facenet:triplet-loss理解与train_tripletloss.py代码理解
对于Facenet进行人脸特征提取,算法内容较为核心和比较难以理解的地方在于三元损失函数Triplet-loss。
 神经网络所要学习的目标是:使得Anchor到Positive的距离要比Anchor到Negative的距离要短(Anchor为一个样本,Positive为与Anchor同类的样本,Negative为与Anchor不同类的样本)。通过学习使得类别内部的样本距离大于不同类别样本的距离即可。
神经网络所要学习的目标是:使得Anchor到Positive的距离要比Anchor到Negative的距离要短(Anchor为一个样本,Positive为与Anchor同类的样本,Negative为与Anchor不同类的样本)。通过学习使得类别内部的样本距离大于不同类别样本的距离即可。
通过数学表达式如下所示,alpha为一个常数:
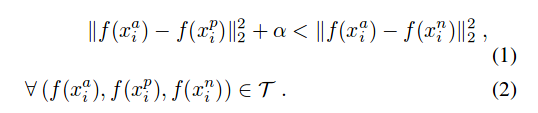
损失函数的定义如下所示:
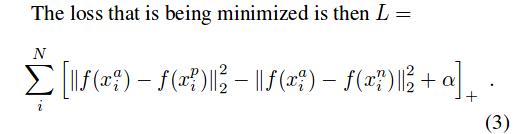
利用随机梯度下降法不断让loss变小,第一个范式为(a,p)距离,第二个范式为(a,n)距离,alpha为常数,因此可以理解为网络学习的过程就是使得类内距离变小,类见距离变大。
损失函数确定好之后如何在训练时寻找anchor对应的negative样本和positive样本成为一个要着重考虑的问题。理论上讲,我们应当选择hard positive与hard negative,如下论文所示。

但是这种做法是不可行的,而且这种训练方式可能无法达到优的效果。(个人理解:这种方法最麻烦的是需要在整个训练集上找到anchor对应的negative,相当耗时)
因此作者的办法是在训练时,在一个batch上寻找negative,选择的标准是满足如下表达式:

这里找到的negative样本叫做semi-hard,意思是在batch的范围内,只要(a,n)的距离大于(a,p)的距离即可。
以上便是对triplet-loss的理解。
对于如何训练该模型,可以参考github上 https://github.com/davidsandberg/facenet 的实现(tf版本),以下我做了一些关于train_tripletloss.py的注释,注释为个人理解,有不对的地方请大家指正,其中有些部分参考(http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-2096766.html ).
另外说明一点,程序实现找到negative:
在满足(a,n)距离-(a,p)"""Training a face recognizer with TensorFlow based on the FaceNet paper
FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering: http://arxiv.org/abs/1503.03832
"""
# MIT License
#
# Copyright (c) 2016 David Sandberg
#
# Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
# of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
# in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
# to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
# copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
# furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
#
# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
# copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#
# THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
# IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
# AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
# LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
# OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
# SOFTWARE.
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from datetime import datetime
import os.path
import time
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import importlib
import itertools
import argparse
import facenet
import lfw
from tensorflow.python.ops import data_flow_ops
from six.moves import xrange # @UnresolvedImport
def main(args):
network = importlib.import_module(args.model_def)
subdir = datetime.strftime(datetime.now(), '%Y%m%d-%H%M%S')
log_dir = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser(args.logs_base_dir), subdir)
if not os.path.isdir(log_dir): # Create the log directory if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs(log_dir)
model_dir = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser(args.models_base_dir), subdir)
if not os.path.isdir(model_dir): # Create the model directory if it doesn't exist
os.makedirs(model_dir)
# Write arguments to a text file
facenet.write_arguments_to_file(args, os.path.join(log_dir, 'arguments.txt'))
# Store some git revision info in a text file in the log directory
src_path,_ = os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))
facenet.store_revision_info(src_path, log_dir, ' '.join(sys.argv))
np.random.seed(seed=args.seed)
train_set = facenet.get_dataset(args.data_dir)
print('Model directory: %s' % model_dir)
print('Log directory: %s' % log_dir)
if args.pretrained_model:
print('Pre-trained model: %s' % os.path.expanduser(args.pretrained_model))
if args.lfw_dir:
print('LFW directory: %s' % args.lfw_dir)
# Read the file containing the pairs used for testing
pairs = lfw.read_pairs(os.path.expanduser(args.lfw_pairs))
# Get the paths for the corresponding images
lfw_paths, actual_issame = lfw.get_paths(os.path.expanduser(args.lfw_dir), pairs)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
tf.set_random_seed(args.seed)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
# Placeholder for the learning rate
learning_rate_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='learning_rate')
batch_size_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, name='batch_size')
phase_train_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, name='phase_train')
image_paths_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.string, shape=(None,3), name='image_paths')
labels_placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None,3), name='labels')
input_queue = data_flow_ops.FIFOQueue(capacity=100000,
dtypes=[tf.string, tf.int64],
shapes=[(3,), (3,)],
shared_name=None, name=None)
enqueue_op = input_queue.enqueue_many([image_paths_placeholder, labels_placeholder])
