C++学习之路(一)
此篇博文为C++学习之路第一篇,如前所述,我们的资料主要依据《C++ Primer Plus》这本书,顺序也基本按照书中的理解;欢迎大家指正交流!
using name space;
std::cout std::endl 名称空间std
short的范围是【-32768,32767】 unsigned short范围【0,65535】注意上下溢出
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed,ios_base::floatfield); //setf()主要用来修改结果的显示方式ios_base::floatfield是设置输出时按浮点格式,小数点后有6位数字;注意float类型表示有效位数的能力有限
int yamcosts[3]={20,30,5}; 定义数组大小为3并初始化值,如果没有初始化则元素值将是不确定的,值是以前驻留在该内存中的值。
sizeof单位是字节
float hotelTips[5]={5.0,2.5}; 其他三个被自动设置为0
short things[]={1,5,3,8}; 自动计算有几个成员元素;
char dog[5]={'b','e','a','u','x'}; 不是字符串
char cat[5]={'f','a','t','s','\0'}; 是字符串,要有空字符
char fish[]="Bubbles"; 字符串常量
char shirt_size='S' 'S'=83
char shirt_size="S" 非法,“S”实际表示字符串所在的内存地址
字符串自动拼接
cout<<"I'd give my right ar"
"m to be a great violinist.\n";
// strings.cpp -- storing strings in an array
#include
#include // for the strlen() function
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int Size = 15;
char name1[Size]; // empty array
char name2[Size] = "C++owboy"; // initialized array
// NOTE: some implementations may require the static keyword
// to initialize the array name2
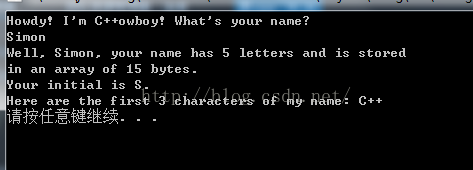
cout << "Howdy! I'm " << name2;
cout << "! What's your name?\n";
cin >> name1;
cout << "Well, " << name1 << ", your name has ";
cout << strlen(name1) << " letters and is stored\n"; //空字符不计入
cout << "in an array of " << sizeof(name1) << " bytes.\n";
cout << "Your initial is " << name1[0] << ".\n";
name2[3] = '\0'; // 使用\0截短字符串 后面其实还有其他字符
cout << "Here are the first 3 characters of my name: ";
cout << name2 << endl;
system("pause"); //暂停为了能够方便查看结果,不然程序运行太快
return 0;
}
// instr1.cpp -- reading more than one string
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
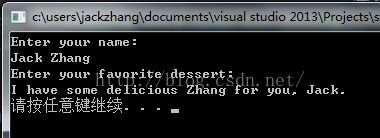
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin >> name;
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin >> dessert;
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;
cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
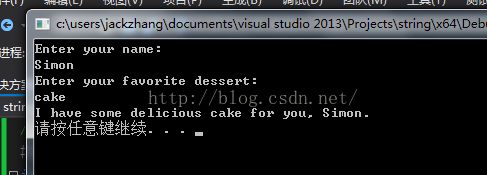
另外一种结果:
Zhang留在输入队列当中,Jack被输入到数组当中;在队列中搜索时发现了Zhang,所以将其输入到dessert数组中;
// instr2.cpp -- reading more than one word with getline
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin.getline(name, ArSize); // reads through newline
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin.getline(dessert, ArSize);
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;
cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
} getline每次读取一行,通过换行符来确定行尾,但不保留换行符,本例中最多存储19个字符,最后一位要自动保存为空字符;
cin.get(name,ArSize);cin.get(); //避免无法读取第二行,因为换行符被留在输入队列中
cin.get(dessert,ArSize);
// instr3.cpp -- reading more than one word with get() & get()
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin.get(name, ArSize).get(); // read string, newline 避免只读到换行符而无法读取第二行 get保留换行符
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin.get(dessert, ArSize);
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;
cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
混合模式下:换行符的问题
// numstr.cpp -- following number input with line input
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "What year was your house built?\n";
int year;
cin >> year;
cin.get(); //(cin >> year).get();如果没有这一步则address就没有机会被输入,cin会因为保留在队列中的换行符而以为address为空行
cout << "What is its street address?\n";
char address[80];
cin.getline(address, 80);
cout << "Year built: " << year << endl;
cout << "Address: " << address << endl;
cout << "Done!\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
string使用:
// strtype1.cpp -- using the C++ string class
#include
#include // make string class available
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char charr1[20]; // create an empty array
char charr2[20] = "jaguar"; // create an initialized array
string str1; // create an empty string object
string str2 = "panther"; // create an initialized string
cout << "Enter a kind of feline: ";
cin >> charr1;
cout << "Enter another kind of feline: ";
cin >> str1; // use cin for input
cout << "Here are some felines:\n";
