率。
- 对于DB,Client都加上了tracing
相关连接
opentracing
zipkin
jaeger
API接口
api文档使用swagger标准。
Example:
from sanic_ms import doc
@user_bp.post('/')
@doc.summary('create user')
@doc.description('create user info')
@doc.consumes(Users)
@doc.produces({'id': int})
async def create_user(request):
data = request['data']
async with request.app.db.transaction(request) as cur:
record = await cur.fetchrow(
""" INSERT INTO users(name, age, city_id, role_id)
VALUES($1, $2, $3, $4, $5)
RETURNING id
""", data['name'], data['age'], data['city_id'], data['role_id']
)
return {'id': record['id']}- summary: api概要
- description: 详细描述
- consumes: request的body数据
- produces: response的返回数据
- tag: API标签
- 在consumes和produces中传入的参数可以是peewee的model,会解析model生成API数据, 在field字段的help_text参数来表示引用对象
- http://host:ip/openapi/spec.json 获取生成的json数据
相关连接
swagger
Response 数据
在返回时,不要返回sanic的response,直接返回原始数据,会在Middleware中对返回的数据进行处理,返回统一的格式,具体的格式可以[查看]
单元测试
单元测试使用unittest。 mock是自己创建了MockClient,因为unittest还没有asyncio的mock,并且sanic的测试接口也是发送request请求,所以比较麻烦. 后期可以使用pytest。
Example:
from sanic_ms.tests import APITestCase
from server import app
class TestCase(APITestCase):
_app = app
_blueprint = 'visit'
def setUp(self):
super(TestCase, self).setUp()
self._mock.get('/cities/1',
payload={'id': 1, 'name': 'shanghai'})
self._mock.get('/roles/1',
payload={'id': 1, 'name': 'shanghai'})
def test_create_user(self):
data = {
'name': 'test',
'age': 2,
'city_id': 1,
'role_id': 1,
}
res = self.client.create_user(data=data)
body = ujson.loads(res.text)
self.assertEqual(res.status, 200)- 其中_blueprint为blueprint名称
- 在setUp函数中,使用_mock来注册mock信息, 这样就不会访问真实的服务器, payload为返回的body信息
- 使用client变量调用各个函数, data为body信息,params为路径的参数信息,其他参数是route的参数
代码覆盖
coverage erase
coverage run --source . -m sanic_ms tests
coverage xml -o reports/coverage.xml
coverage2clover -i reports/coverage.xml -o reports/clover.xml
coverage html -d reports- coverage2colver 是将coverage.xml 转换成 clover.xml,bamboo需要的格式是clover的。
相关连接
unittest
coverage
异常处理
使用 app.error_handler = CustomHander() 对抛出的异常进行处理
Example:
from sanic_ms.exception import ServerError
@visit_bp.delete('/users/')
async def del_user(request, id):
raise ServerError(error='内部错误',code=10500, message="msg")- code: 错误码,无异常时为0,其余值都为异常
- message: 状态码信息
- error: 自定义错误信息
- status_code: http状态码,使用标准的http状态码