nrof_preprocess_threads = 4
images_and_labels = []
for _ in range(nrof_preprocess_threads):
filenames, label = input_queue.dequeue()
images = []
for filename in tf.unstack(filenames):
file_contents = tf.read_file(filename)
image = tf.image.decode_image(file_contents, channels=3)
if args.random_crop:
image = tf.random_crop(image, [args.image_size, args.image_size, 3])
else:
image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image, args.image_size, args.image_size)
if args.random_flip:
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
#pylint: disable=no-member
image.set_shape((args.image_size, args.image_size, 3))
images.append(tf.image.per_image_standardization(image))
images_and_labels.append([images, label])
image_batch, labels_batch = tf.train.batch_join(
images_and_labels, batch_size=batch_size_placeholder,
shapes=[(args.image_size, args.image_size, 3), ()], enqueue_many=True,
capacity=4 * nrof_preprocess_threads * args.batch_size,
allow_smaller_final_batch=True)
image_batch = tf.identity(image_batch, 'image_batch')
image_batch = tf.identity(image_batch, 'input')
labels_batch = tf.identity(labels_batch, 'label_batch')
# Build the inference graph
prelogits, _ = network.inference(image_batch, args.keep_probability,
phase_train=phase_train_placeholder, bottleneck_layer_size=args.embedding_size,
weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
embeddings = tf.nn.l2_normalize(prelogits, 1, 1e-10, name='embeddings')
# Split embeddings into anchor, positive and negative and calculate triplet loss
anchor, positive, negative = tf.unstack(tf.reshape(embeddings, [-1,3,args.embedding_size]), 3, 1)
triplet_loss = facenet.triplet_loss(anchor, positive, negative, args.alpha)
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate_placeholder, global_step,
args.learning_rate_decay_epochs*args.epoch_size, args.learning_rate_decay_factor, staircase=True)
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', learning_rate)
# Calculate the total losses
regularization_losses = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES)
total_loss = tf.add_n([triplet_loss] + regularization_losses, name='total_loss')
# Build a Graph that trains the model with one batch of examples and updates the model parameters
train_op = facenet.train(total_loss, global_step, args.optimizer,
learning_rate, args.moving_average_decay, tf.global_variables())
# Create a saver
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.trainable_variables(), max_to_keep=3)
# Build the summary operation based on the TF collection of Summaries.
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
# Start running operations on the Graph.
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=args.gpu_memory_fraction)
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
# Initialize variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer(), feed_dict={phase_train_placeholder:True})
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer(), feed_dict={phase_train_placeholder:True})
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(log_dir, sess.graph)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord, sess=sess)
with sess.as_default():
if args.pretrained_model:
print('Restoring pretrained model: %s' % args.pretrained_model)
saver.restore(sess, os.path.expanduser(args.pretrained_model))
# Training and validation loop
epoch = 0
while epoch < args.max_nrof_epochs:
step = sess.run(global_step, feed_dict=None)
epoch = step // args.epoch_size
# Train for one epoch
train(args, sess, train_set, epoch, image_paths_placeholder, labels_placeholder, labels_batch,
batch_size_placeholder, learning_rate_placeholder, phase_train_placeholder, enqueue_op, input_queue, global_step,
embeddings, total_loss, train_op, summary_op, summary_writer, args.learning_rate_schedule_file,
args.embedding_size, anchor, positive, negative, triplet_loss)
# Save variables and the metagraph if it doesn't exist already
save_variables_and_metagraph(sess, saver, summary_writer, model_dir, subdir, step)
# Evaluate on LFW
if args.lfw_dir:
evaluate(sess, lfw_paths, embeddings, labels_batch, image_paths_placeholder, labels_placeholder,
batch_size_placeholder, learning_rate_placeholder, phase_train_placeholder, enqueue_op, actual_issame, args.batch_size,
args.lfw_nrof_folds, log_dir, step, summary_writer, args.embedding_size)
return model_dir
def train(args, sess, dataset, epoch, image_paths_placeholder, labels_placeholder, labels_batch,
batch_size_placeholder, learning_rate_placeholder, phase_train_placeholder, enqueue_op, input_queue, global_step,
embeddings, loss, train_op, summary_op, summary_writer, learning_rate_schedule_file,
embedding_size, anchor, positive, negative, triplet_loss):