cout << charr1 << " " << charr2 << " "
<< str1 << " " << str2 // use cout for output
<< endl;
cout << "The third letter in " << charr2 << " is " //数组
<< charr2[2] << endl;
cout << "The third letter in " << str2 << " is "
<< str2[2] << endl; // use array notation //字符串访问
system("pause");
return 0;
}
string对象间操作:
// strtype2.cpp -- assigning, adding, and appending
#include
#include // make string class available
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string s1 = "penguin";
string s2, s3;
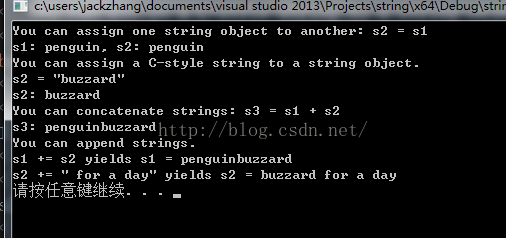
cout << "You can assign one string object to another: s2 = s1\n";
s2 = s1;
cout << "s1: " << s1 << ", s2: " << s2 << endl;
cout << "You can assign a C-style string to a string object.\n";
cout << "s2 = \"buzzard\"\n"; //转义表示双引号
s2 = "buzzard";
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
cout << "You can concatenate strings: s3 = s1 + s2\n";
s3 = s1 + s2;
cout << "s3: " << s3 << endl;
cout << "You can append strings.\n";
s1 += s2;
cout << "s1 += s2 yields s1 = " << s1 << endl;
s2 += " for a day";
cout << "s2 += \" for a day\" yields s2 = " << s2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
string类的其他操作:
// strtype3.cpp -- more string class features
#include
#include // make string class available
#include // C-style string library
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char charr1[20];
char charr2[20] = "jaguar";
string str1;
string str2 = "panther";
// assignment for string objects and character arrays
str1 = str2; // copy str2 to str2 使用字符串类
strcpy_s(charr1, charr2); // copy charr2 to charr1 对应字符数组 使用C字符串函数
// appending for string objects and character arrays
str1 += " paste"; // add paste to end of str1
strcat_s(charr1, " juice"); // add juice to end of charr1 对应字符数组
// finding the length of a string object and a C-style string
int len1 = str1.size(); // obtain length of str1 字符串
int len2 = strlen(charr1); // obtain length of charr1 字符数组
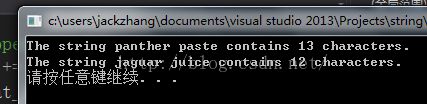
cout << "The string " << str1 << " contains "
<< len1 << " characters.\n";
cout << "The string " << charr1 << " contains "
<< len2 << " characters.\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
下面这段代码需要特别留意一下!
// strtype4.cpp -- line input
#include
#include // make string class available
#include // C-style string library
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char charr[20];
string str; //自动调整
cout << "Length of string in charr before input: "
<< strlen(charr) << endl; //我理解为内存中原来保存到大小
cout << "Length of string in str before input: "
<< str.size() << endl; //string类自动将未被初始化的对象长度设置为0
cout << "Enter a line of text:\n";
cin.getline(charr, 20); // indicate maximum length getline不包括换行符
cout << "You entered: " << charr << endl;
cout << "Enter another line of text:\n";
getline(cin, str); // cin now an argument; no length specifier
cout << "You entered: " << str << endl;
cout << "Length of string in charr after input: "
<< strlen(charr) << endl;
cout << "Length of string in str after input: "
<< str.size() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 声明结构体并使用结构体:struct
// structur.cpp -- a simple structure
#include
#include
struct inflatable // structure declaration结构体定义
{
char name[20]; //字符数组
float volume;
double price;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std;
inflatable guest = //可以理解为实例化?
{
"Glorious Gloria", // name value 逗号分隔
1.88, // volume value
29.99 // price value
}; // guest is a structure variable of type inflatable
// It's initialized to the indicated values
inflatable pal =
{
"Audacious Arthur",
3.12,
32.99
}; // pal is a second variable of type inflatable
// NOTE: some implementations require using
// static inflatable guest =
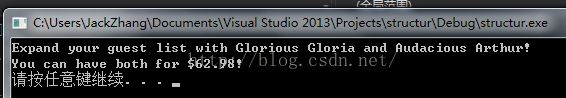
cout << "Expand your guest list with " << guest.name;
cout << " and " << pal.name << "!\n";
// pal.name is the name member of the pal variable
cout << "You can have both for $";
cout << guest.price + pal.price << "!\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}