batch_number = 0
if args.learning_rate>0.0:
lr = args.learning_rate
else:
lr = facenet.get_learning_rate_from_file(learning_rate_schedule_file, epoch)
while batch_number < args.epoch_size:
# Sample people randomly from the dataset
#从dataset中随机抽取样本数据
image_paths, num_per_class = sample_people(dataset, args.people_per_batch, args.images_per_person)
print('Running forward pass on sampled images: ', end='')
start_time = time.time()
#样本个数nrof_examples=batch中的人数people_per_batch×每个人对应的照片数量images_per_person
nrof_examples = args.people_per_batch * args.images_per_person
labels_array = np.reshape(np.arange(nrof_examples),(-1,3))
image_paths_array = np.reshape(np.expand_dims(np.array(image_paths),1), (-1,3))
sess.run(enqueue_op, {image_paths_placeholder: image_paths_array, labels_placeholder: labels_array})
#emb_array为所有样本对应的embedding特征信息
emb_array = np.zeros((nrof_examples, embedding_size))
#需要运行的batch数量nrof_batches为总样本数除以batch_size
nrof_batches = int(np.ceil(nrof_examples / args.batch_size))
for i in range(nrof_batches):
batch_size = min(nrof_examples-i*args.batch_size, args.batch_size)
#喂数据,得到一个batch的emb和lab信息
emb, lab = sess.run([embeddings, labels_batch], feed_dict={batch_size_placeholder: batch_size,
learning_rate_placeholder: lr, phase_train_placeholder: True})
emb_array[lab,:] = emb
print('%.3f' % (time.time()-start_time))
# Select triplets based on the embeddings
print('Selecting suitable triplets for training')
#select_triplets用来找寻triplets
triplets, nrof_random_negs, nrof_triplets = select_triplets(emb_array, num_per_class,
image_paths, args.people_per_batch, args.alpha)
selection_time = time.time() - start_time
print('(nrof_random_negs, nrof_triplets) = (%d, %d): time=%.3f seconds' %
(nrof_random_negs, nrof_triplets, selection_time))
# Perform training on the selected triplets
#nrof_batches代表需要运行的batch数=nrof_triplets×3(图片数量)/batch_size
nrof_batches = int(np.ceil(nrof_triplets*3/args.batch_size))
#triplet_paths表示所有选中的图片路径
triplet_paths = list(itertools.chain(*triplets))
labels_array = np.reshape(np.arange(len(triplet_paths)),(-1,3))
triplet_paths_array = np.reshape(np.expand_dims(np.array(triplet_paths),1), (-1,3))
sess.run(enqueue_op, {image_paths_placeholder: triplet_paths_array, labels_placeholder: labels_array})
nrof_examples = len(triplet_paths)
train_time = 0
i = 0
emb_array = np.zeros((nrof_examples, embedding_size))
loss_array = np.zeros((nrof_triplets,))
summary = tf.Summary()
step = 0
#不断运行batch
while i < nrof_batches:
start_time = time.time()
batch_size = min(nrof_examples-i*args.batch_size, args.batch_size)
feed_dict = {batch_size_placeholder: batch_size, learning_rate_placeholder: lr, phase_train_placeholder: True}
err, _, step, emb, lab = sess.run([loss, train_op, global_step, embeddings, labels_batch], feed_dict=feed_dict)
emb_array[lab,:] = emb
loss_array[i] = err
duration = time.time() - start_time
print('Epoch: [%d][%d/%d]\tTime %.3f\tLoss %2.3f' %
(epoch, batch_number+1, args.epoch_size, duration, err))
batch_number += 1
i += 1
train_time += duration
summary.value.add(tag='loss', simple_value=err)
# Add validation loss and accuracy to summary
#pylint: disable=maybe-no-member
summary.value.add(tag='time/selection', simple_value=selection_time)
summary_writer.add_summary(summary, step)
return step
def select_triplets(embeddings, nrof_images_per_class, image_paths, people_per_batch, alpha):
""" Select the triplets for training
"""
trip_idx = 0
#某个人的图片的embedding在emb_arr中的开始索引
emb_start_idx = 0
num_trips = 0
triplets = []
# VGG Face: Choosing good triplets is crucial and should strike a balance between
# selecting informative (i.e. challenging) examples and swamping training with examples that
# are too hard. This is achieve by extending each pair (a, p) to a triplet (a, p, n) by sampling
# the image n at random, but only between the ones that violate the triplet loss margin. The
# latter is a form of hard-negative mining, but it is not as aggressive (and much cheaper) than
# choosing the maximally violating example, as often done in structured output learning.
#遍历每一个人
for i in xrange(people_per_batch):
#这个人有多少张图片
nrof_images = int(nrof_images_per_class[i])
#遍历第i个人所有照片对应的embedding特征
for j in xrange(1,nrof_images):
#a_idx表示第j张图片在emb_arr中的位置
a_idx = emb_start_idx + j - 1
#neg_dists_sqr表示这张图片跟其他所有图片的欧式距离
neg_dists_sqr = np.sum(np.square(embeddings[a_idx] - embeddings), 1)
for pair in xrange(j, nrof_images): # For every possible positive pair.
#在同一个人下我们找postive图片
p_idx = emb_start_idx + pair
#(a,p)之间的欧式距离
pos_dist_sqr = np.sum(np.square(embeddings[a_idx]-embeddings[p_idx]))
#同一个人的图片不作为negative ,所以将其另为nan
neg_dists_sqr[emb_start_idx:emb_start_idx+nrof_images] = np.NaN
#all_neg = np.where(np.logical_and(neg_dists_sqr-pos_dist_sqr